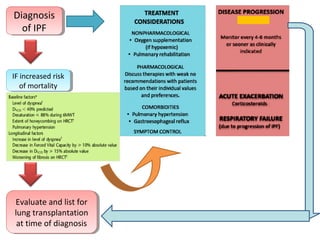
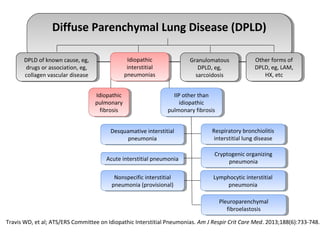
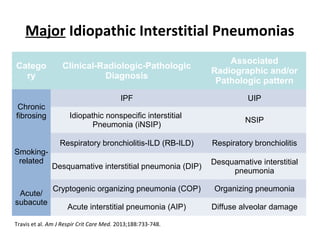
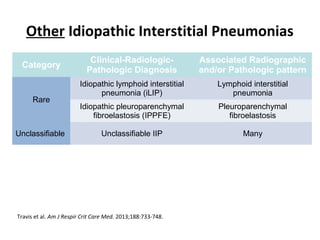
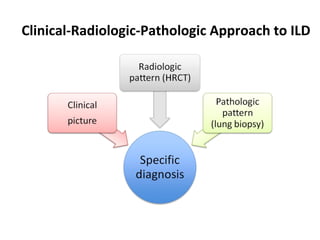
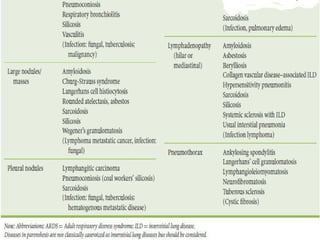
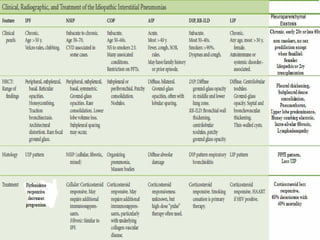
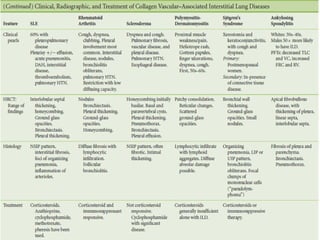
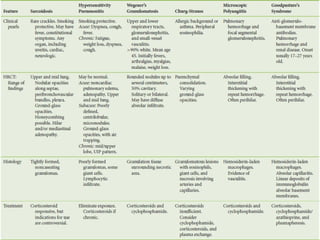
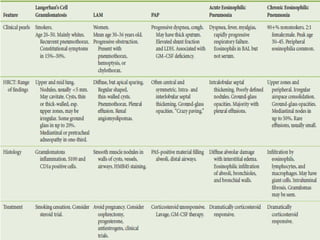
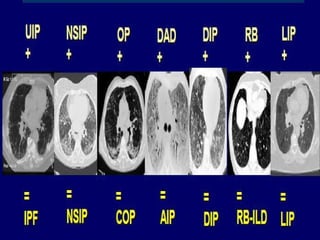
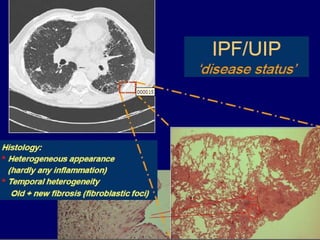
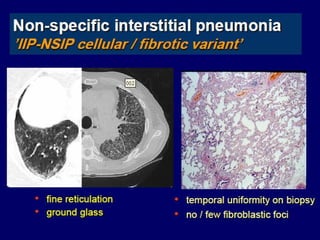
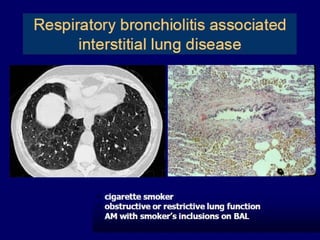
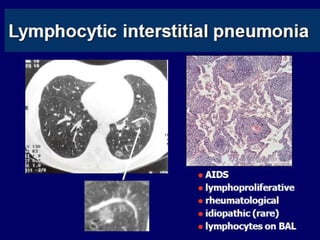
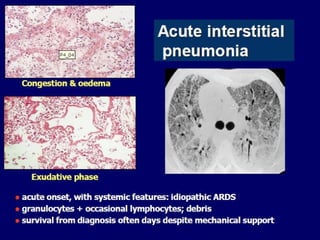
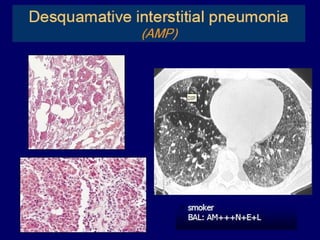
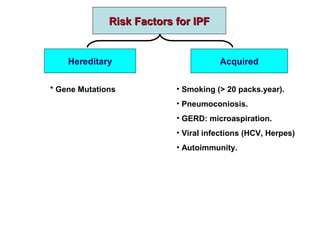
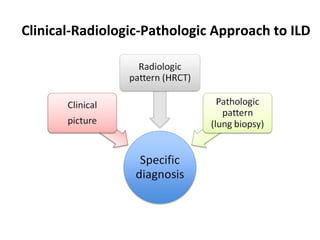
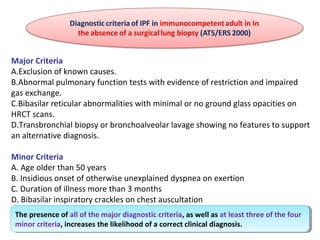
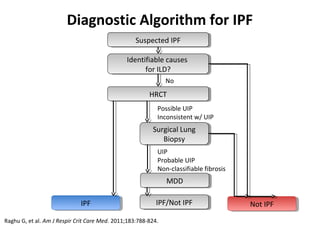
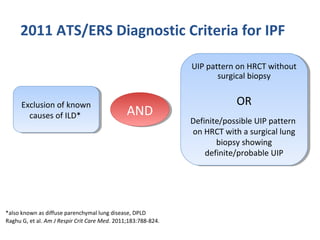
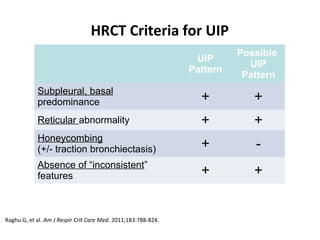
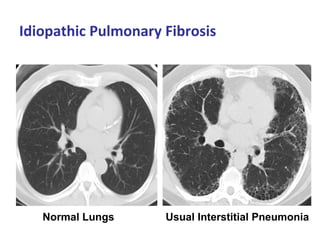
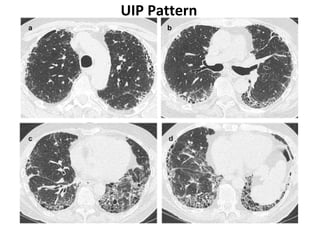
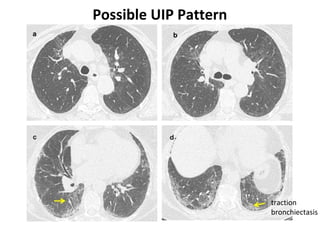
