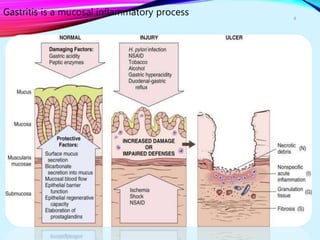
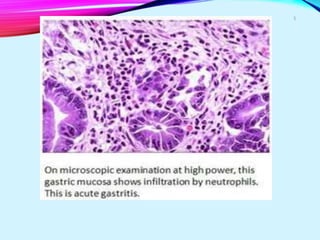
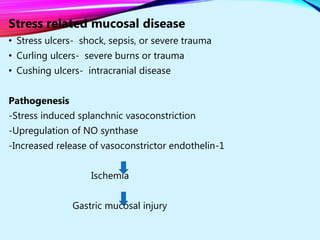
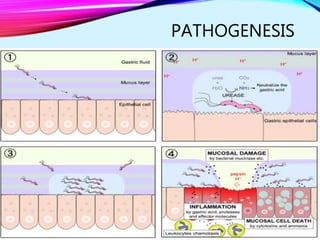
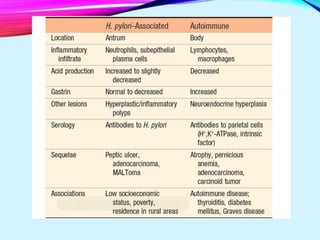
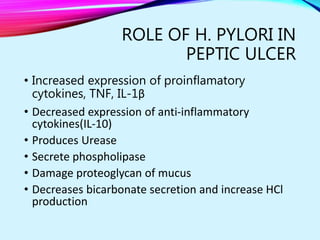
Helicobacter pylori plays a key role in both acute and chronic gastritis. It is the main cause of chronic gastritis and is associated with peptic ulcer disease. H. pylori infection leads to inflammation of the stomach lining through the actions of its virulence factors such as urease, adhesins, and toxins. This weakens the mucosal defenses and increases acid production, contributing to ulcer development. Autoimmune gastritis is characterized by antibodies against parietal cells, reduced acid and intrinsic factor secretion, and vitamin B12 deficiency.