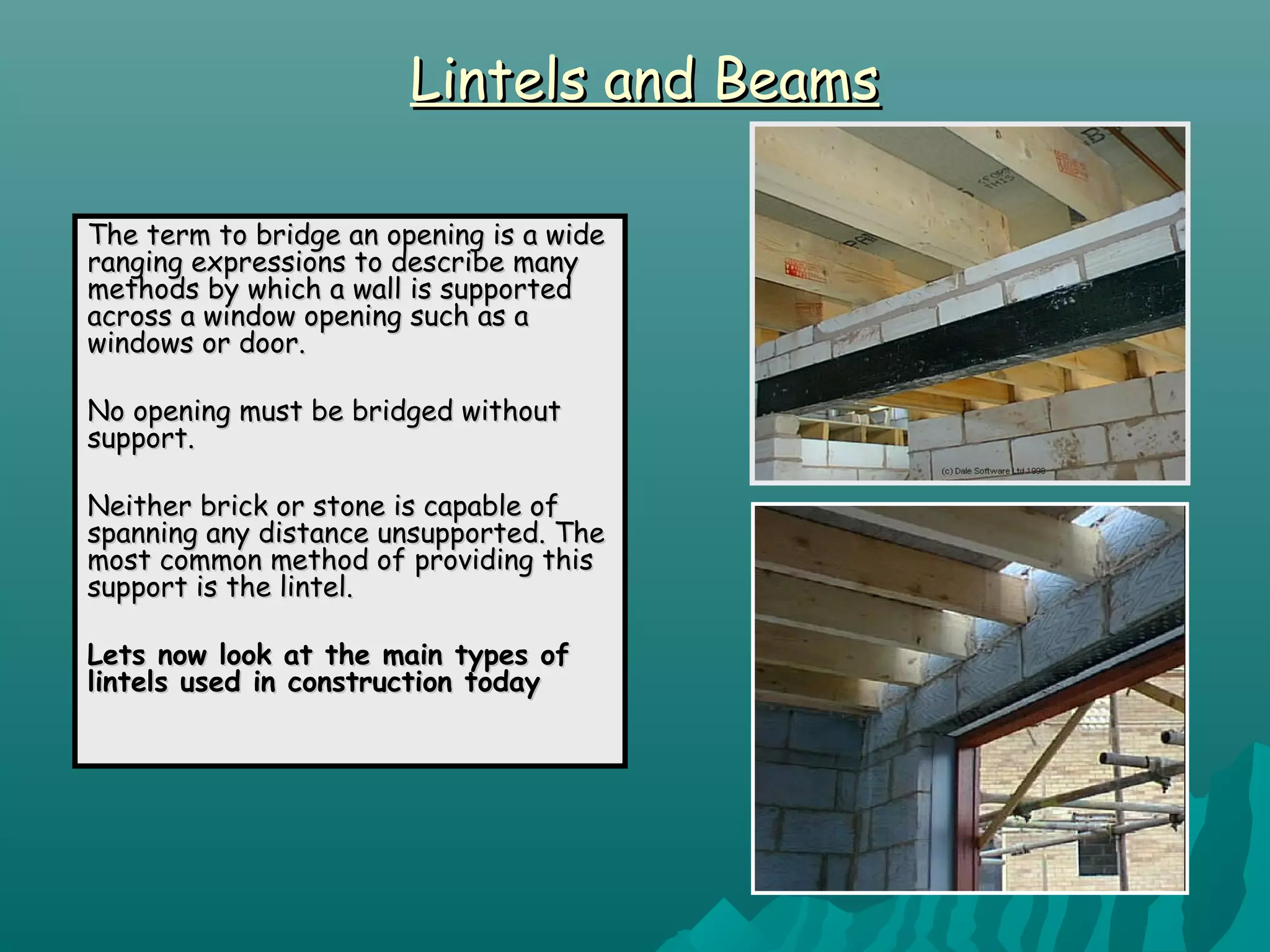
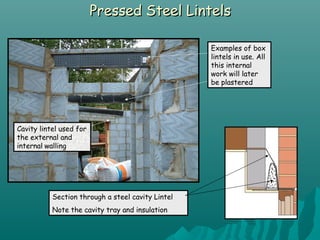
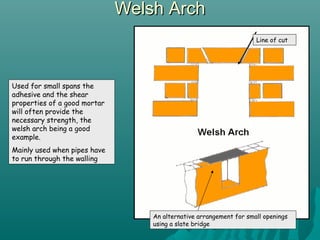
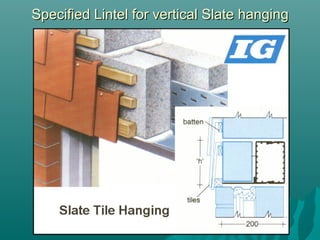
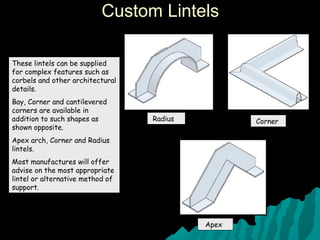
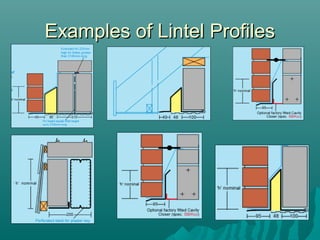
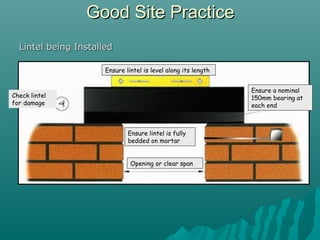
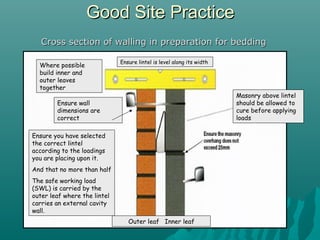
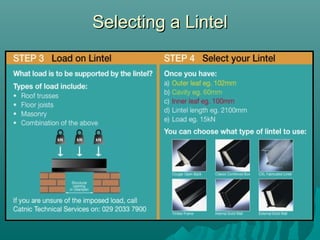
The document discusses various types of lintels and beams used in construction to support walls over openings such as doors and windows. It details materials like steel and reinforced concrete, highlighting their advantages and uses for different architectural requirements. The text also emphasizes proper installation practices and selection criteria based on load requirements.