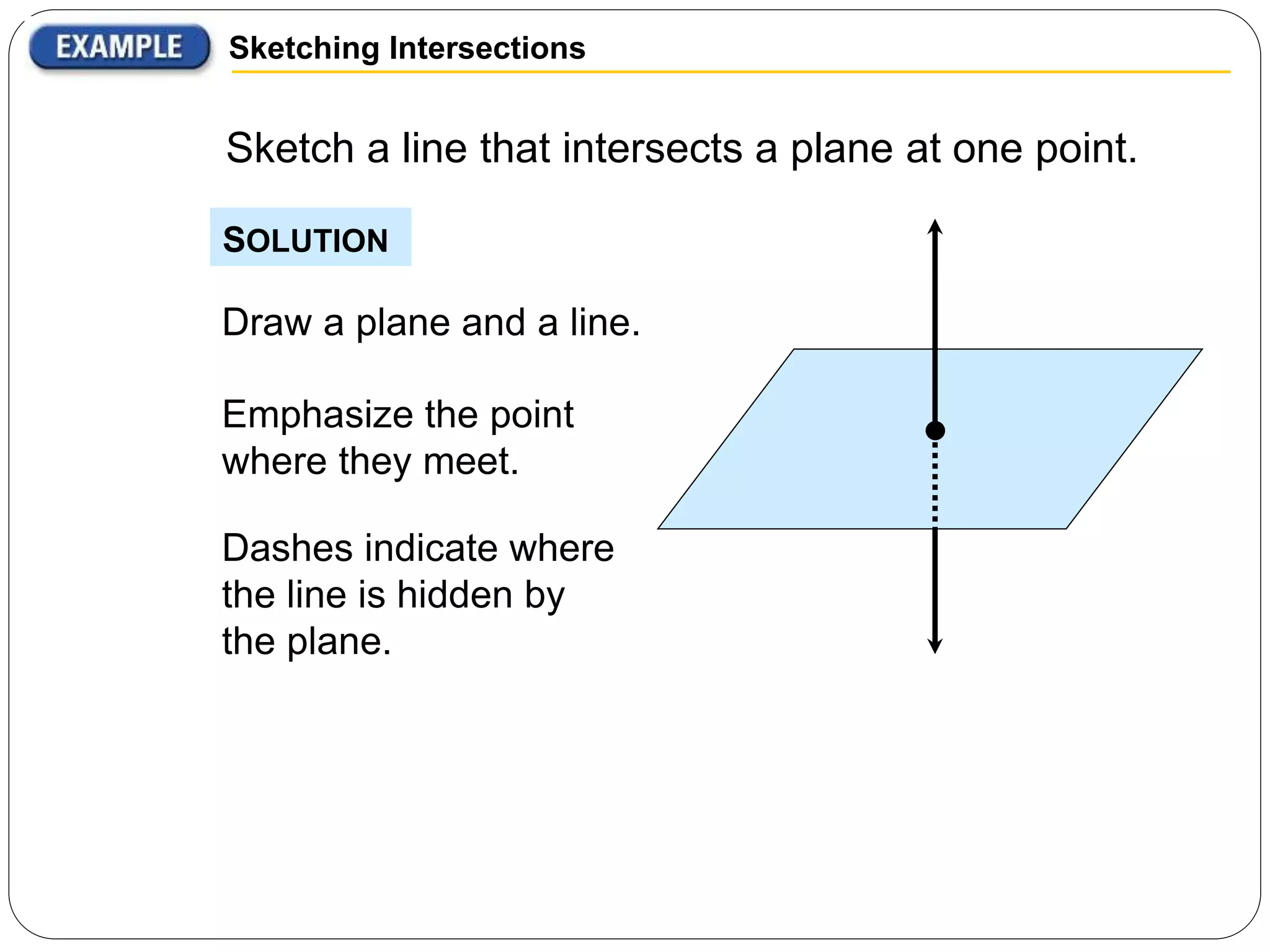
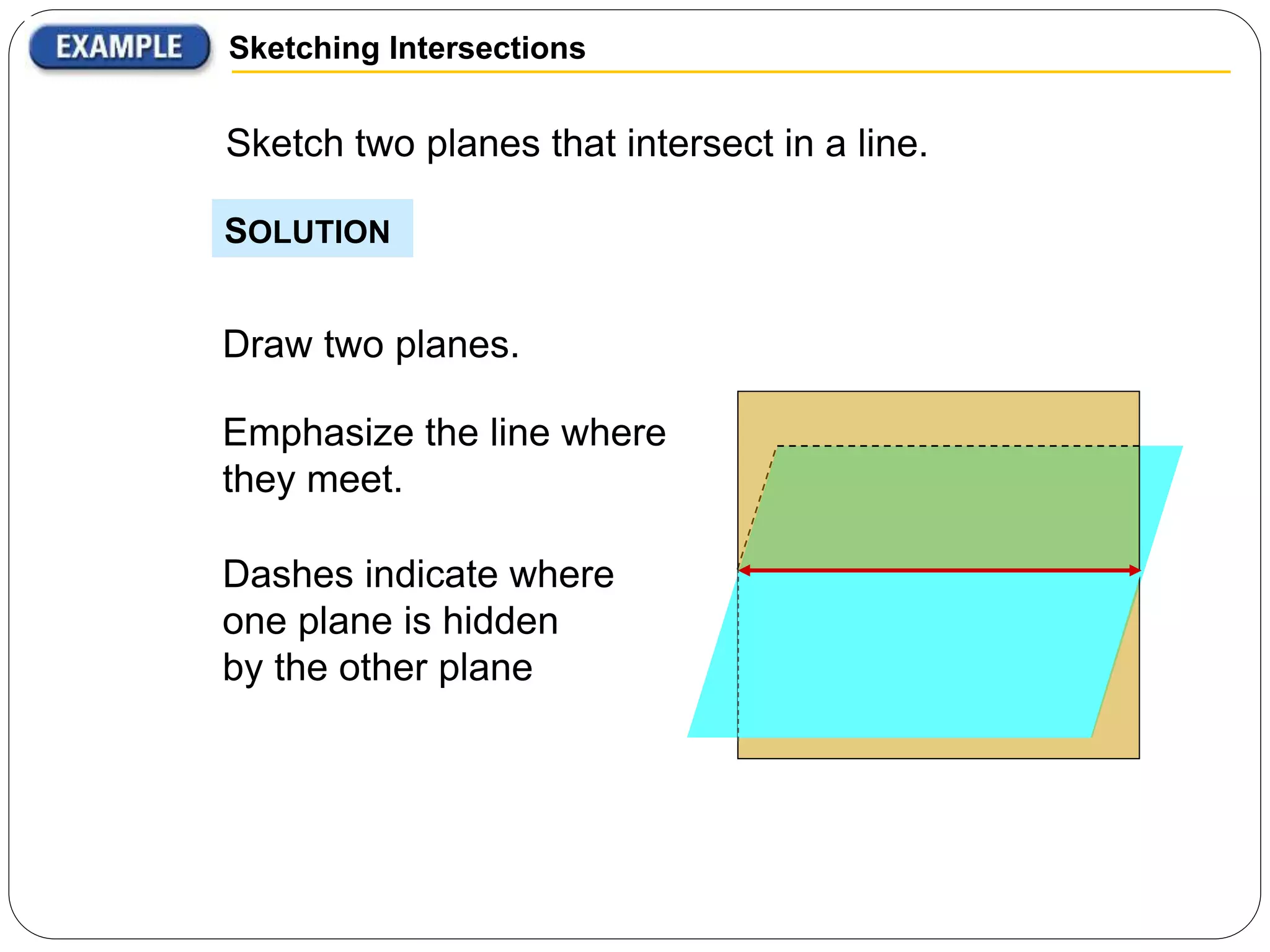
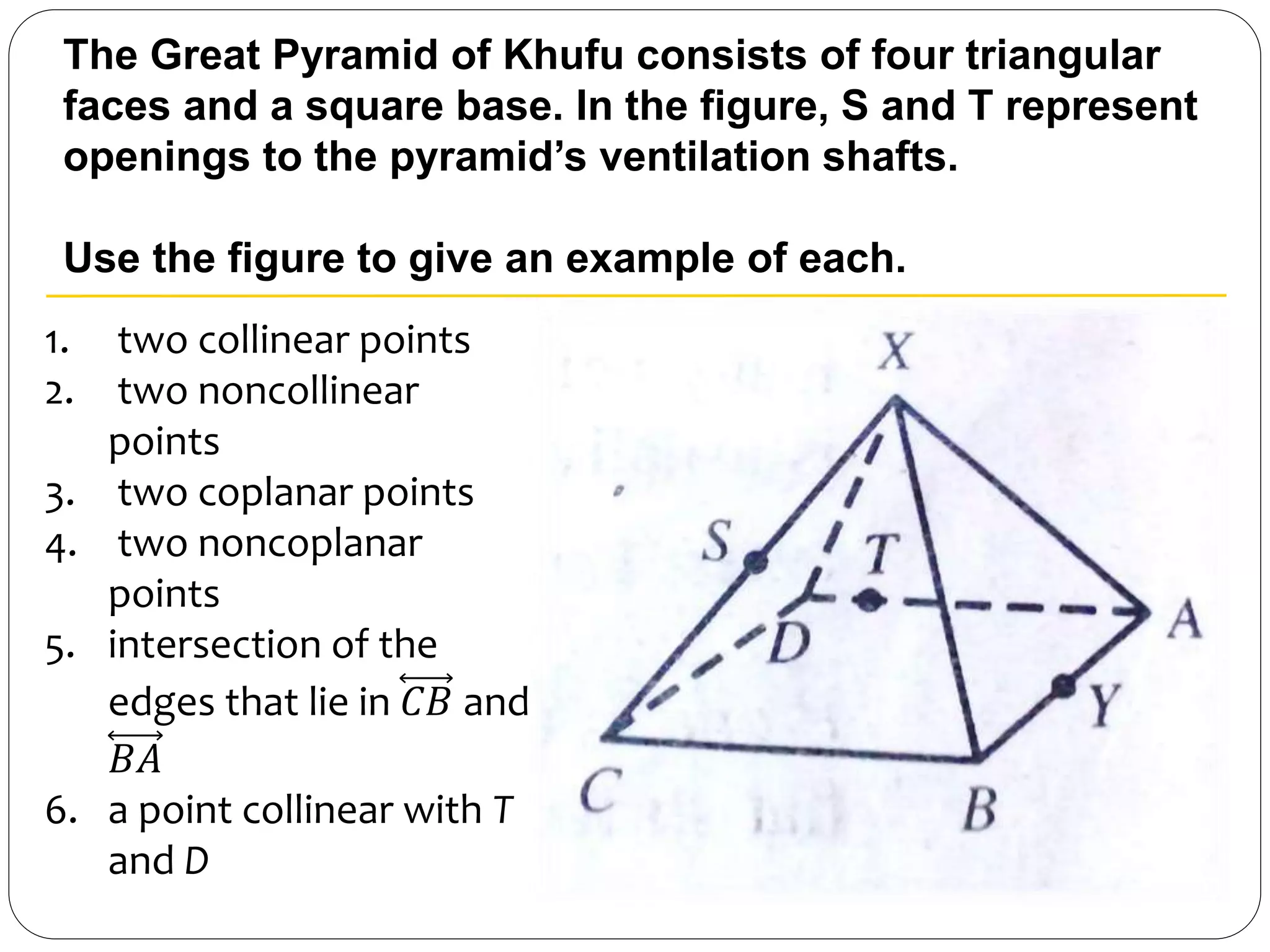
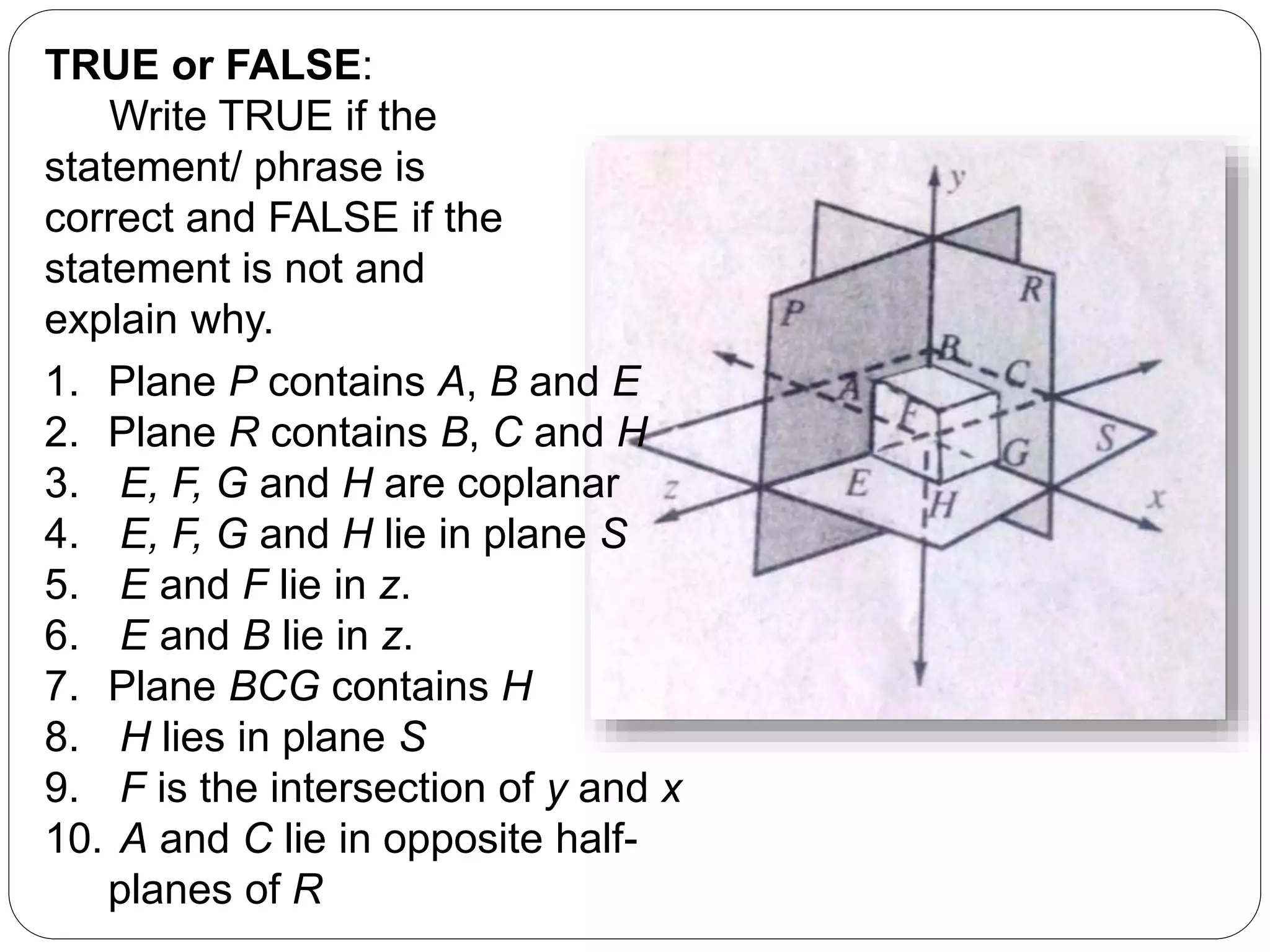
