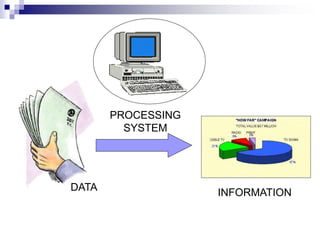
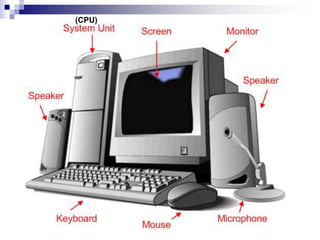
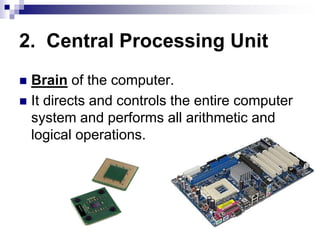
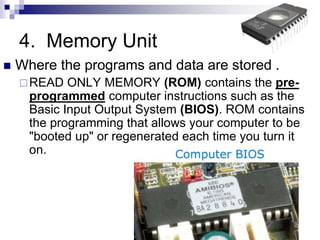
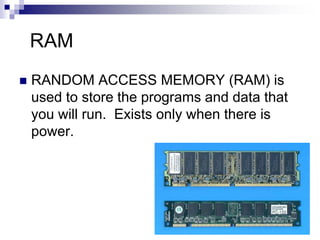
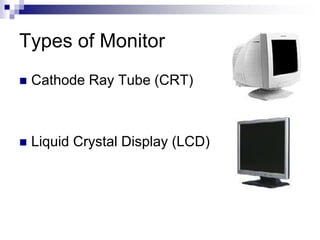
This document discusses fundamentals of computer information processing systems. It defines key terms like data, information, and data processing. It then describes the basic components of an information processing system including input, processing, storage, and output. The three major components are hardware, software, and people-ware. It proceeds to describe basic PC hardware components like the CPU, input devices, output devices, memory unit, and secondary storage devices. It concludes with descriptions of system software, application software, graphical user interfaces, and files.