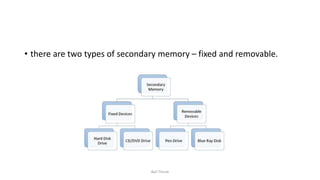
Computer memory can be divided into three main types: cache memory, primary/main memory, and secondary memory. Primary memory is the working memory of the computer, usually made up of semiconductor devices like RAM and ROM. Secondary memory is for long-term storage, includes magnetic disks, optical disks like CDs/DVDs, and tapes. Memory is also divided into smaller units called cells that each have a unique address from 0 to the total memory size minus one.