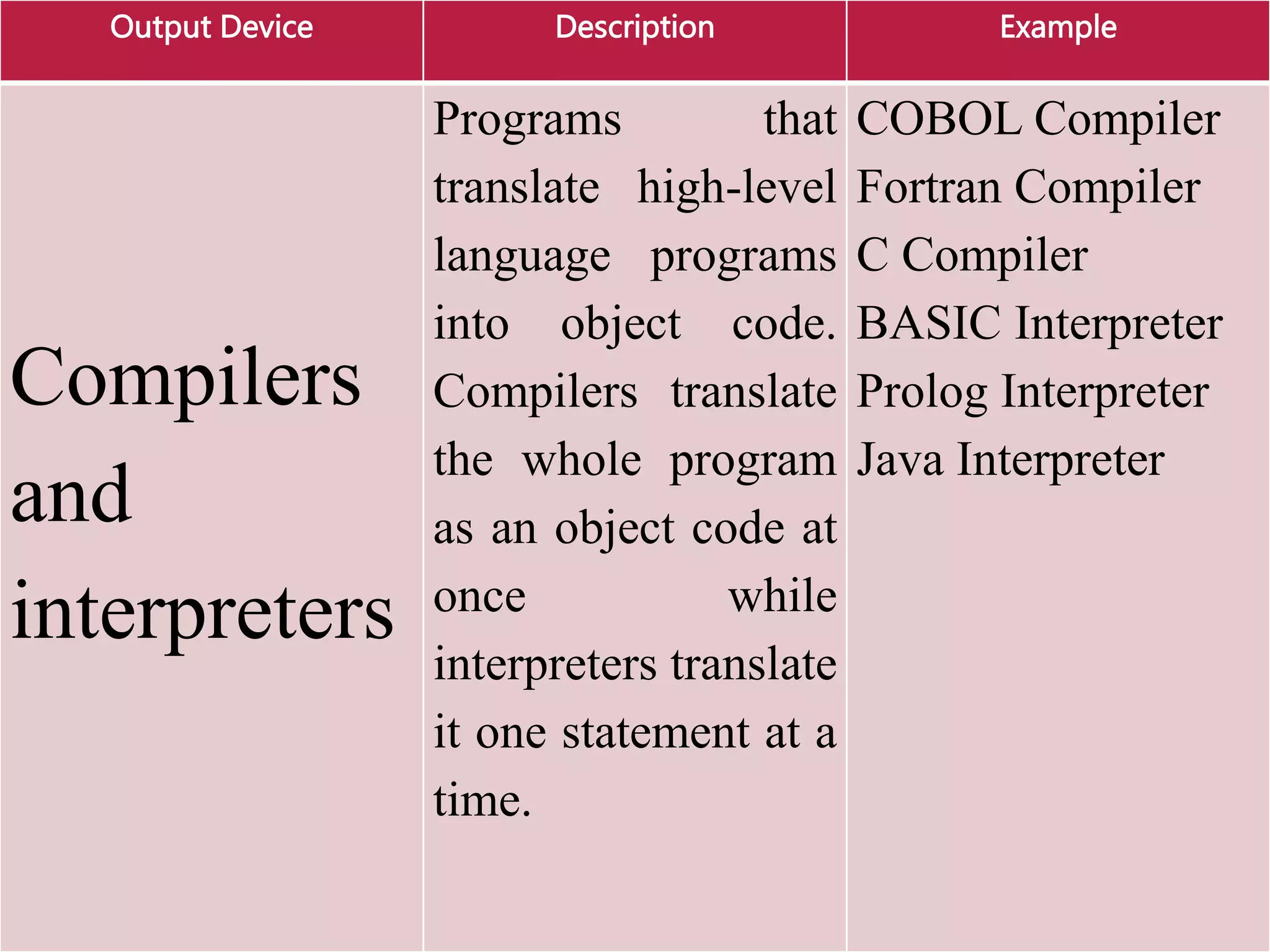
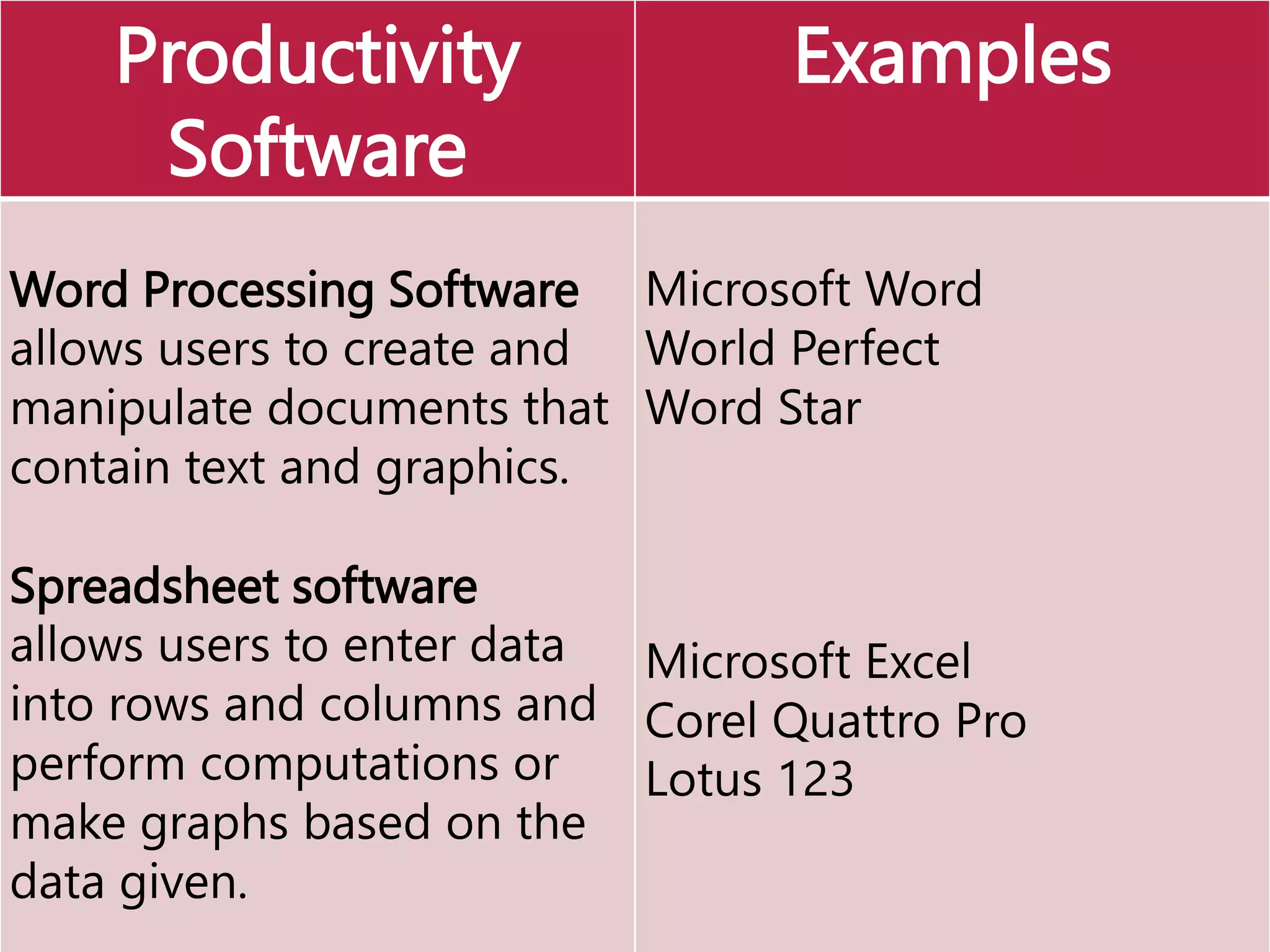
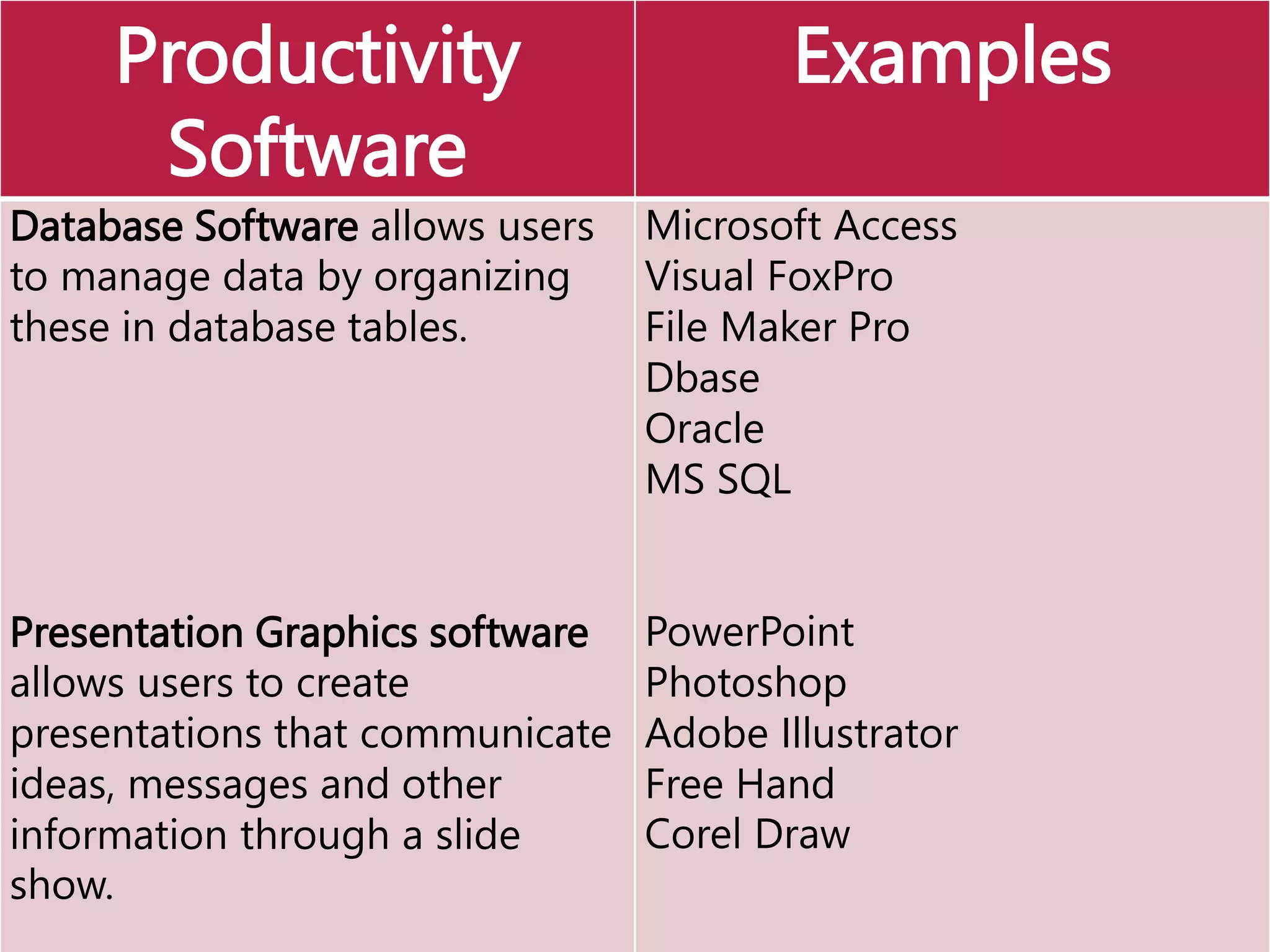
