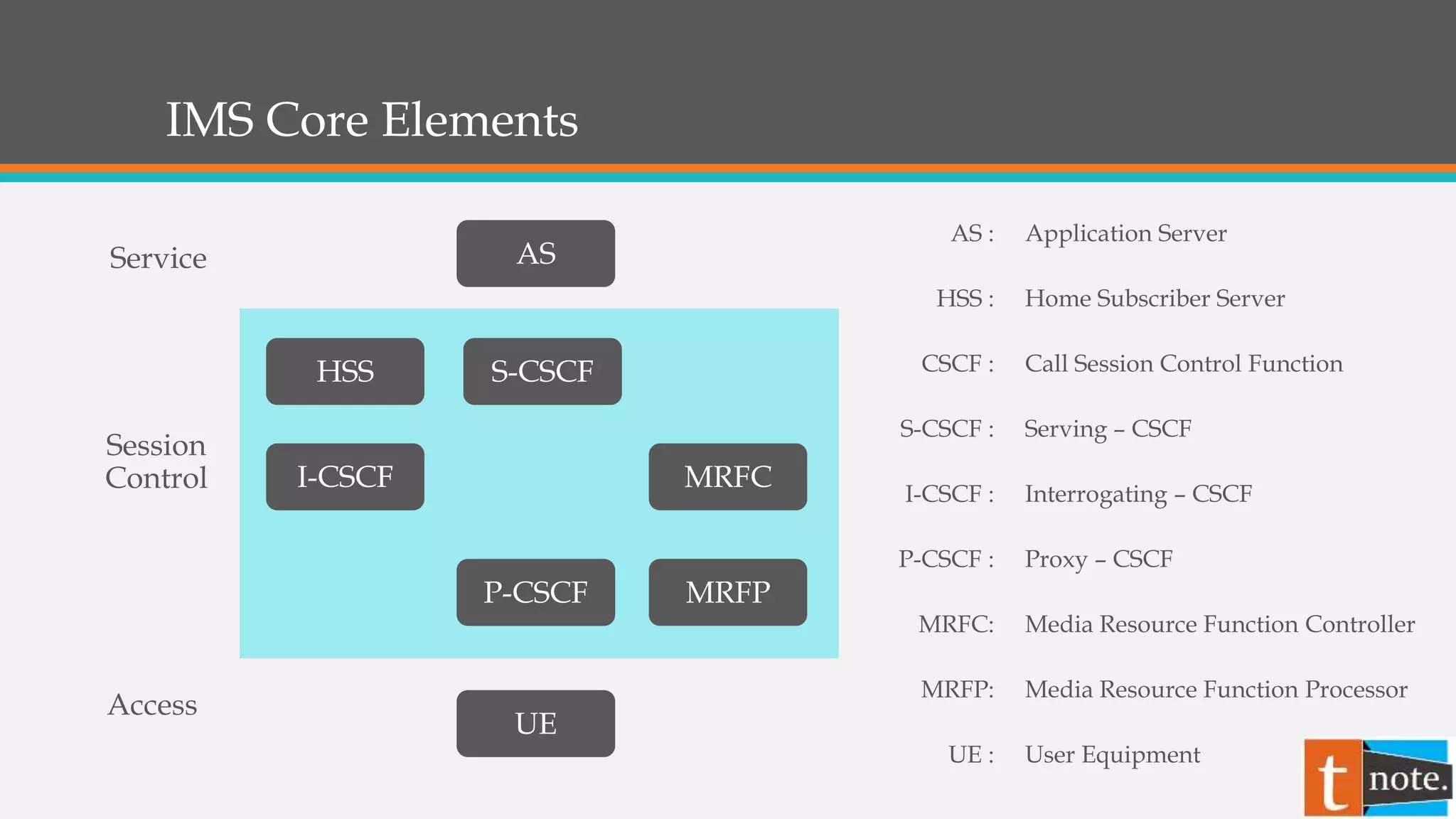
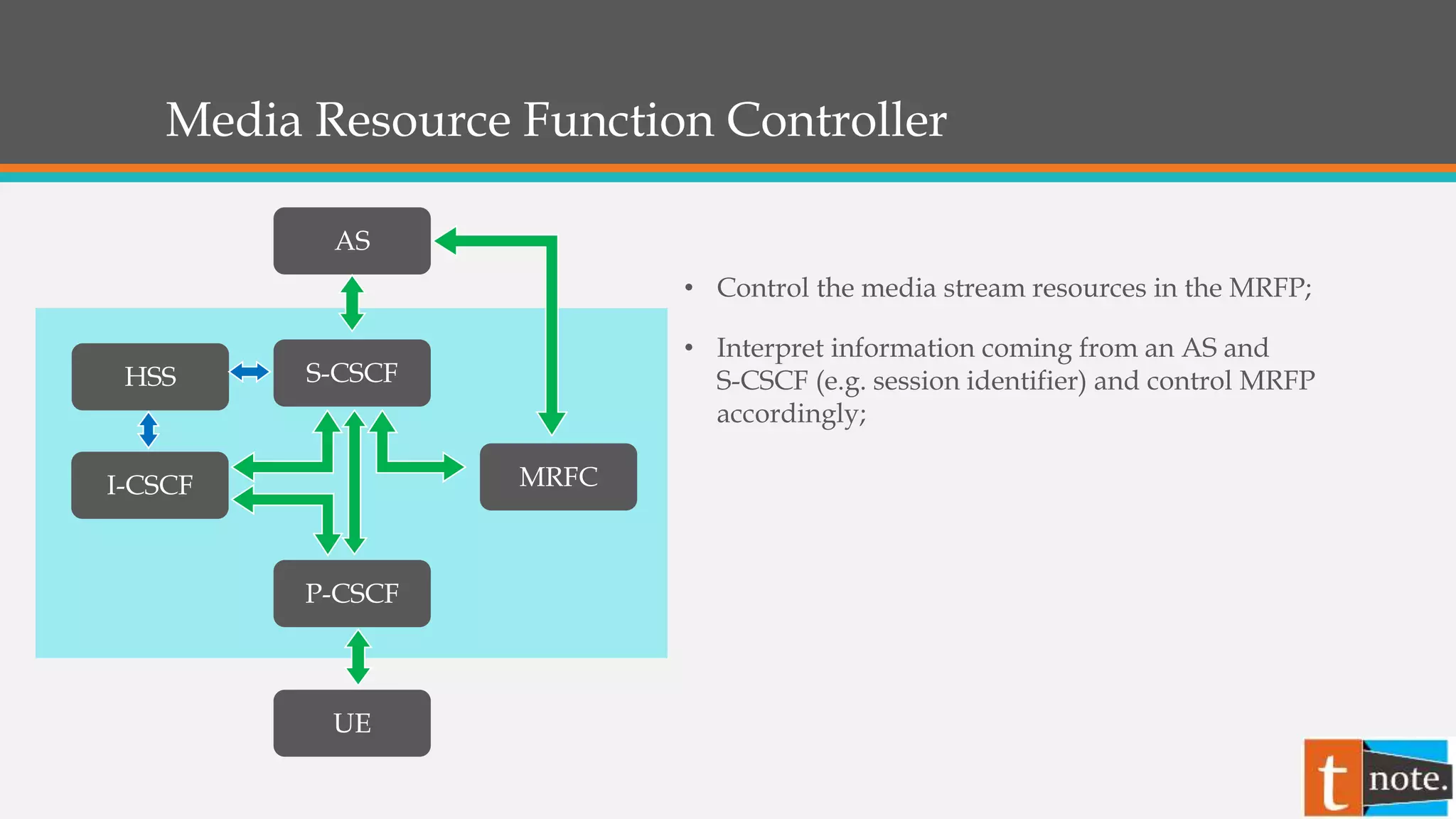
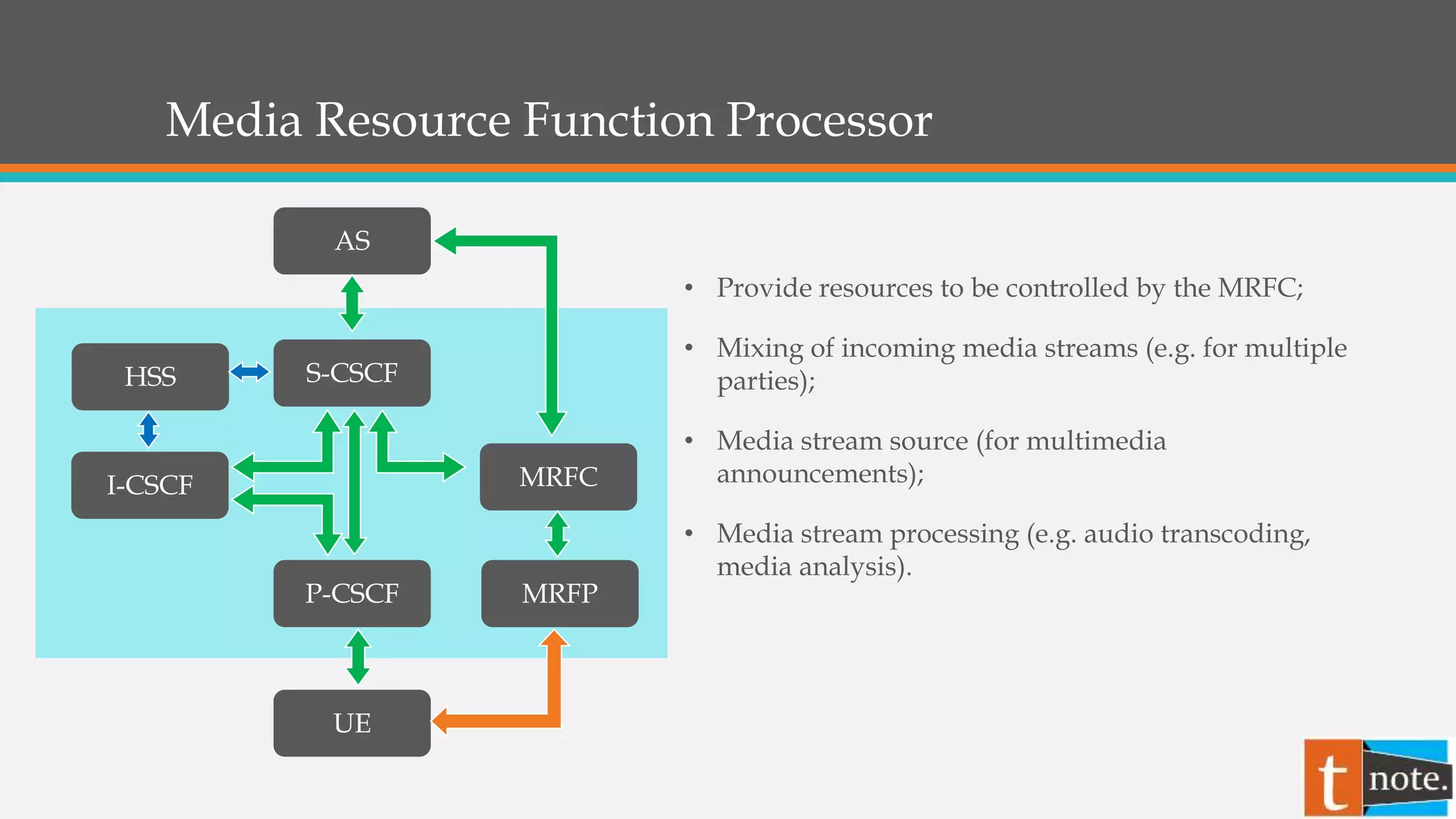