This document introduces basic geometric concepts including points, lines, and planes. It defines these terms and provides examples of representing them visually. Key points covered include:
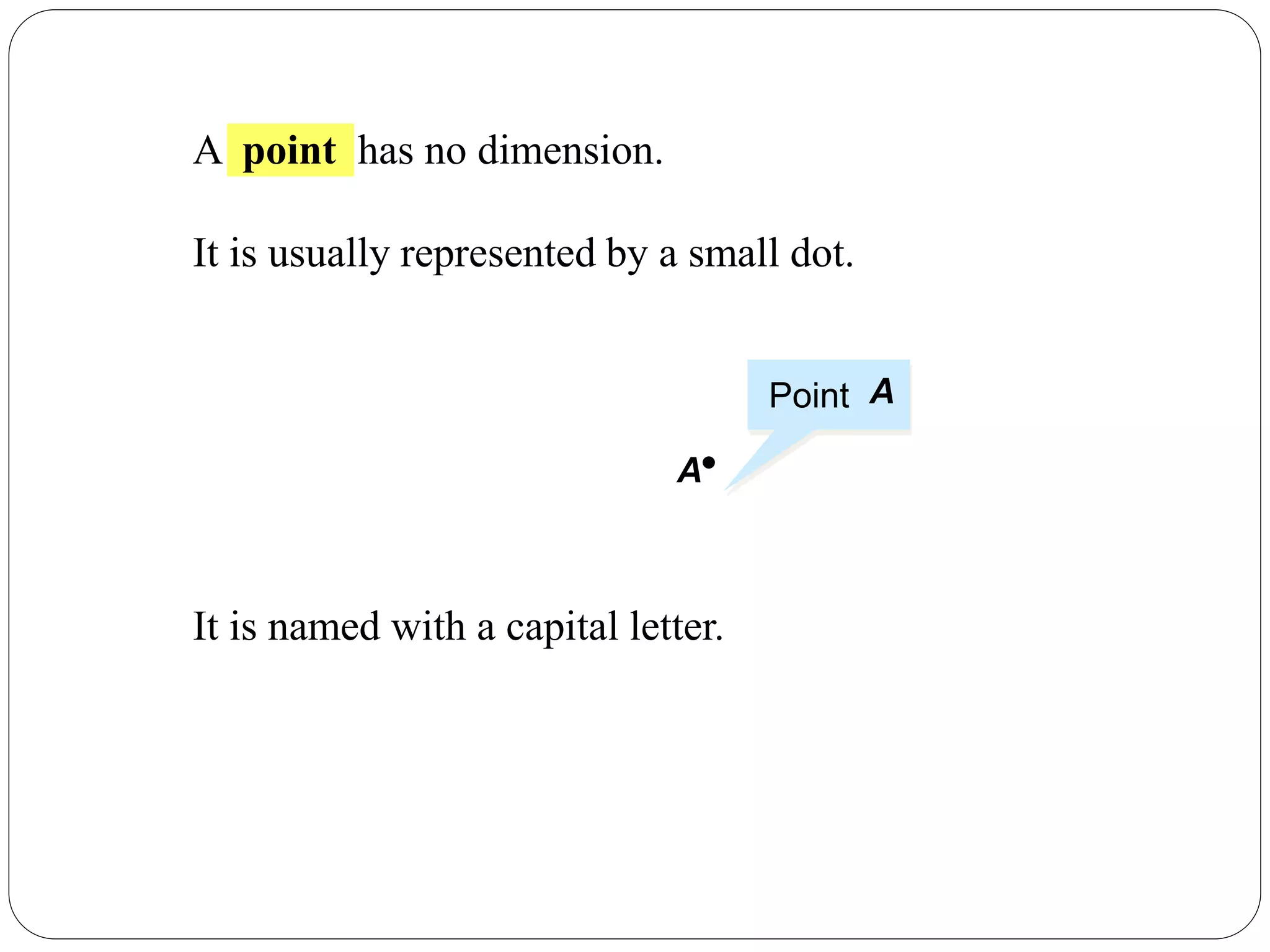
- A point has no dimension and is represented by a dot.
