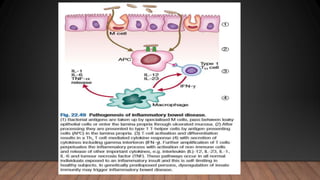
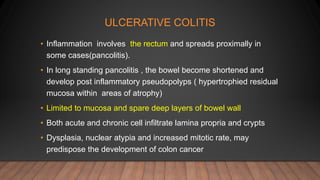
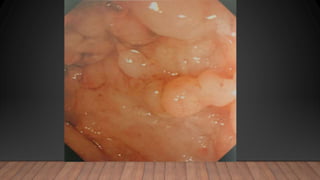
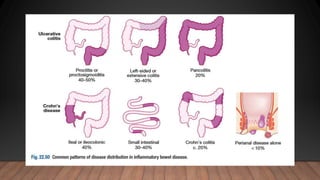
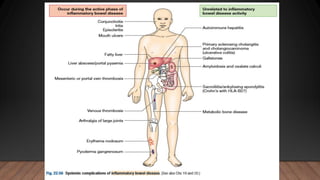
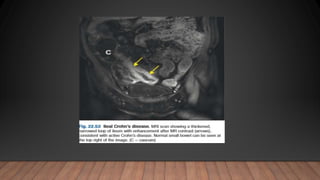
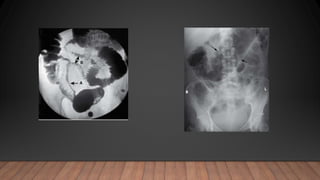
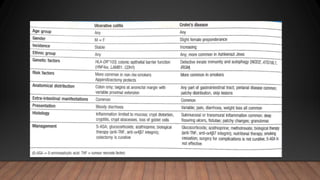
This document discusses inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. IBD is characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract due to an inappropriate immune response. Ulcerative colitis only involves the colon, while Crohn's disease can involve any part of the GI tract. Risk factors include genetics, smoking status, and an altered gut microbiome. Symptoms vary depending on the location of inflammation. Treatment involves medications to induce and maintain remission, as well as surgery for complications or non-responsive cases.