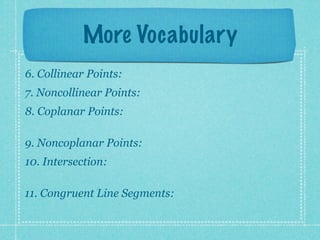
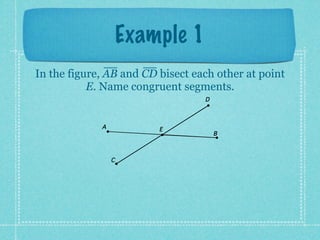
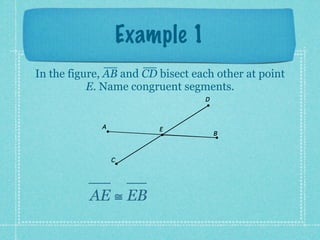
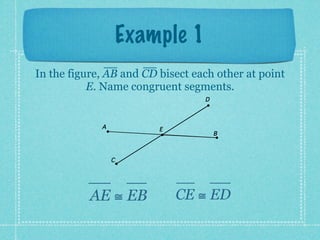
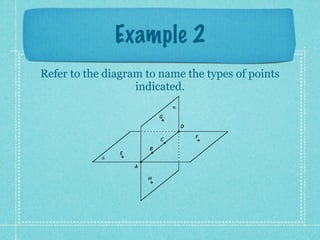
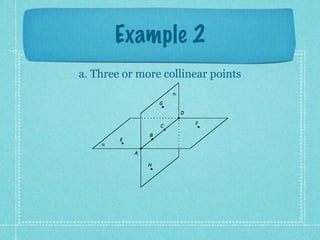
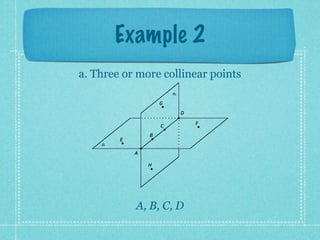
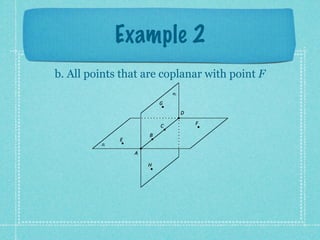
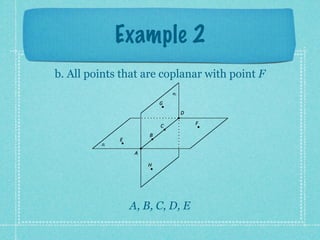
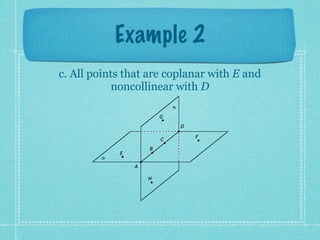
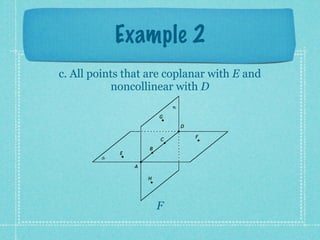
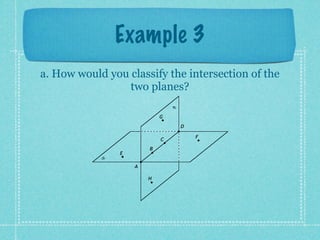
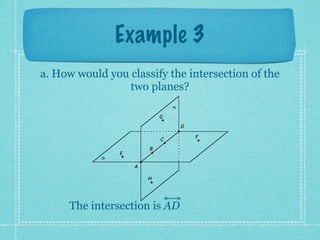
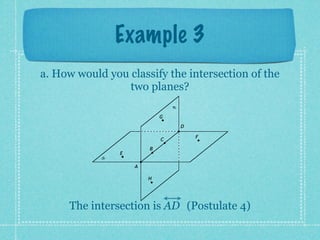
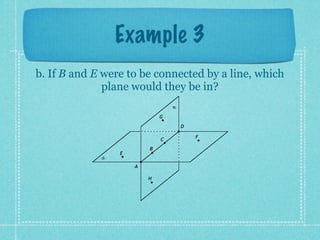
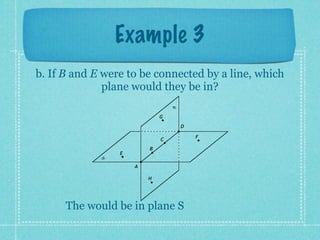
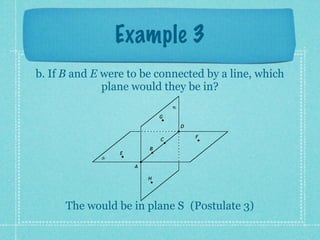
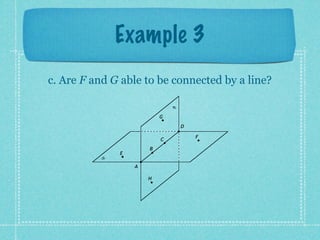
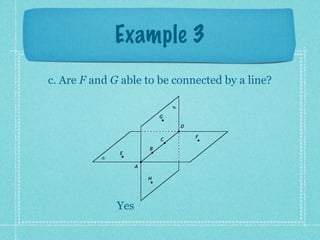
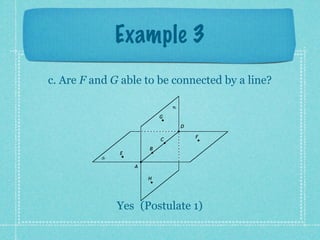
This document provides an overview of fundamental geometric concepts. It begins by defining geometry as the study of points and collections of points in space. Key terms are introduced such as point, line, plane, and space. Properties of these concepts like collinear points, coplanar points, and intersections are explained. Examples are provided to demonstrate classifying types of points and intersections. The document concludes by presenting postulates about points, lines, and planes that are assumed to be true in geometry. For homework, problems 1-29 on page 194 are assigned.