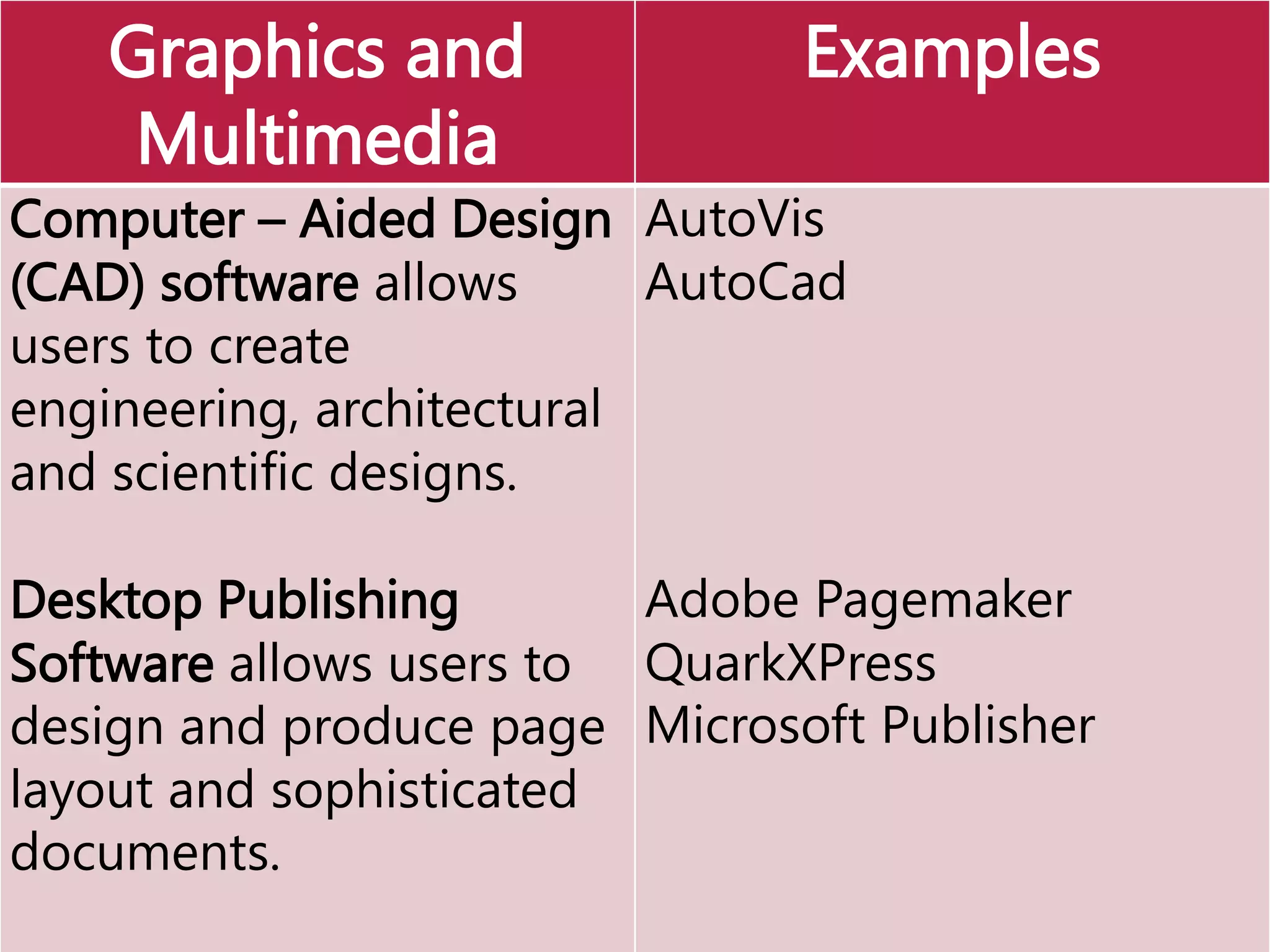
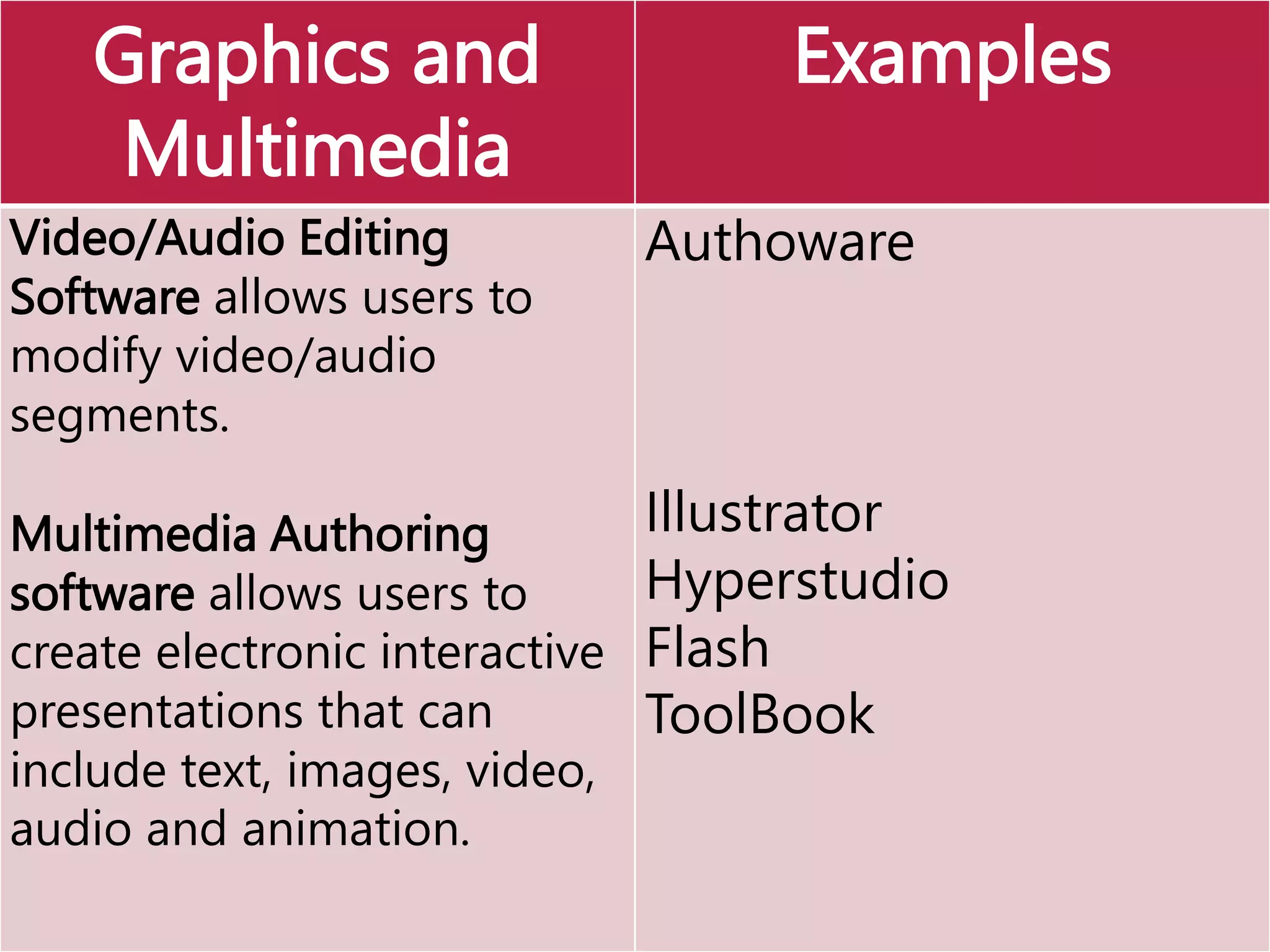
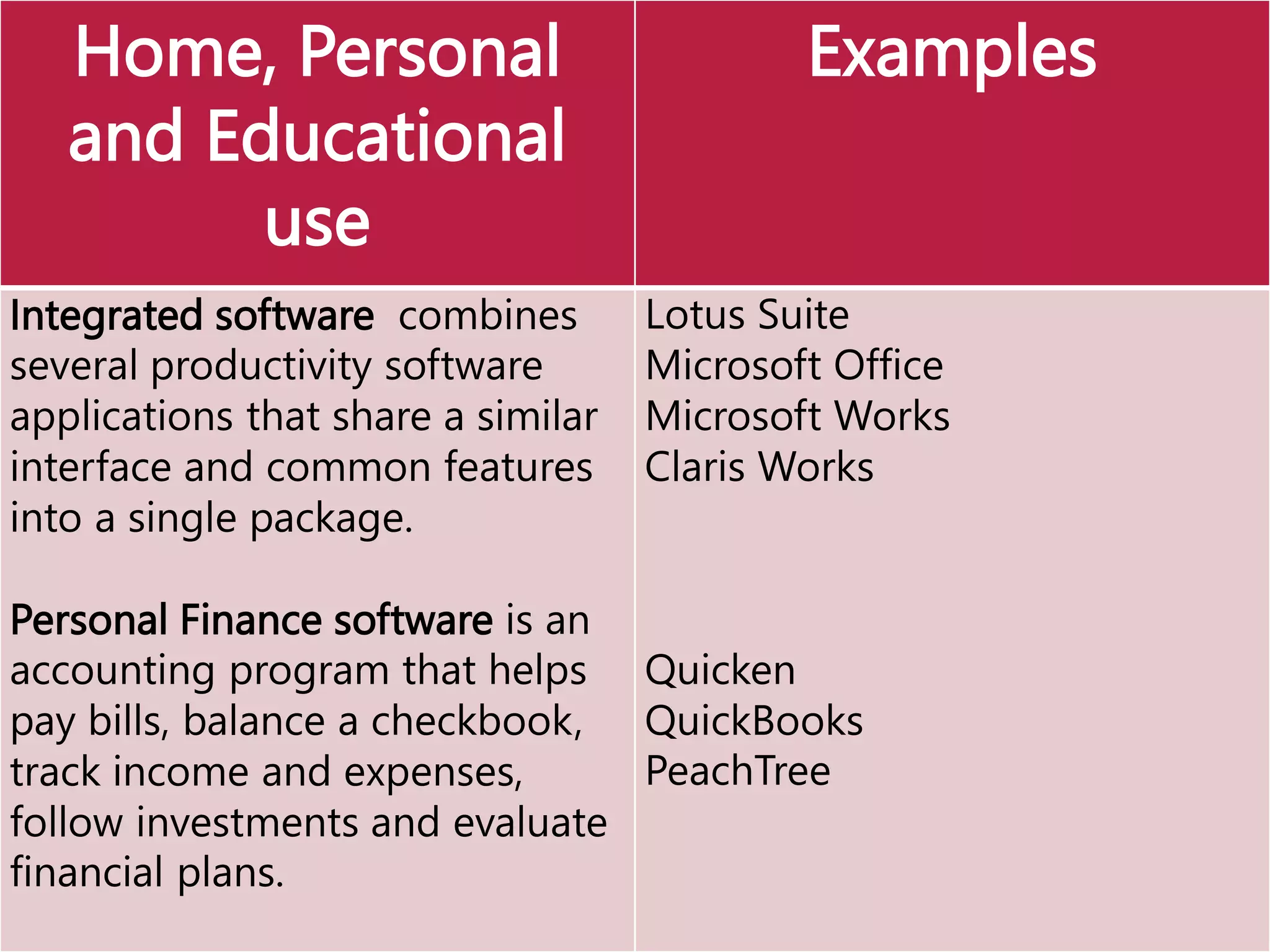
