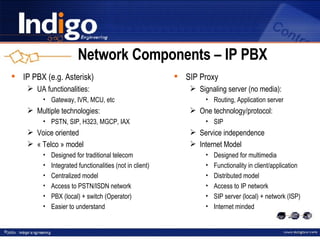
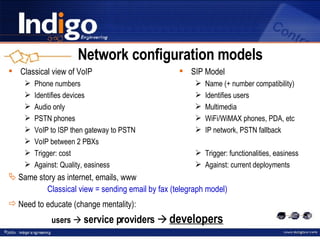
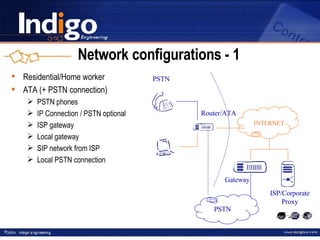
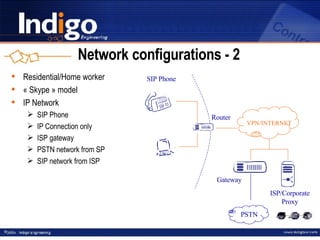
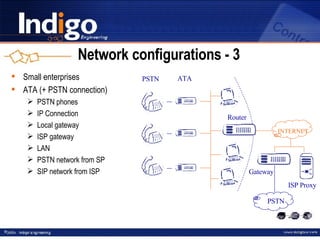
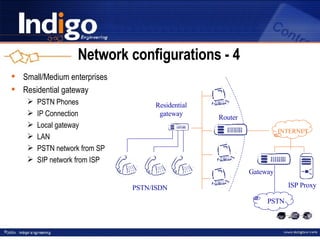
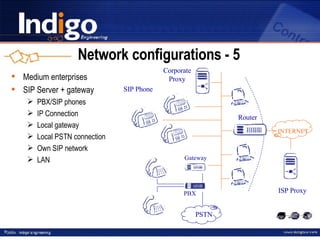
The document provides an overview of Indigo Group and their SIP technology and products. It discusses SIP protocol and how it works for real-time communications over IP networks. It describes network components like user agents, servers, and gateways. It also outlines different network configuration options and examples of SIP services like multimedia sessions and event notification.







![Principle /1 Registrar Server Location Server Proxy Server Private network / Internet Domain 1 Domain 2 [email_address] [email_address] DNS Server registration [email_address] Proxy Server call [email_address] domain2 ? user2 ? Media](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indigo-product-and-technology-overivew-20054933/85/Indigo-Product-And-Technology-Overivew-2005-9-320.jpg)
![Principle /2 call info @indigosw.com Directed to the user Caller [email_address] [email_address] 022303594 [email_address] Desk A Desk B Forking](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indigo-product-and-technology-overivew-20054933/85/Indigo-Product-And-Technology-Overivew-2005-10-320.jpg)




![Network configurations - 6 Medium/large enterprises Distributed / centralized Gateway PBX Router VPN/INTERNET Corporate Proxy PSTN Gateway PBX Router Corporate Proxy PSTN Router Road Warriors Home worker [distributed only]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indigo-product-and-technology-overivew-20054933/85/Indigo-Product-And-Technology-Overivew-2005-25-320.jpg)



















