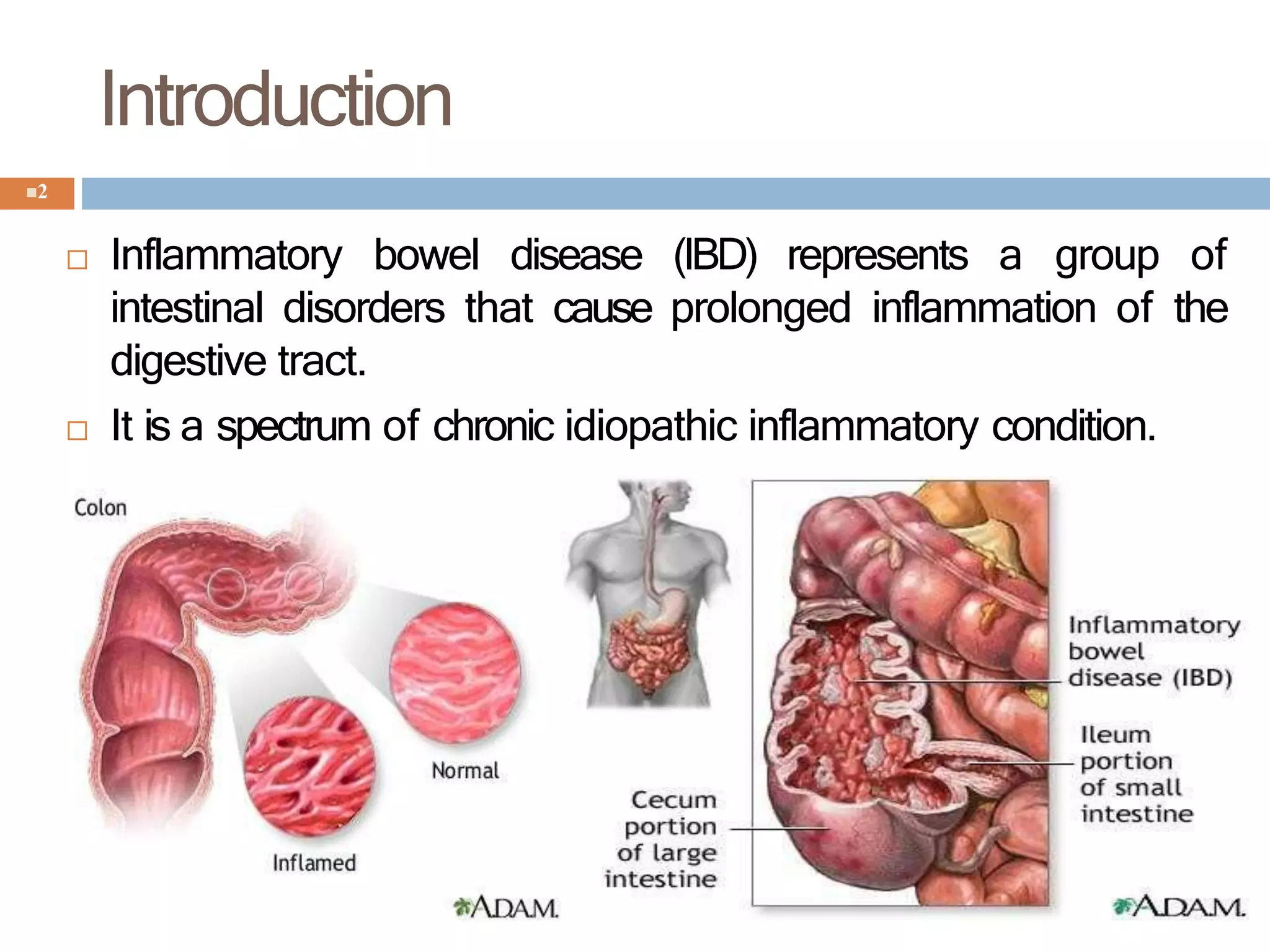
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) represents a group of chronic disorders that cause prolonged inflammation of the digestive tract. The two main types are ulcerative colitis, which causes inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the large intestine, and Crohn's disease, which is a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus. IBD is treated through a combination of medications, dietary changes, and sometimes surgery, with the goals of inducing and maintaining remission of symptoms, preventing complications, and avoiding surgery if possible. Treatments include aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, biologics that target tumor necrosis factor, and antimicrobial agents.