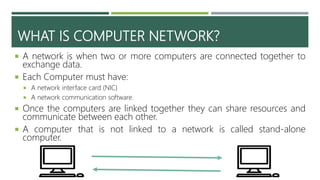
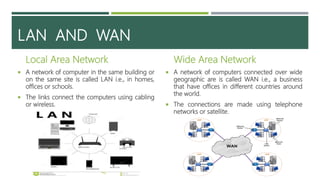
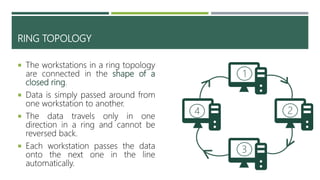
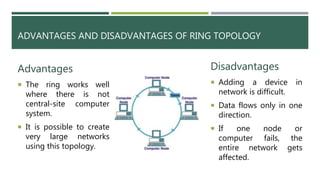
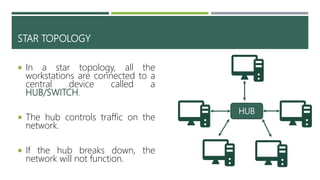
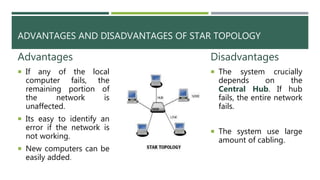
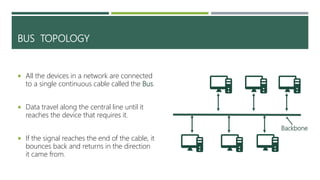
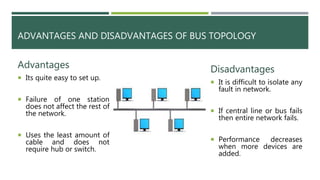
A computer network connects two or more computers to share resources and communicate, requiring a network interface card and software. Different types of networks include LAN (local area network) for smaller areas and WAN (wide area network) for broader geographic connections, with Wi-Fi enabling wireless communication. The document also discusses network topologies (ring, star, and bus) which determine how devices are interconnected, along with the advantages and disadvantages of each type.