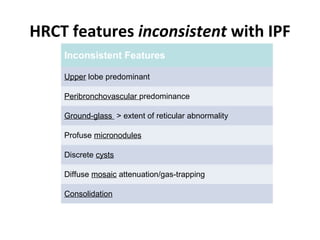
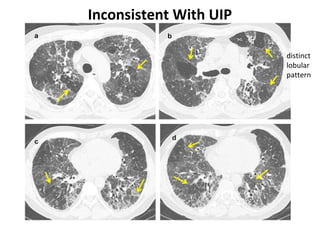
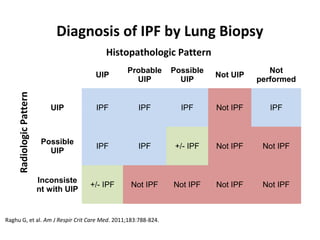
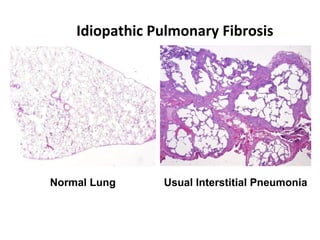
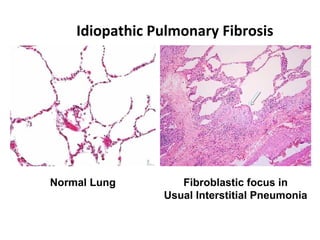
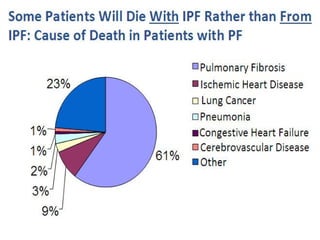
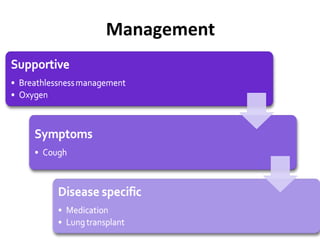
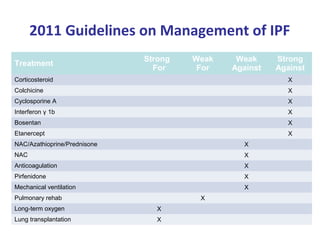
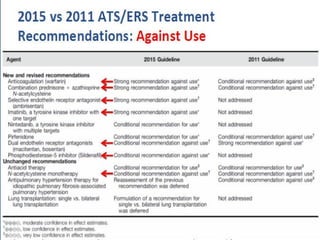
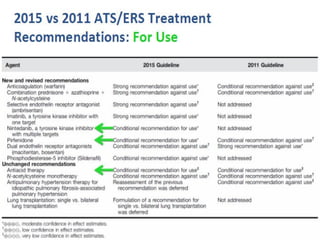
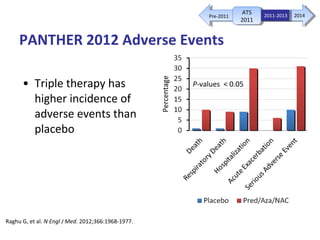
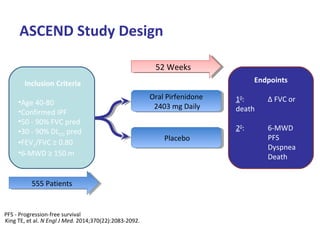
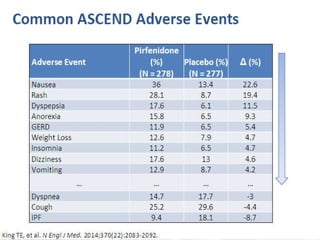
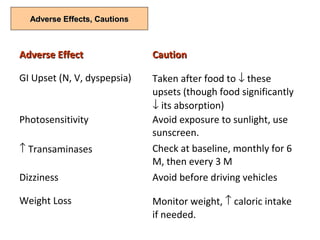
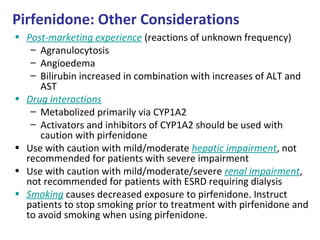
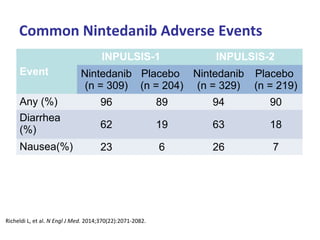
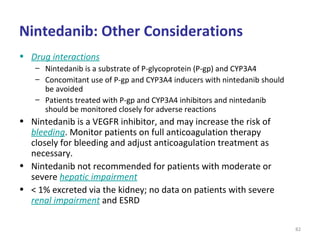
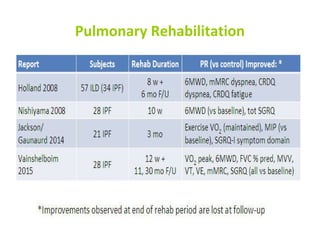
This document discusses idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a chronic, progressive fibrosing interstitial pneumonia of unknown cause associated with a histopathologic pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). It defines IPF and outlines the diagnostic criteria, which involves ruling out known causes, abnormal pulmonary function tests, characteristic radiologic findings on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), and surgical lung biopsy showing UIP pattern. HRCT features that are consistent and inconsistent with UIP are described. Guidelines for management of IPF are provided, including recommendations for pirfenidone and nintedanib based on recent clinical trials. Lung transplantation is the only treatment that increases long-term survival for patients with IPF.


























![Lung Transplantation for IPF:
2014 Referral Guidelines
• Histopathologic or radiographic evidence of usual
interstitial pneumonitis (UIP)
• Abnormal lung function: FVC < 80% predicted or
DLCO < 40% predicted
• Any dyspnea or functional limitation attributable to
lung disease
• Any oxygen requirement, even if only during exertion
Weill D, et al. J Heart Lung Transplant.2014 Jun 26. [Epub ahead of print].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ild-160105004146/85/Interstitial-Lung-Diseases-89-320.jpg)