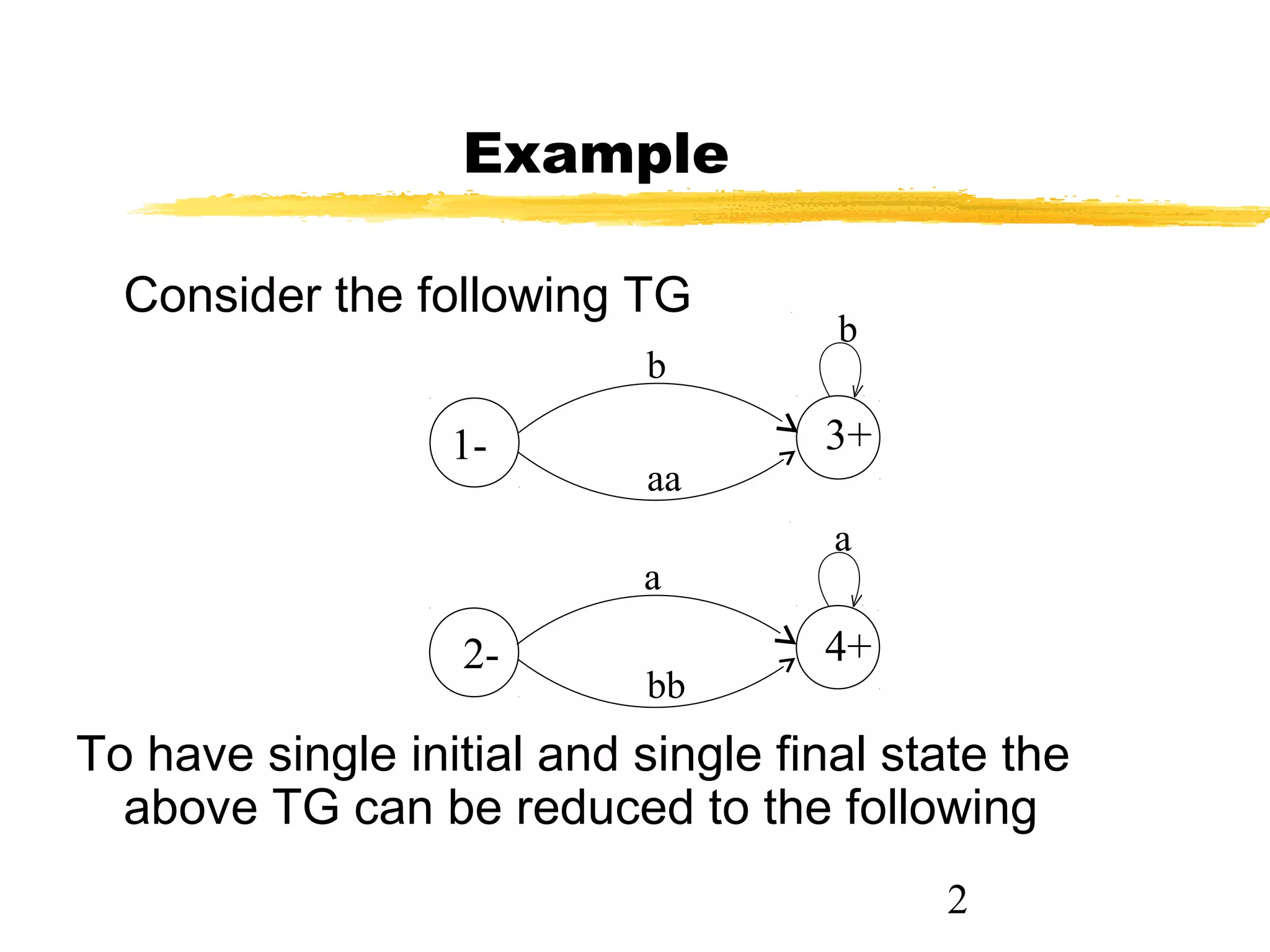
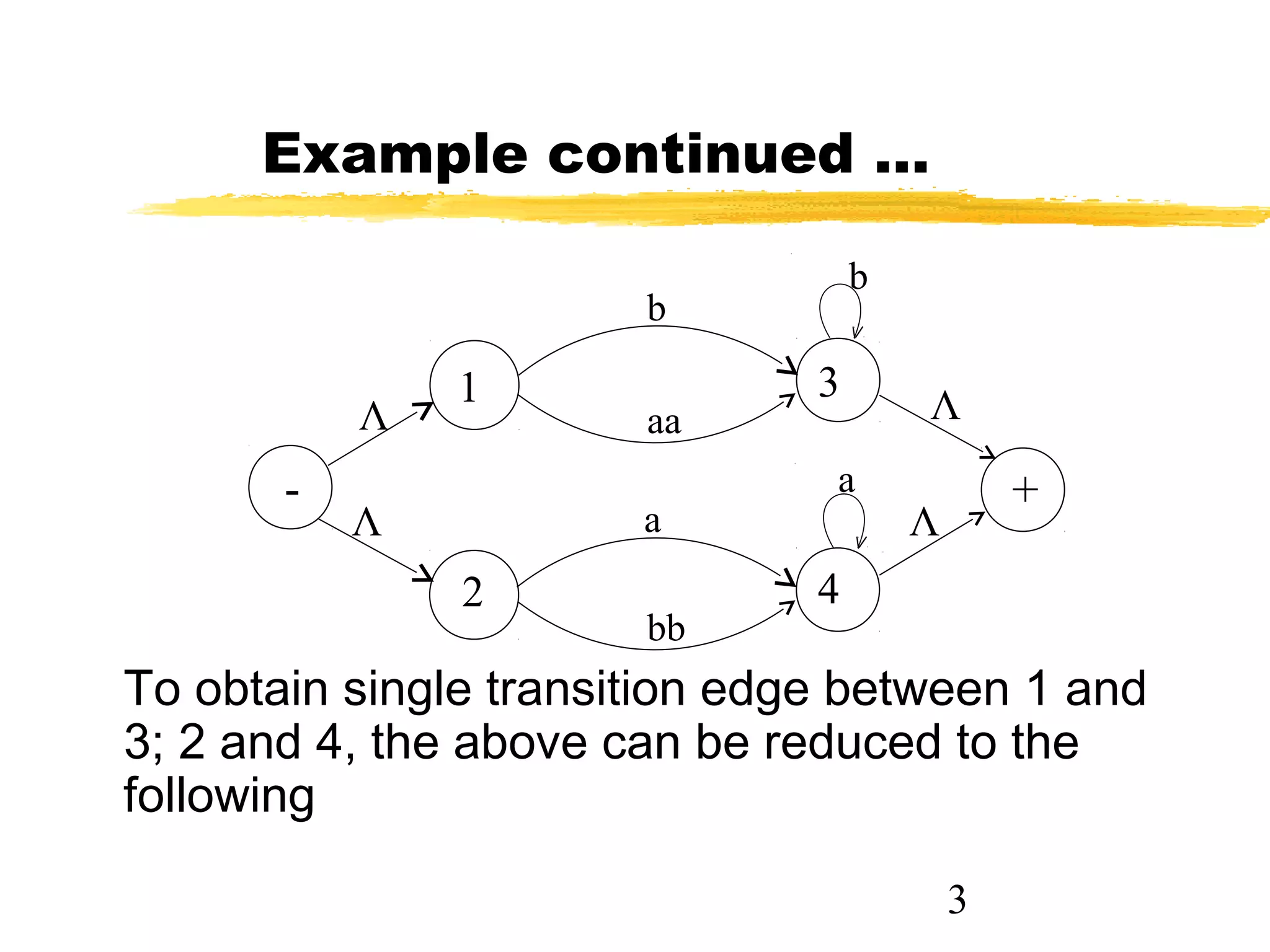
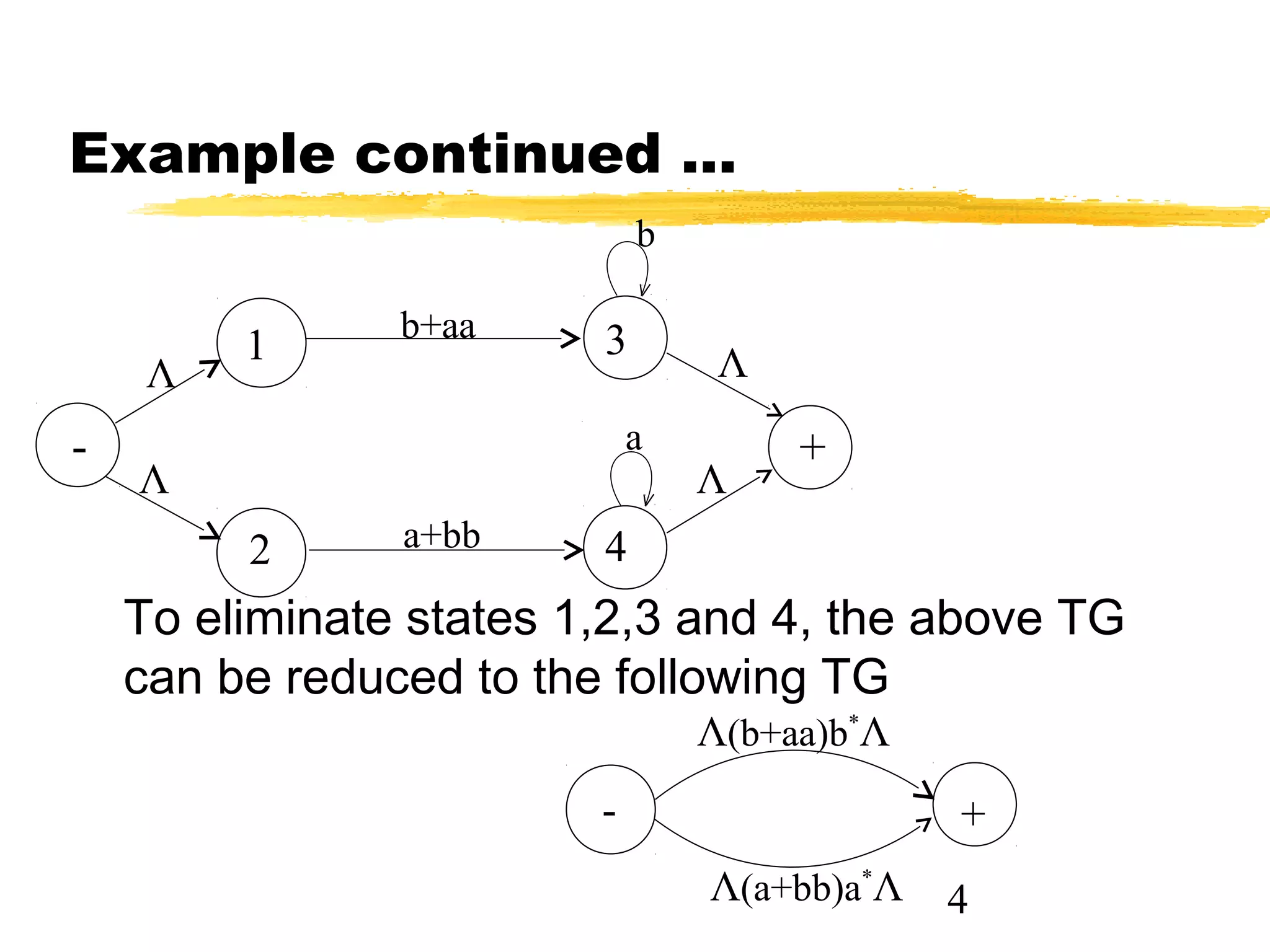