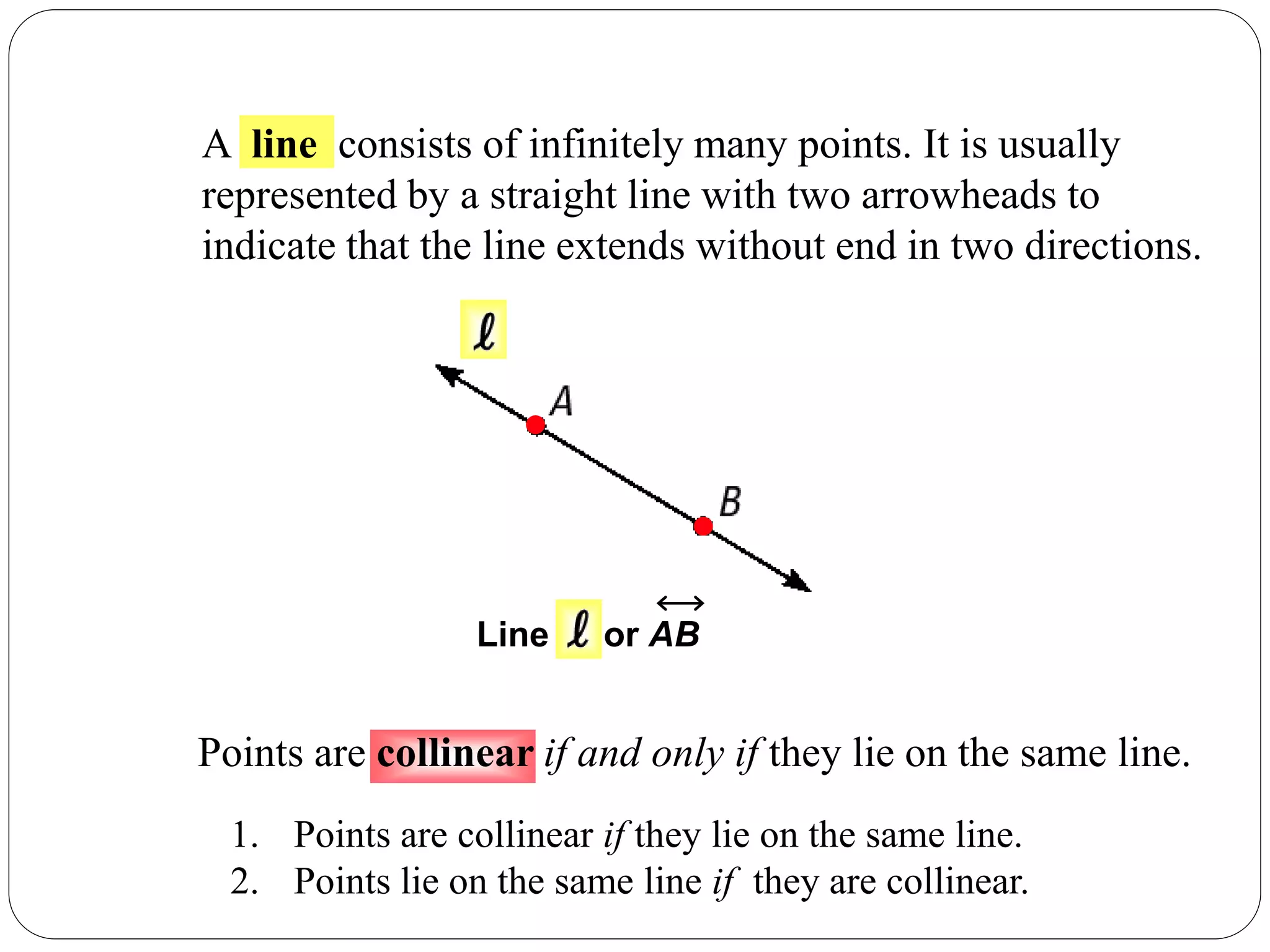
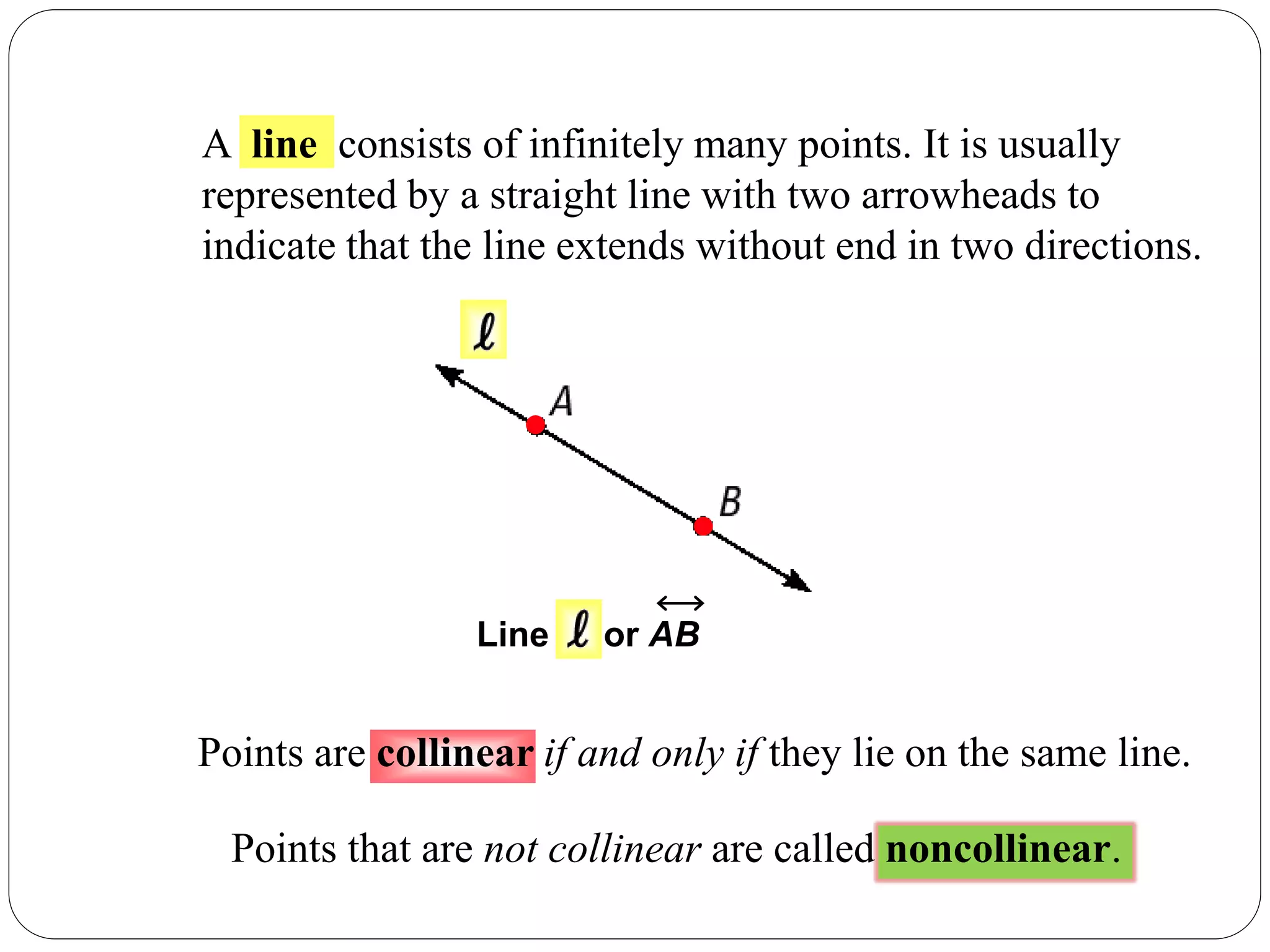
- A line consists of infinitely many points and