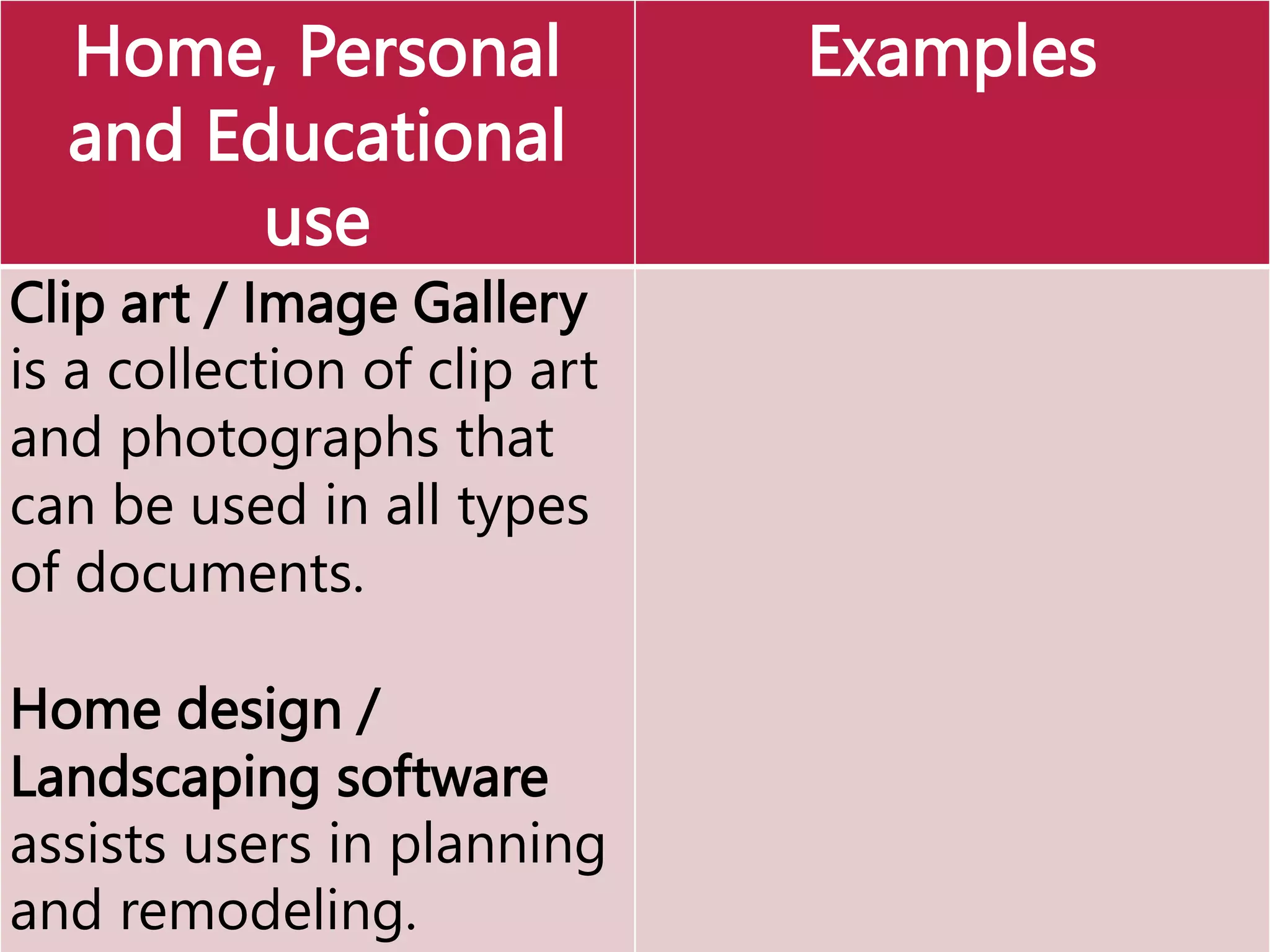
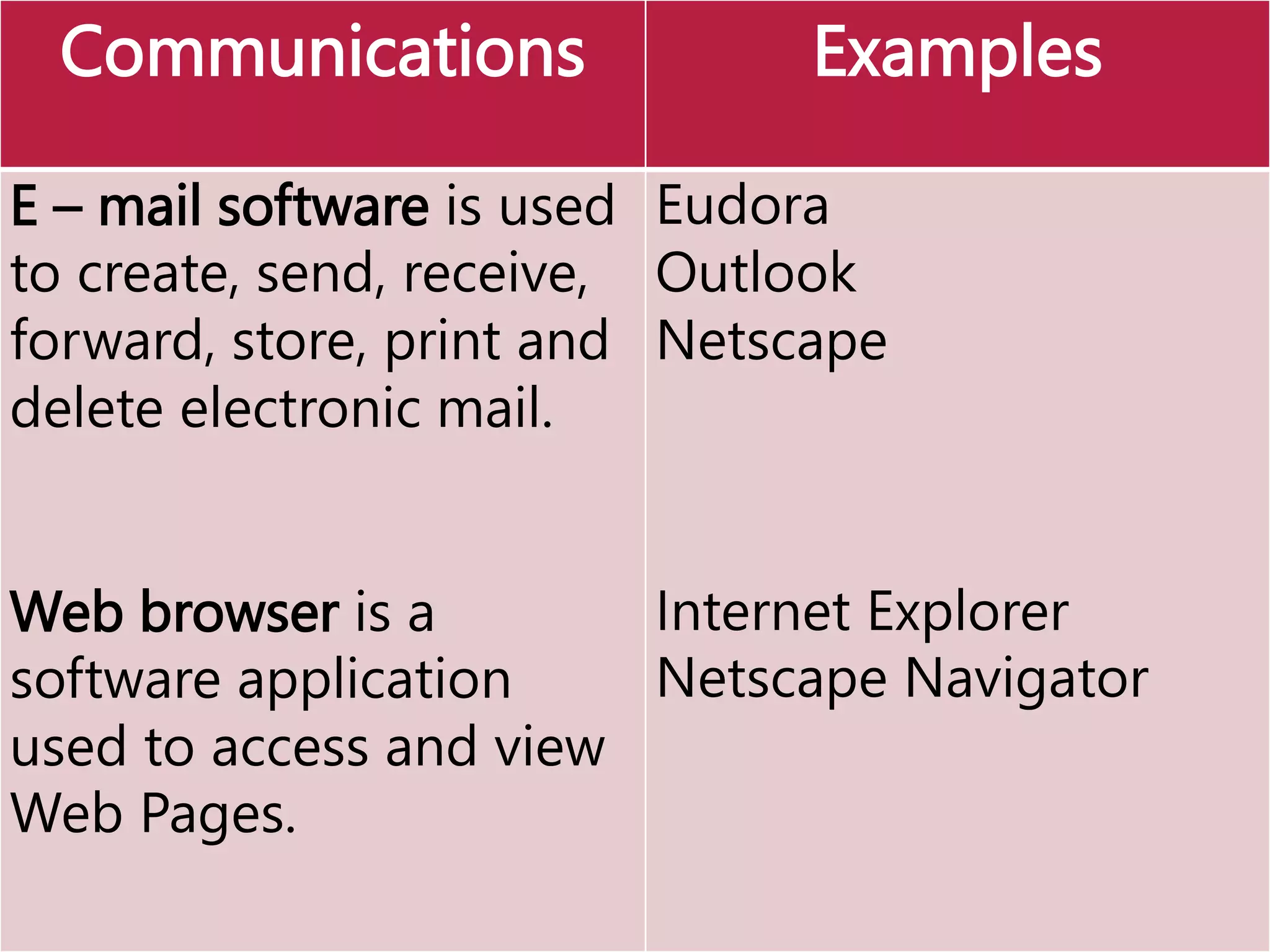
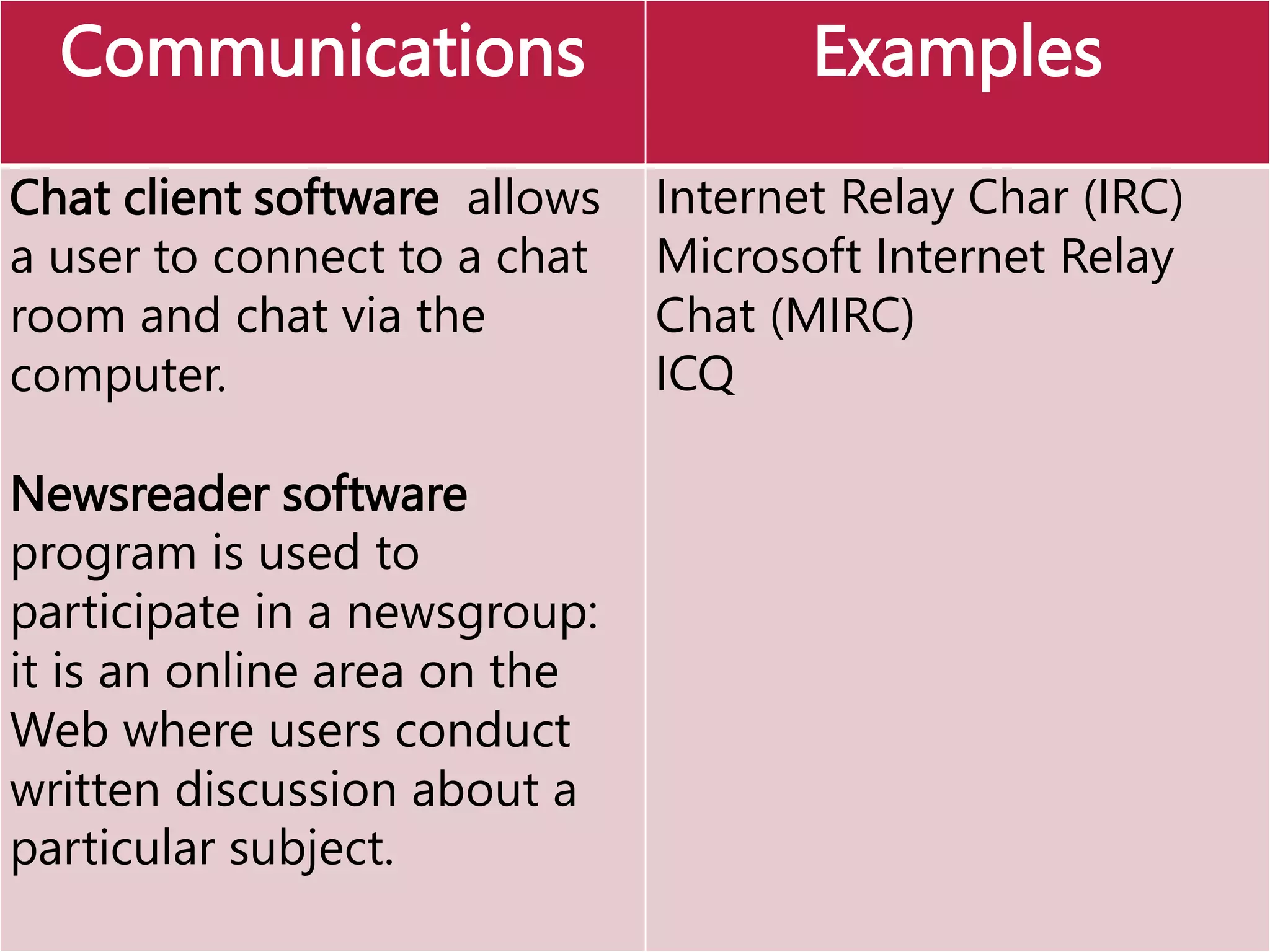
