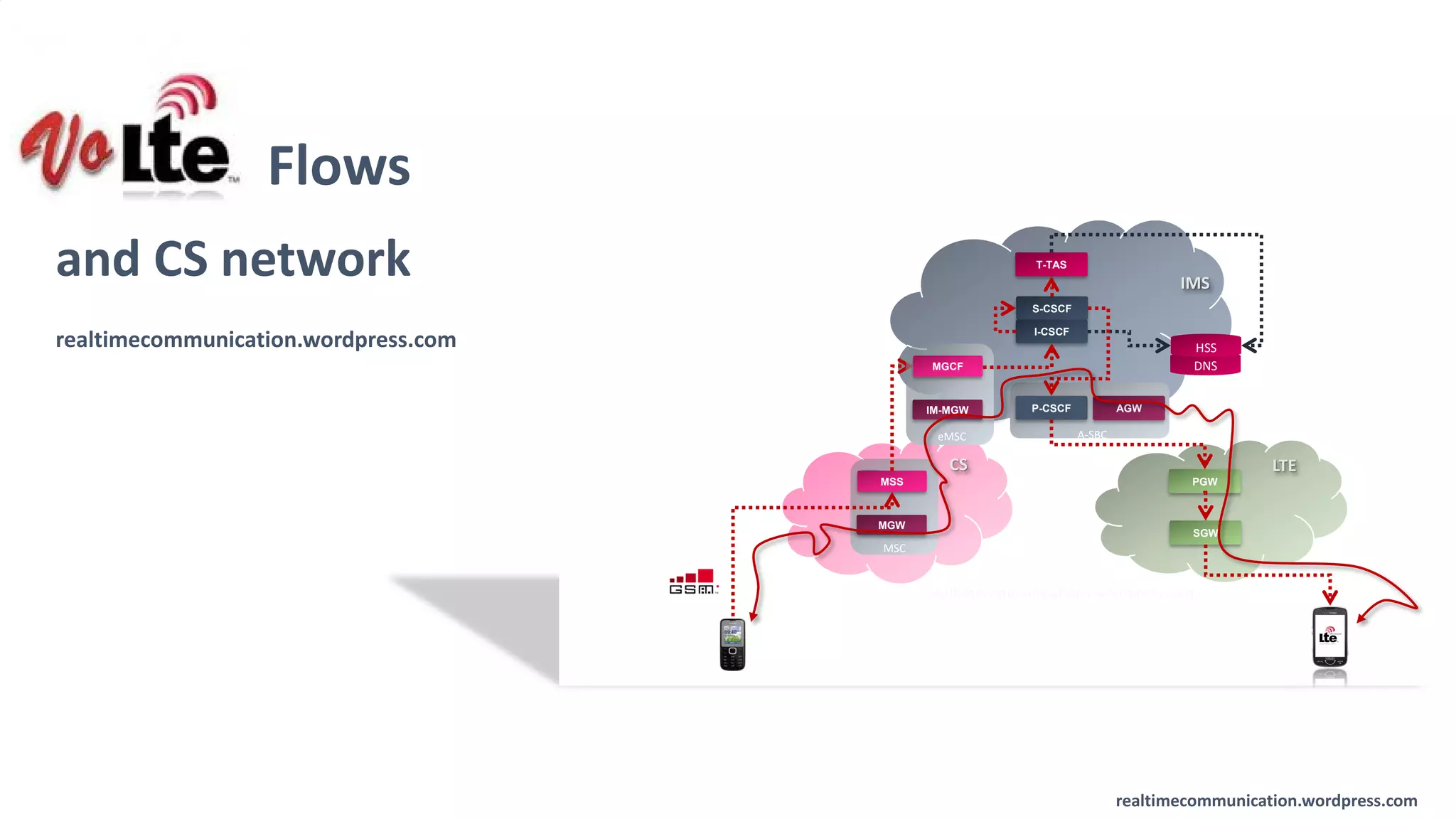
