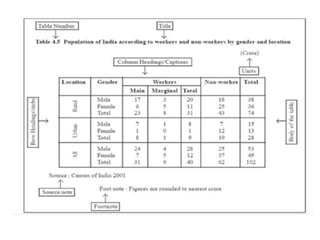
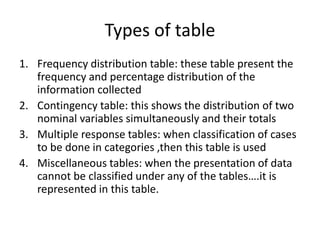
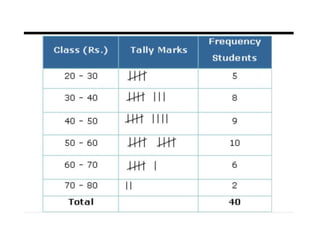
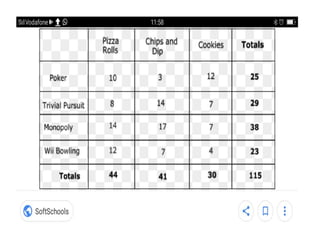
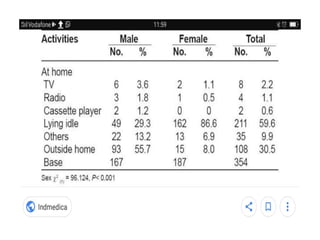
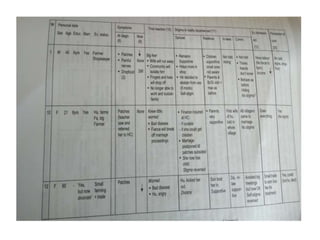
This document discusses the processes of data analysis and data processing. It defines data analysis as discovering useful information through inspecting, cleansing, transforming and modeling data, while data processing refers to rearranging data that has already been analyzed. The key steps in data processing are: 1) identifying data structures, 2) editing data for completeness and accuracy, 3) coding data numerically or alphabetically, 4) classifying data into groups, 5) transcribing data manually or via computer, 6) tabulating data into frequency distributions, contingency tables or other table types, and 7) summarizing data using manual or computerized data sheets, compilation sheets, matrices, figures or tables.