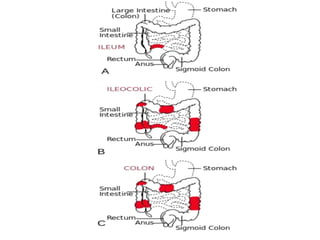
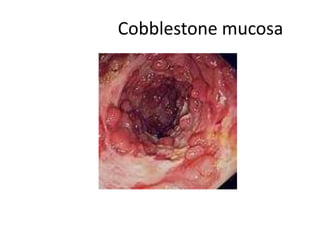
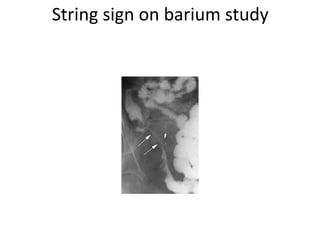
This document provides information on inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), specifically Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. It discusses the etiology, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnostic findings, complications, and management of these conditions. IBD is characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract that results in abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies. Both diseases involve an inappropriate immune response to environmental factors in genetically predisposed individuals. They differ in that Crohn's disease can affect any part of the GI tract and causes transmural inflammation, while ulcerative colitis only involves the colon and superficial mucosal layers. Treatment aims to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and prevent complications through medications, nutrition,

















![Pharmacologic therapy
1. Aminosalicylate formulations; sulfasalazine
(azulfidine)
- treat inflammation and prevent recurrences
2. Antibiotics; metronidazole & ciprofloxacin
- In secondary infections
3. Corticosteroids
- suppress the acute clinical symptoms
4. Immunomodulators; (eg. Azathioprene
[Imuran], 6mercaptopurine, methotrexate)
- Alter immune response](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflammatoryboweldisease-140114235545-phpapp01/85/Inflammatory-bowel-disease-21-320.jpg)