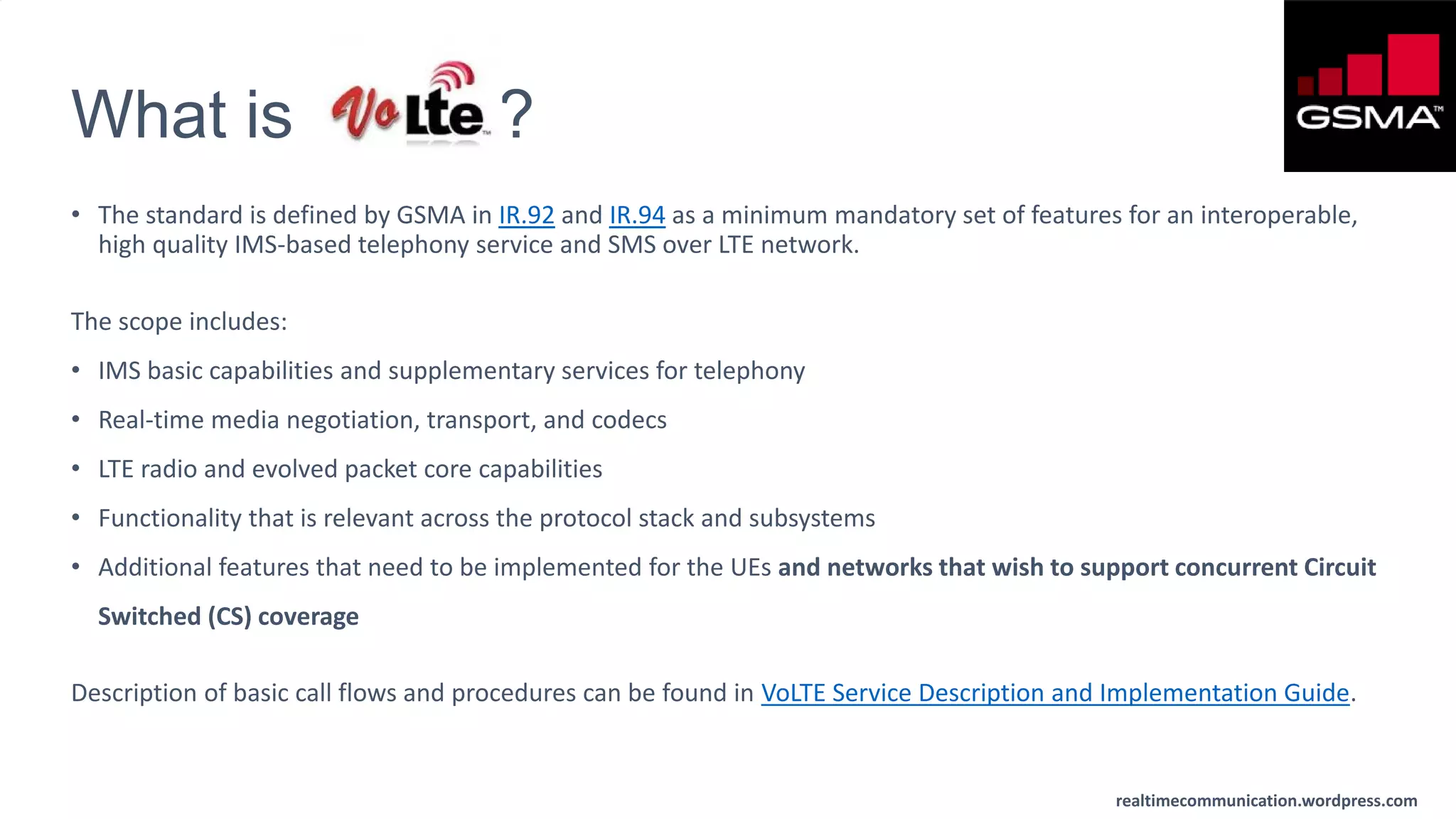
