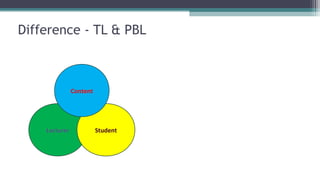
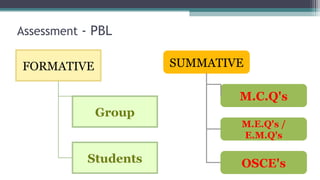
The document discusses Problem-Based Learning (PBL) in medical education, detailing its history from the 1950s to its widespread adoption in the 2000s. It highlights the characteristics of PBL, comparing it to traditional teaching methods, and emphasizes advantages such as enhanced student engagement but also notes challenges like assessment difficulties. PBL is defined as a student-centered approach that uses problems as a starting point for acquiring knowledge and skills.