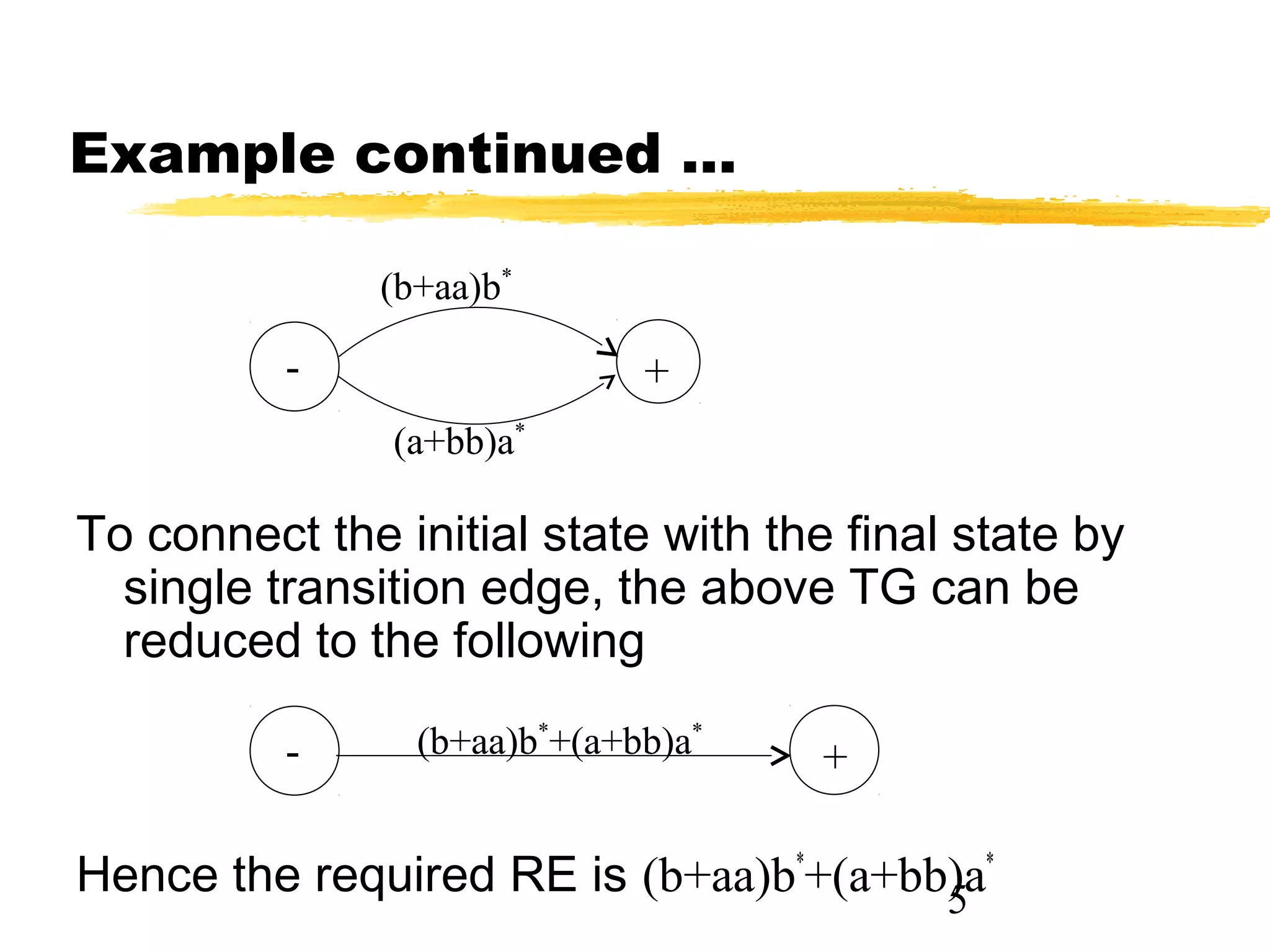
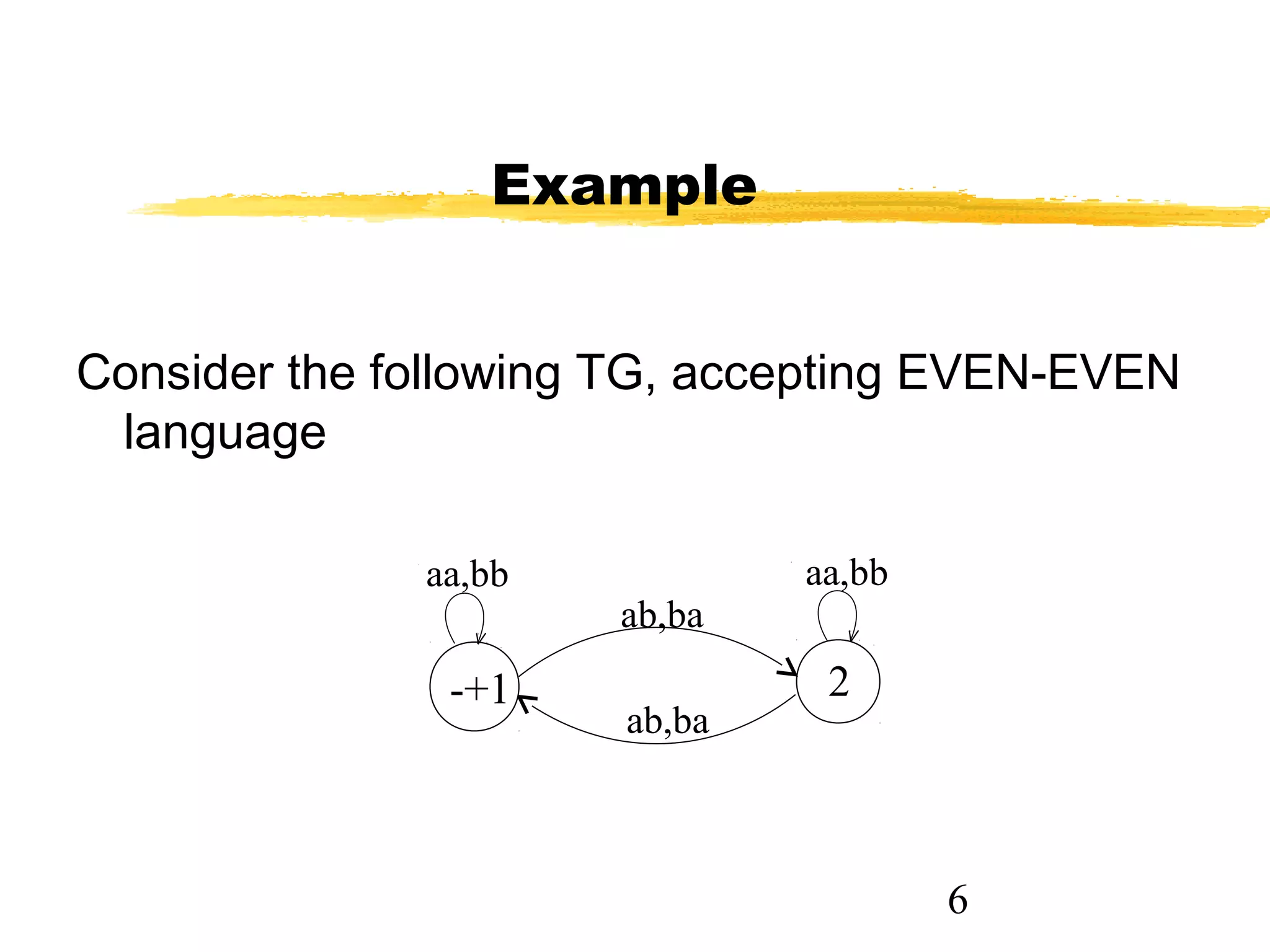
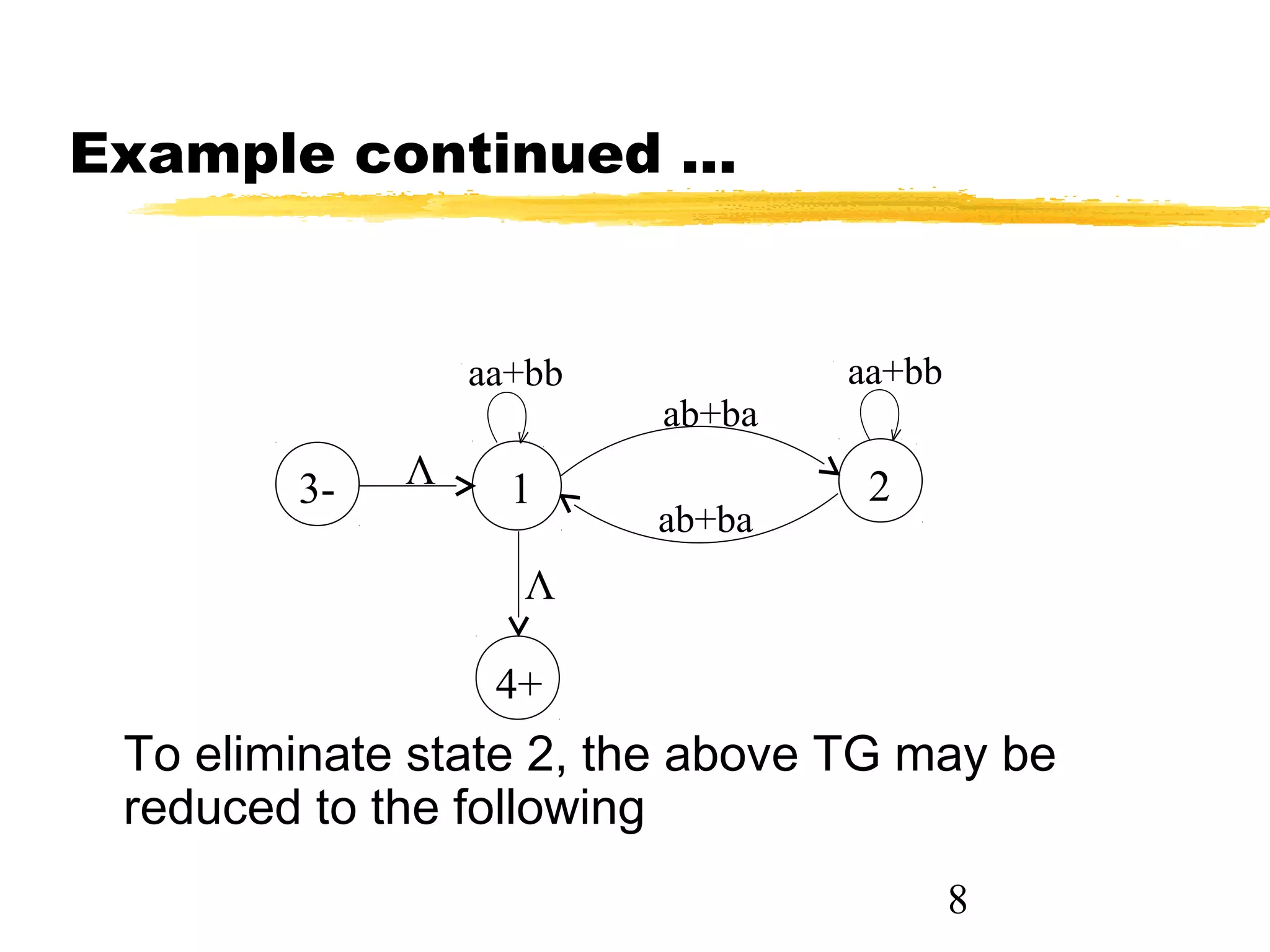
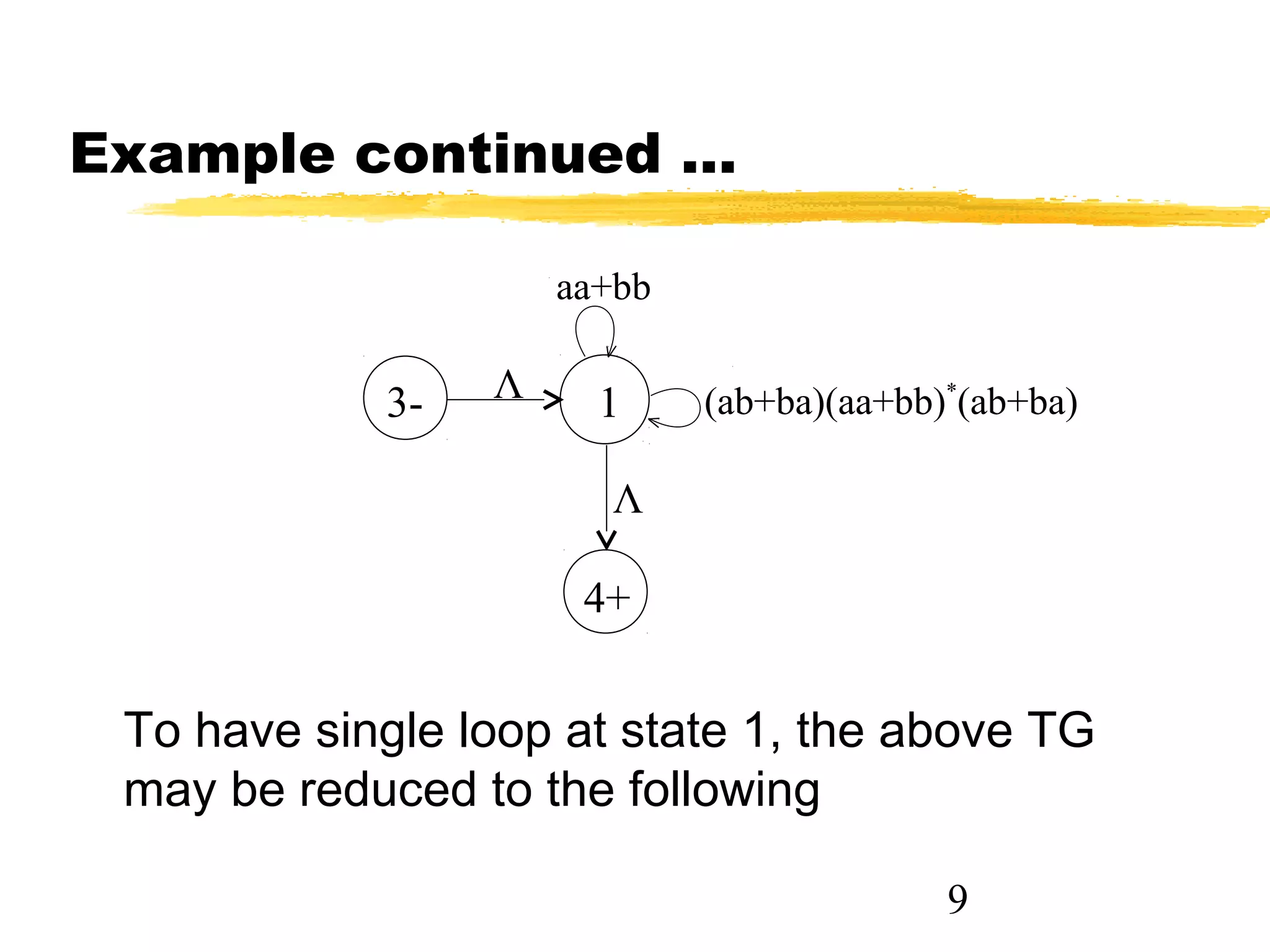
