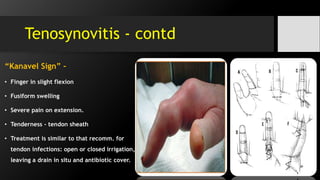
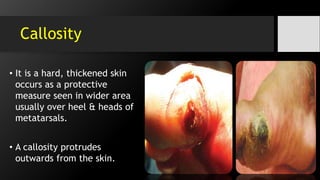
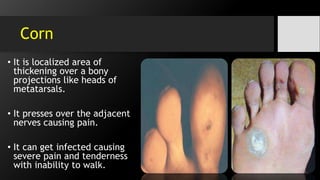
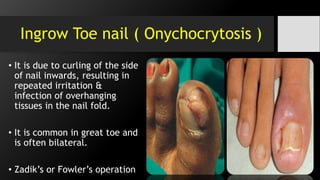
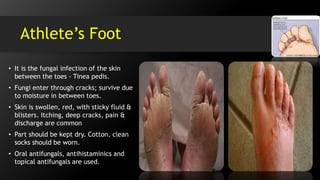
The document discusses hand and foot infections, detailing their causes, symptoms, classifications, and treatments. It outlines specific types of infections such as paronychia, felon, and deep space infections, along with diagnostics and complications. Key principles and management strategies for these infections are also emphasized, including the importance of careful examination and appropriate interventions.




![Classification
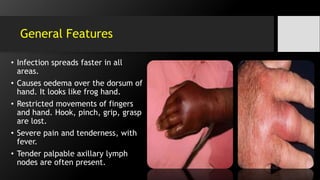
[I] Cut.& sub-cut.infections:
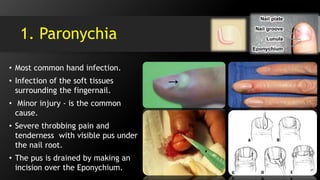
• Paronychia
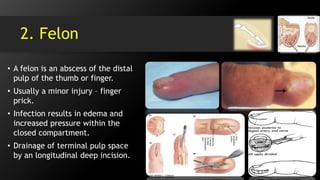
• Pulp Space Infection (Felon)
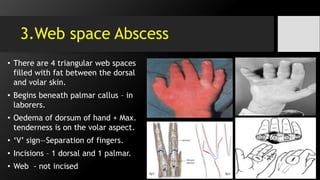
• Web Space Abscess
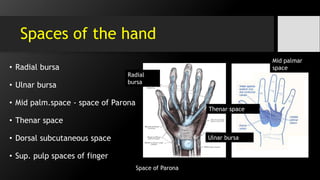
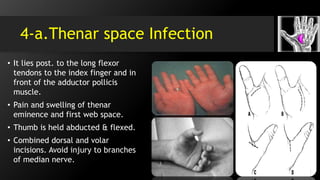
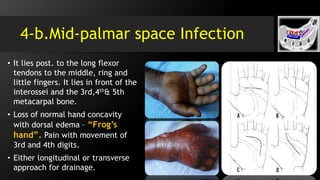
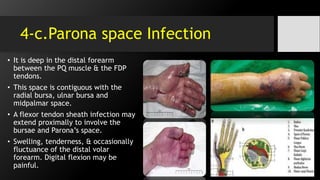
[II] Fascial spaces infection :
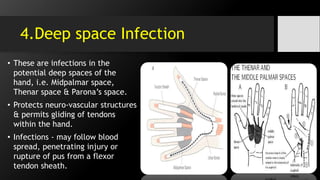
• Deep Space Infection i.e.
midpalmar space, thenar space
& Parona’s space.
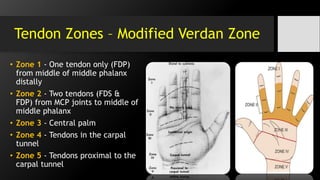
• [III] Inf. of the tendon with
its synovial sheath -
“tenosynovitis”.
• [IV] Inf. of the bone & joint -
“septic arthritis”.
• [V] Miscellaneous infections.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handinfections-dr-151028054444-lva1-app6891/85/Hand-Foot-infections-9-320.jpg)
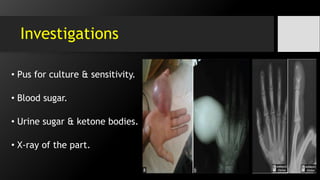
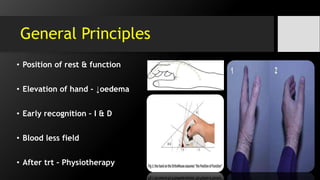
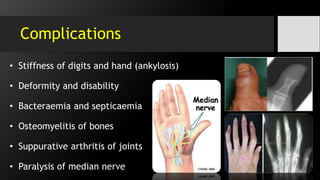
![6.Tenosynovitis
• It is the bacterial inf. of flexor tendon sheaths.
• It is the inflam. the fluid-filled sheath (called
the synovium) that surrounds a tendon.
• Common flexor synovial sheath (ulnar bursa)
[FDP / FDS]
• The synovial sheath of the tendon of flexor
pollicis longus (radial bursa).
• Both comm. with each other in 80% of cases.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handinfections-dr-151028054444-lva1-app6891/85/Hand-Foot-infections-21-320.jpg)