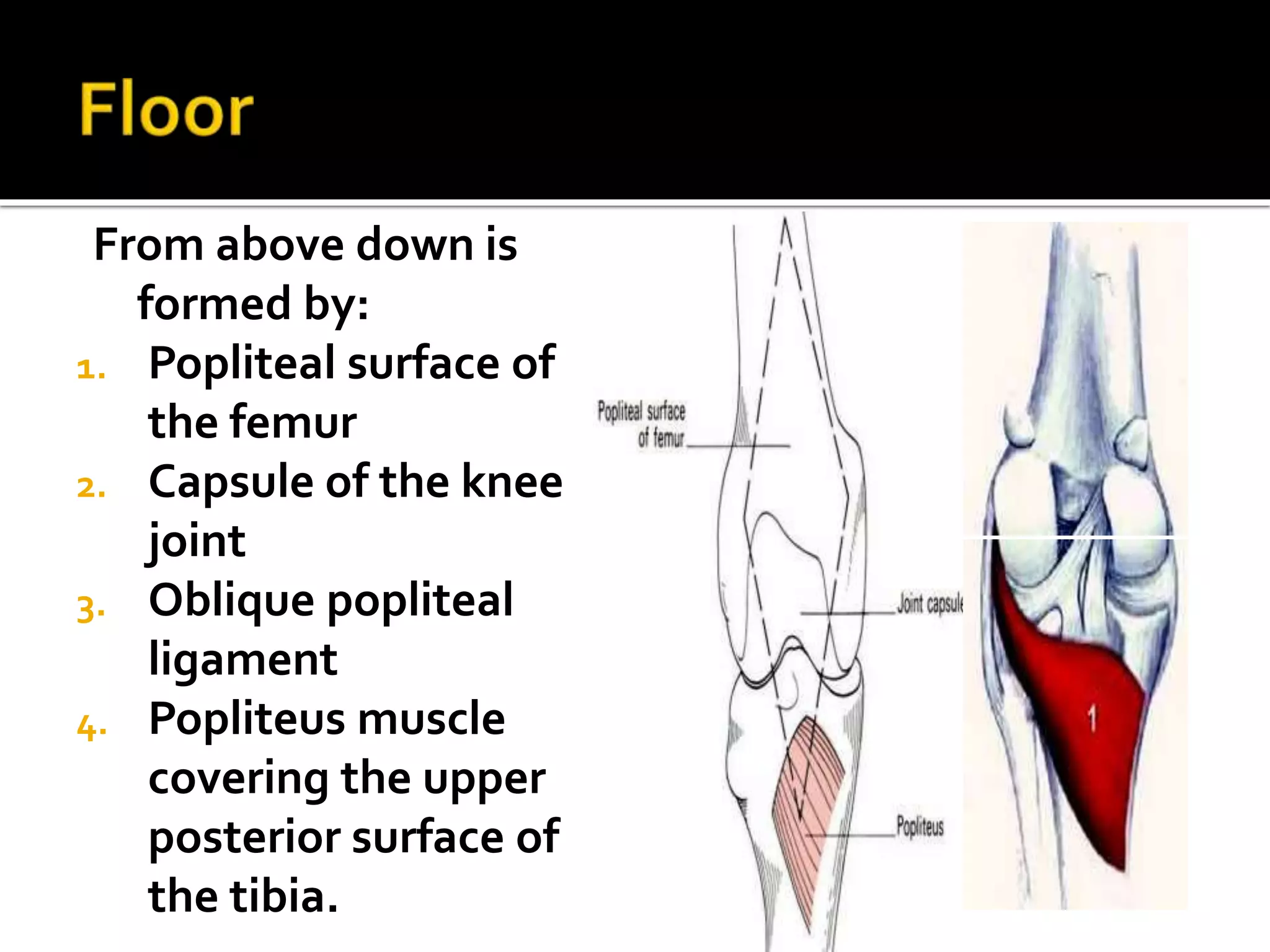
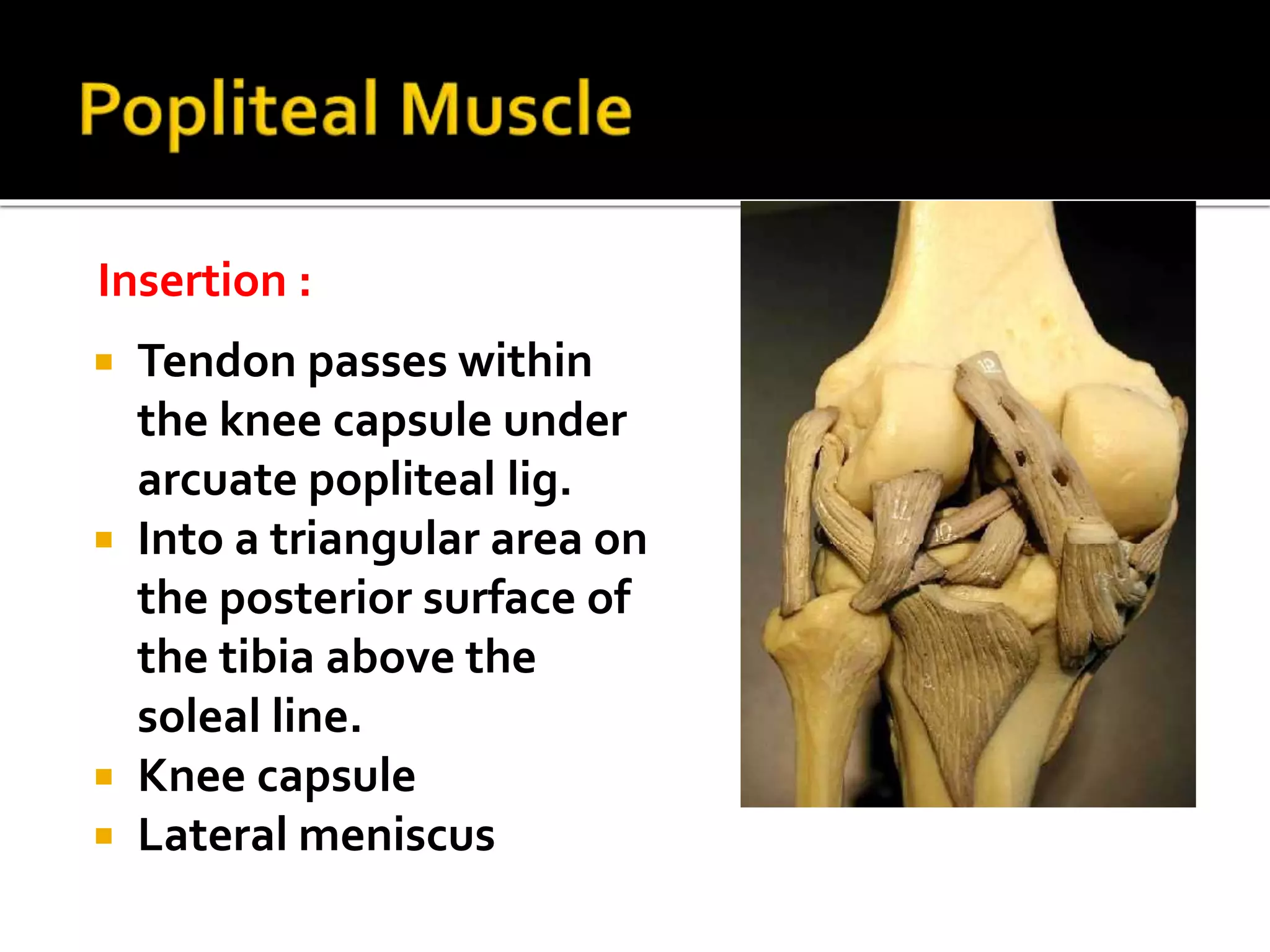
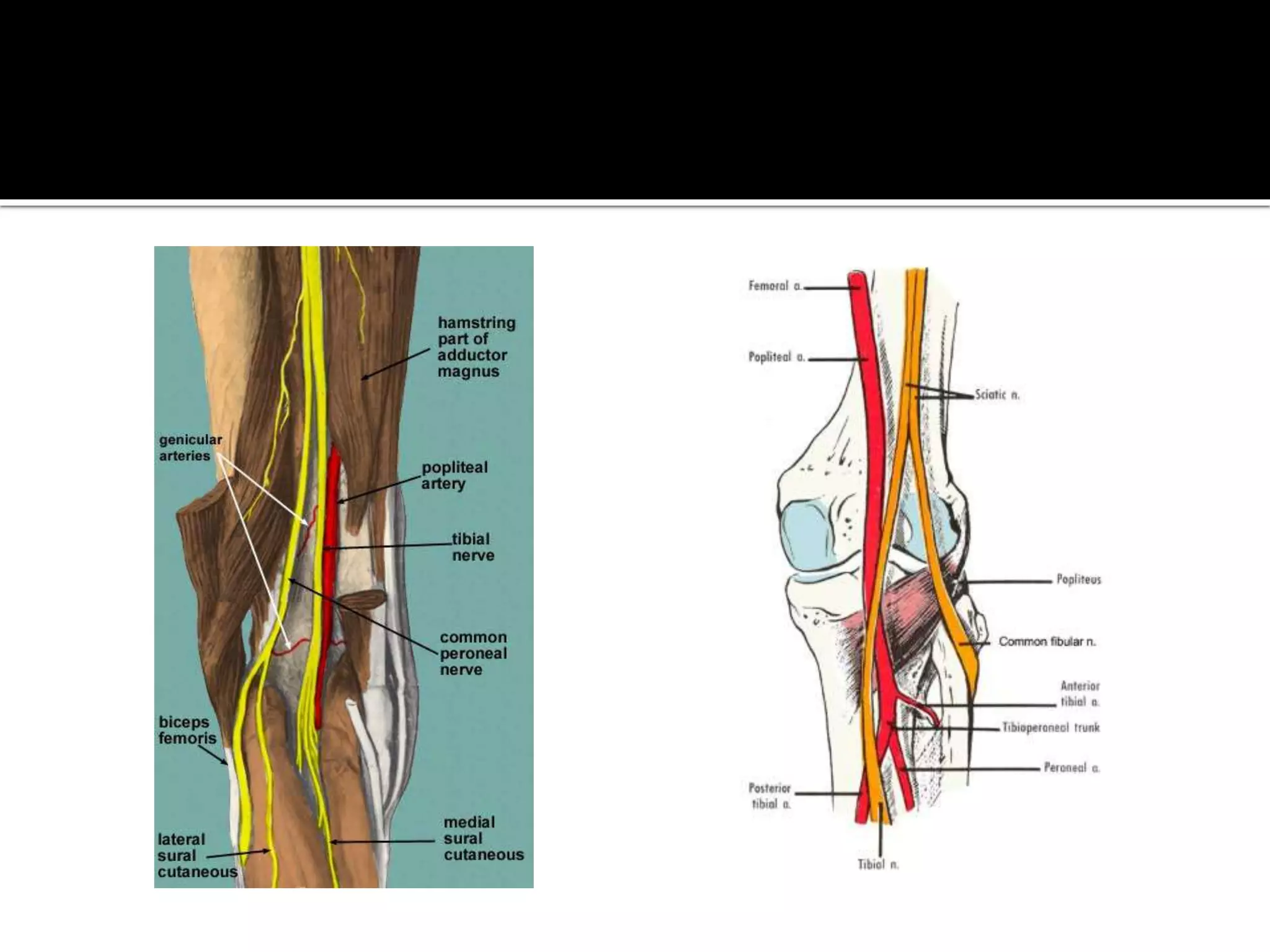