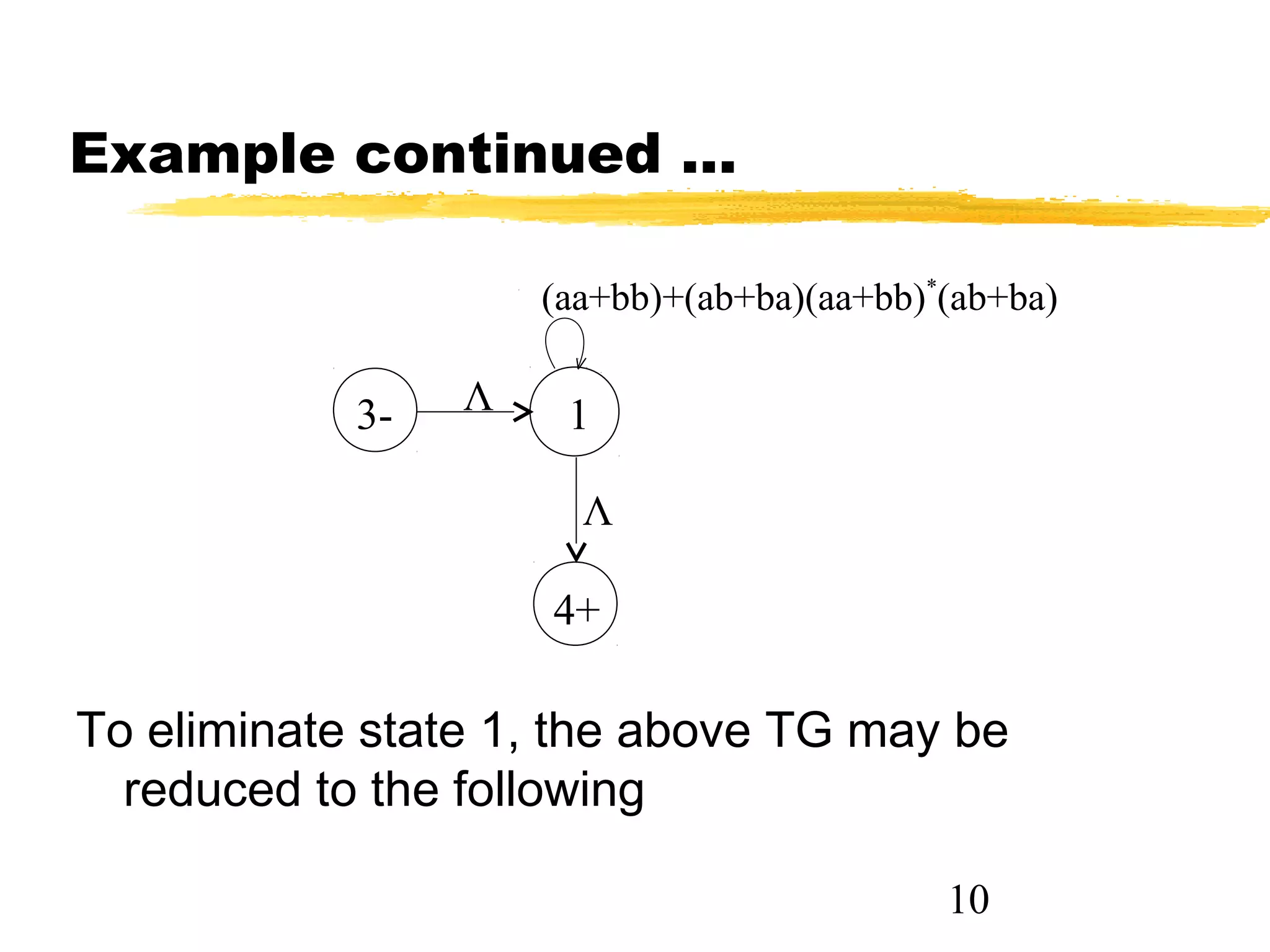
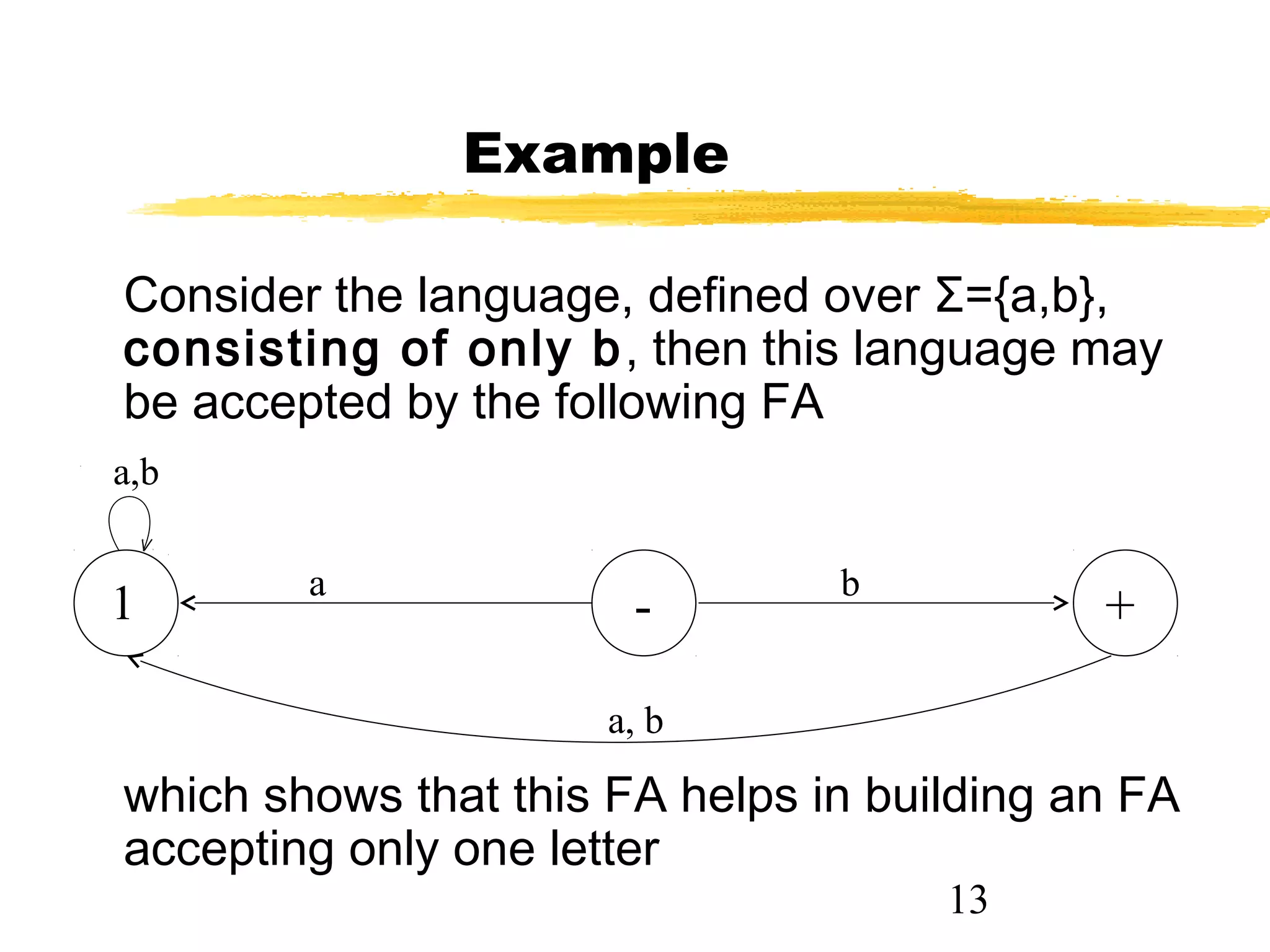
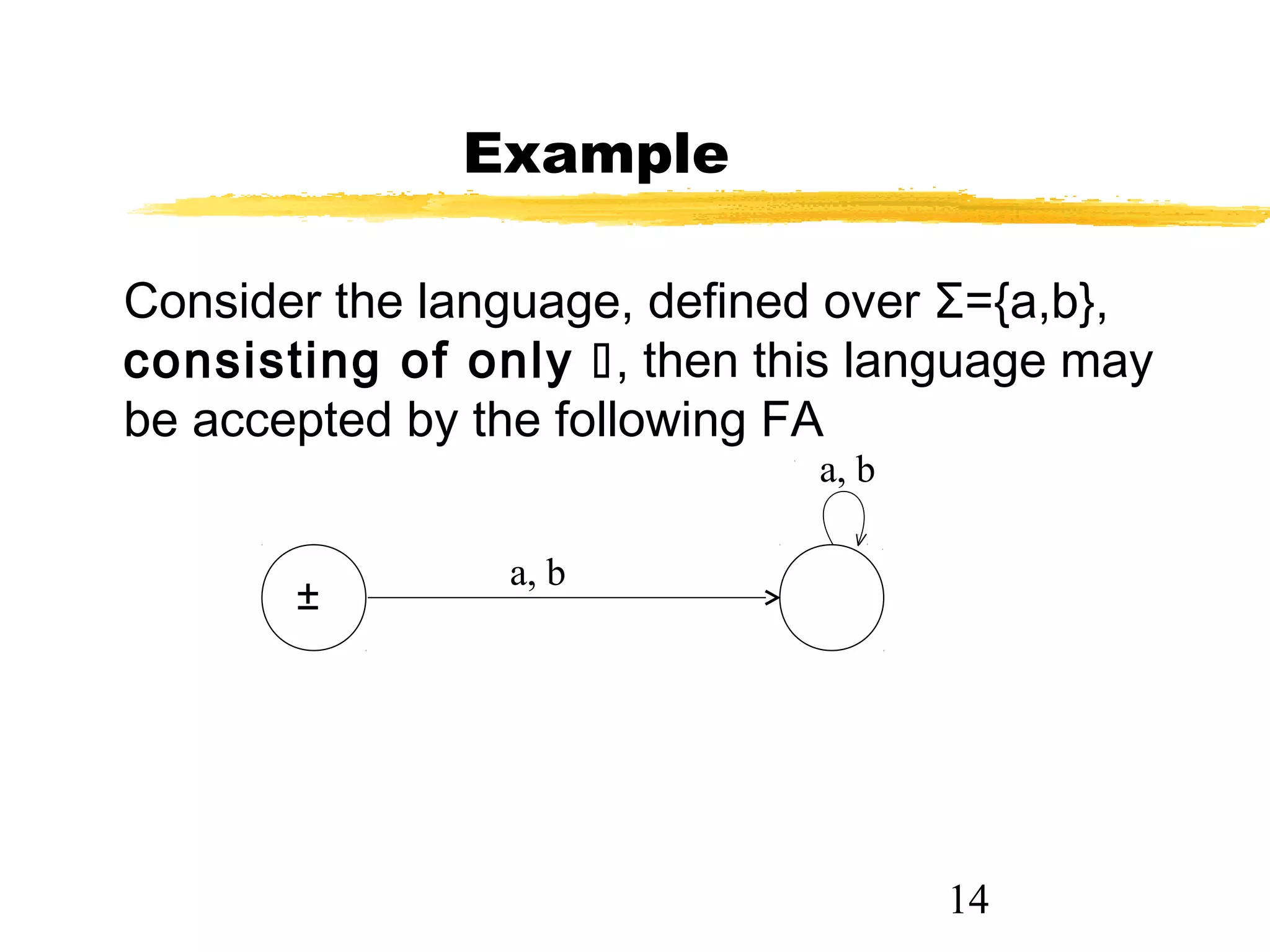
