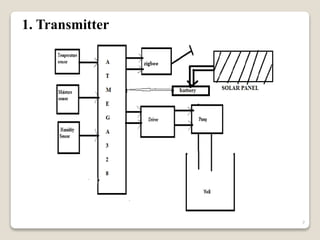
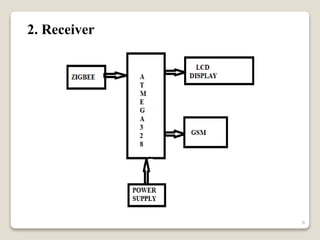
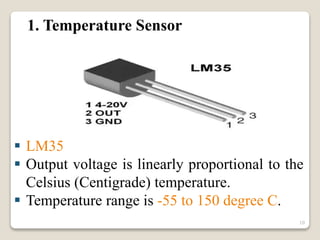
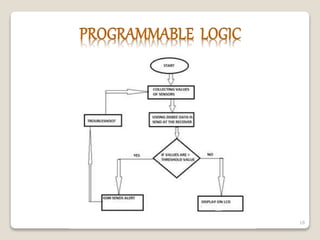
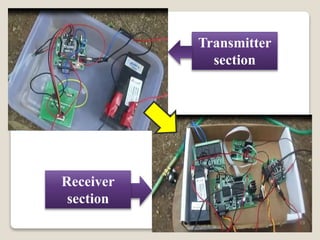
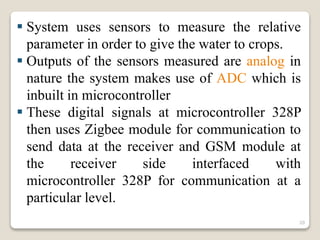
This document describes a smart irrigation system that uses sensors to measure soil moisture, temperature, humidity and water levels. The system has a transmitter section with sensors that sends the sensor readings via Zigbee modules to a receiver section. The receiver section has a microcontroller that receives the data and sends messages to farmers via GSM if irrigation is needed. The system automatically provides water to crops based on sensor readings to save water and reduce human intervention in agriculture.