This document provides a summary of an presentation on IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS). It discusses:
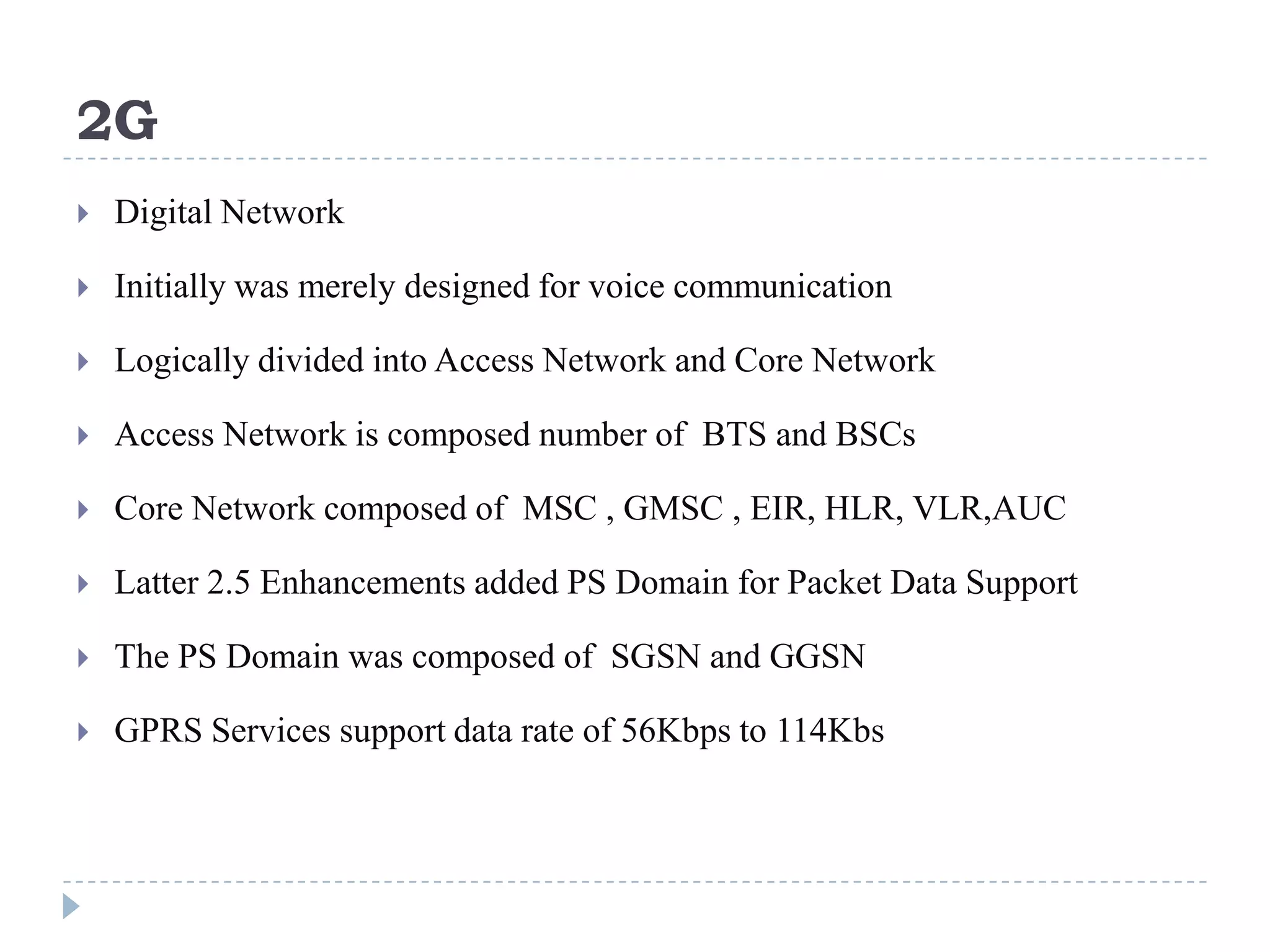
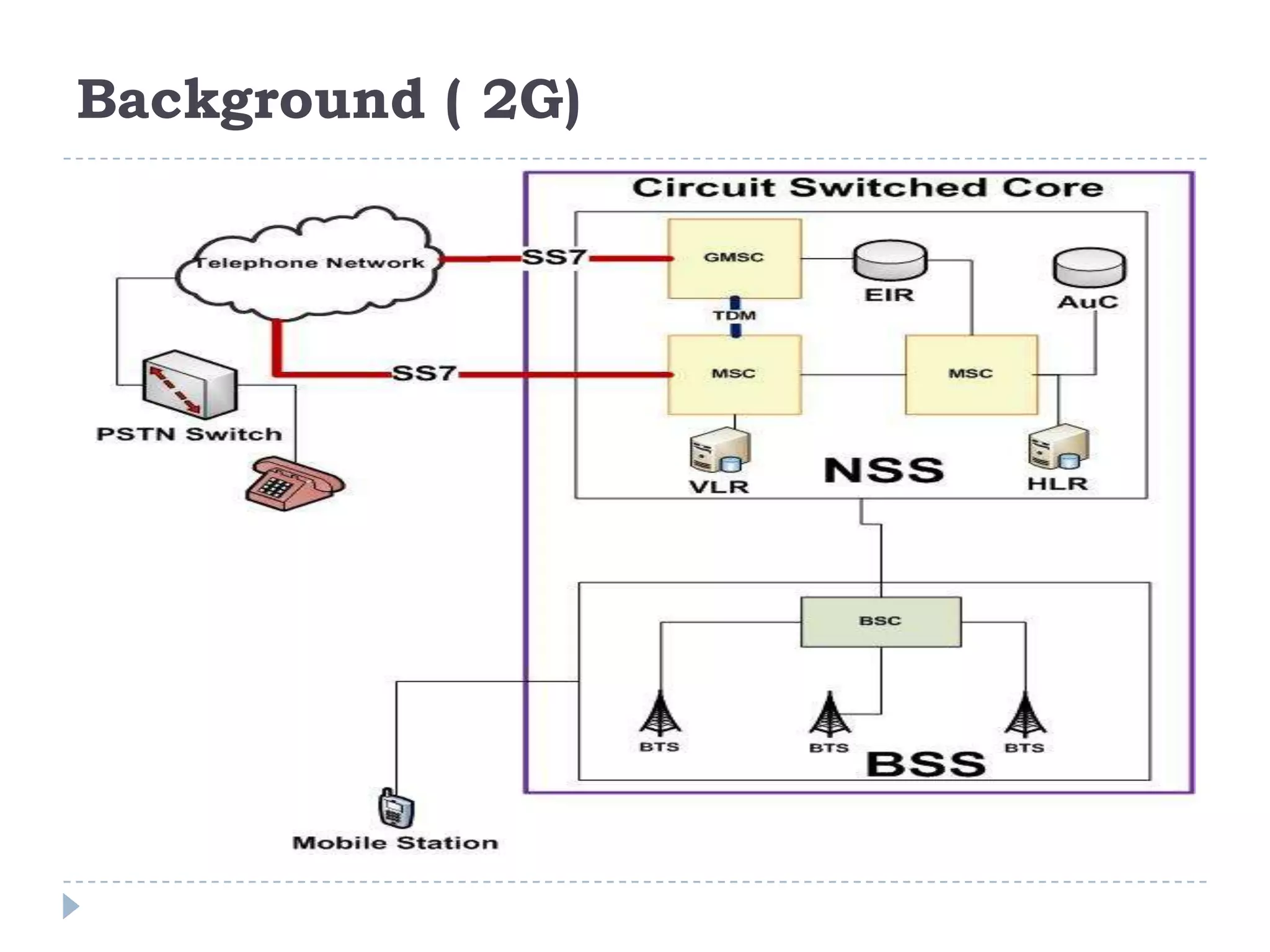
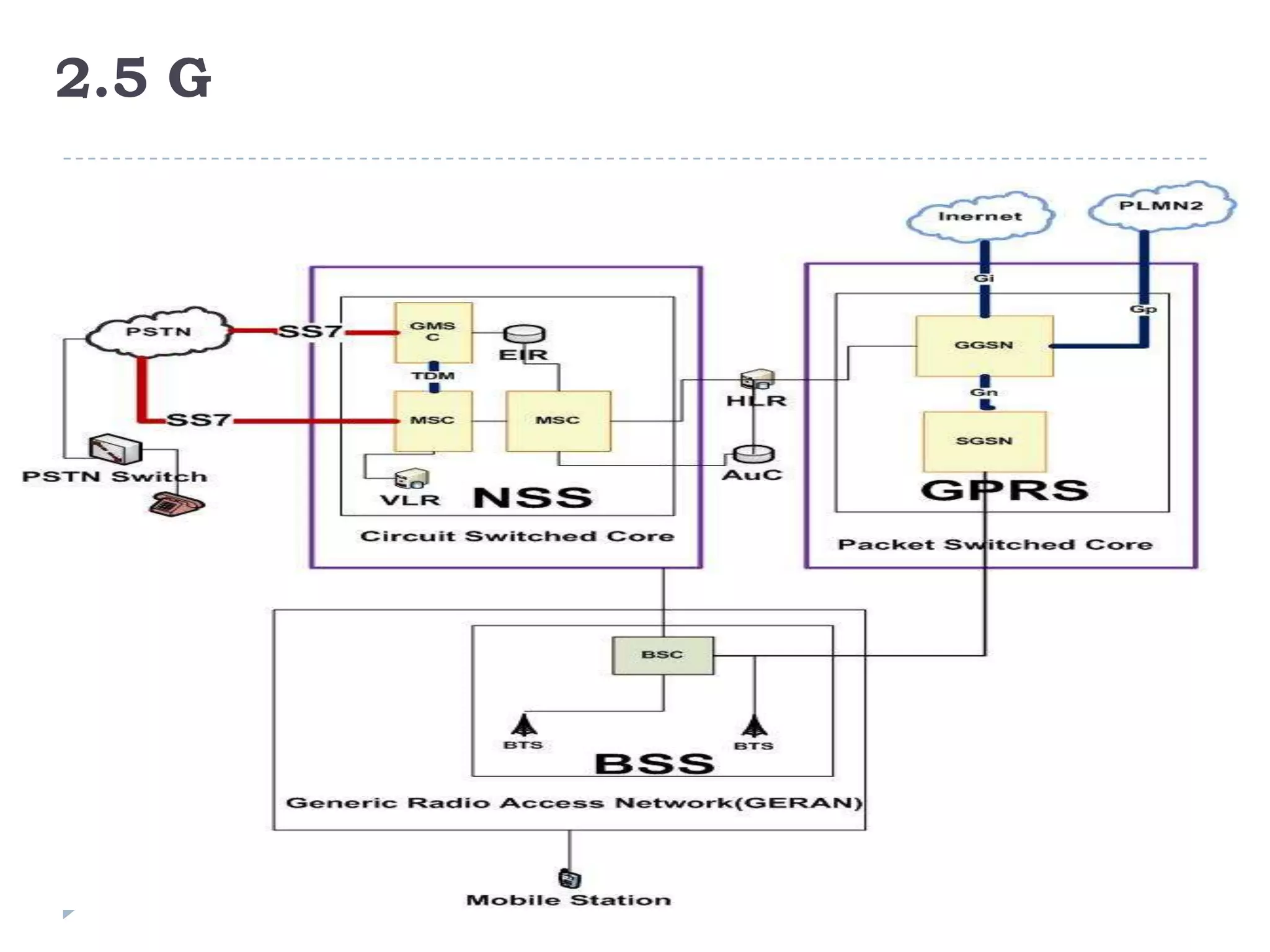
