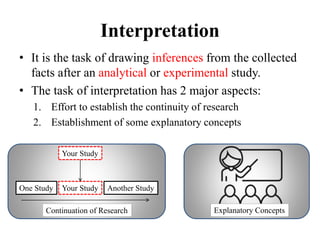
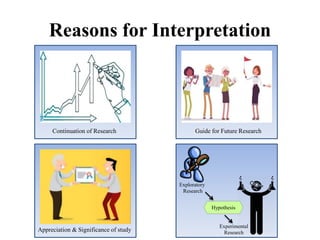
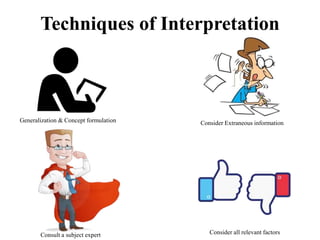
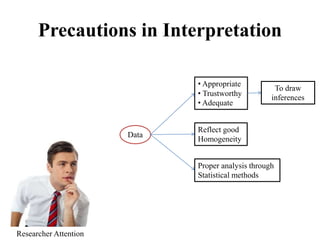
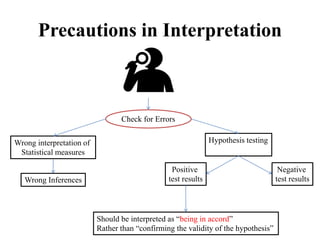
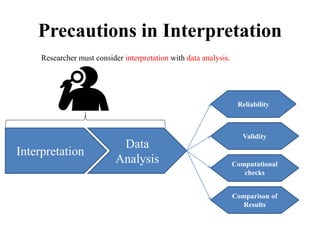
This document discusses interpretation in research methodology. Interpretation involves drawing inferences from collected facts after analytical or experimental study. It has two main aspects: establishing continuity of research and explanatory concepts. Interpretation allows researchers to understand abstract principles, link findings across studies, serve as a guide for future research, and better appreciate the significance of their own study. Techniques of interpretation include generalization, considering extraneous information, consulting experts, and considering all relevant factors. Precautions in interpretation involve ensuring accurate data, avoiding wrong statistical interpretation, distinguishing broad vs restricted generalizations, and interacting empirical observation with theoretical concepts.