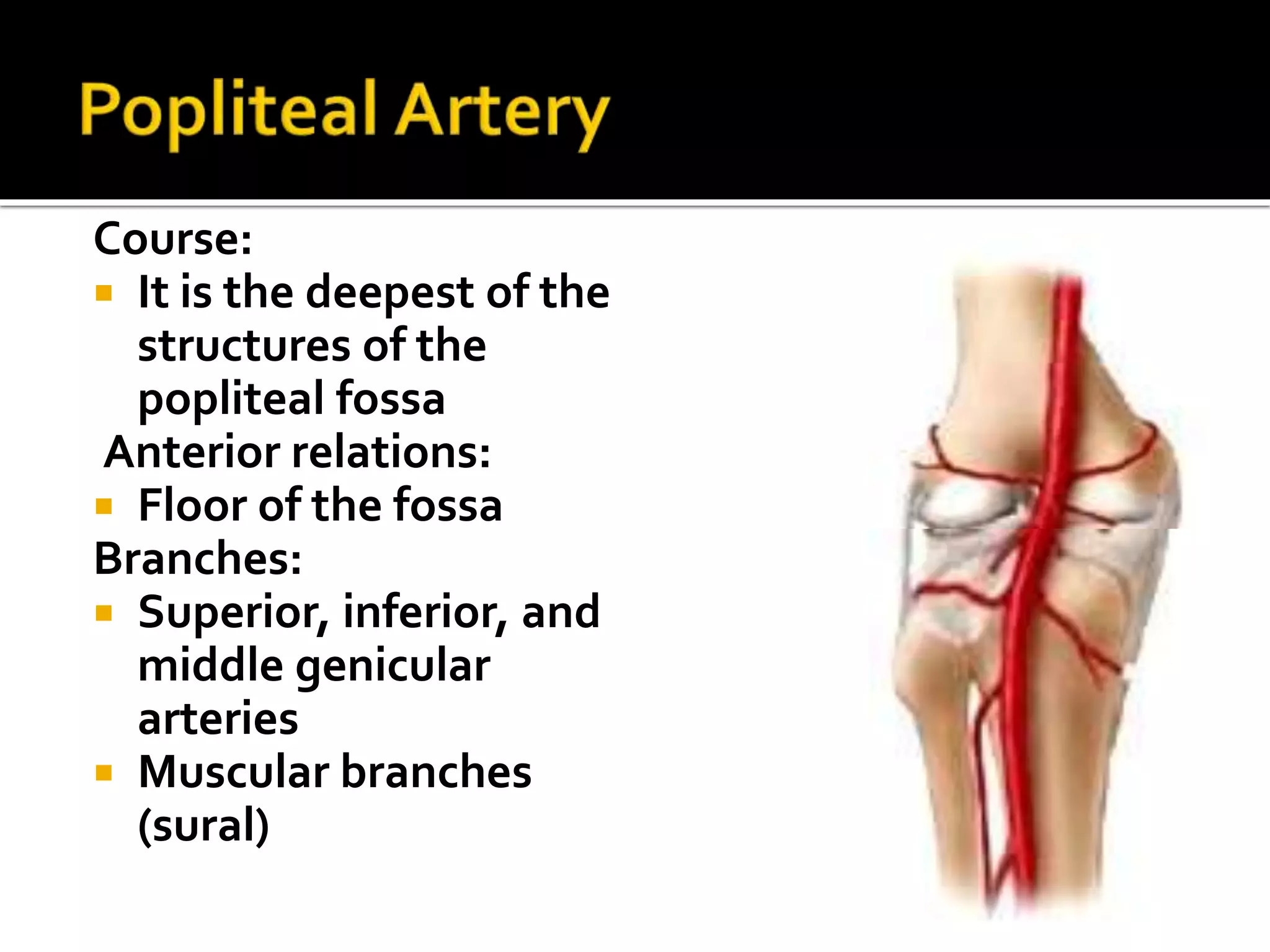
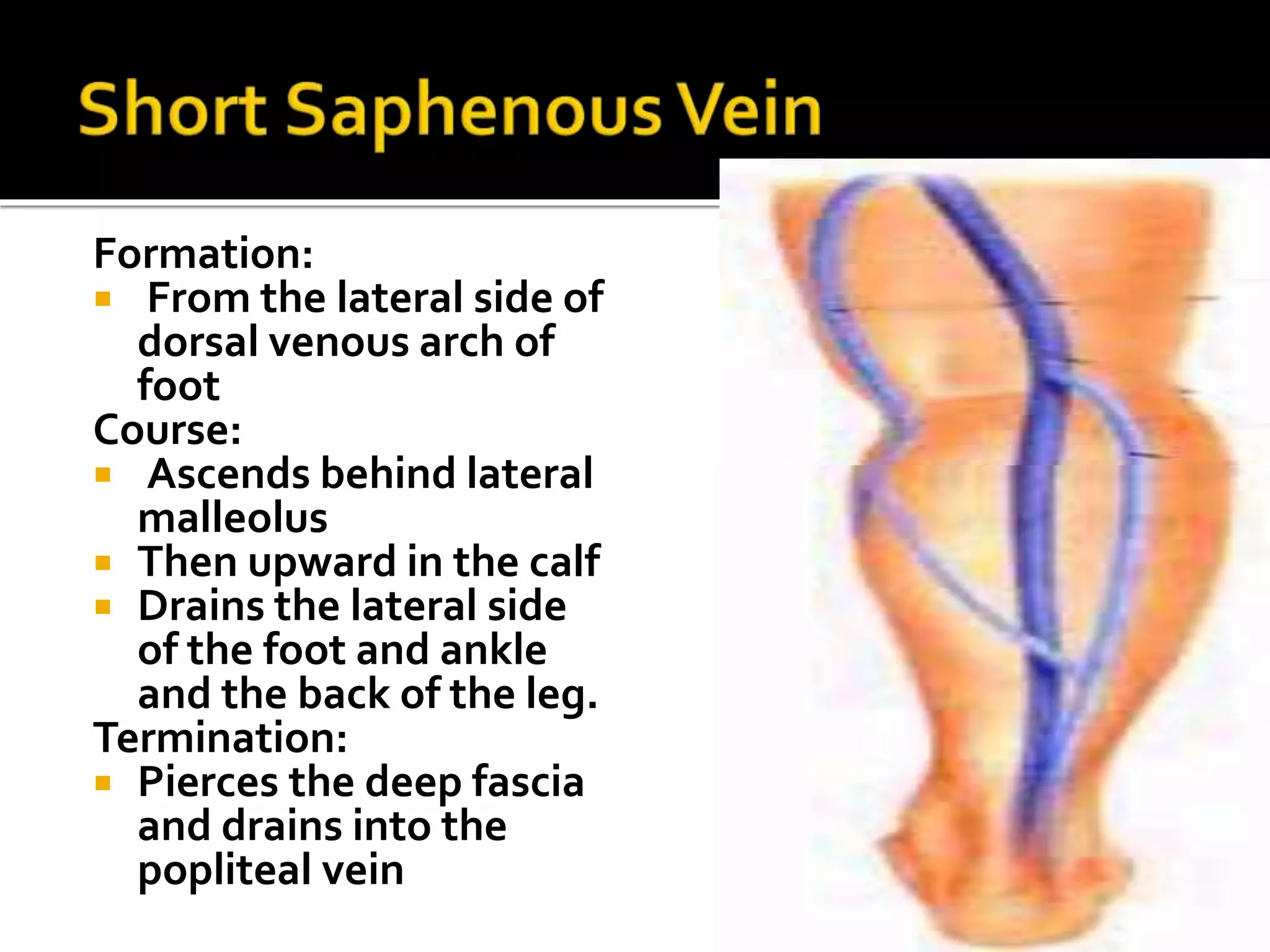
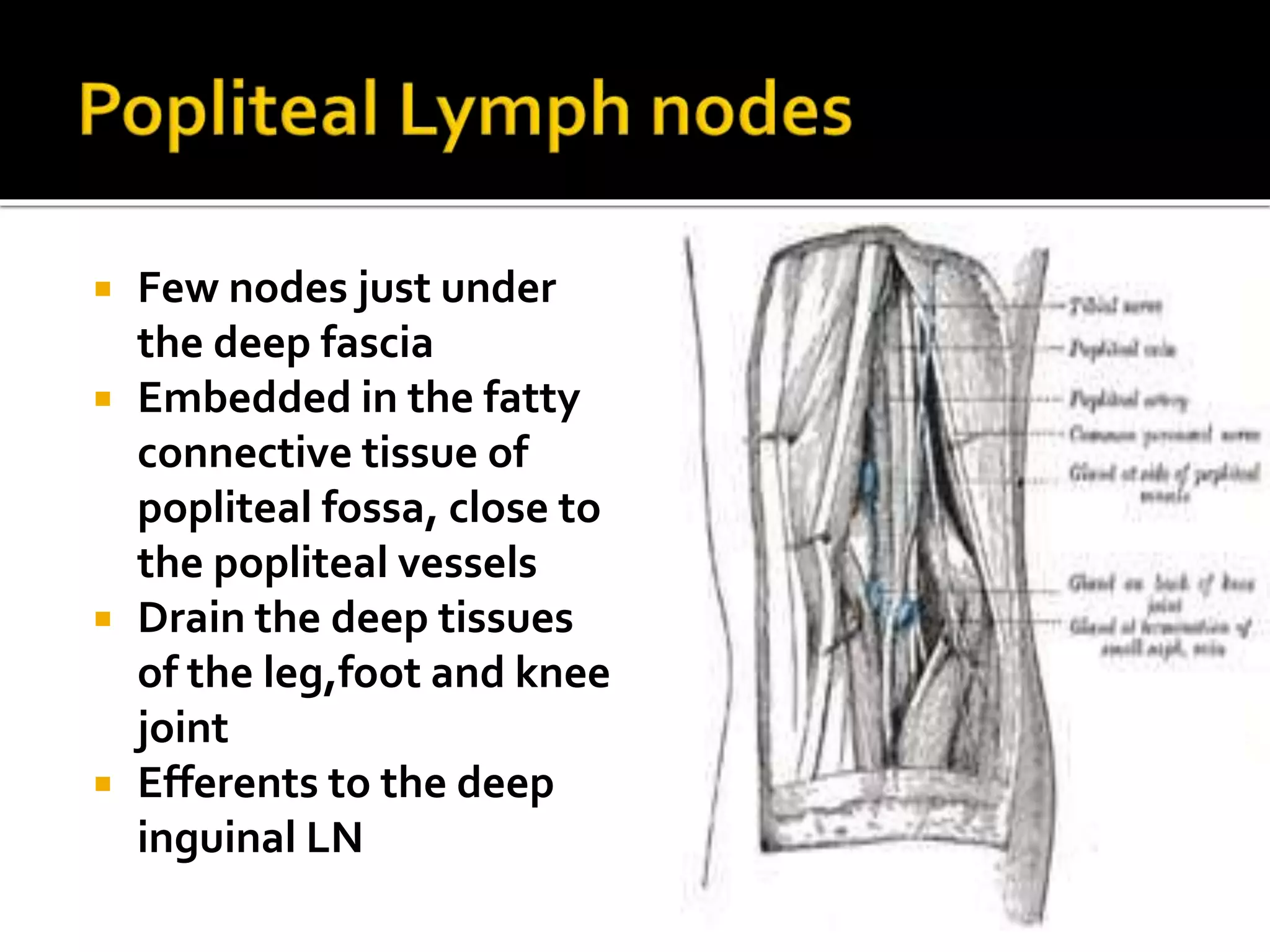