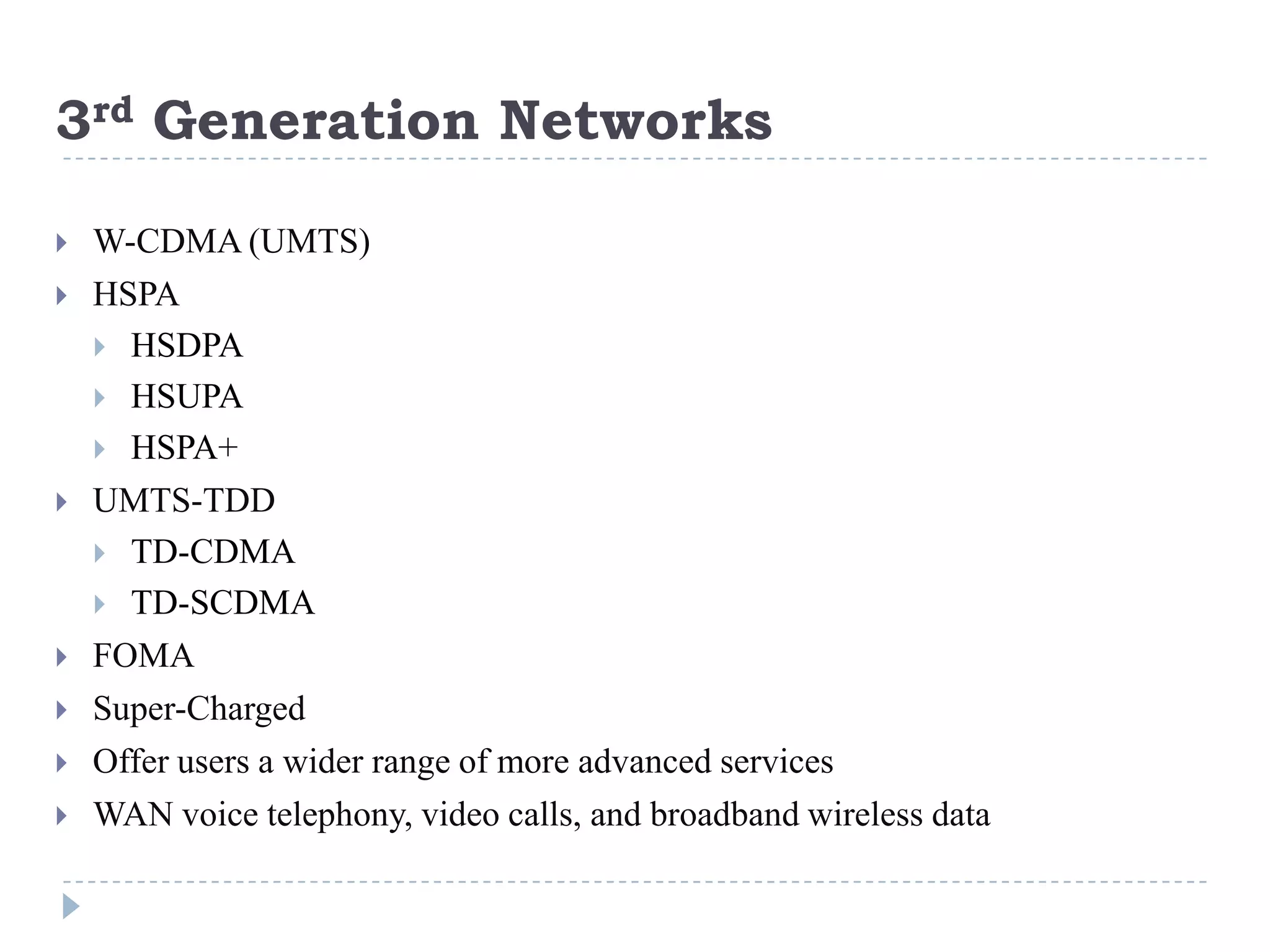
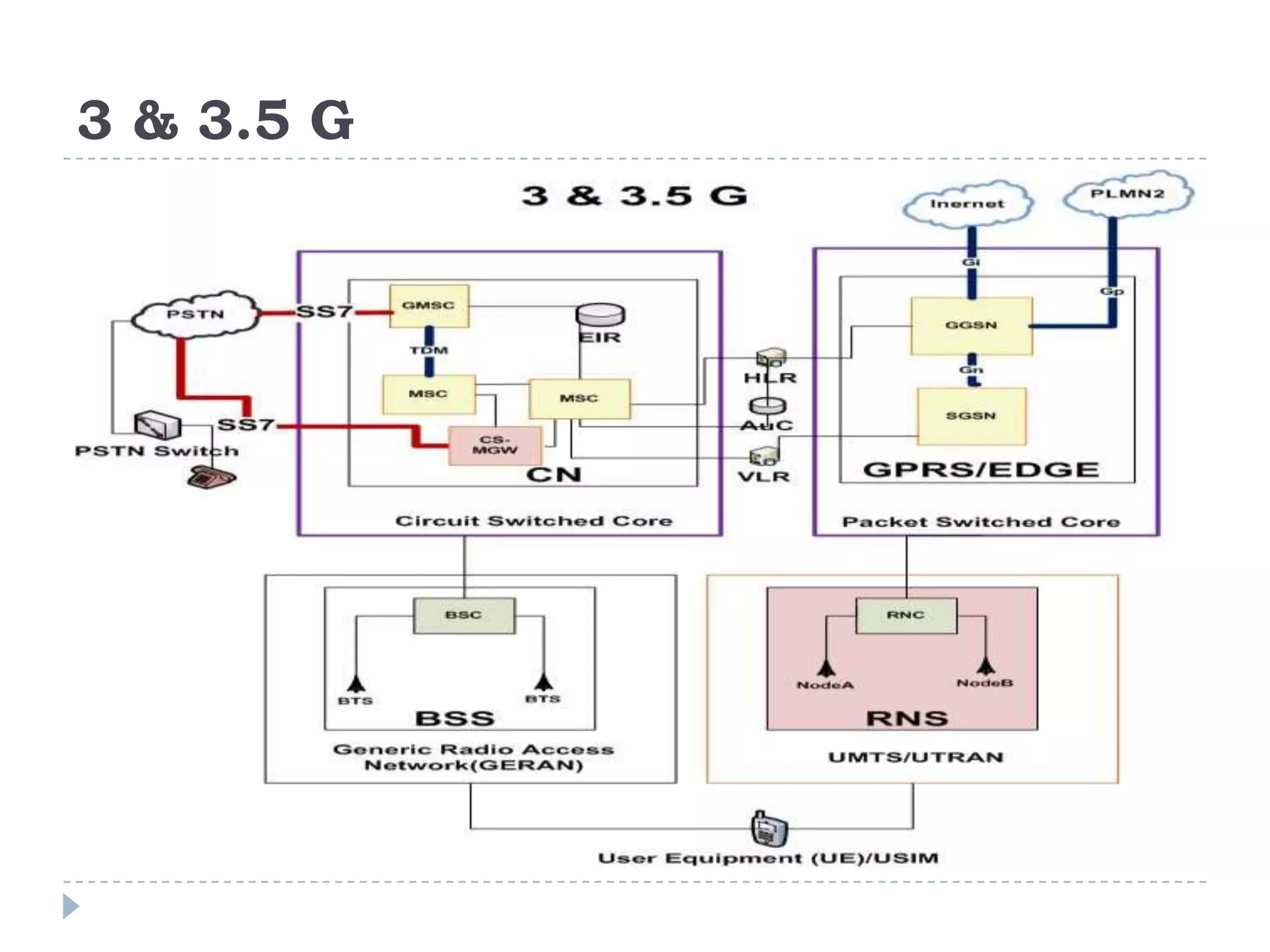
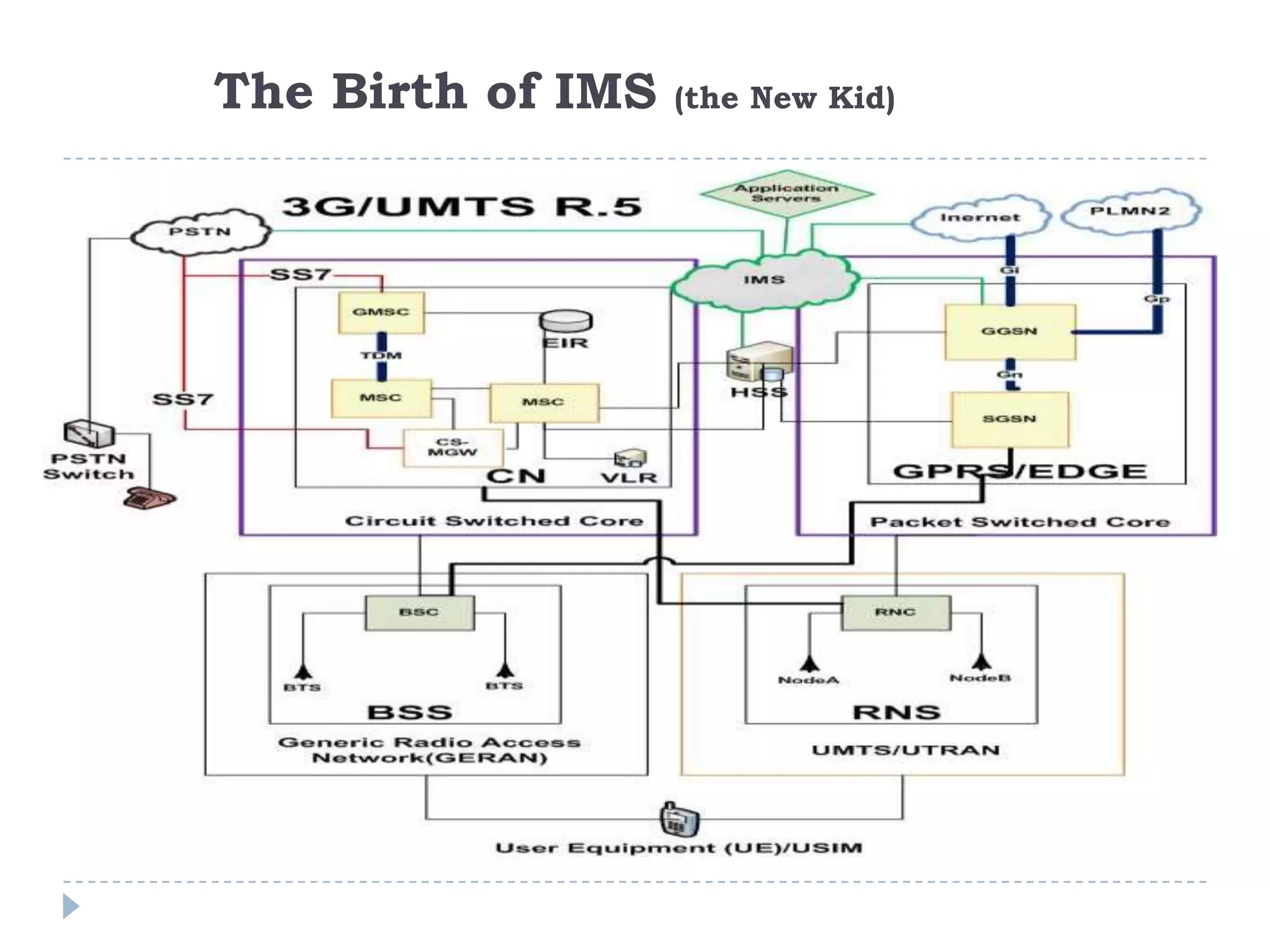