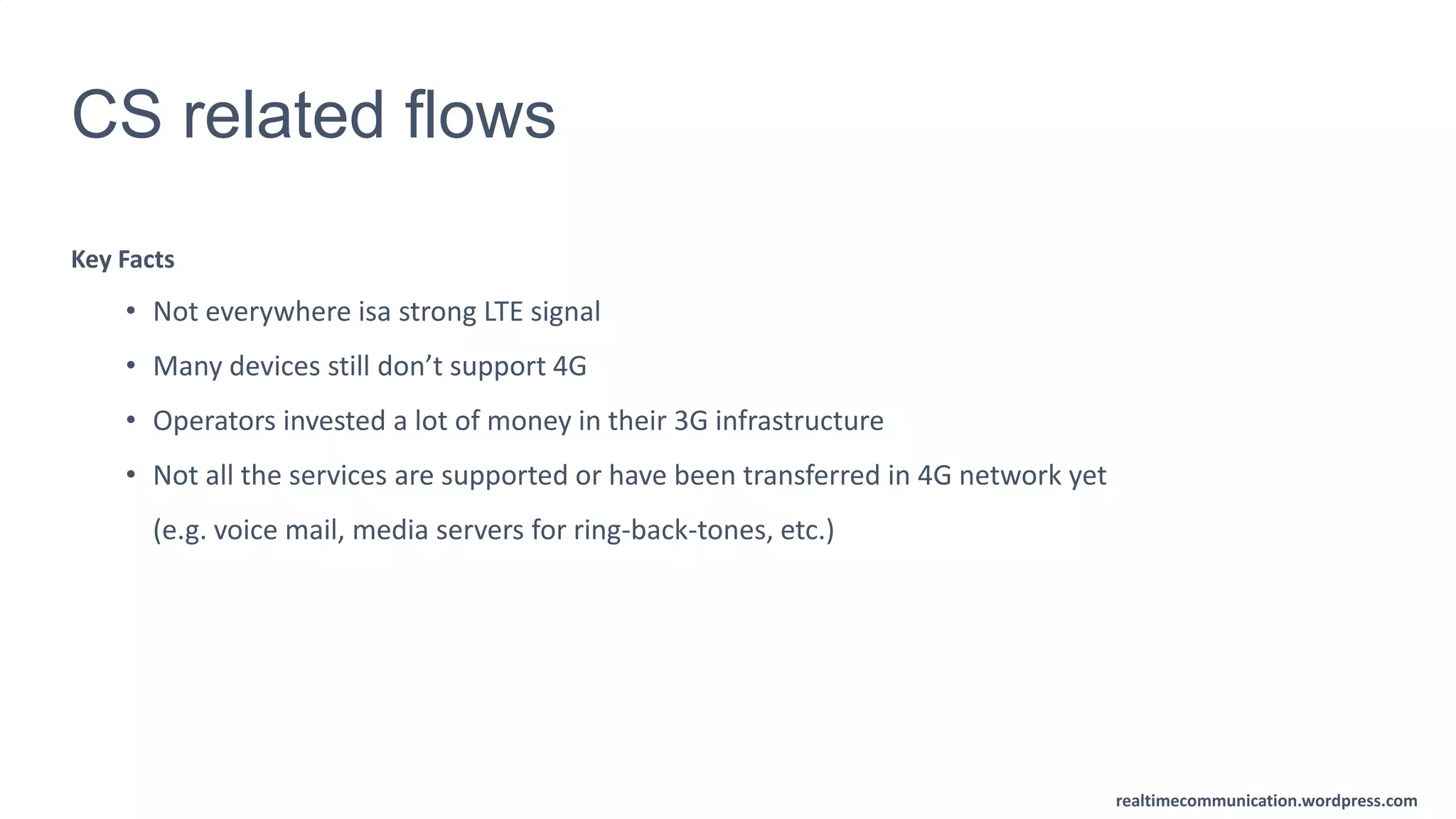