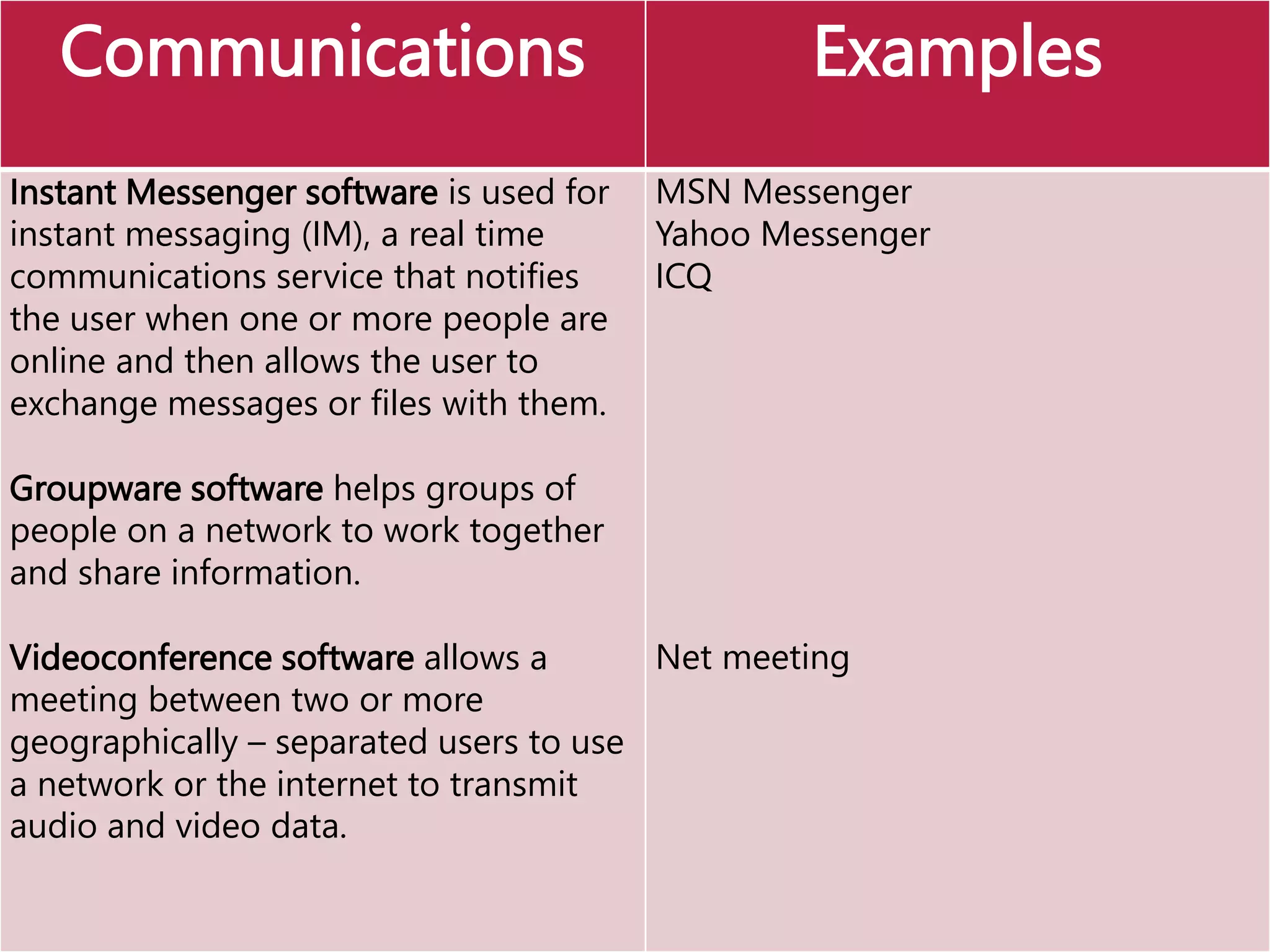
This document provides an overview of the key elements of a computer system, including hardware, software, and how they work together. It describes the main components of hardware like the CPU, RAM, hard drives, input devices like keyboards and mice, and output devices like monitors and printers. It then explains the basic functions of system software like operating systems and utilities, and how application software allows users to perform tasks. Overall, the document outlines the main physical and programmatic parts that comprise a computer system and how they interact.