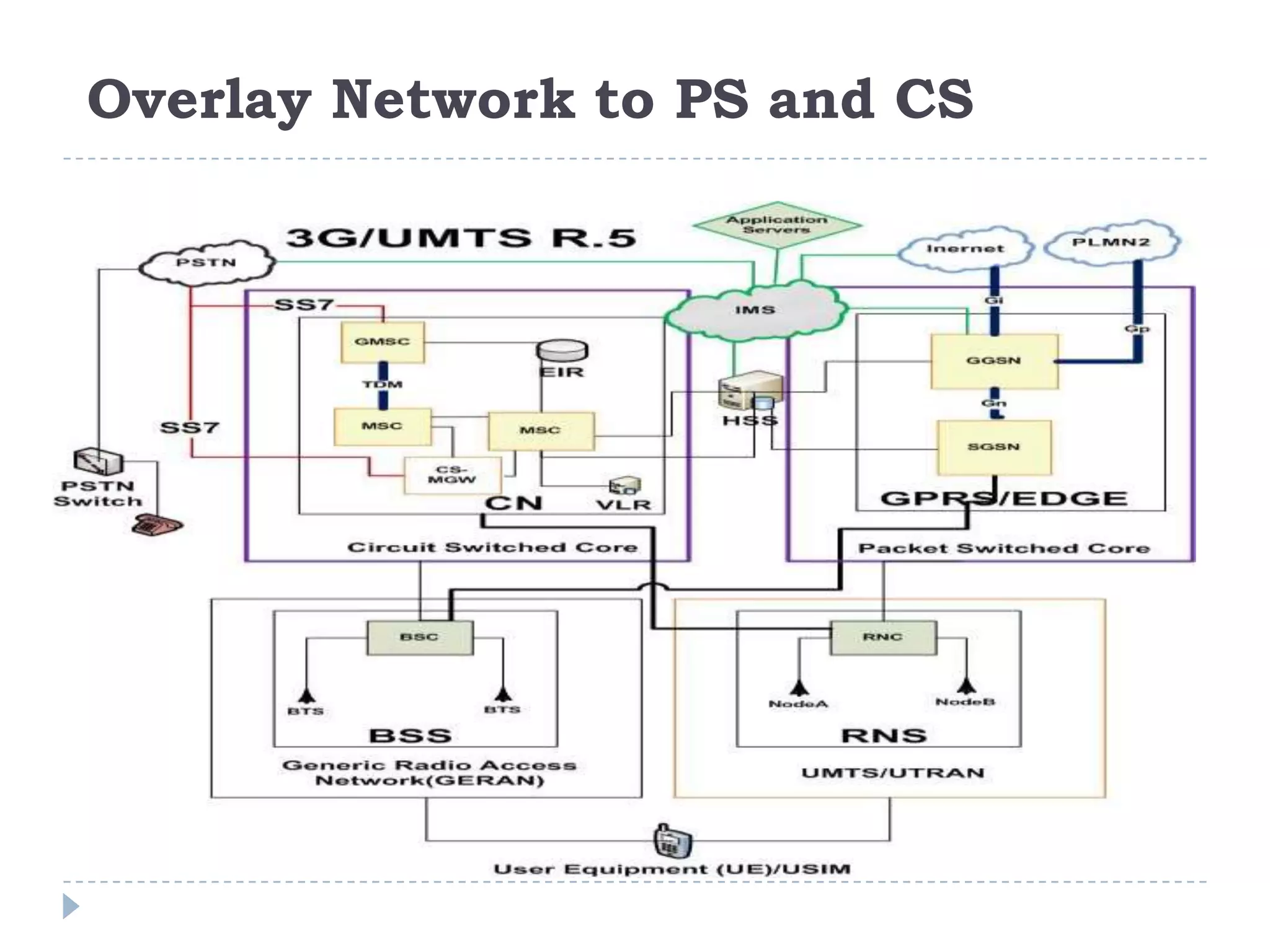
- The evolution of 2G, 2.5G, and 3G mobile networks and the birth of IMS as a new architecture.