is shown as an arrowed line.
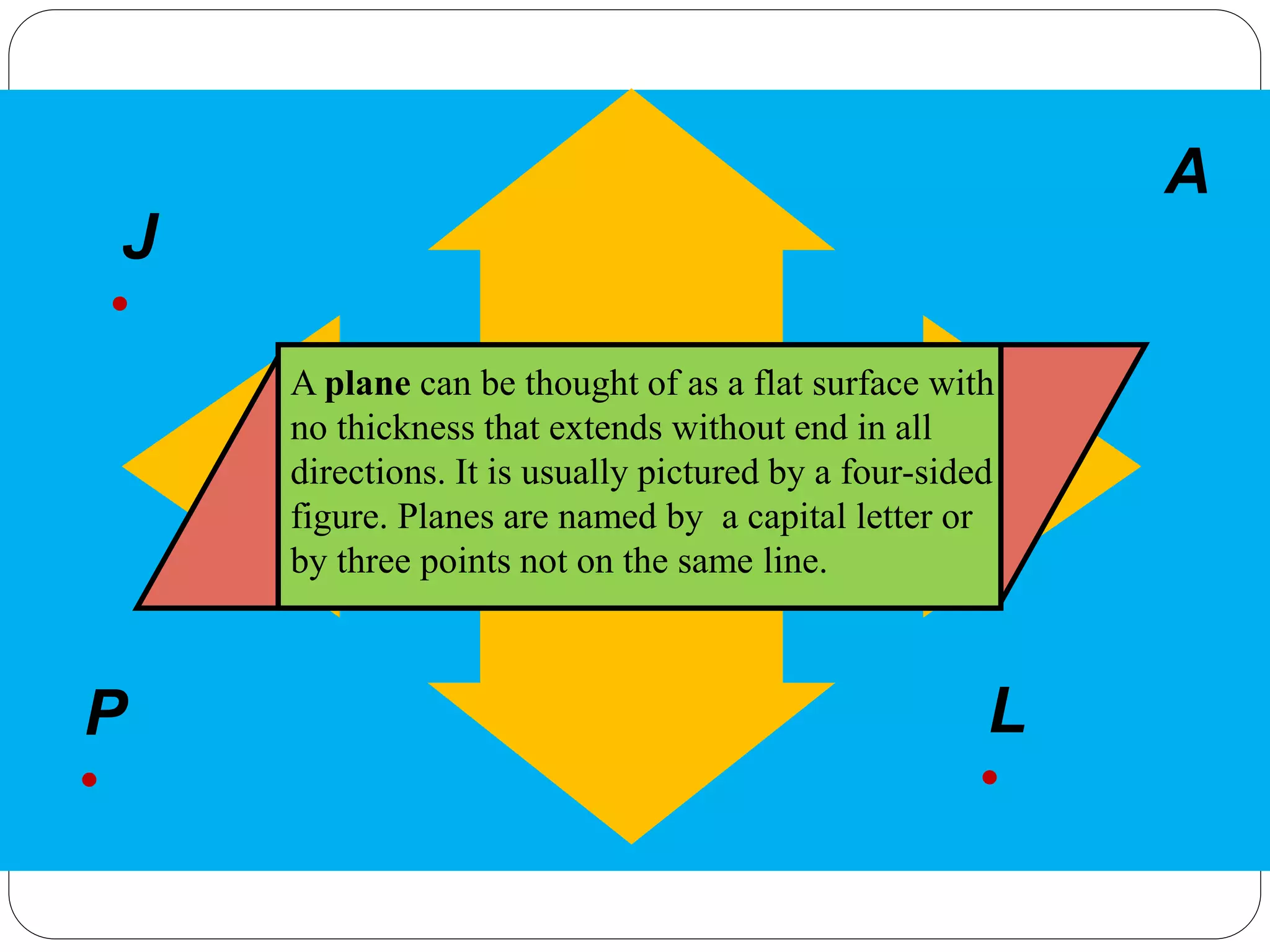
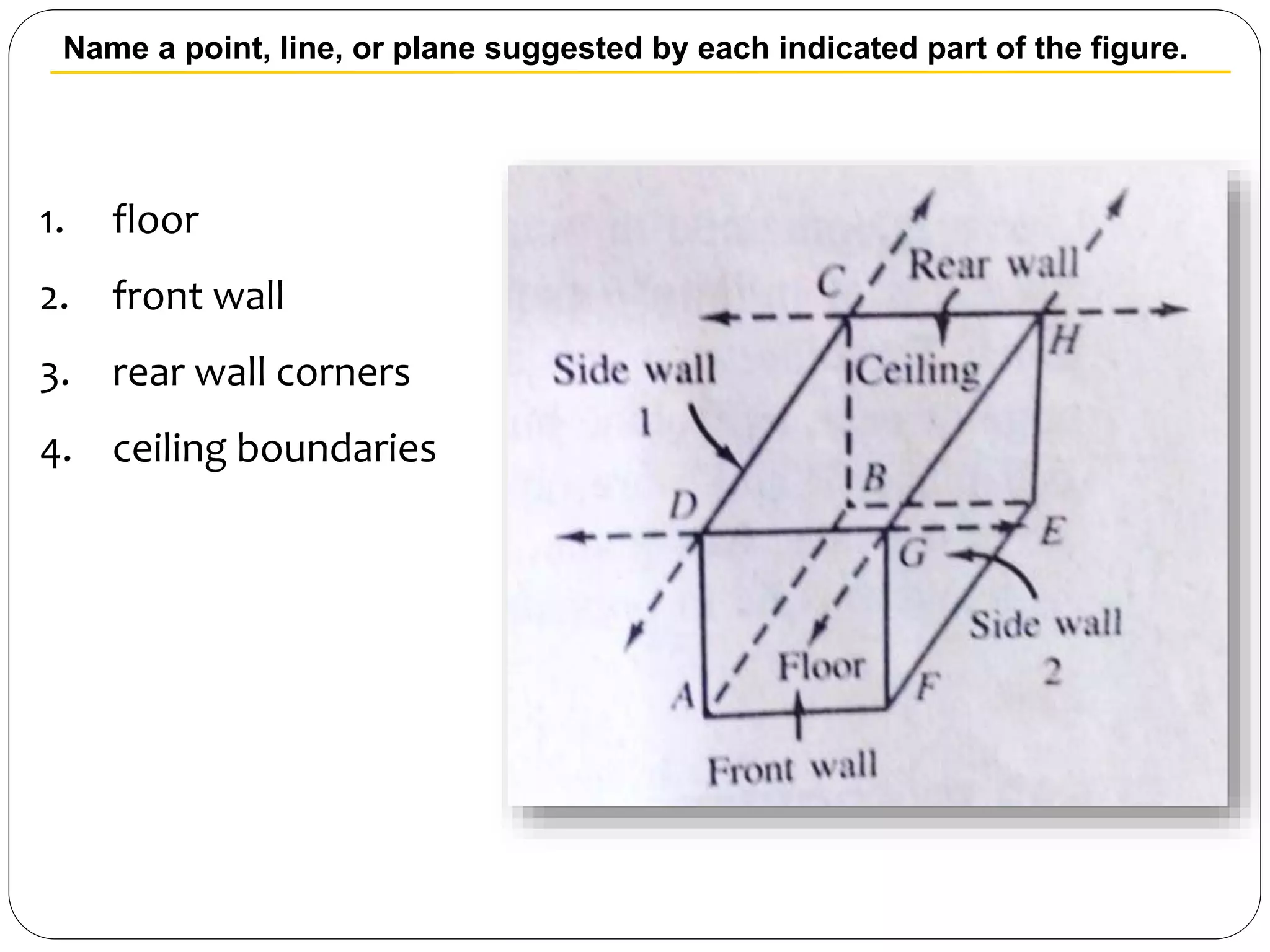
