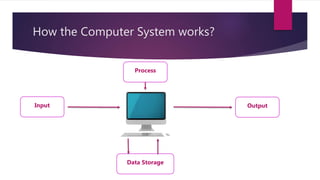
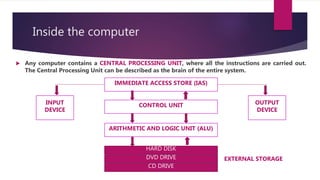
Information systems take in raw data through various input devices, store the data, process it by performing functions like calculating and sorting, and output the results through devices like screens and printers. A computer is an example of an information system, with a central processing unit that controls data movement and performs arithmetic/logical operations, internal memory, and connections to external storage and input/output devices. The basic components of a desktop computer system include the system unit, screen, keyboard, mouse, and drives for storage media.