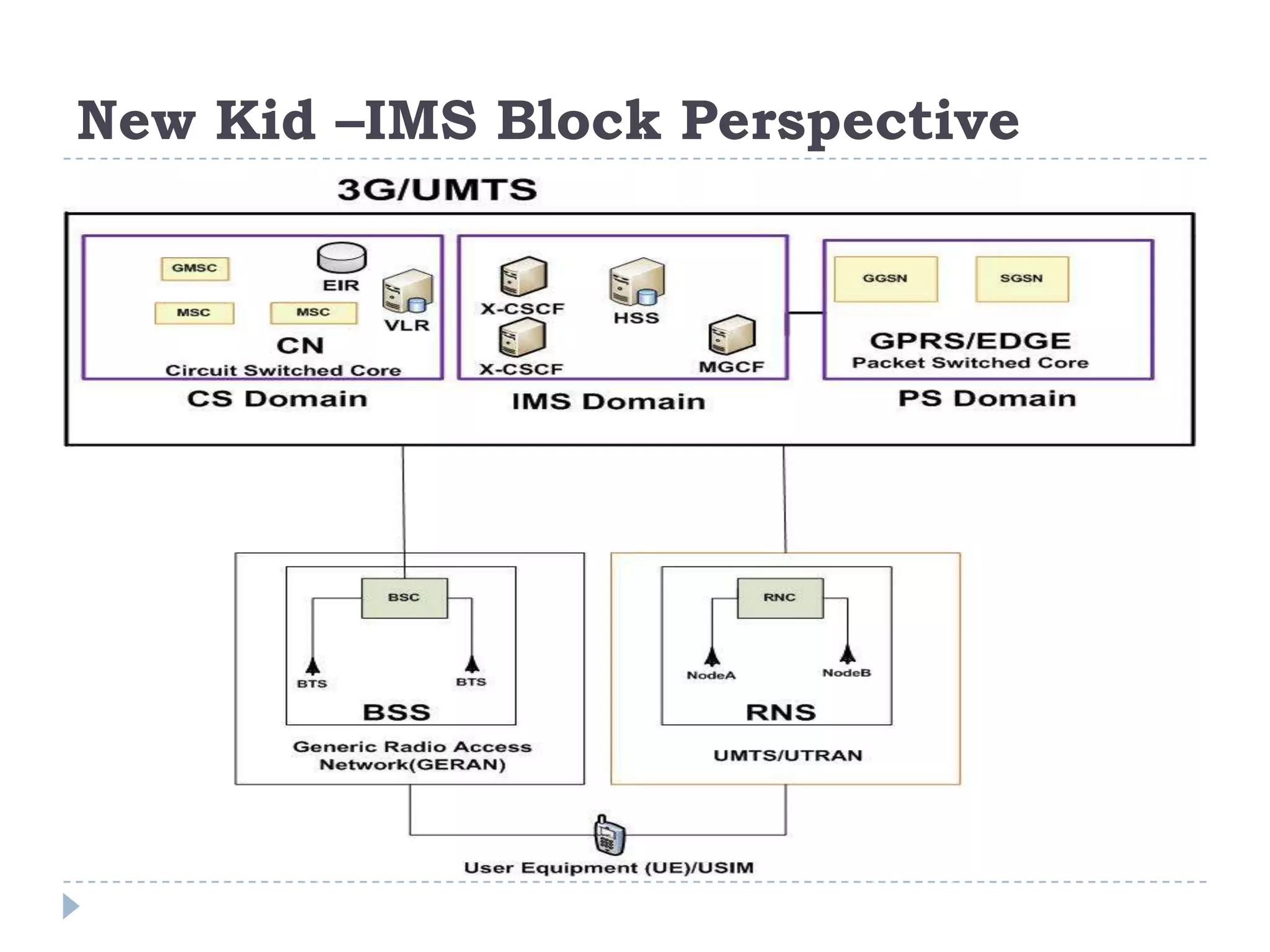
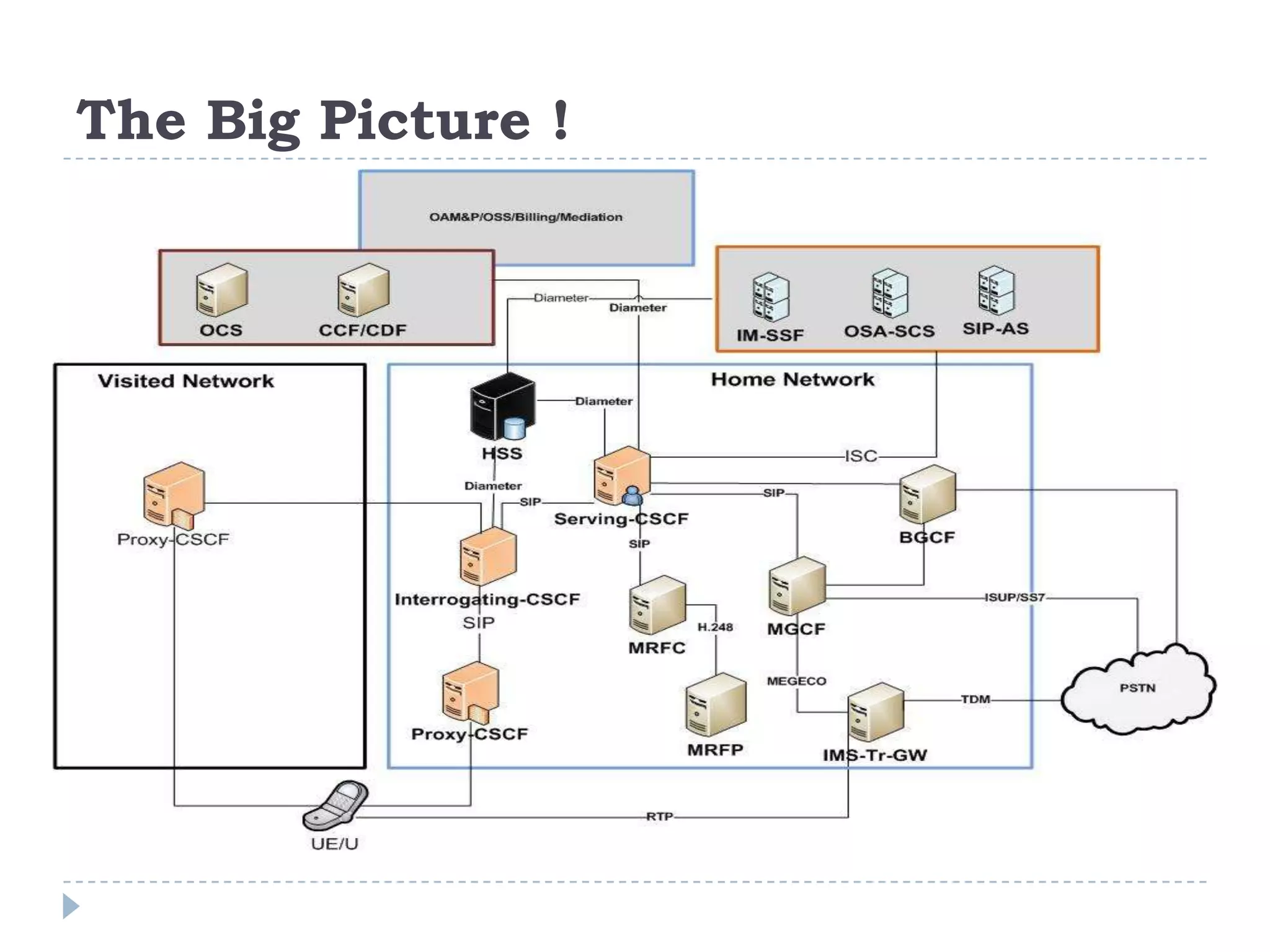
- IMS allows support for IP-based interactive multimedia services with QoS guarantees across both circuit-switched and packet-switched networks.
