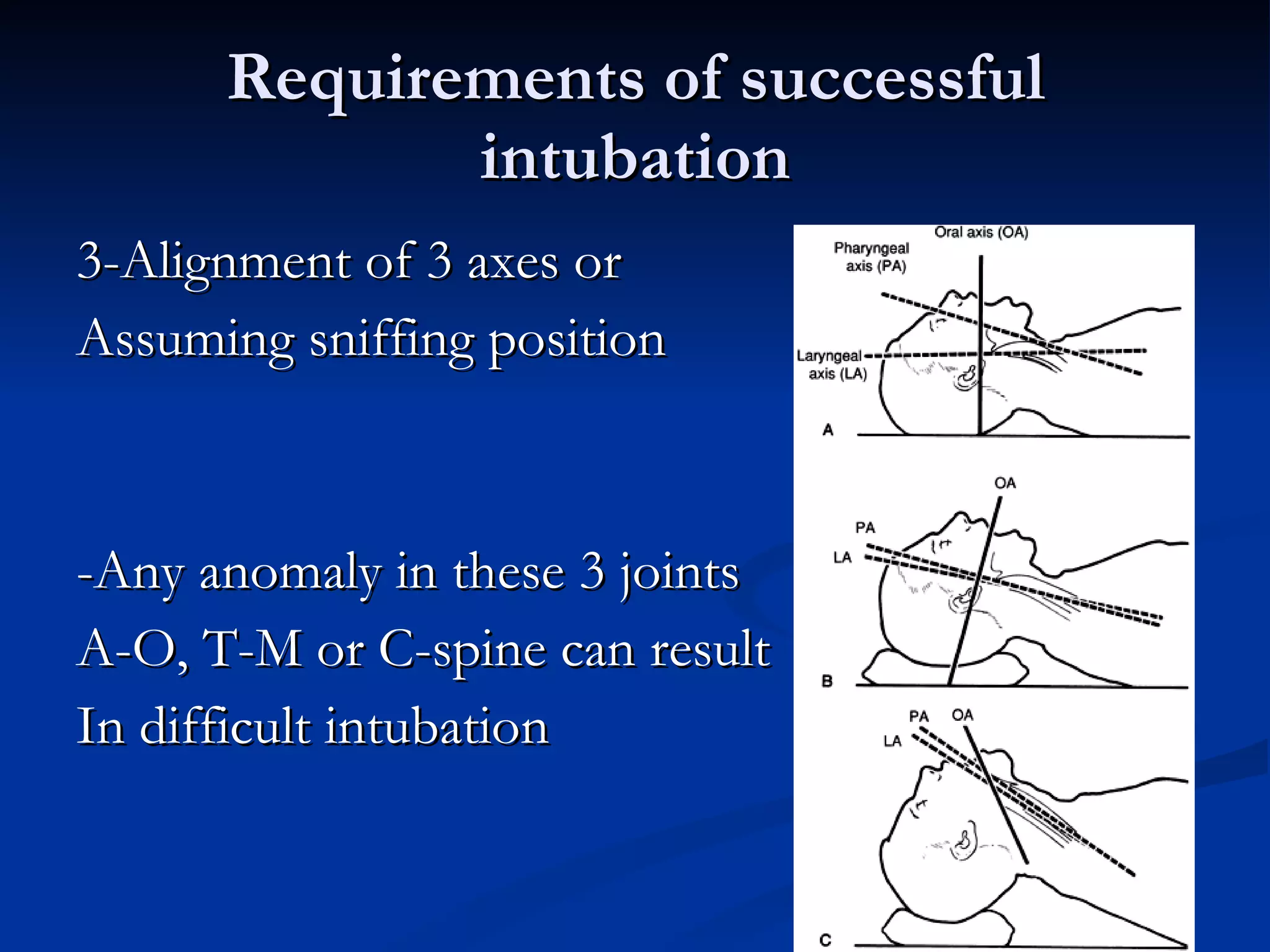
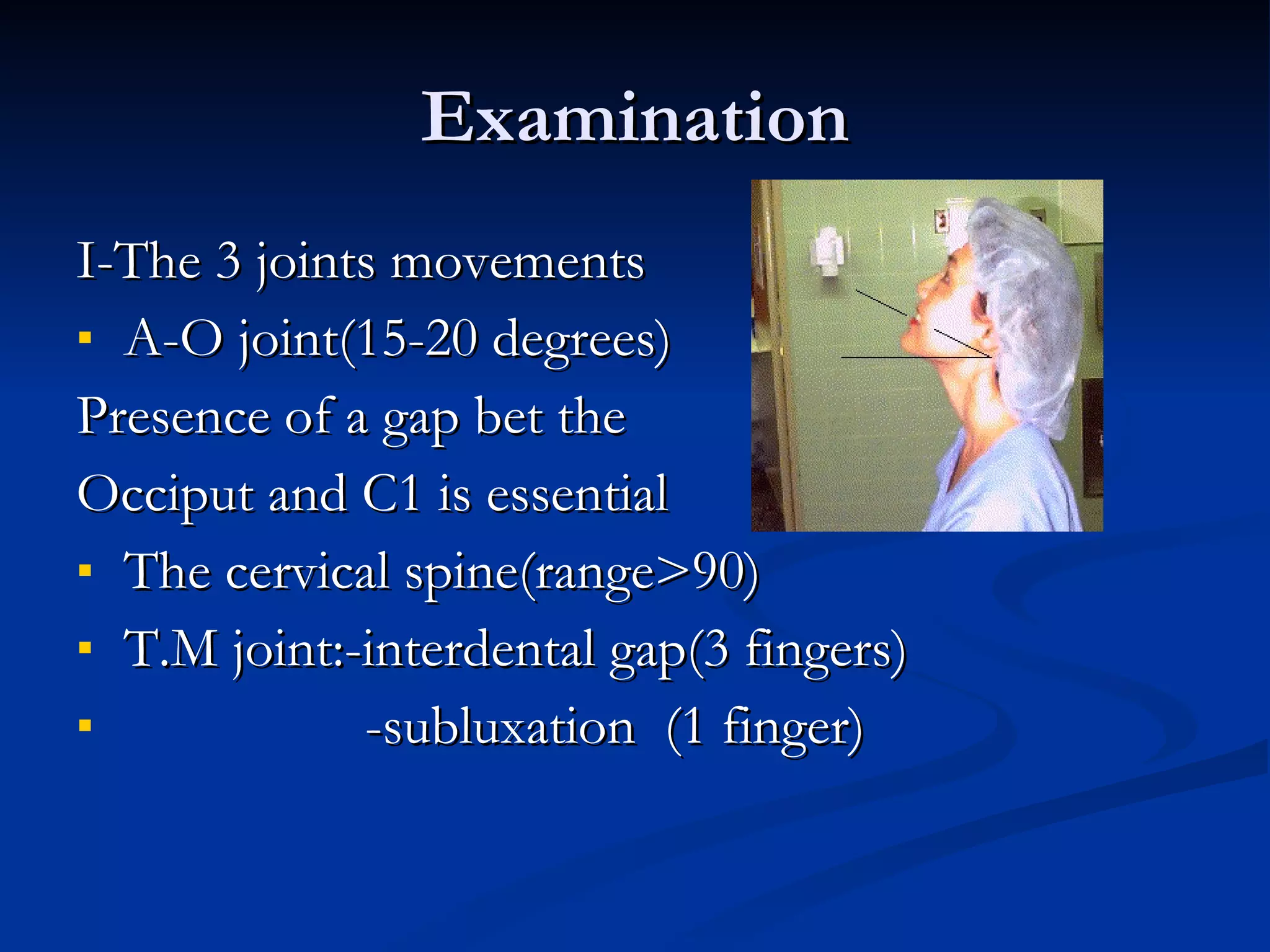
This document discusses airway evaluation, management of intubation, and complications. It outlines indications for intubation including resuscitation, prevention of lung soiling, and respiratory failure. Successful intubation requires a normal anatomy of the mandible, temporomandibular joint, atlanto-occipital joint, and cervical spine. Proper equipment and gadgets are also needed. Tests like the Mallampatti and Wilson scores can predict difficulty, and a history of previous issues is also informative. Securing the airway awake is recommended for expected difficult airways, and maintenance of oxygenation should be the primary aim with backup plans in place for unexpected difficulties.