The document summarizes the core elements of an IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) network. The key elements are:
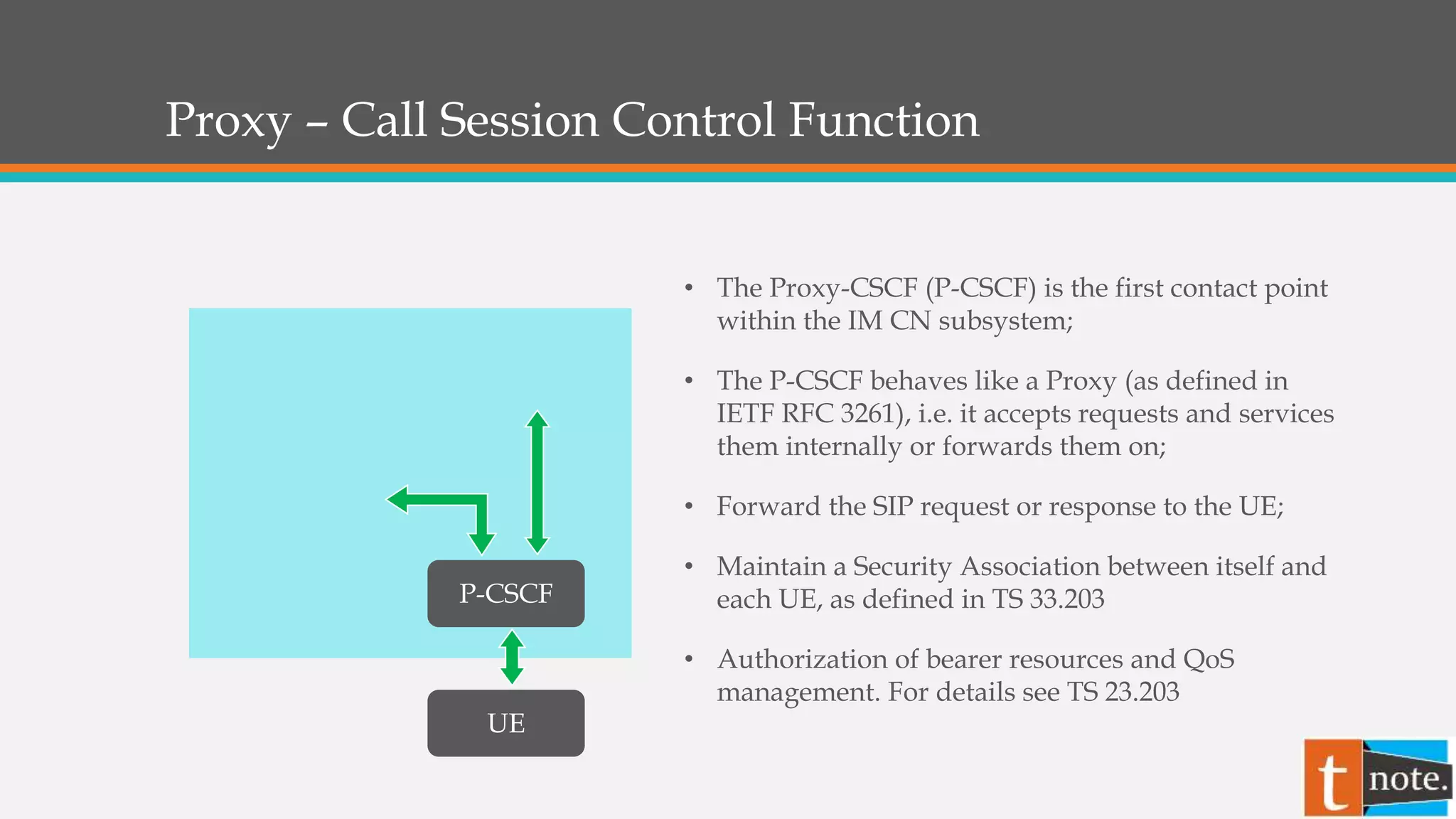
- The Proxy-CSCF (P-CSCF) is the first contact point for the user and handles security, authorization, and forwarding requests.