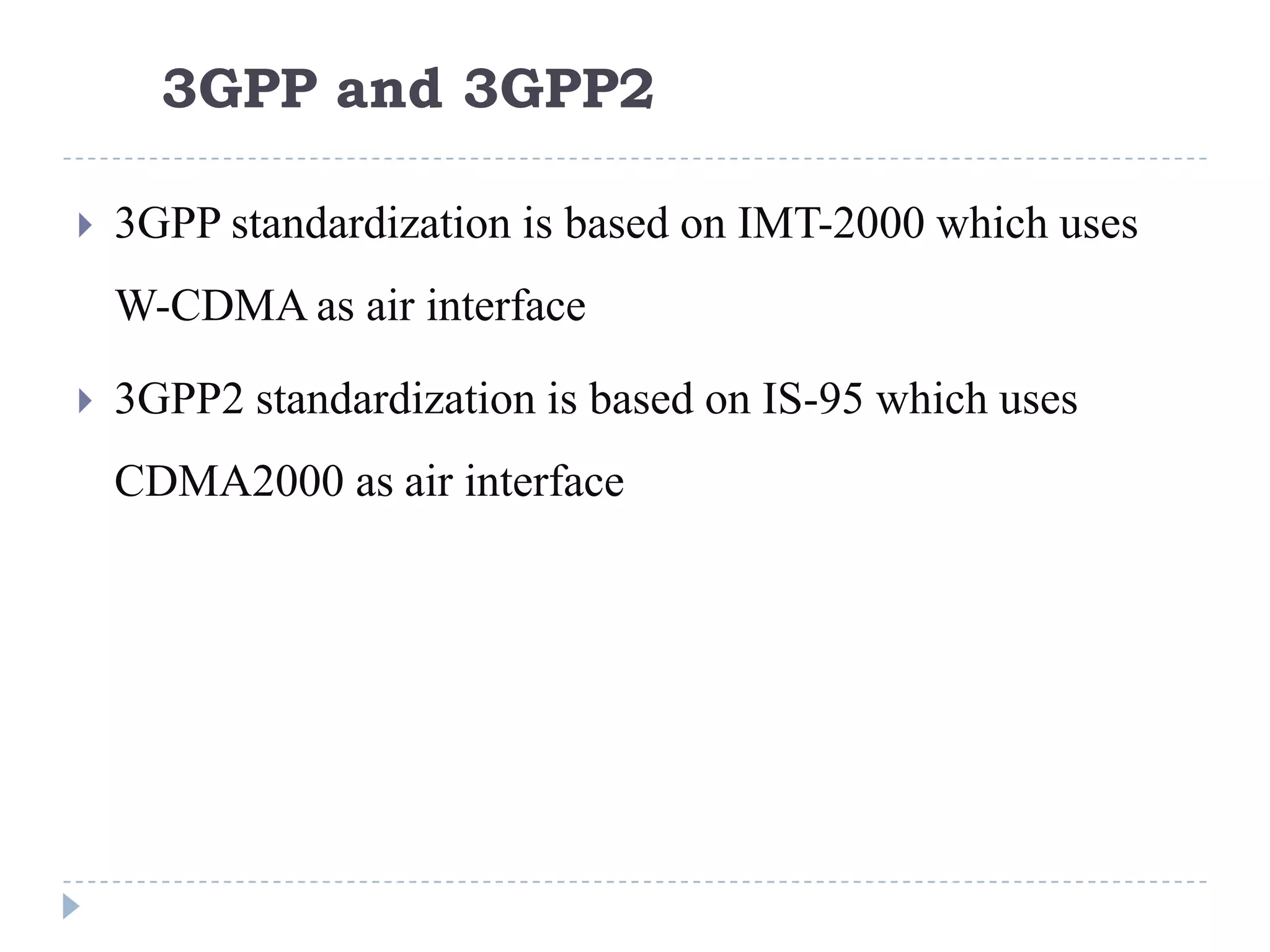
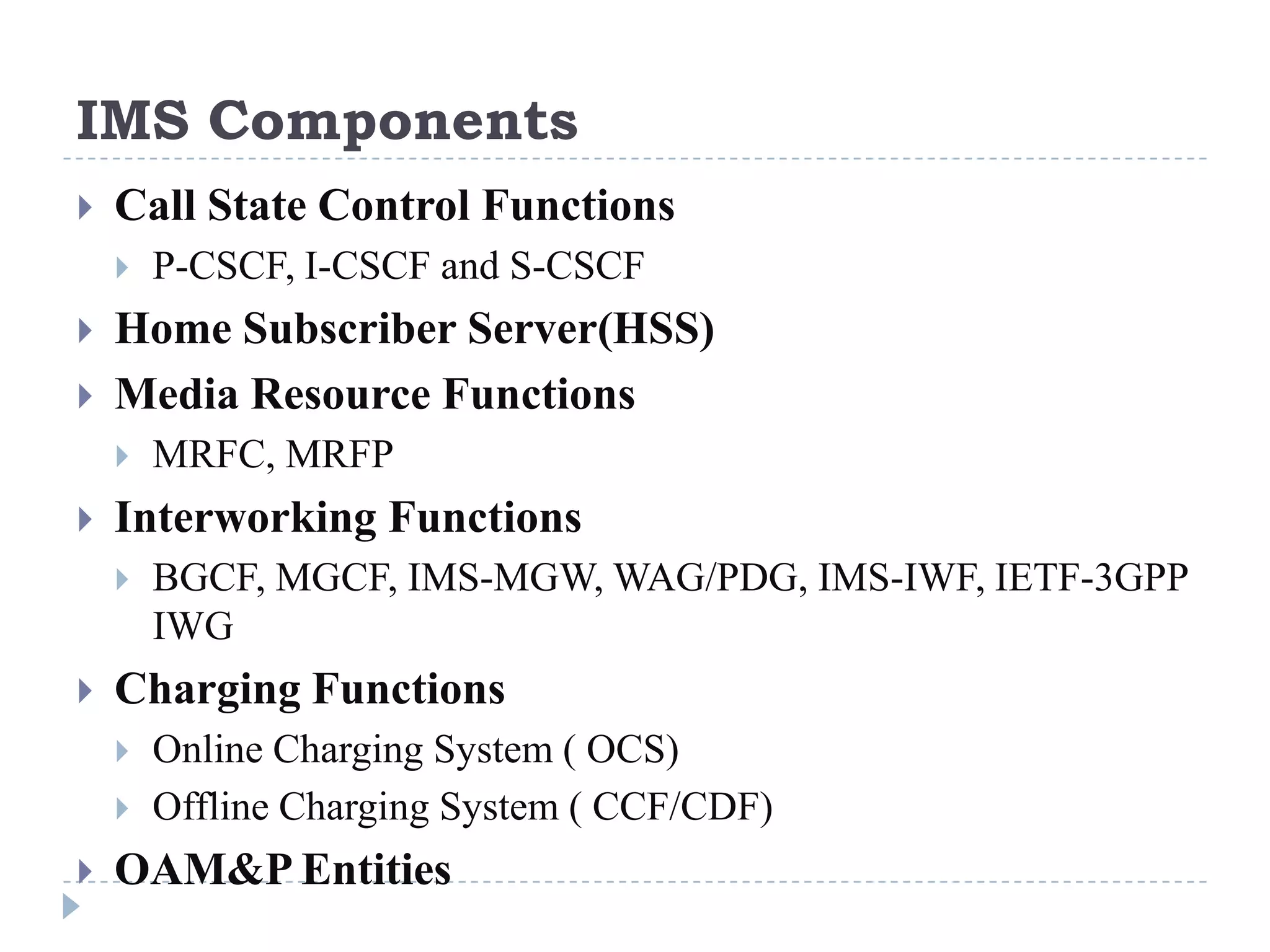
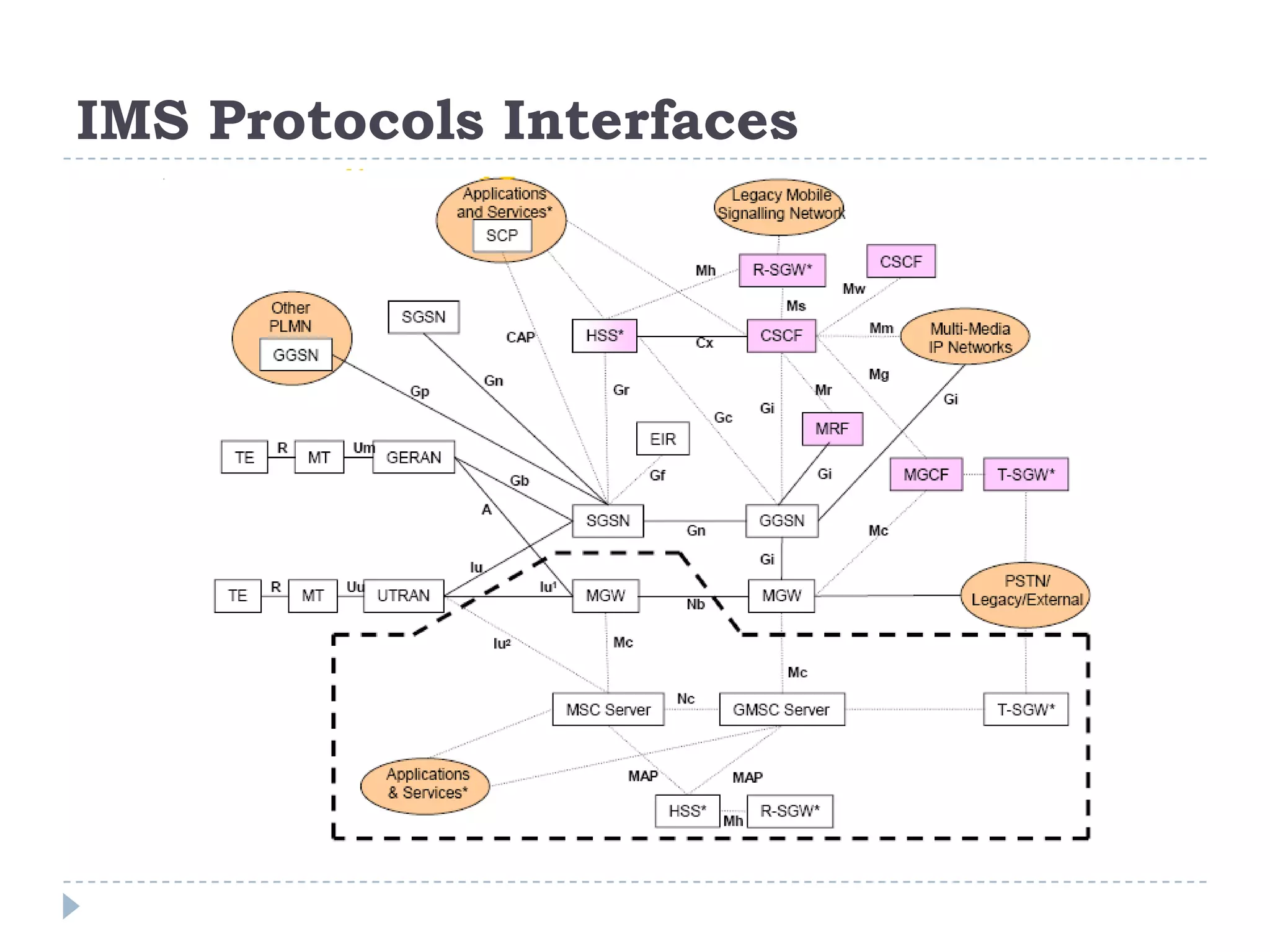
