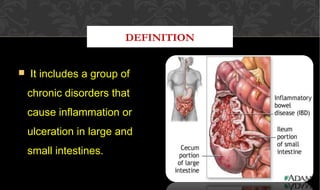
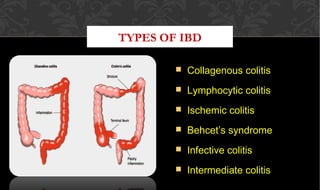
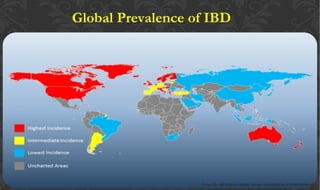
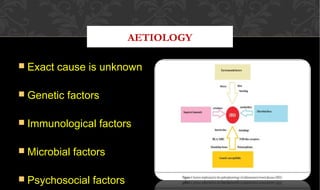
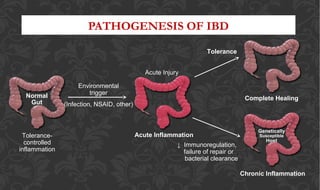
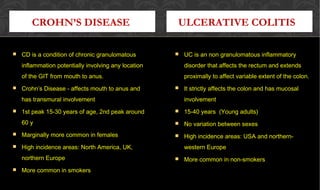
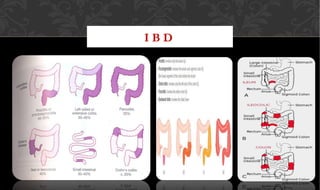
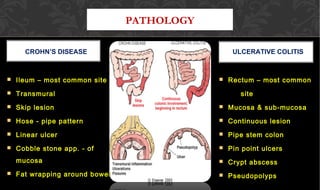
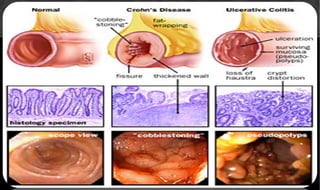
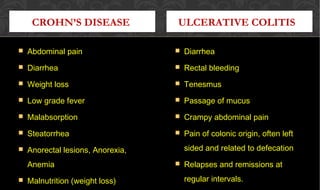
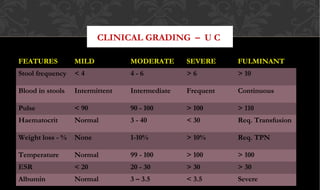
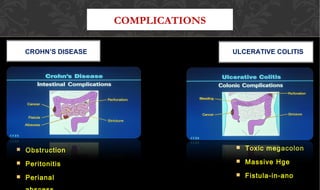
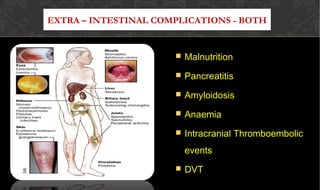
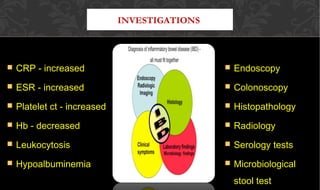
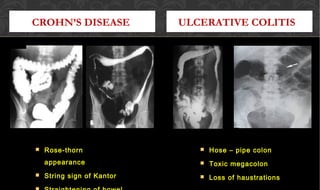
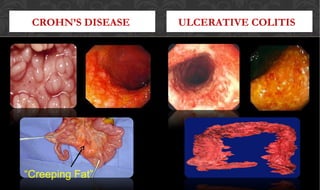
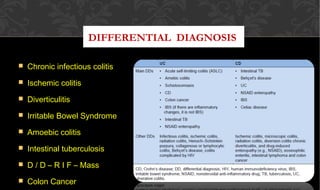
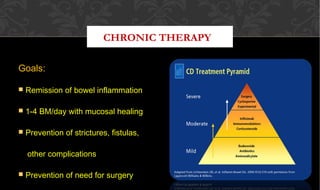
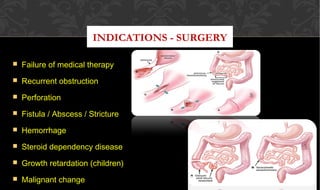
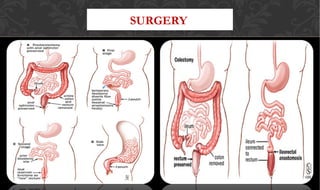
The document outlines the disease processes of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, highlighting their clinical presentations, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. It describes inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) as a group of chronic disorders affecting the gastrointestinal tract, with distinct characteristics and complications for each condition. The document also emphasizes the importance of understanding the differences in pathogenesis, symptoms, and risk factors associated with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.