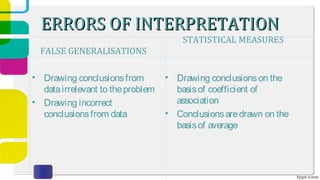
The document discusses interpretation in research, which involves drawing meaningful conclusions from analyzed data. Interpretation reveals the significance of research findings and demands fair judgments. Both the analysis of data and its interpretation are interdependent processes. When interpreting data, researchers should consider factors affecting the problem, consult experts, and provide reasonable explanations while avoiding errors like making false generalizations or using improper statistical methods and measures. The goal of interpretation is to understand what was learned and help discover new relationships and predictions.