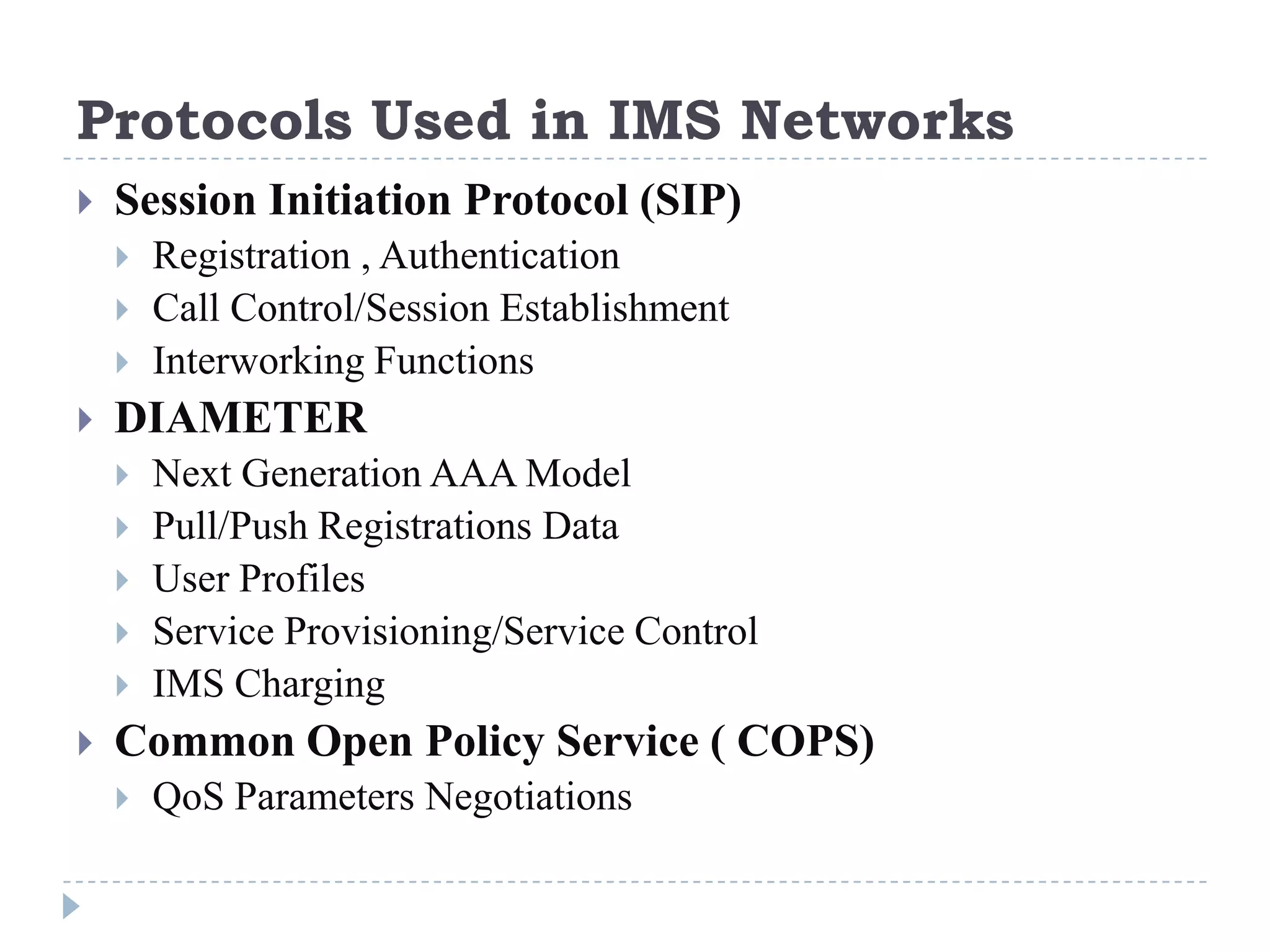
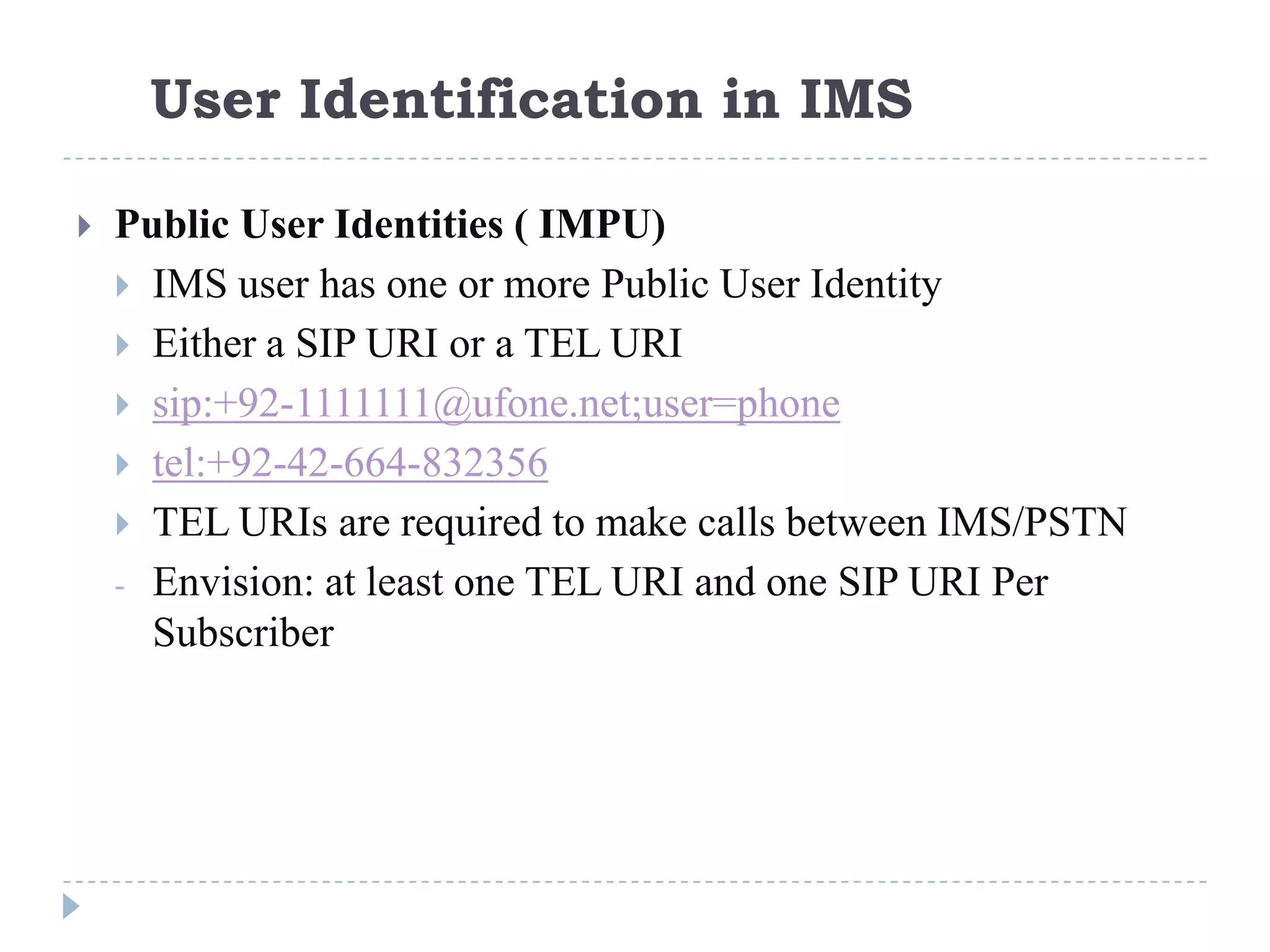
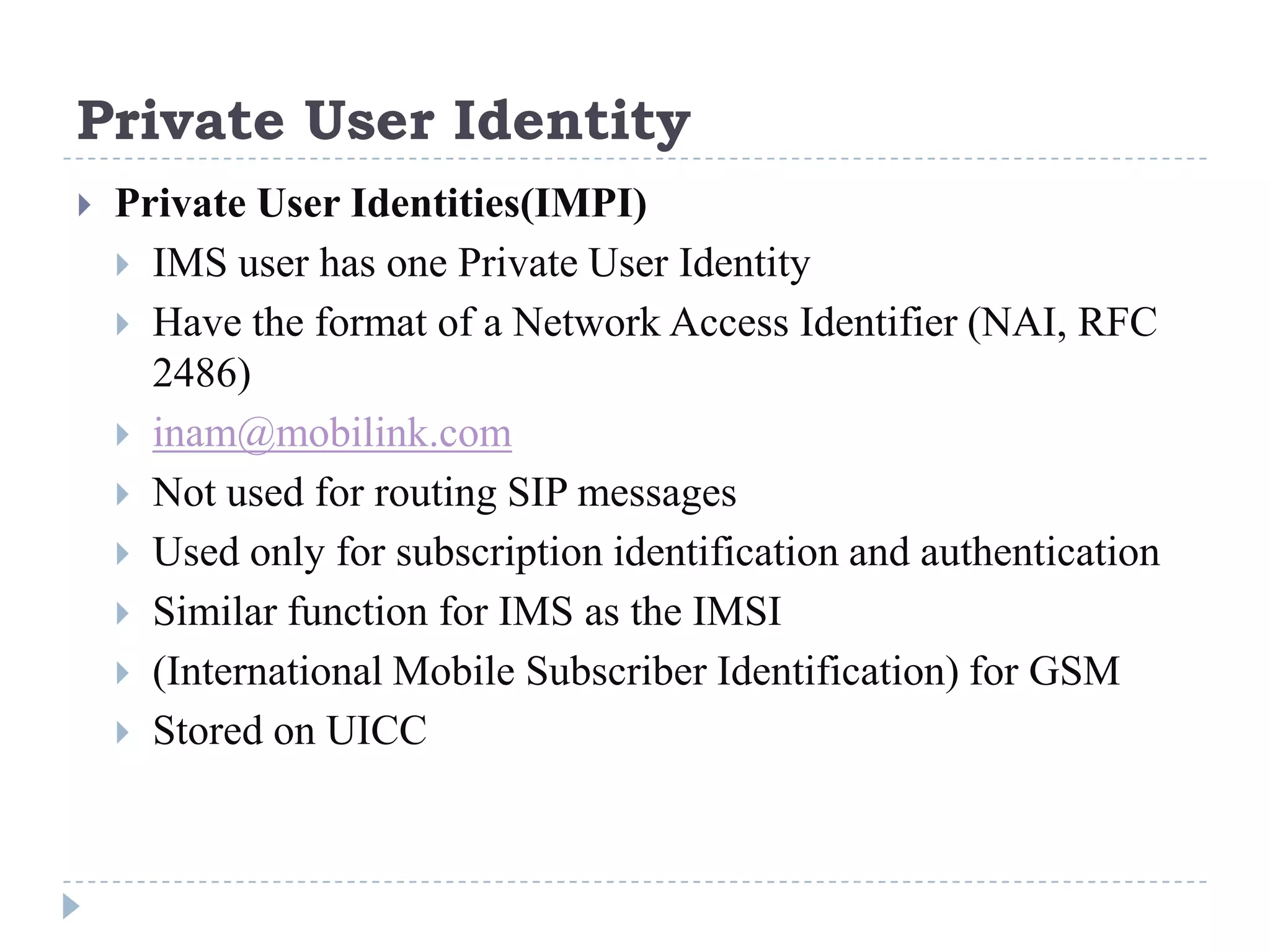
- IMS standardization is led by 3GPP and uses SIP, Diameter, and COPS protocols. The presentation covers IMS components, architecture, services control model, and functions.