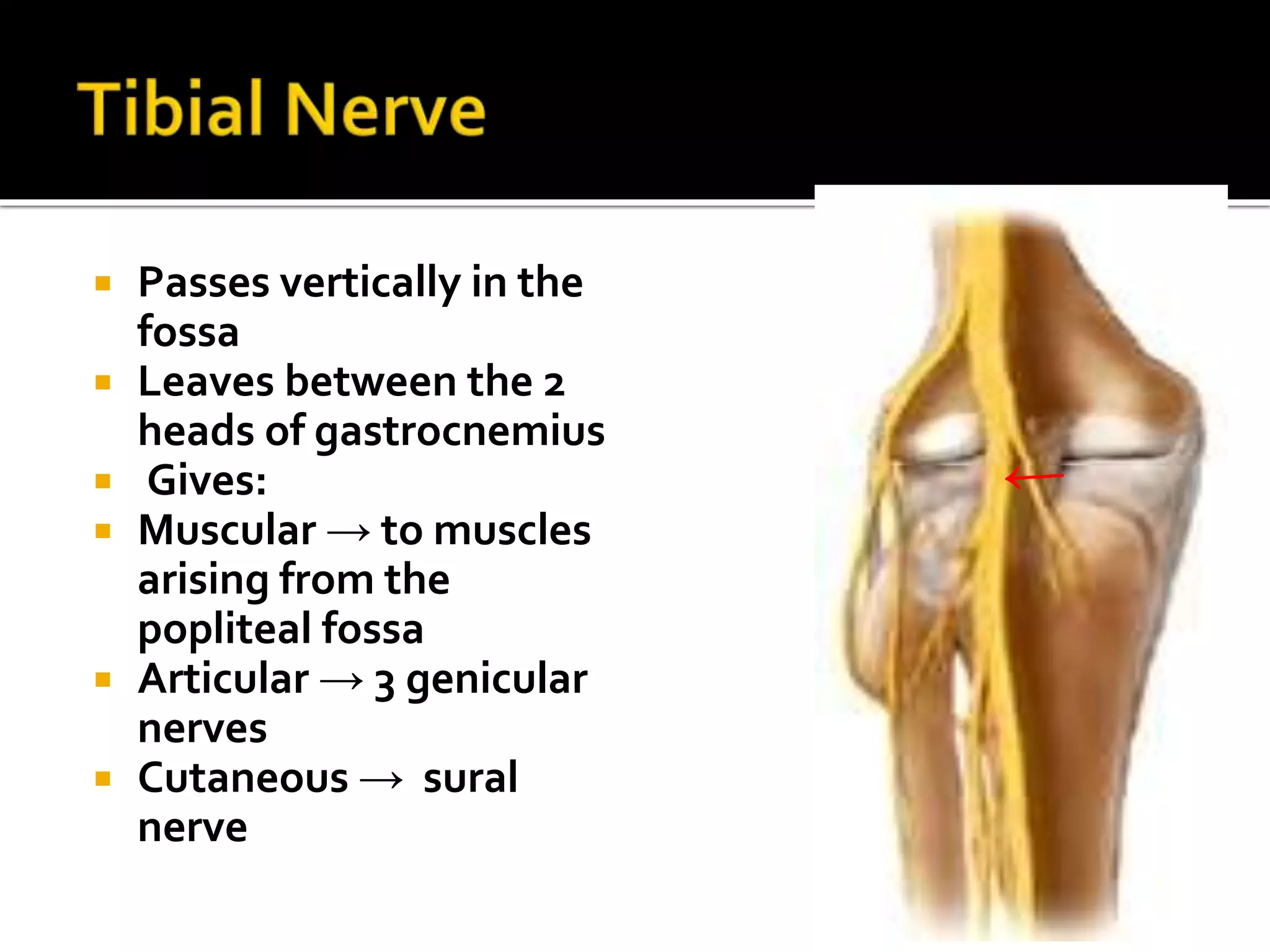
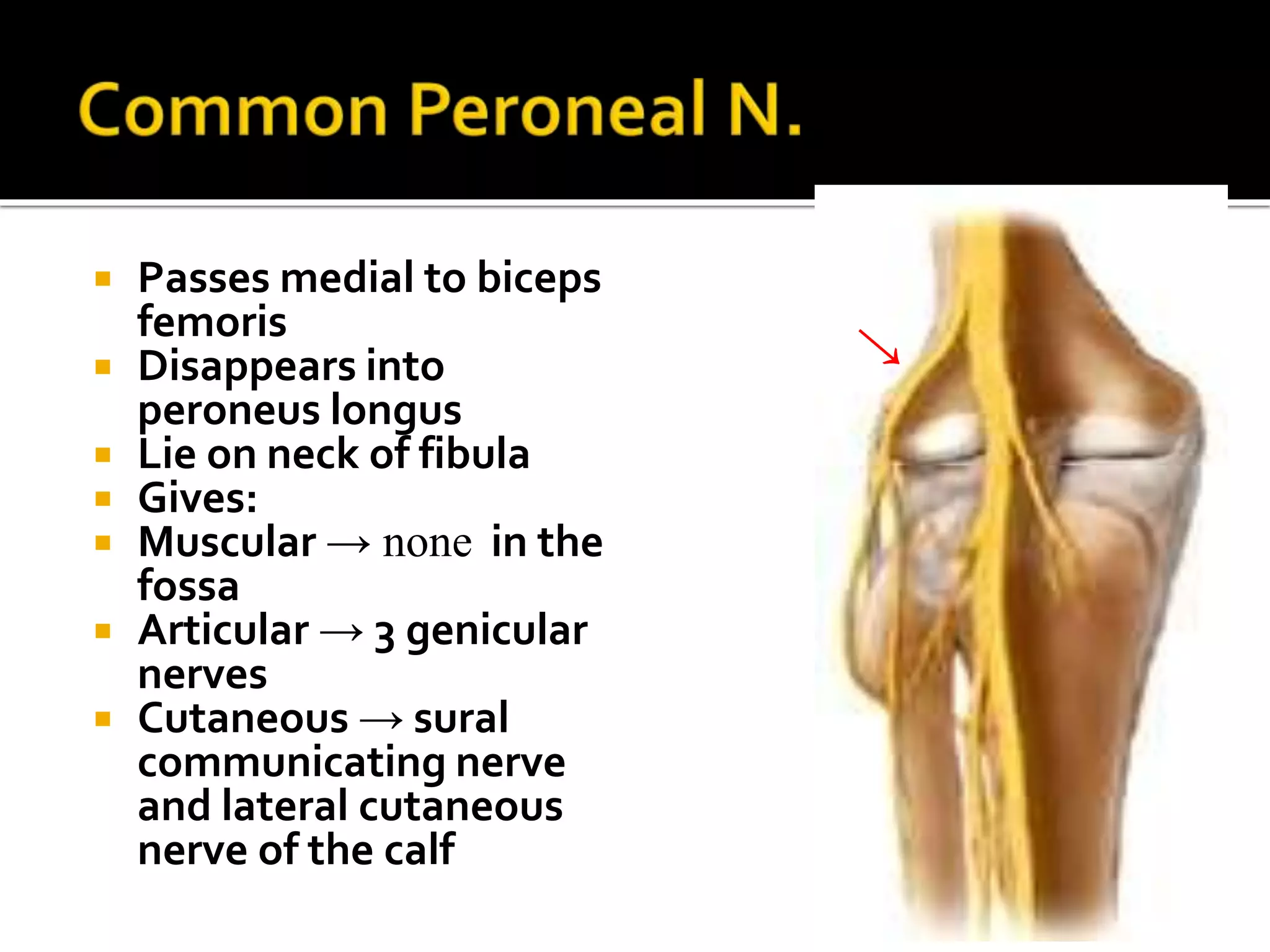