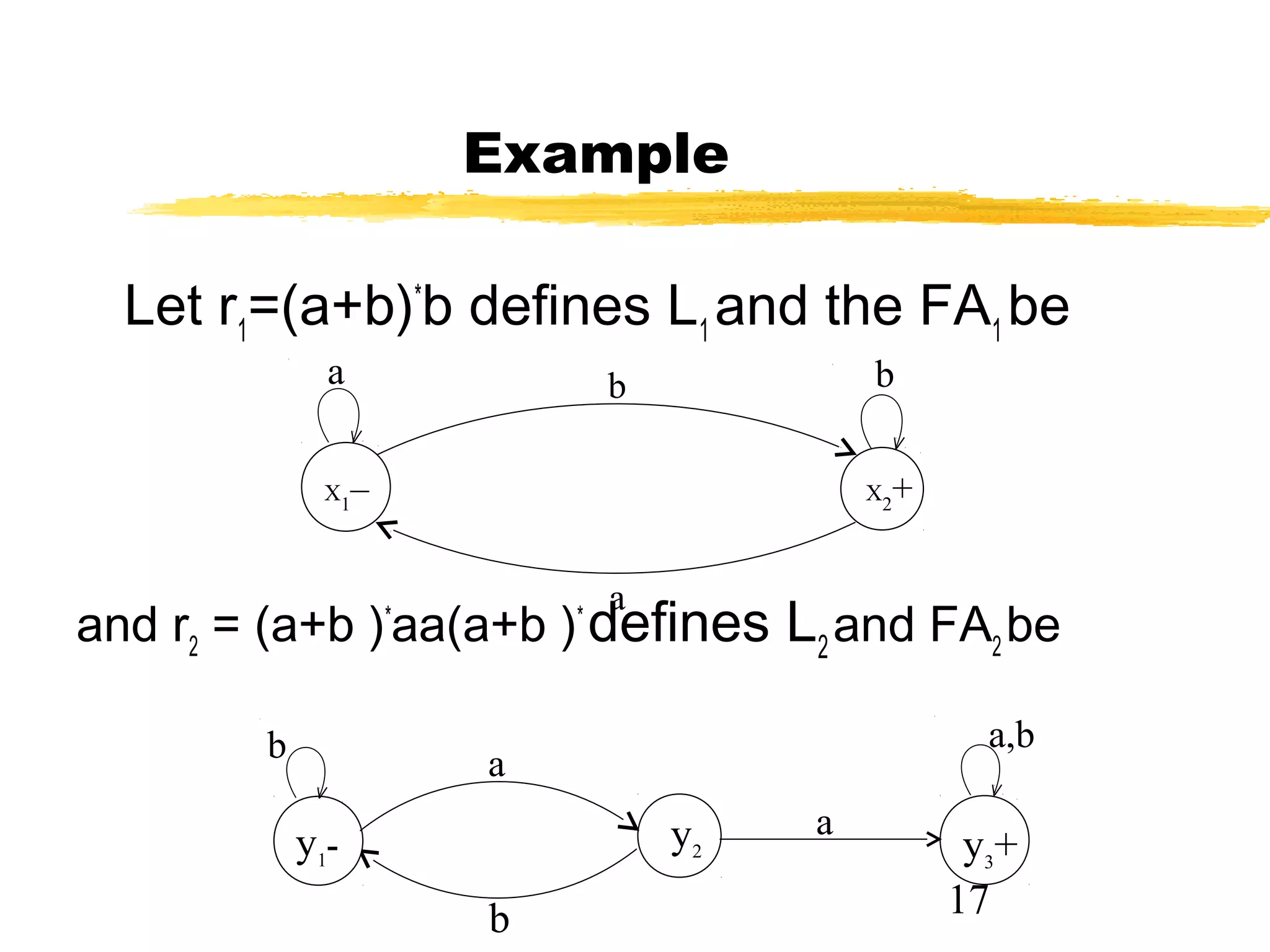
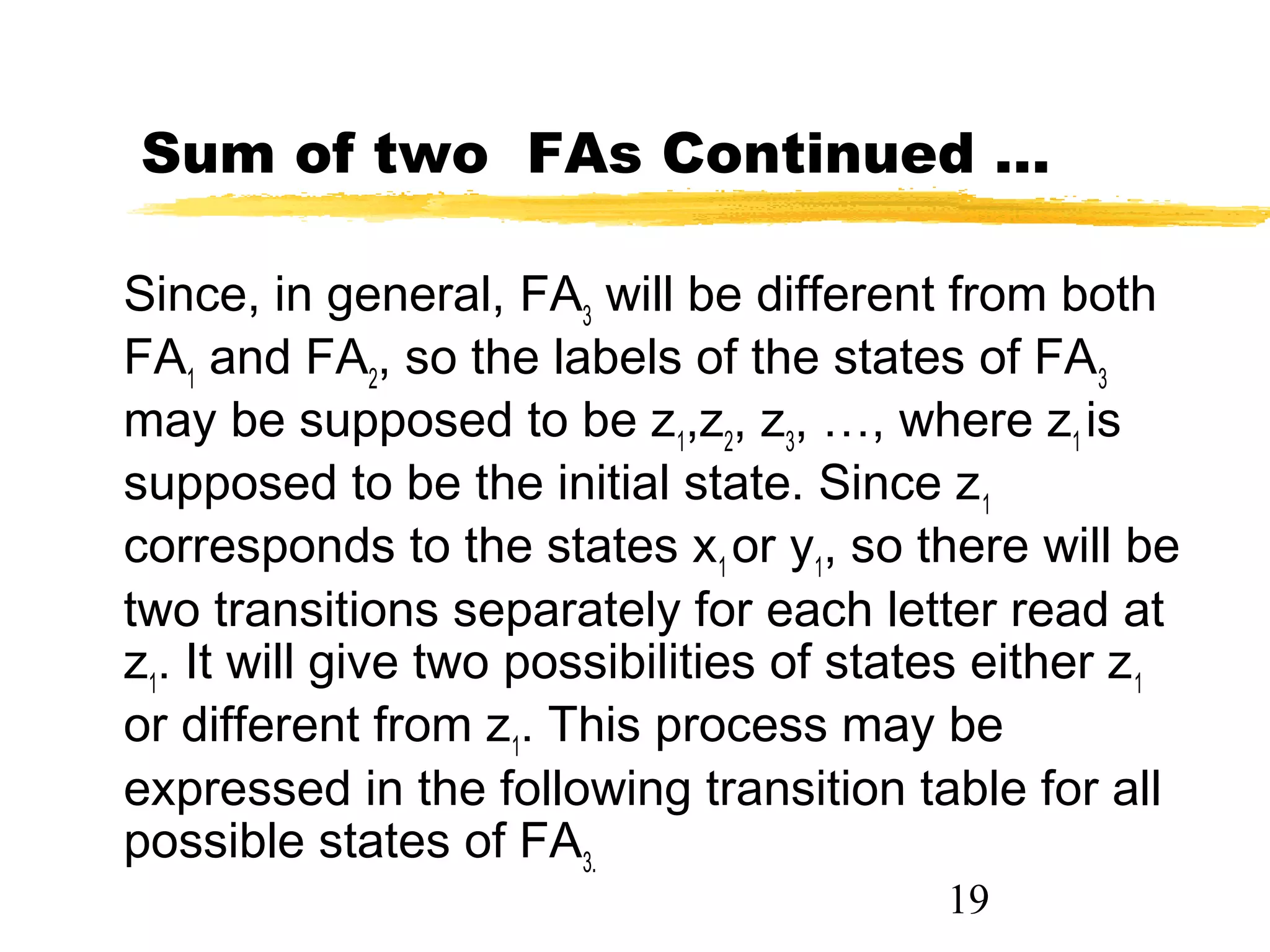
1. The document discusses examples of converting regular expressions (REs) to finite state automata (FAs) and tree grammars (TGs), including an example of a TG for an EVEN-EVEN language and its corresponding RE.
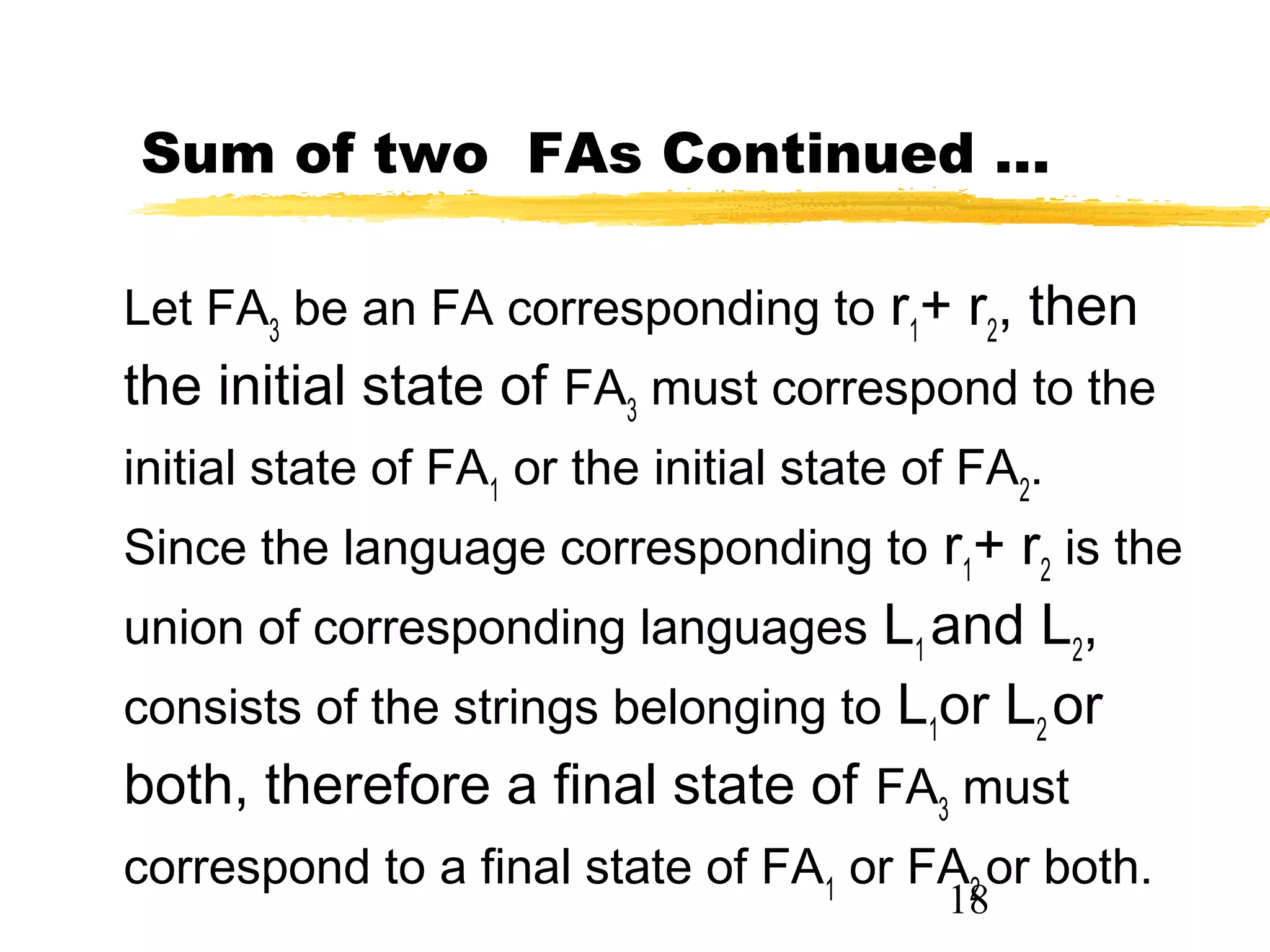
2. It explains Kleene's theorem, which states that any language expressible by a RE has a corresponding accepting FA. It provides Method 1 for building an FA for the union of two REs by taking the union of the FAs for the individual REs.
