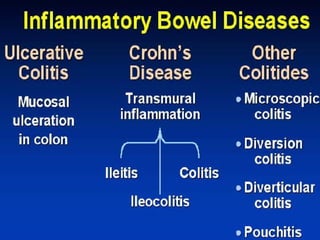
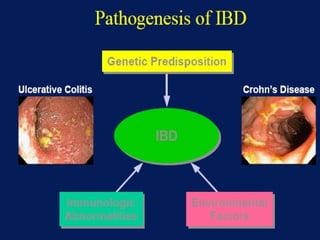
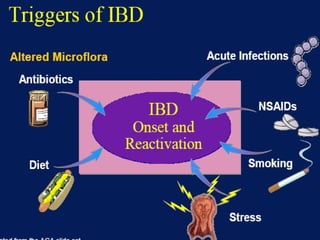
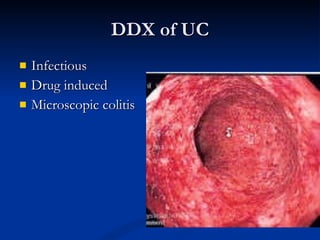
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, both characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. The causes are not fully understood but involve immune dysfunction and genetic factors.
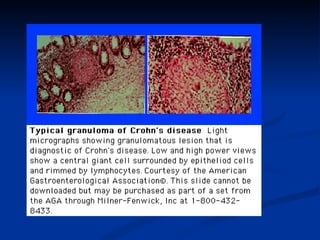
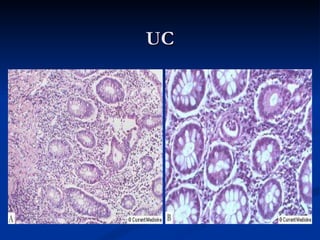
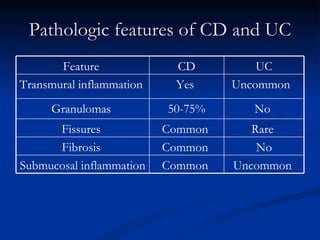
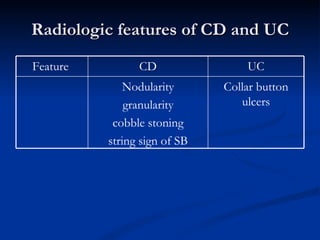
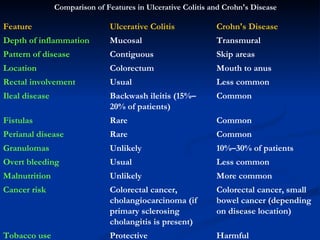
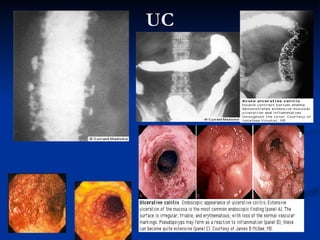
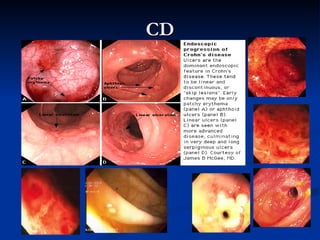
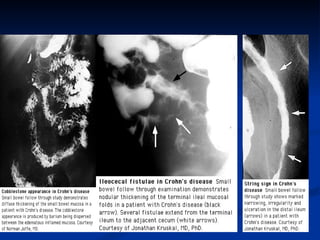
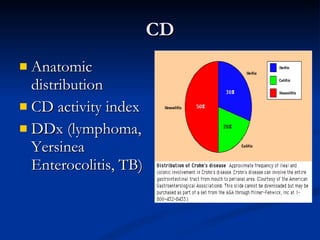
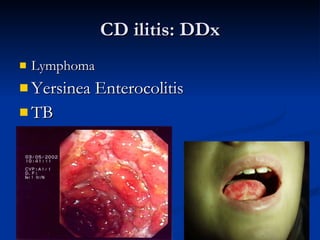
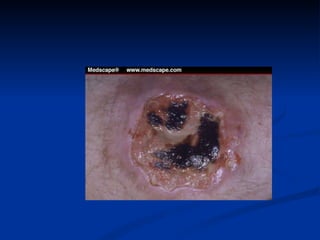
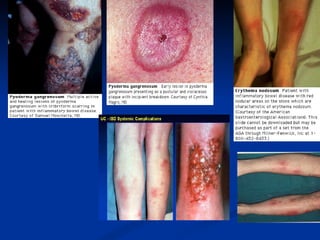
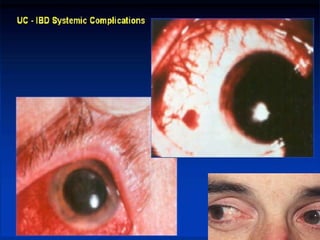
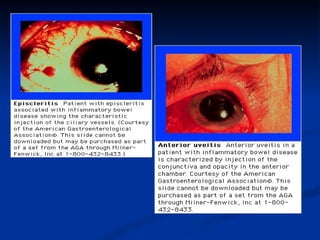
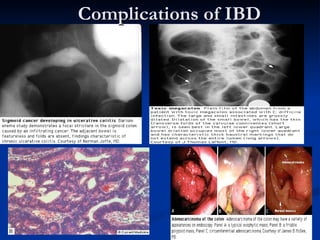
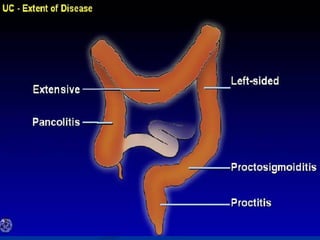
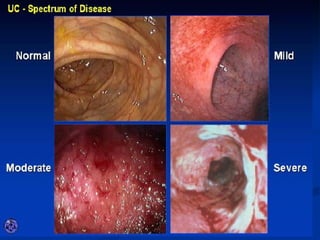
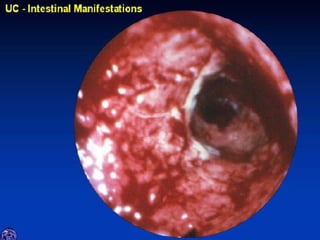