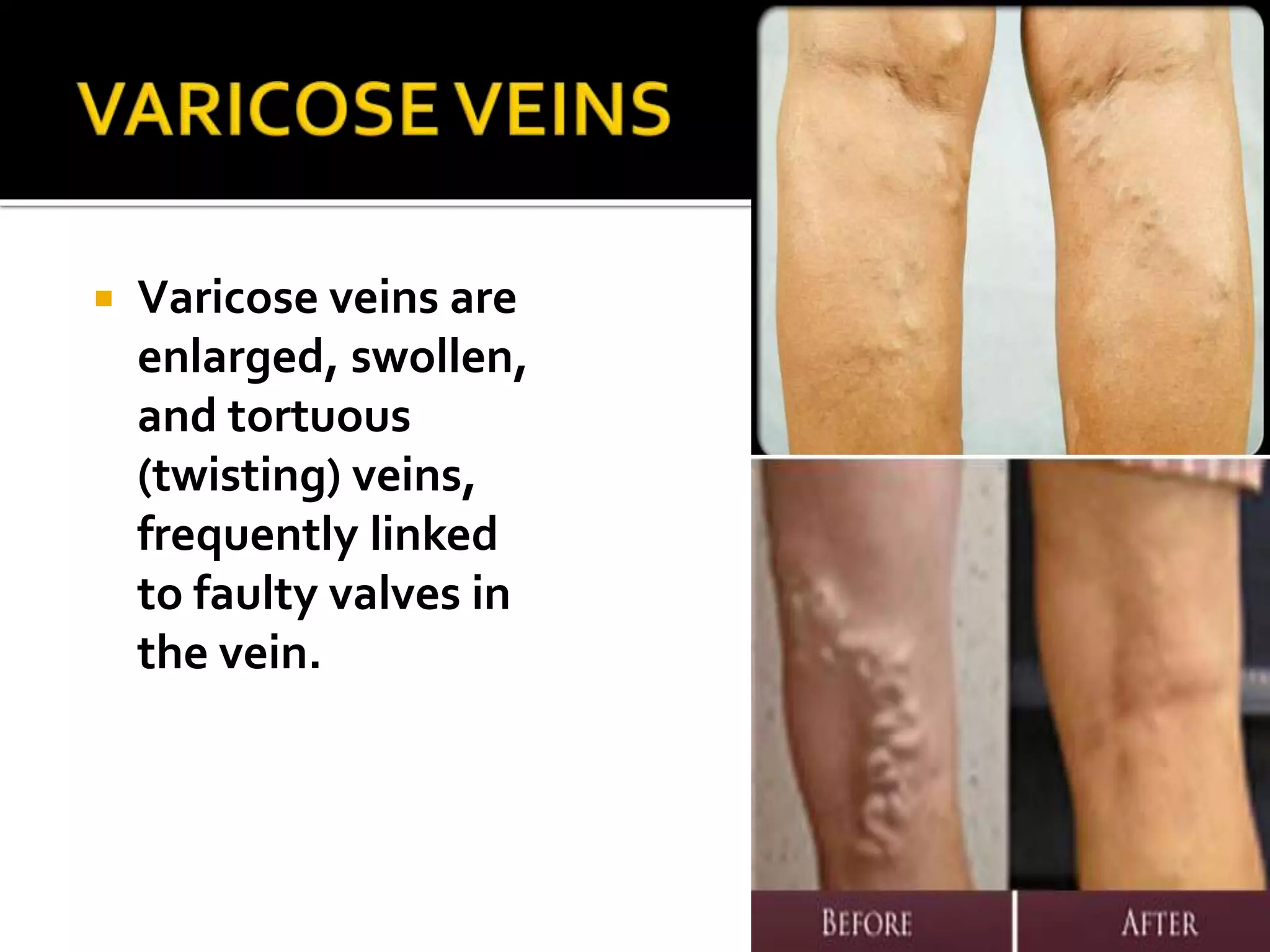
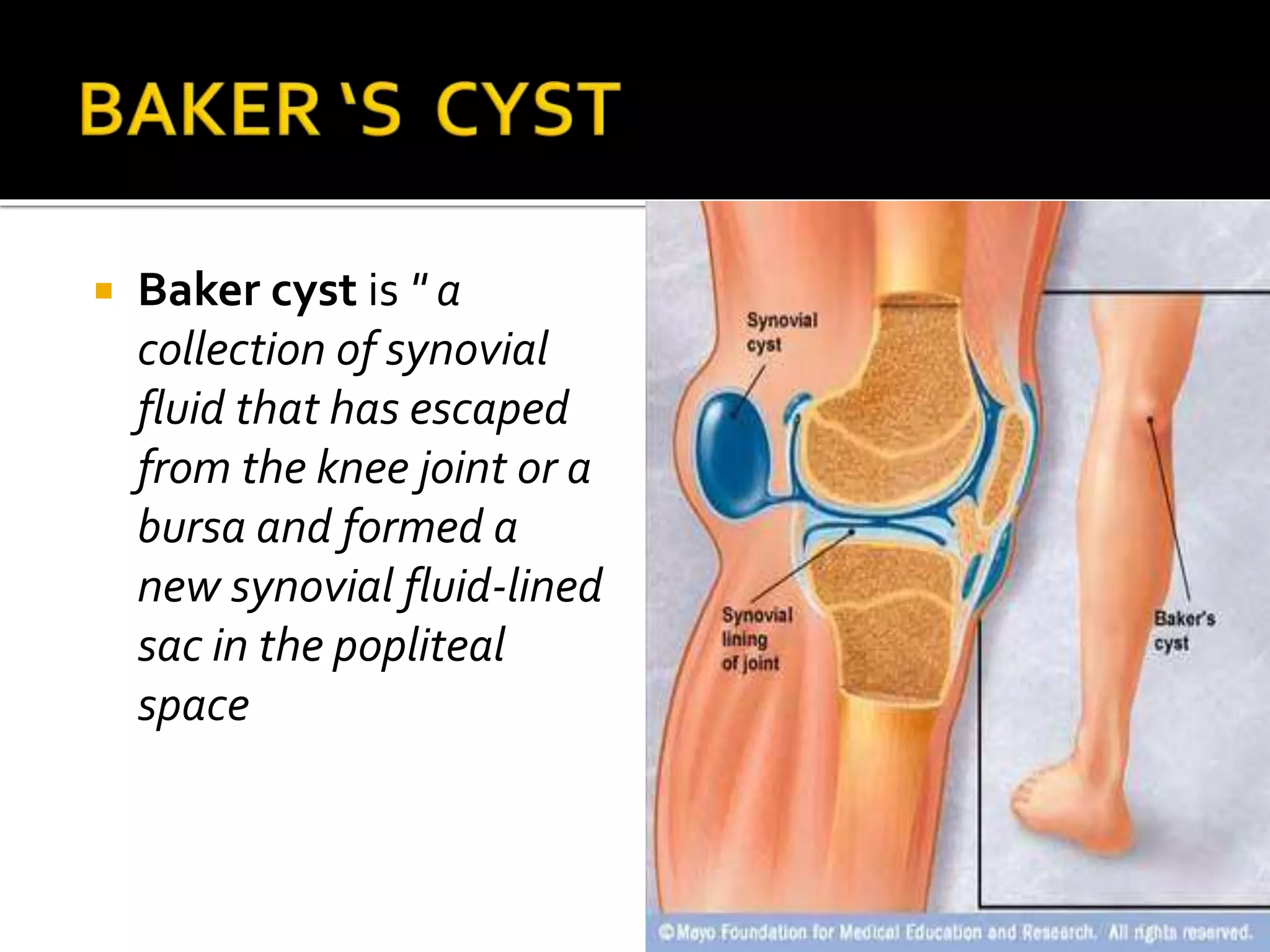
This document describes the anatomy of the popliteal fossa and its contents. It discusses the structures that form the boundaries of the popliteal fossa including the popliteal surface of the femur, knee joint capsule, oblique popliteal ligament, and popliteus muscle. It provides details on the popliteal artery, vein, tibial nerve and common fibular nerve within the fossa. It also mentions varicose veins, popliteal artery entrapment syndrome, and Baker's cysts as conditions that can affect the popliteal fossa.