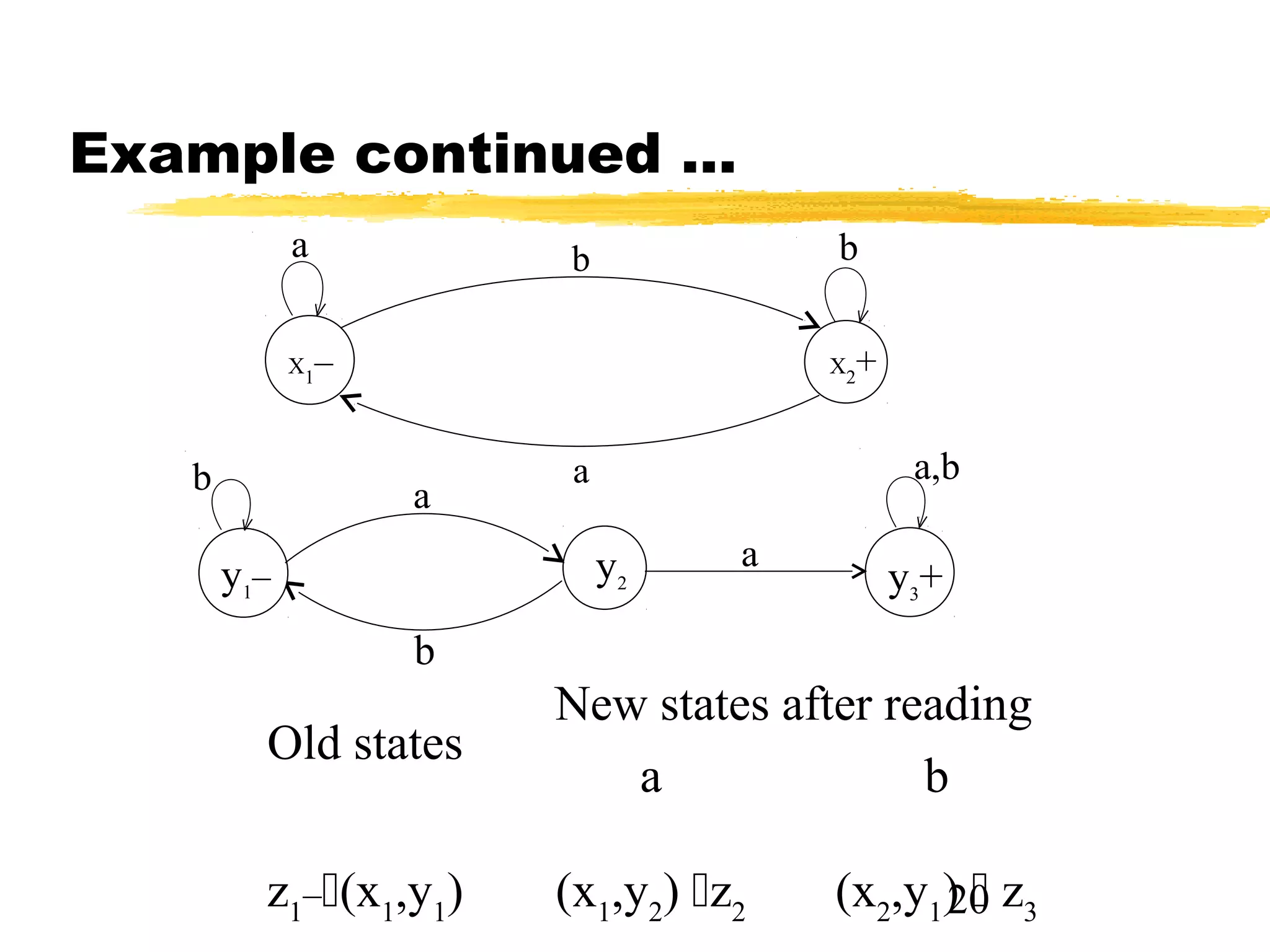
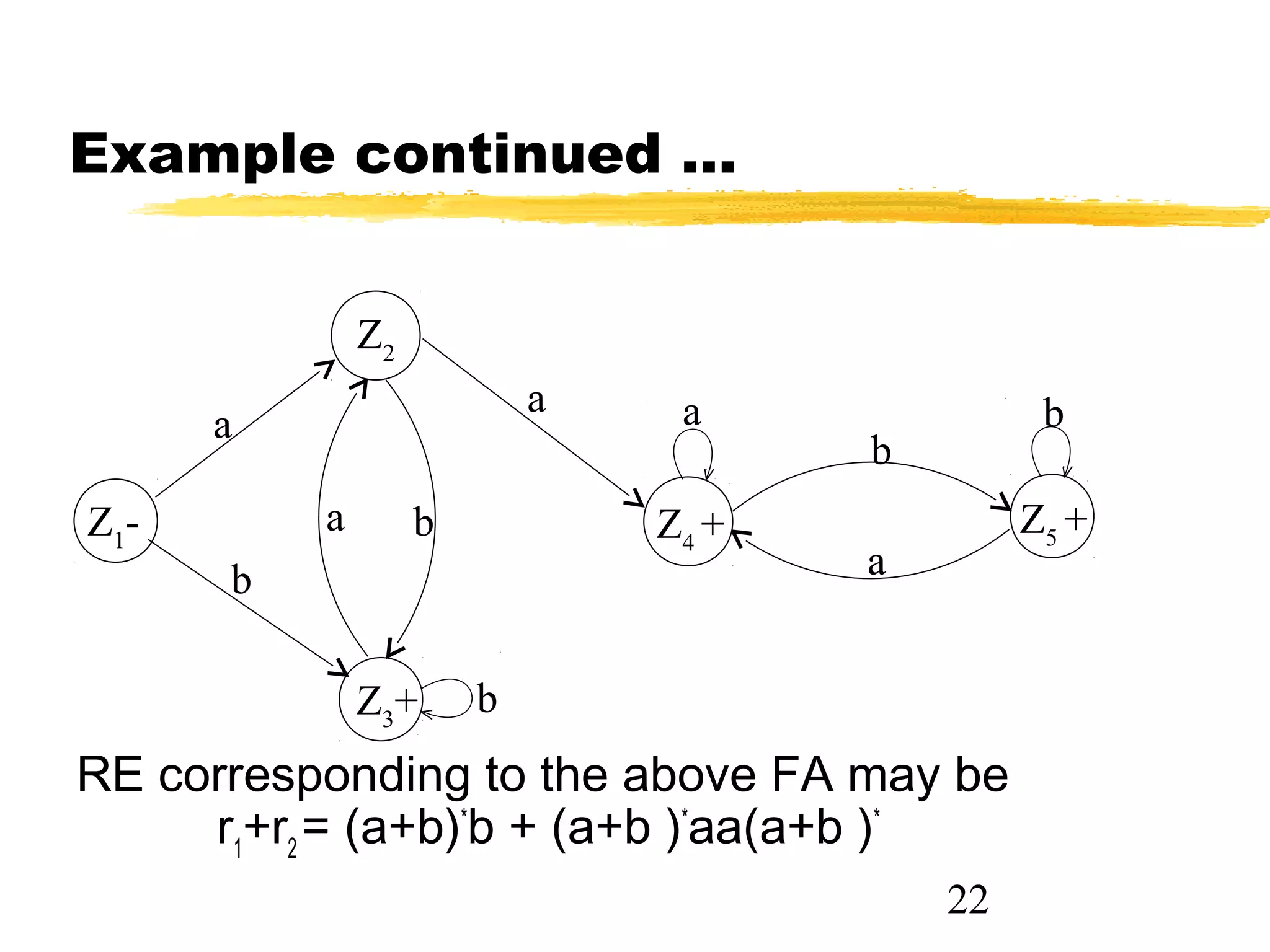
3. An example demonstrates Method 1 by building an FA for the RE r1 + r2 from the FAs for r1 and r2, showing the transition table for the new states.