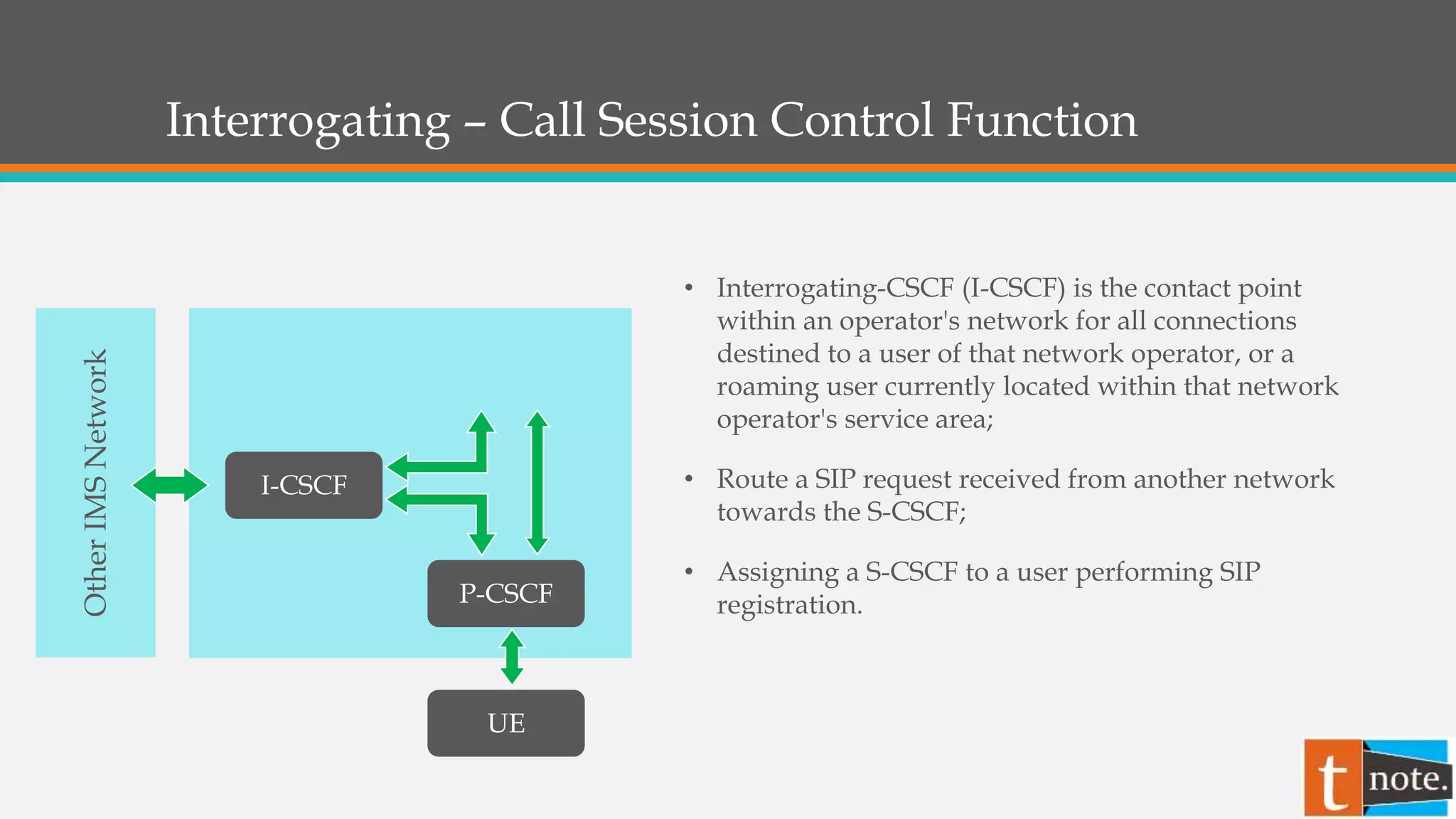
- The Interrogating-CSCF (I-CSCF) routes requests between networks and assigns users a Serving-CSCF (S-CSCF).
