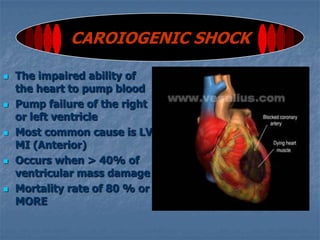
Shock is a condition where the cardiovascular system fails to adequately perfuse tissues. It can be caused by an impaired pump (cardiogenic shock), reduced circulating volume (hypovolemic shock), or maldistribution of blood flow (distributive shock). The main effects are cellular hypoxia, impaired metabolism, and organ damage or failure if not treated. Compensatory mechanisms aim to increase perfusion but eventually fail, leading to irreversible cellular damage and death if shock persists.










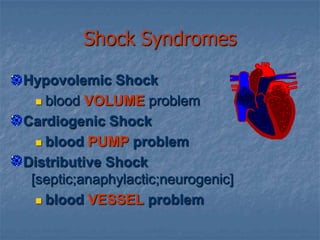








![Shock Syndromes Hypovolemic Shockblood VOLUMEproblem Cardiogenic Shockblood PUMP problem Distributive Shock [septic;anaphylactic;neurogenic]blood VESSEL problem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shock4724/85/Shock-25-320.jpg)

![Pathophysiology of Hypovolemic ShockDecreased intravascular volume leads to…. Decreased venous return (Preload, RAP) leads to... Decreased ventricular filling (Preload, PAWP) leads to…. Decreased stroke volume (HR, Preload, & Afterload) leads to ….. Decreased CO leads to...(Compensatory mechanisms)Inadequate tissue perfusion!!!!Assessment & ManagementS/S vary depending on severity of fluid loss:15%[750ml]- compensatory mechanism maintains CO15-30% [750-1500ml- Hypoxemia, decreased BP & UOP30-40% [1500-2000ml] -Impaired compensation & profound shock along with severe acidosis40-50% - refactory stage: loss of volume= death](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shock4724/85/Shock-29-320.jpg)
















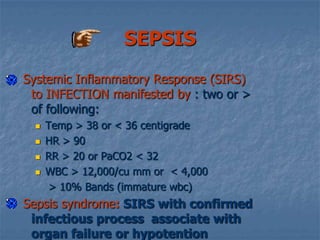











![Maintain ventilatory supportMANAGEMENT OF NEUROGENIC SHOCKObserve for Bradycardia-major dysrhythmiaObserve for DVT- venous pooling in extremities make patients high-risk>>P.E.Use prevention modalities [TEDS,anticoagulation]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shock4724/85/Shock-63-320.jpg)