NTT's Next Generation Network Development
Takashi Ebihara of NTT presented on NTT's next generation network (NGN) development at a 2008 conference. Key points included:
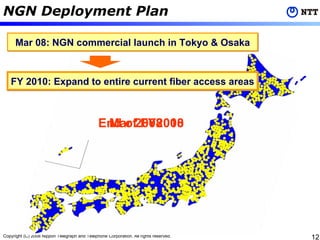
1) NTT plans to deploy its NGN commercially in 2008 in Tokyo and Osaka and expand coverage to all fiber access areas by 2010.
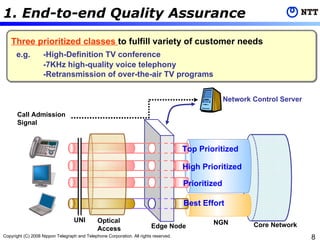
2) NGN combines advantages of traditional telephone networks and IP networks with features like enhanced reliability, security, quality assurance and open interfaces.
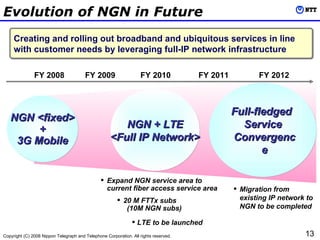
3) NTT will collaborate with partners through forums and test beds to jointly develop innovative new services leveraging NGN's capabilities.