- A plane is a flat, thickness-less surface that extends indefinitely in all directions and is usually pictured as a four-sided shape.
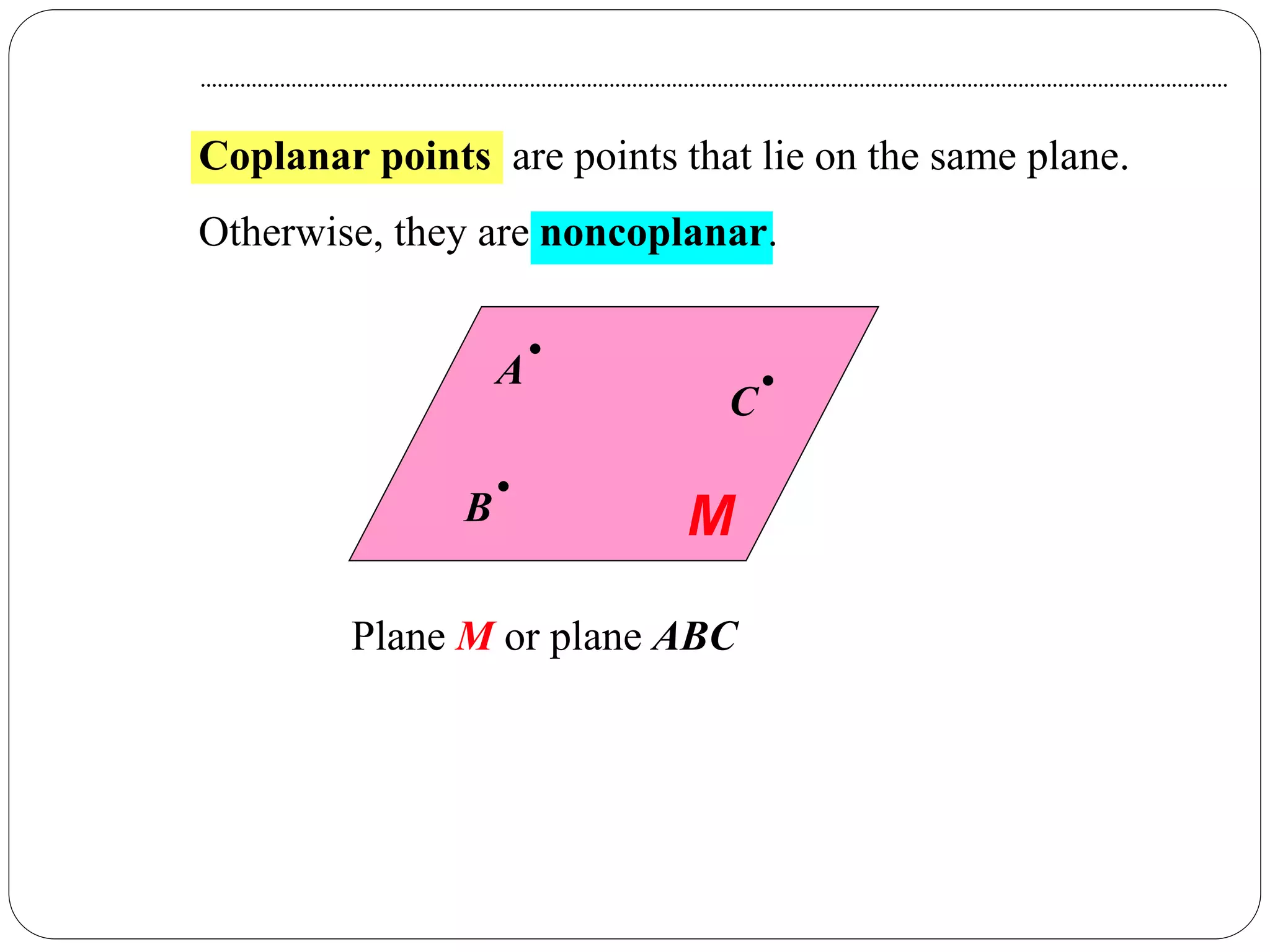
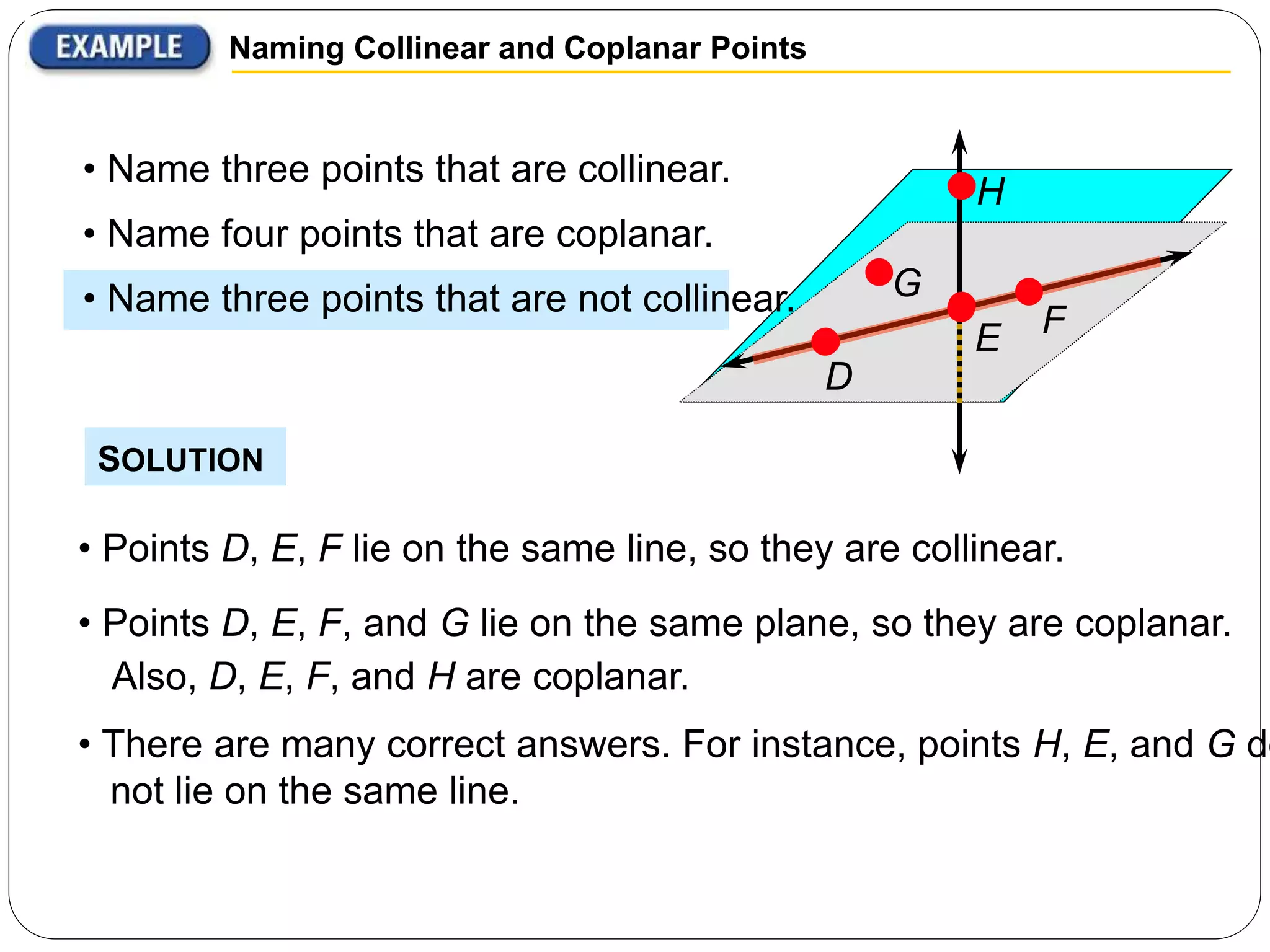
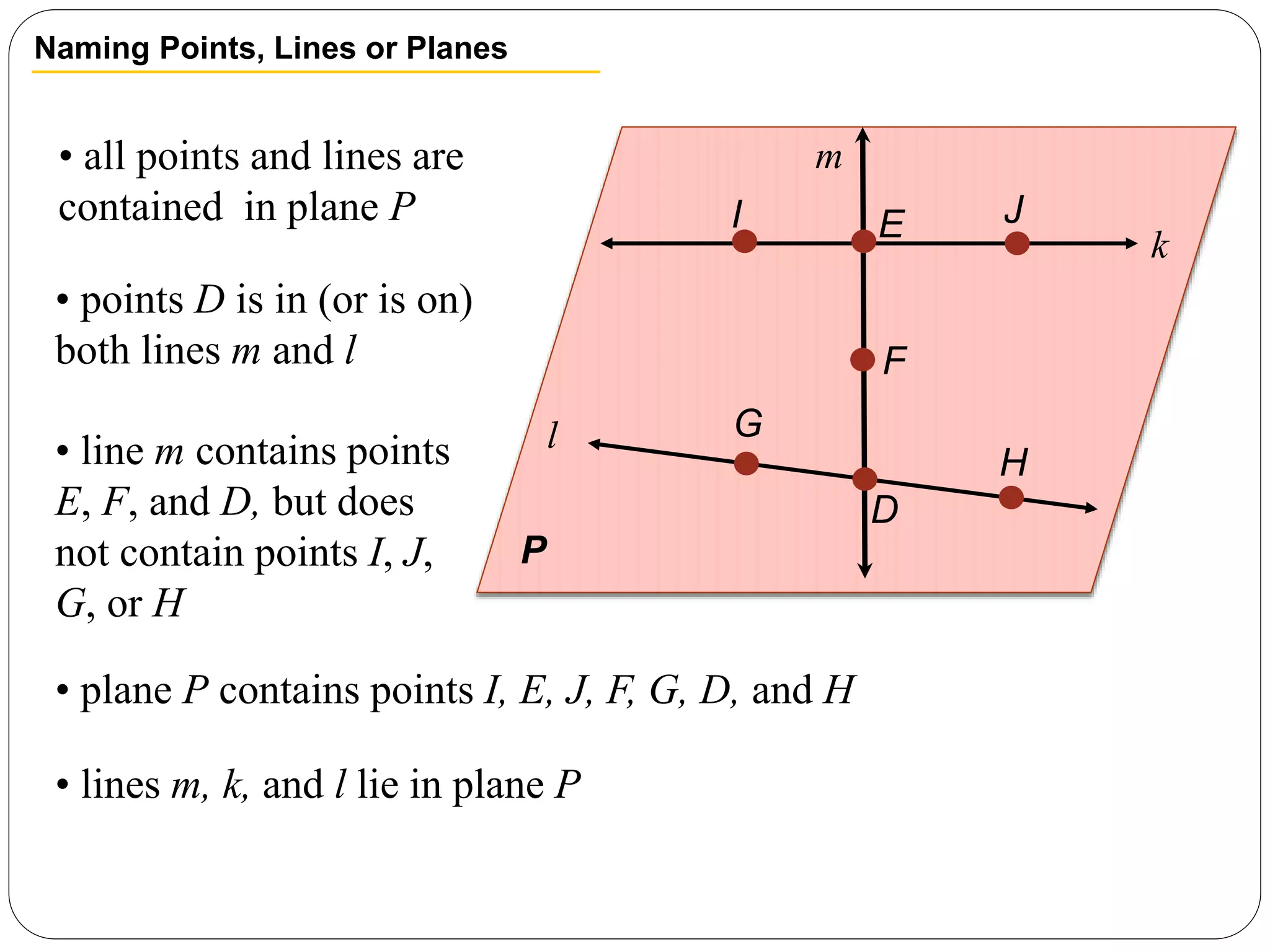
