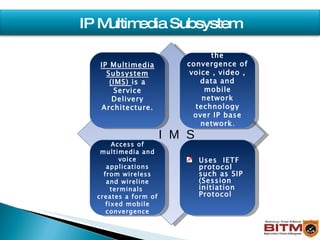
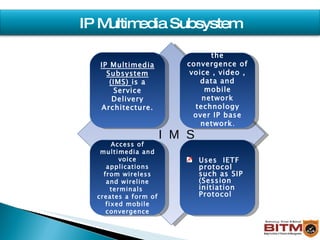
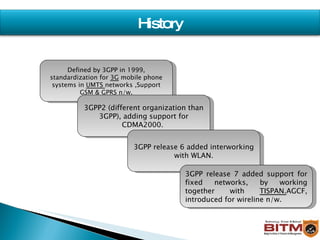
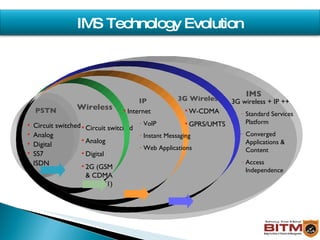
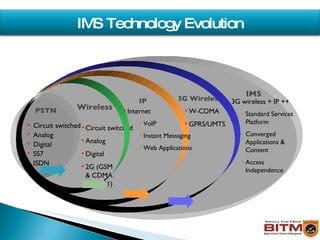
The document provides an overview of IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem), including its history, architecture, layers, benefits, and relationship to SIP (Session Initiation Protocol). IMS allows convergence of voice, video, and data over an IP-based network using SIP and other IETF protocols. It has a service plane for applications, a control plane for session management, and a media plane for transport.




















![Private User Identity Relationship Between User Identities [email_address] Sip:zehan.zeb@newstore.com tel:+17324567888 Sip:zehan.zeb@example.com tel:+88028112347 IMS Subscriber](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imsipmultimediasystem-100121000946-phpapp01/85/Ims-Ip-Multimedia-System-26-320.jpg)














