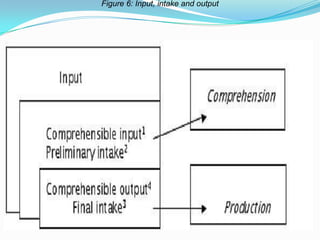
This document summarizes Krashen's input hypothesis and Swain's output hypothesis. The input hypothesis states that language acquisition occurs when learners understand language that is just beyond their current level. The output hypothesis argues that producing language through speaking and writing also contributes to acquisition by pushing learners to focus on expression. Both hypotheses complement each other, and a supportive learning environment, feedback, and engaging materials further help acquisition.