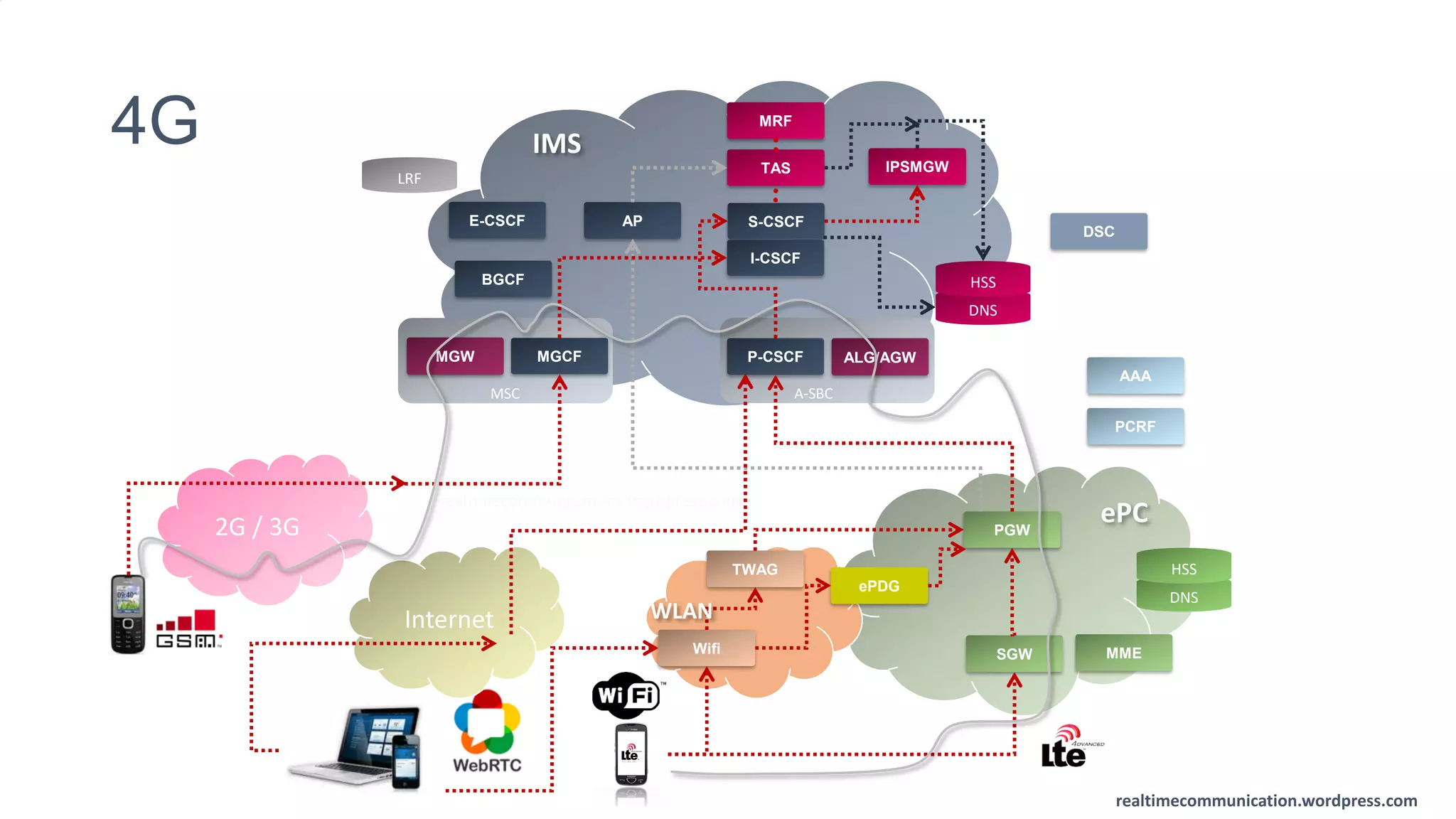