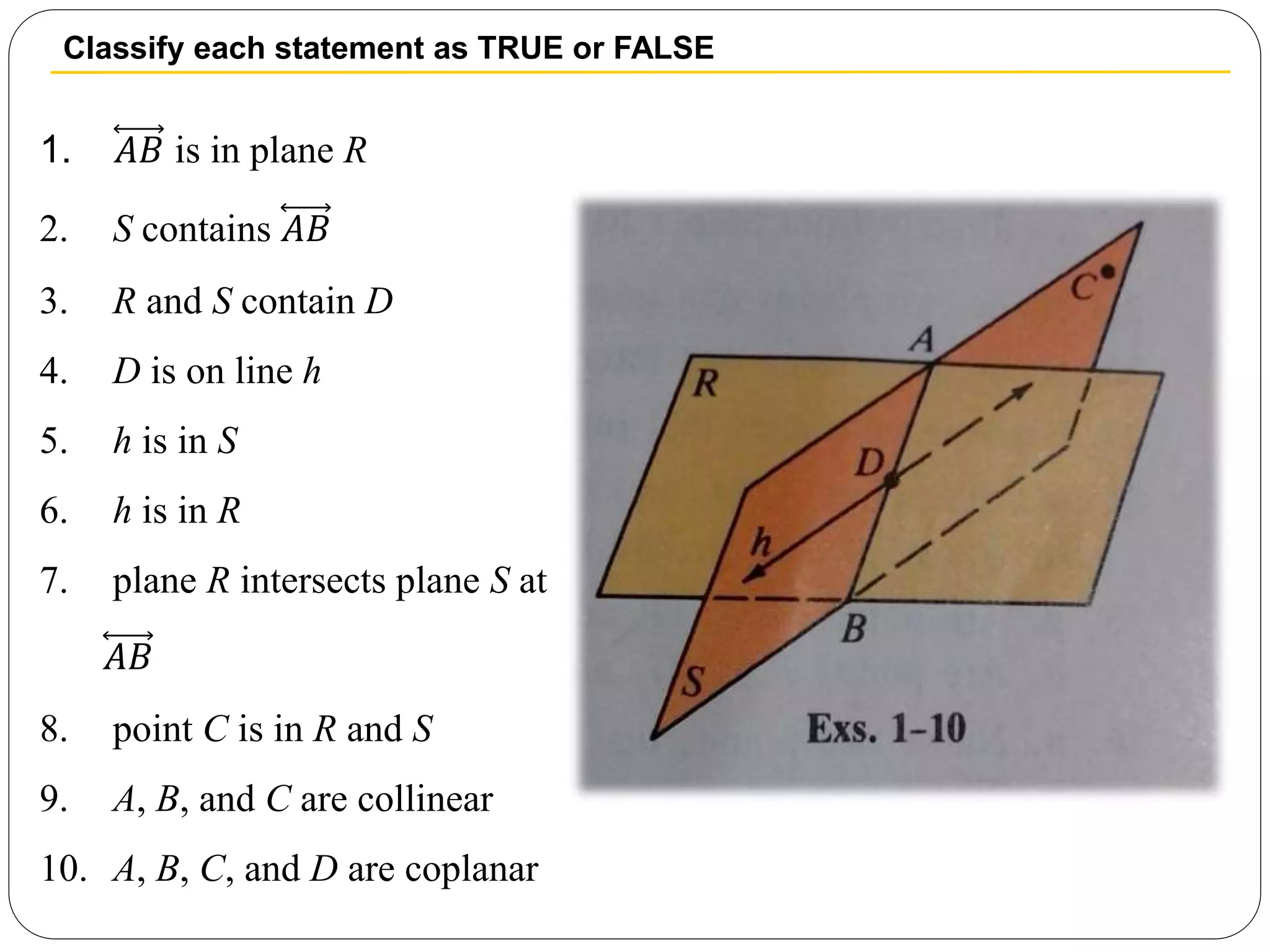
- Coplanar and collinear points are defined in relation to lying on the same plane or line, respectively.