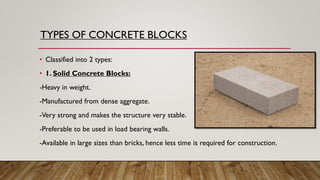
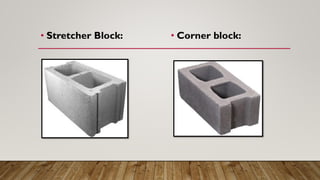
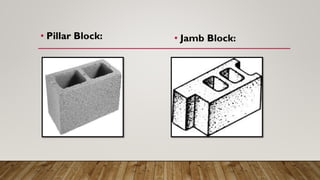
Concrete blocks, also known as concrete masonry units (CMUs), are standard rectangular blocks used in construction, produced in automated or manual plants. They are made by mixing aggregates, cement, and water, molded, and cured to enhance strength, and are classified into solid and hollow blocks with various applications. Advantages include improved thermal insulation and quicker construction, while disadvantages involve potential cracking, shrinkage, and higher costs.