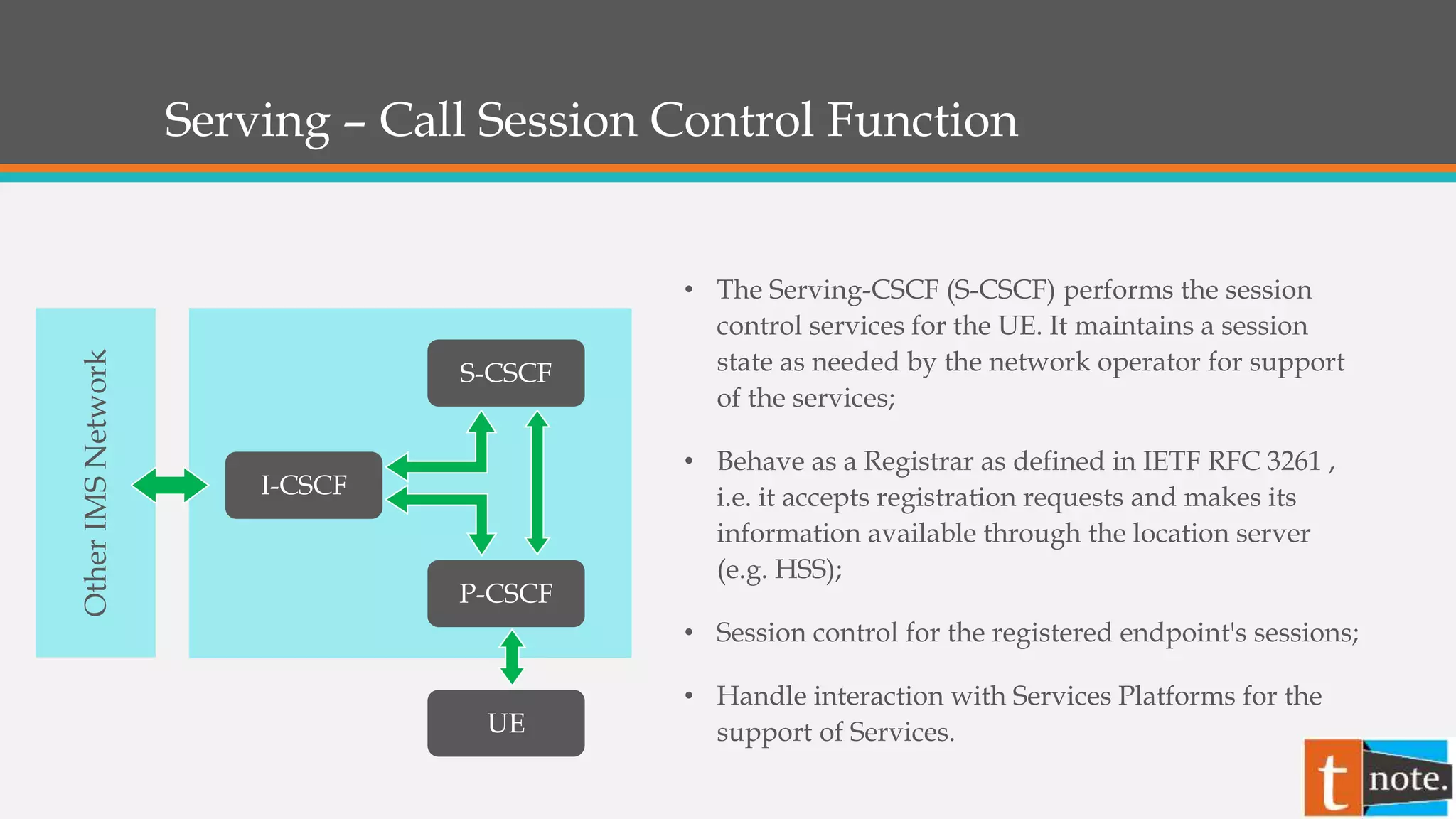
- The S-CSCF manages sessions for registered users and interacts with application servers to provide services.
