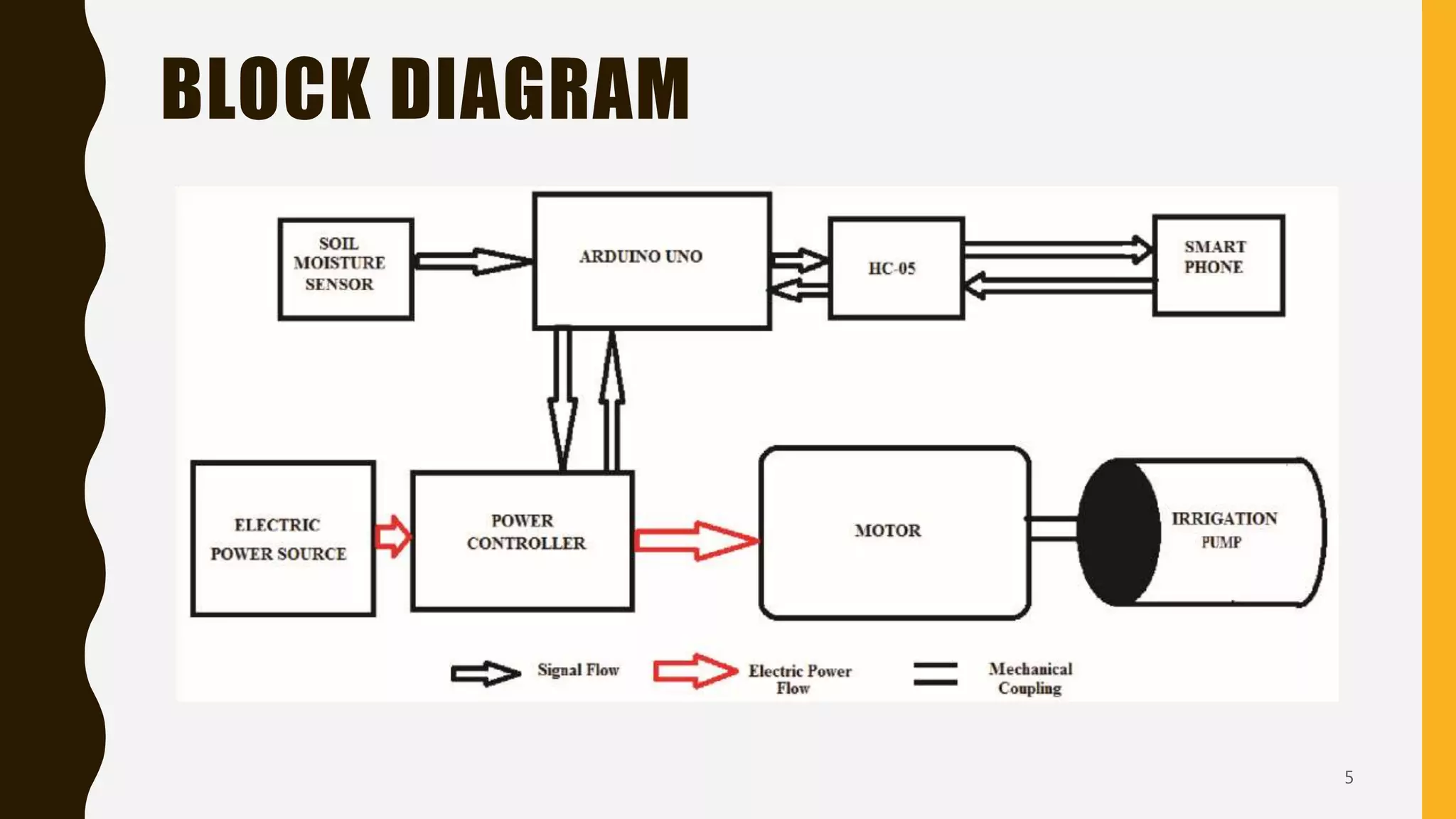
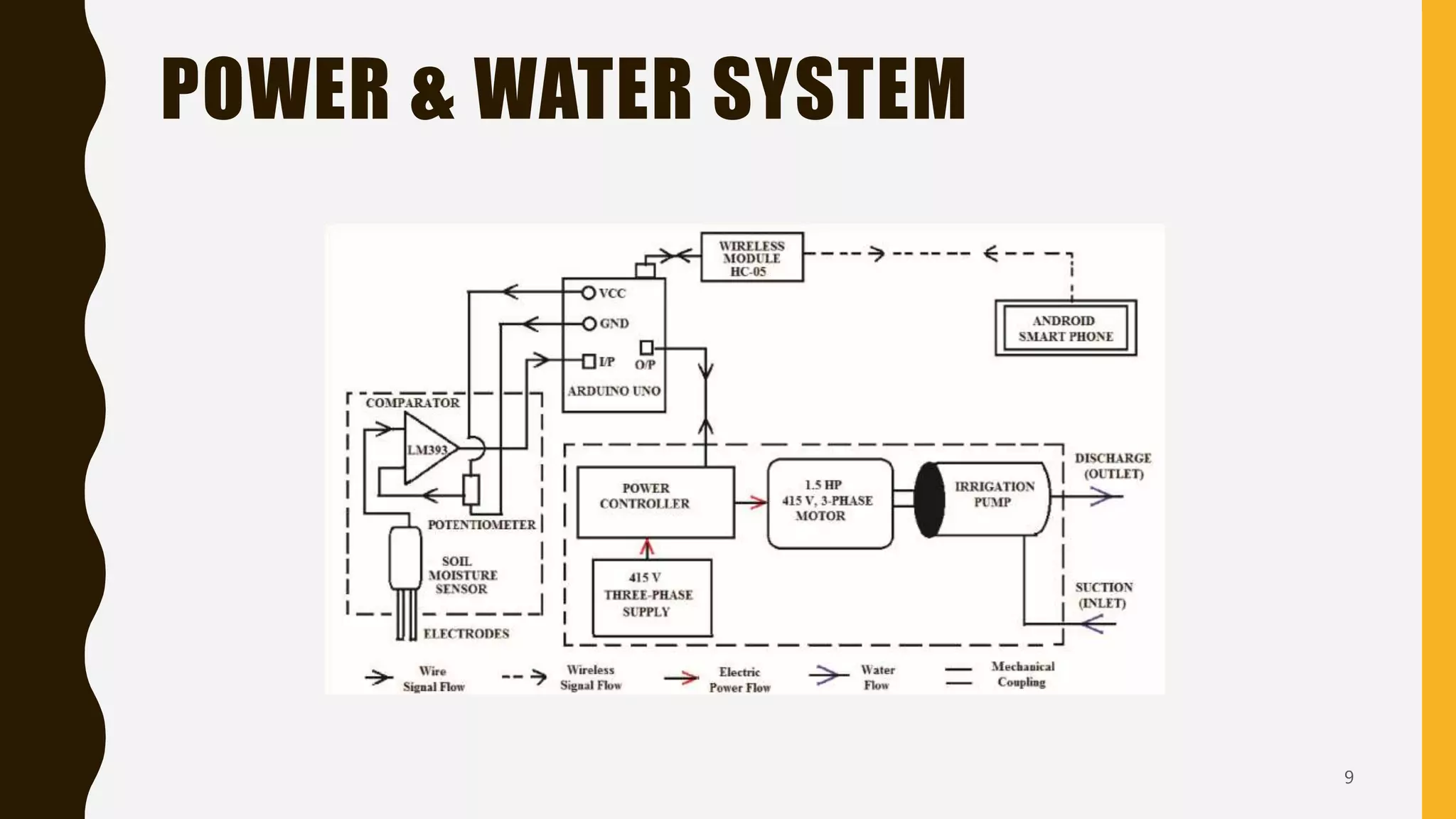
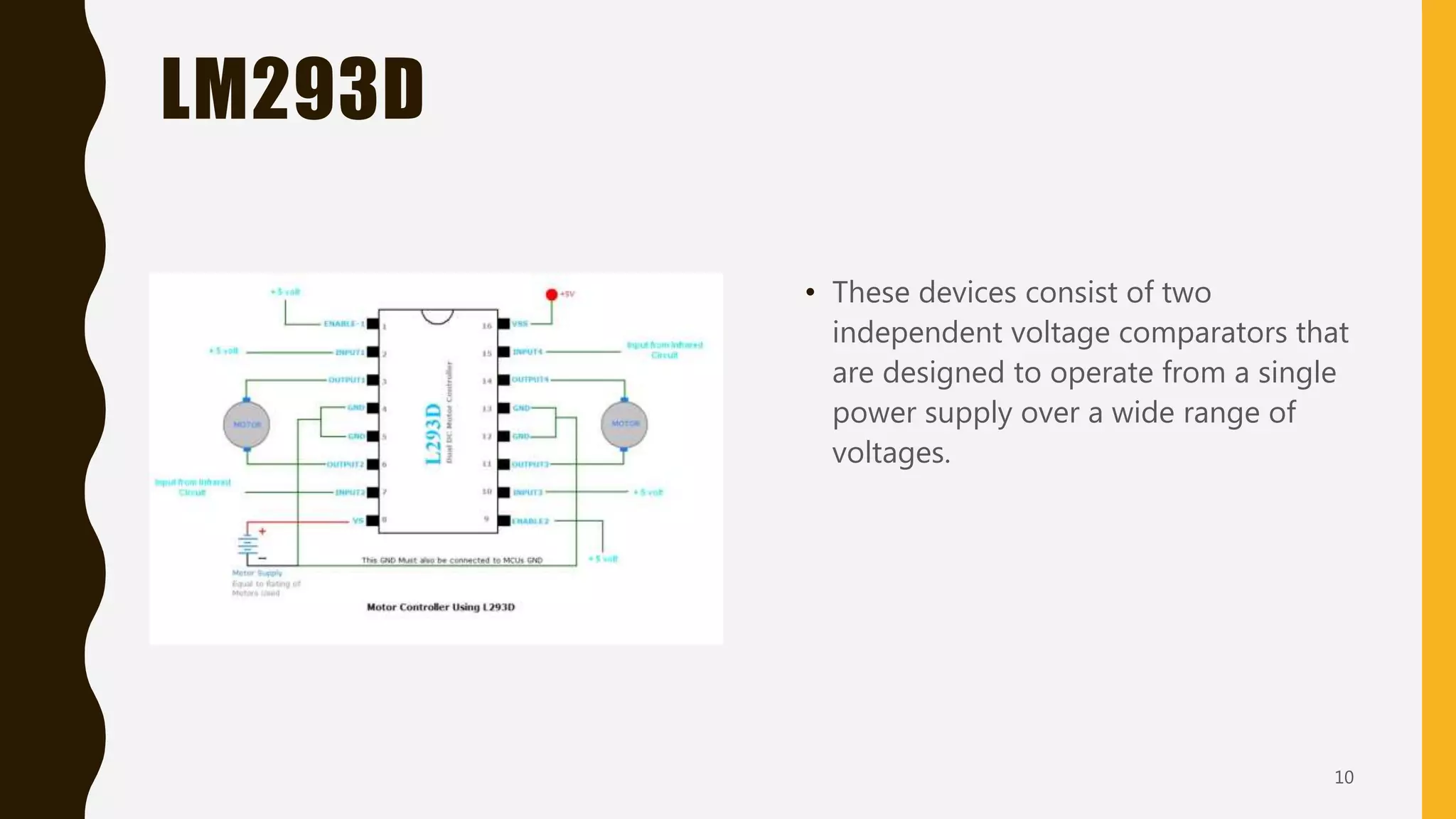
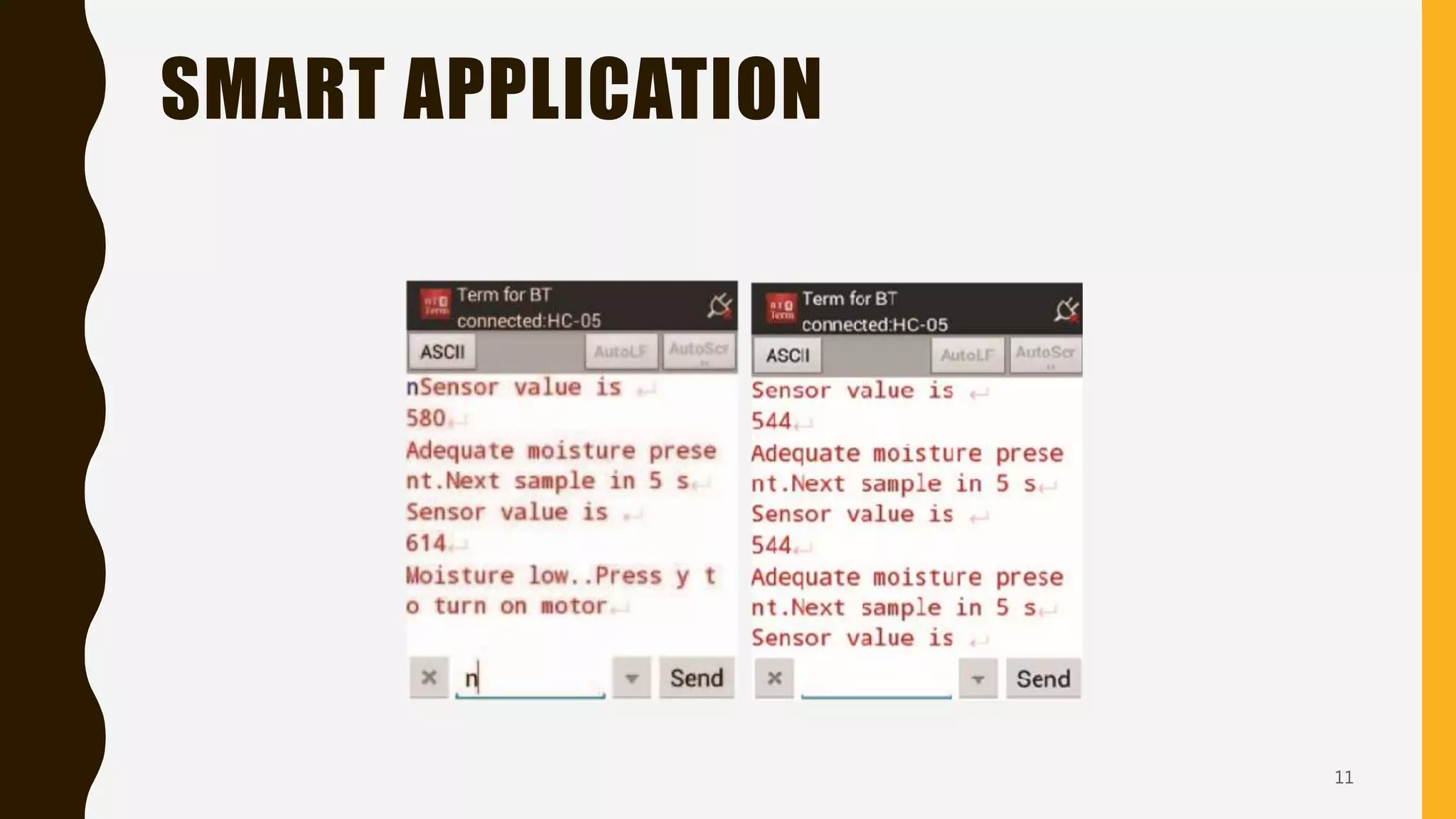
The document details an intelligent irrigation system utilizing eco-friendly technologies and IoT for efficient water management in agriculture. It proposes an automated irrigation setup controlled via a smartphone app, integrating soil moisture sensors and an Arduino microcontroller for real-time regulation. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity of such systems in precision agriculture to combat the effects of global warming.