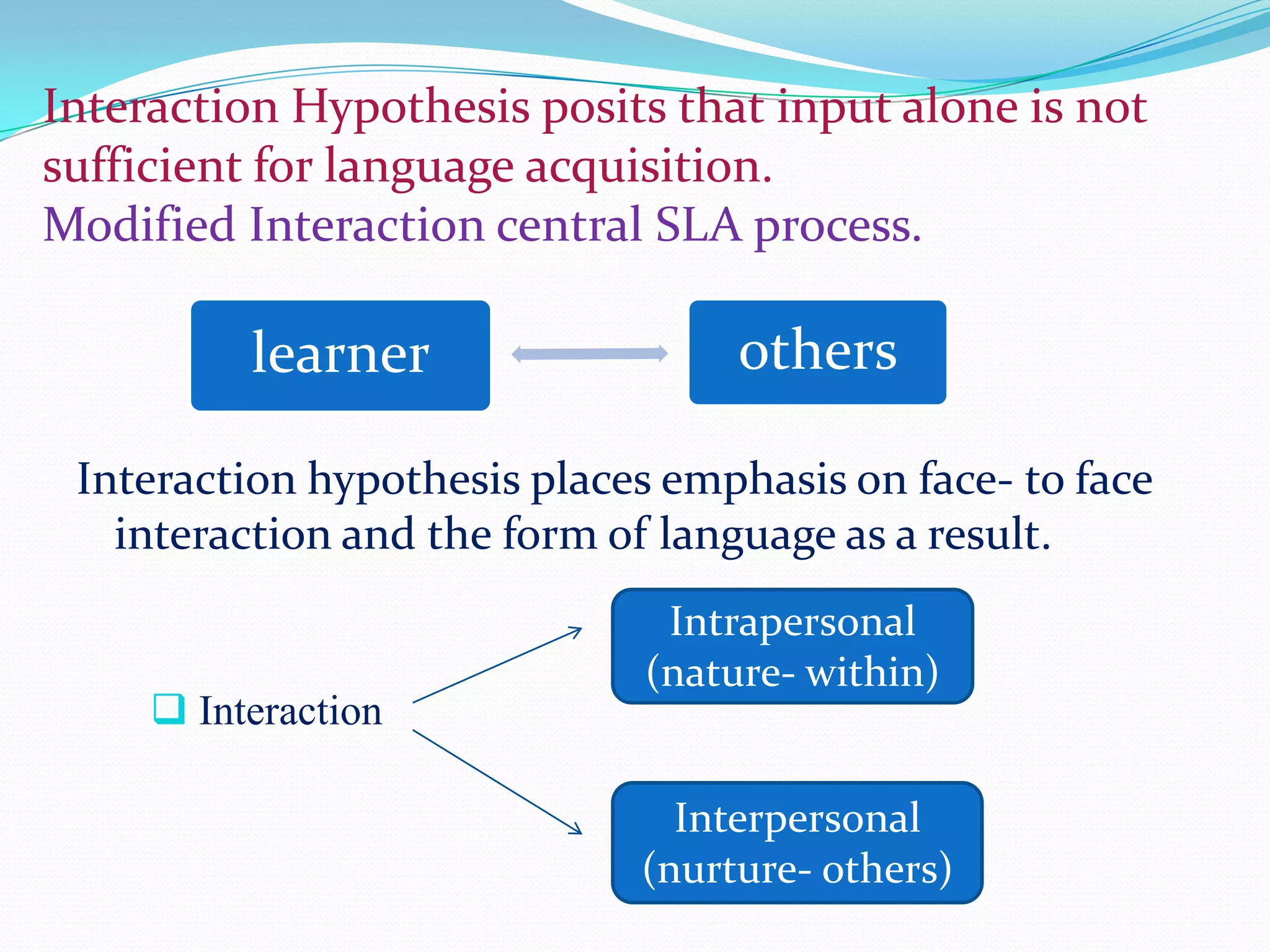
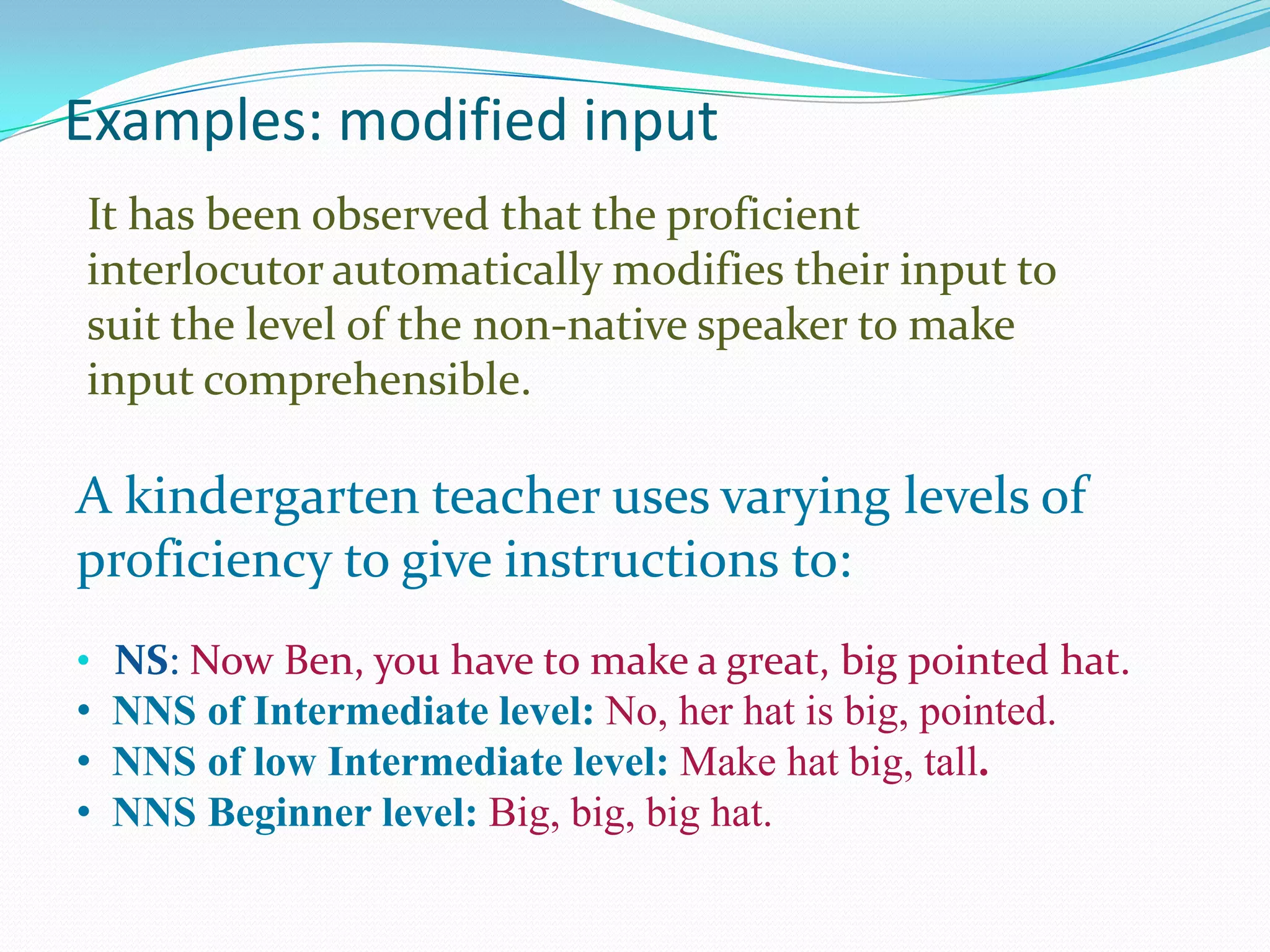
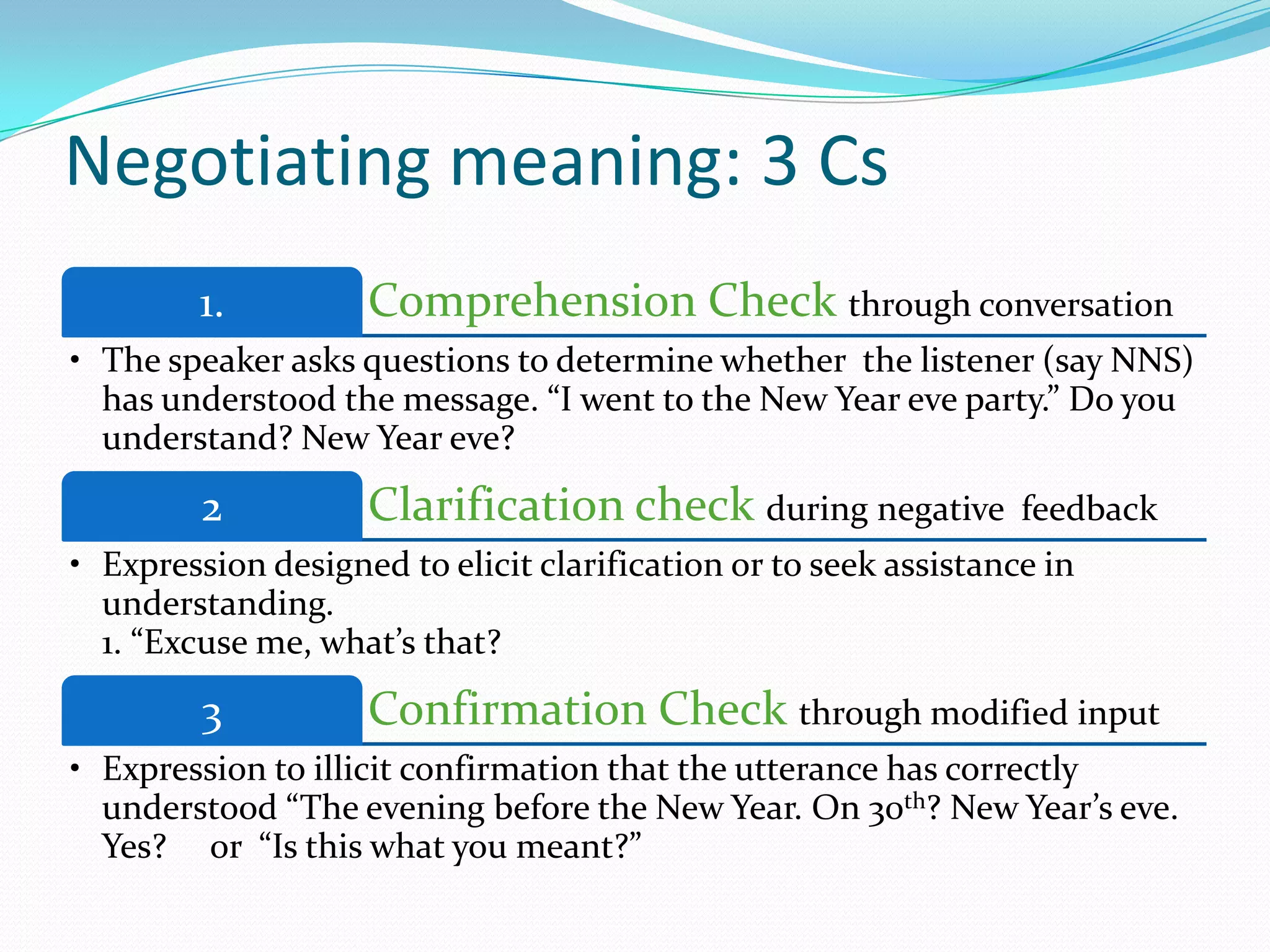
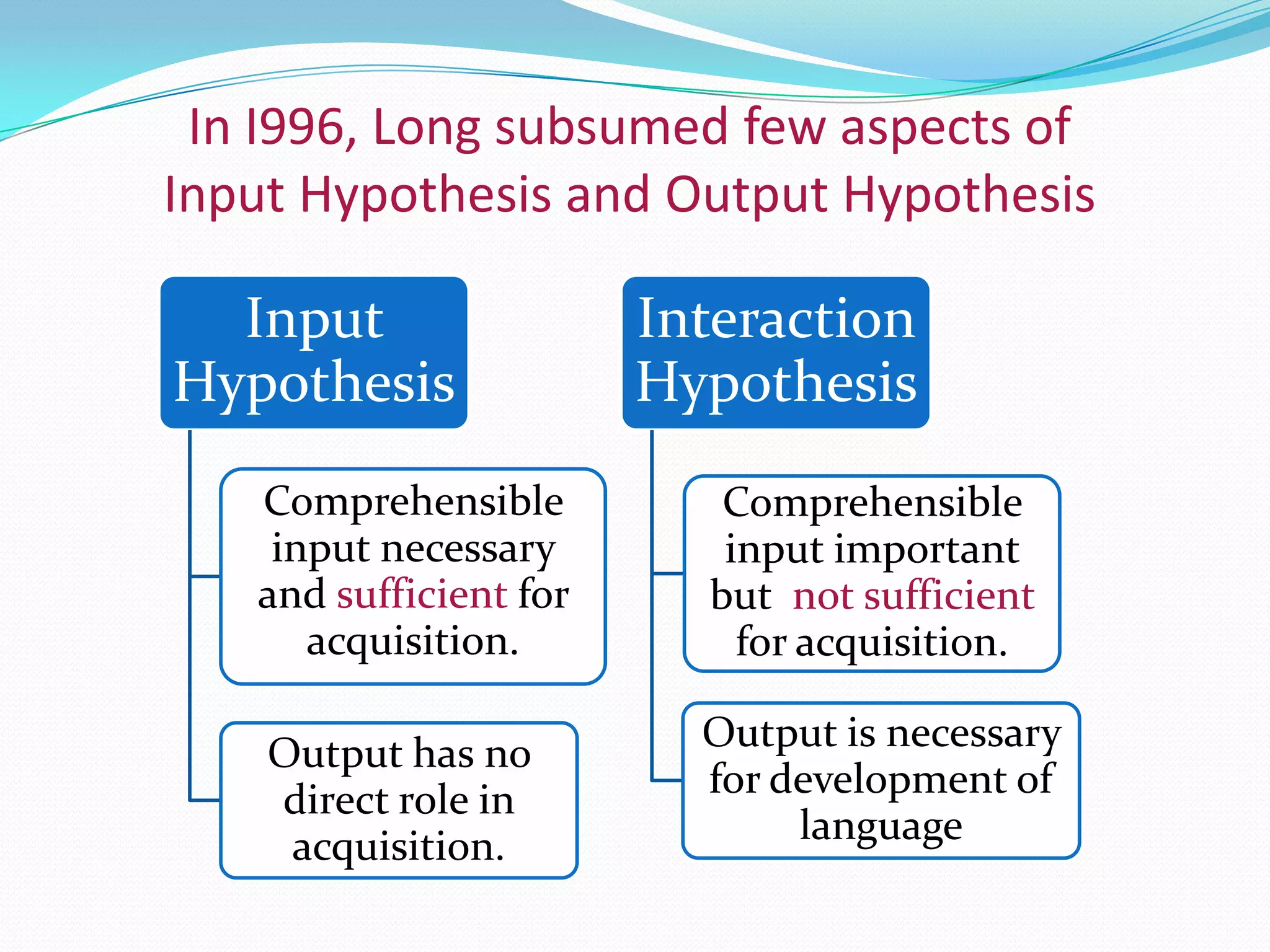