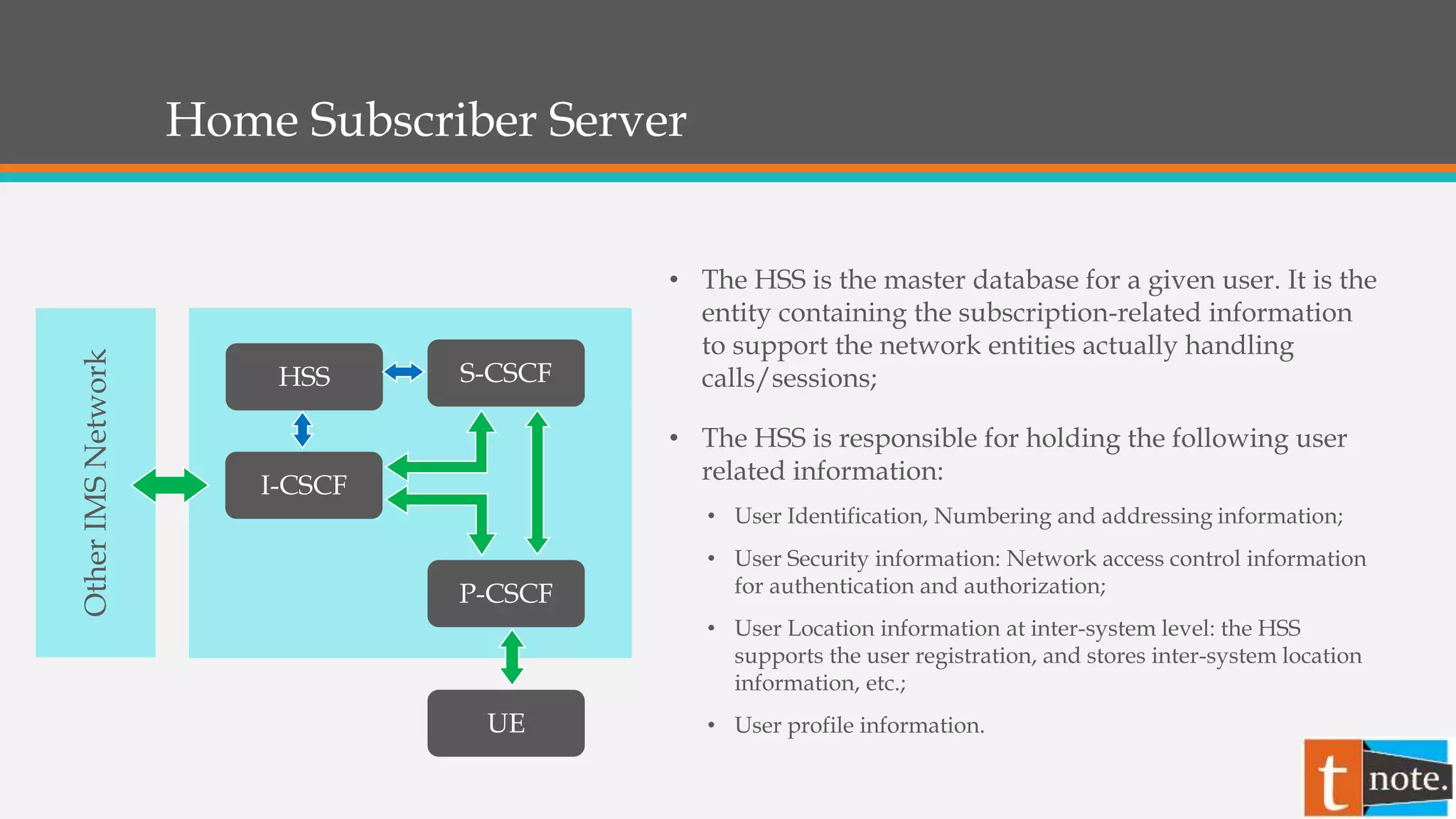
- The Home Subscriber Server (HSS) is the master database that stores user profiles, locations, and security information.