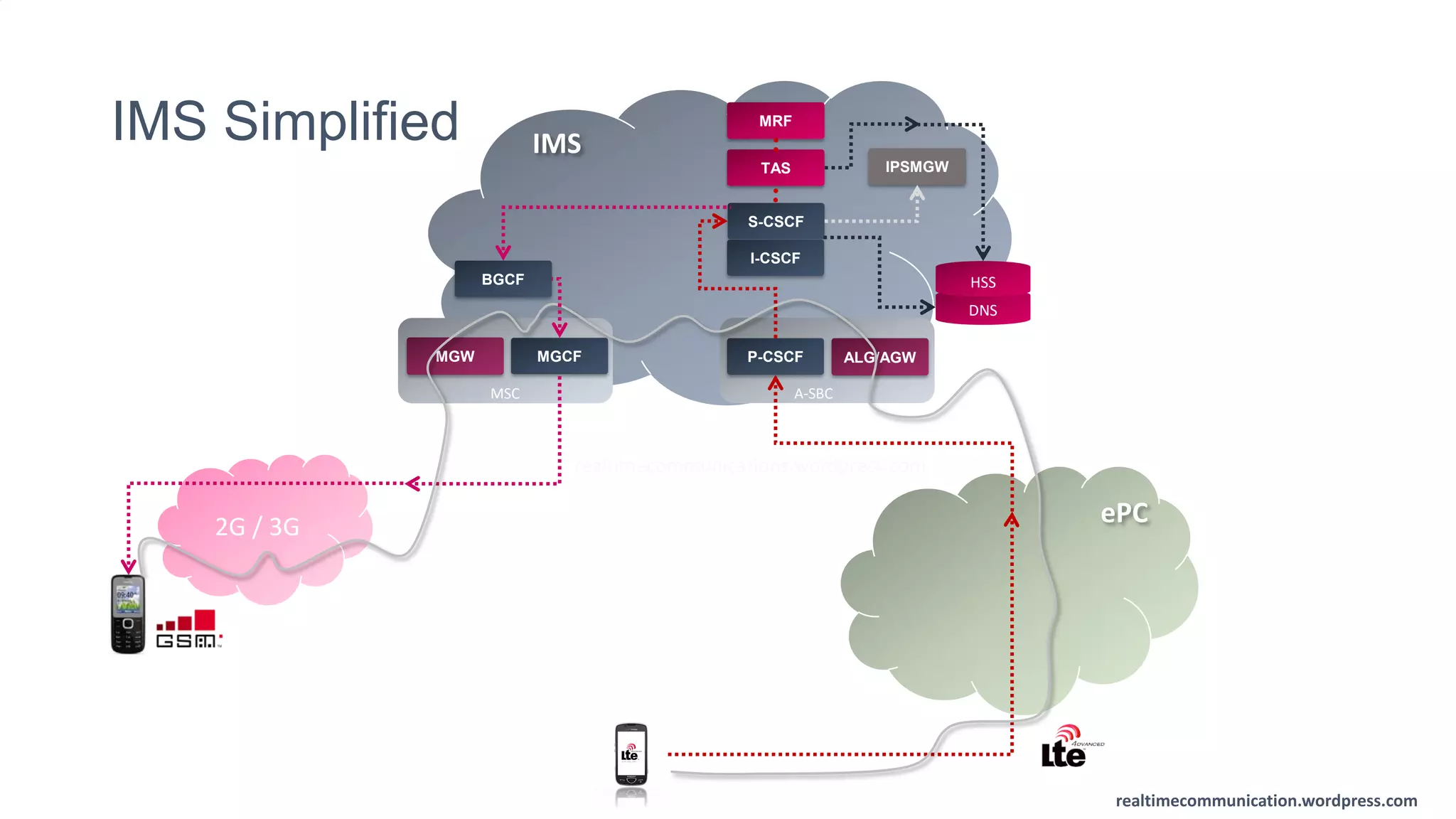