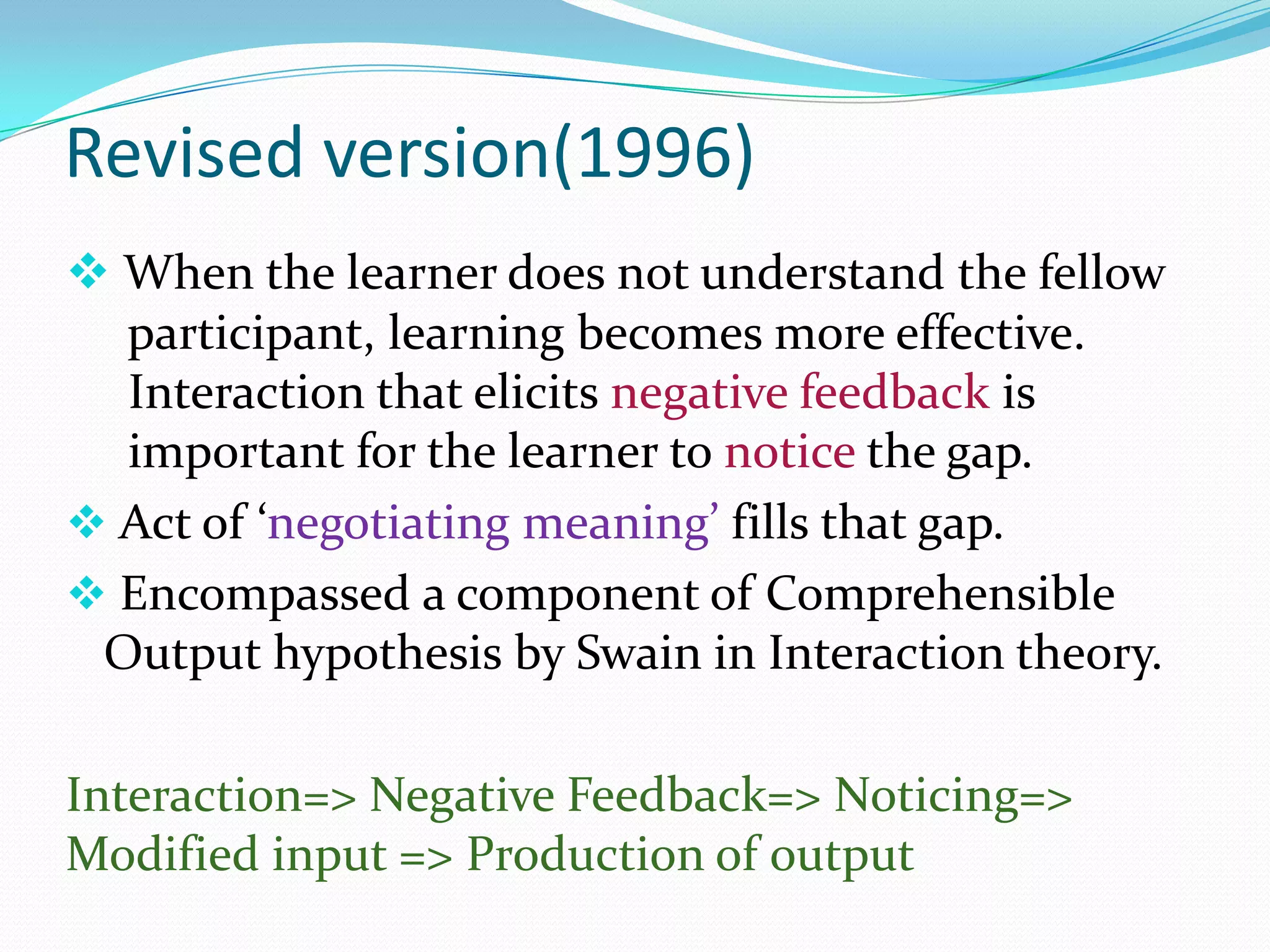
Michael Long developed the Interaction Hypothesis in 1983, which posited that comprehensible input alone is not sufficient for second language acquisition. The hypothesis emphasizes that meaningful interaction and negotiation of meaning between interlocutors is essential. When learners do not understand, interaction provides opportunities to modify input through techniques like clarification requests and confirmation checks. This negotiated interaction allows learners to notice gaps and facilitates acquisition by connecting input, internal processes, and output. Long later incorporated aspects of Merrill Swain's Output Hypothesis by acknowledging the role of output in development.