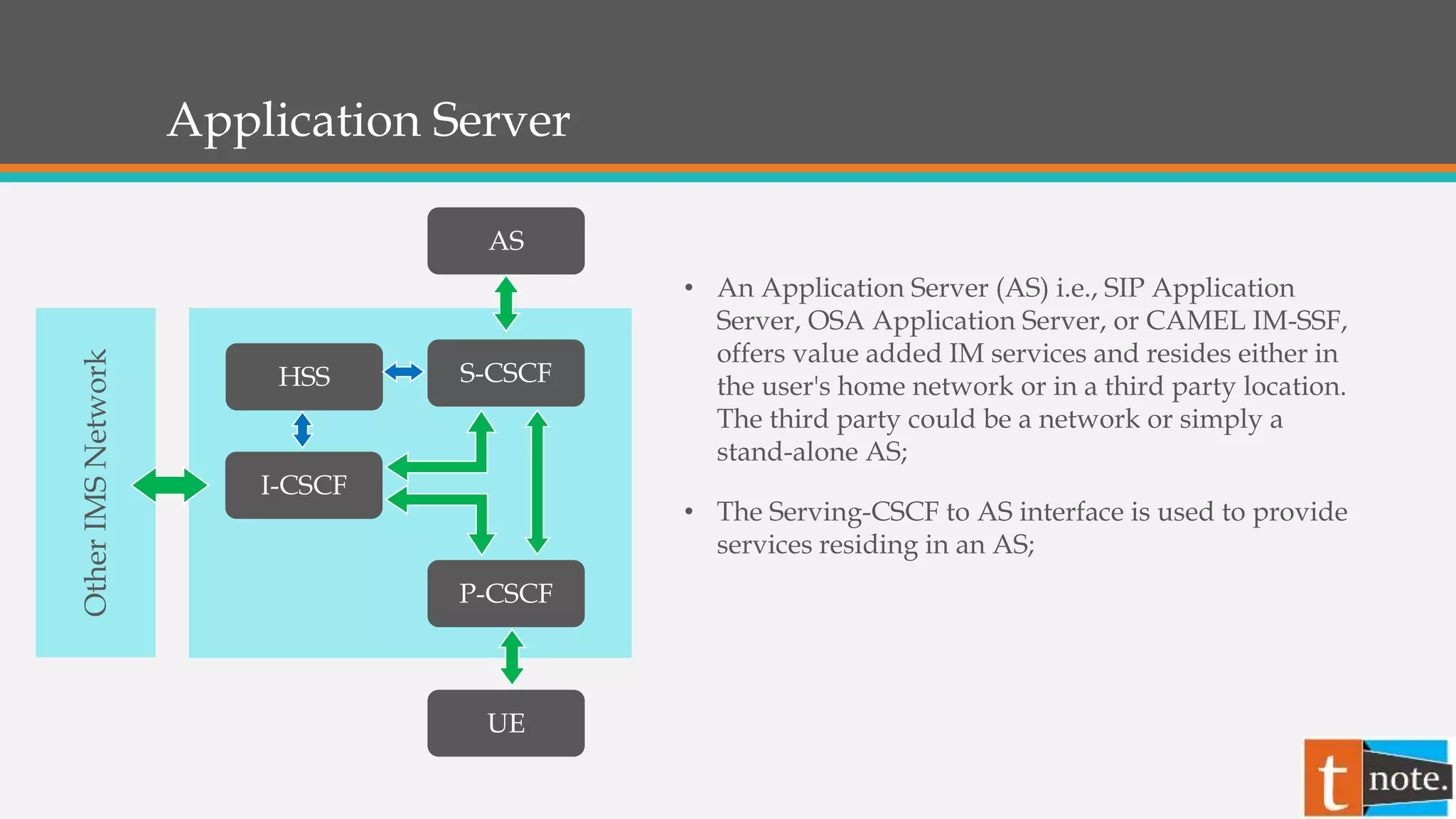
- Application Servers