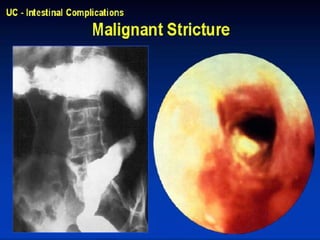
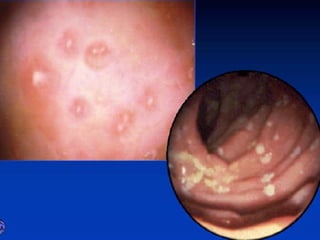
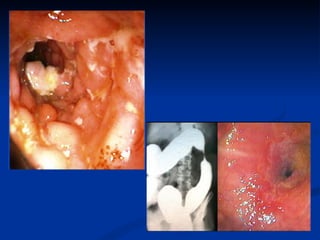
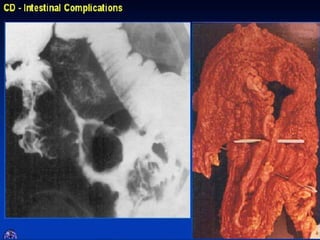
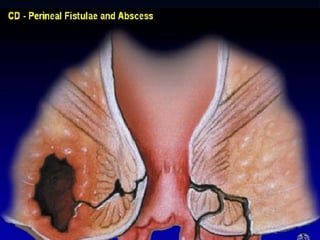
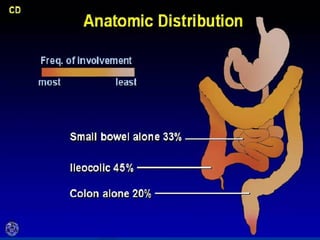
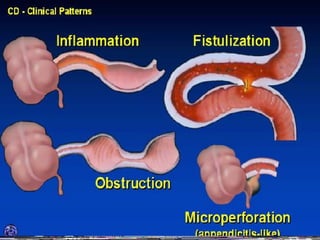
- Crohn's disease can affect any part of the GI tract and cause transmural inflammation and complications like strictures and fistulas. Ulcerative colitis primarily involves only the inner mucosal layer of the colon and rectum.
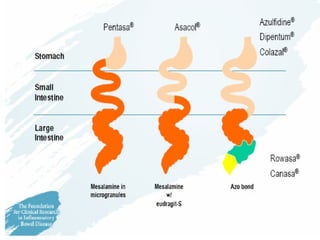
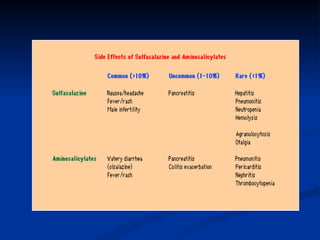
- Treatment depends on disease severity and includes medications to induce and maintain remission as well as surgery for complications. The goals are to control symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent disease progression.









































![Infliximab - mucosal healing Baseline Week 10 Week 54 Rutgeerts et al. DDW 2002: [abstract] W1367.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitibd2010lec-100221105456-phpapp02/85/G-I-T-I-B-D-2010-Lec-72-320.jpg)