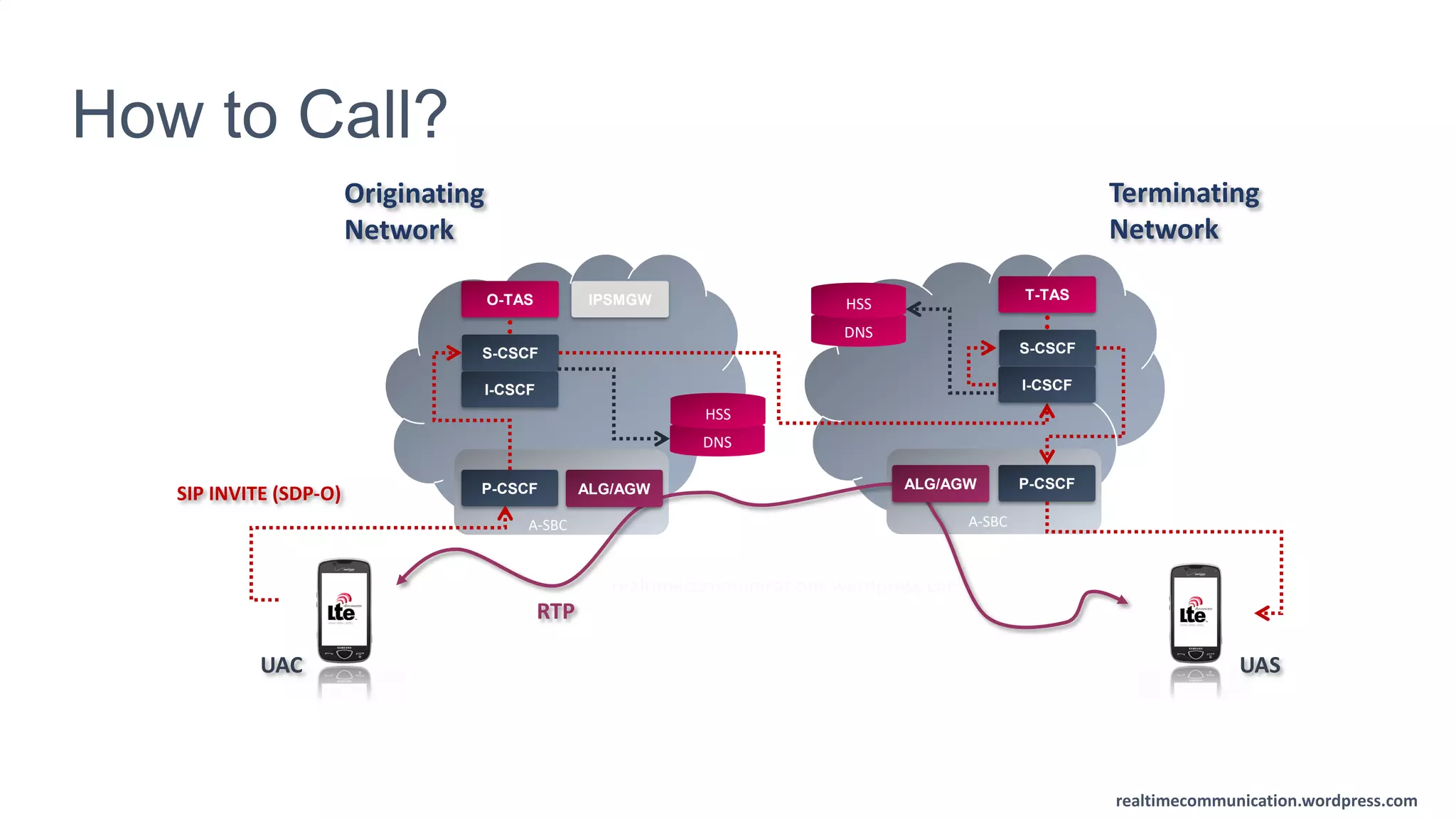
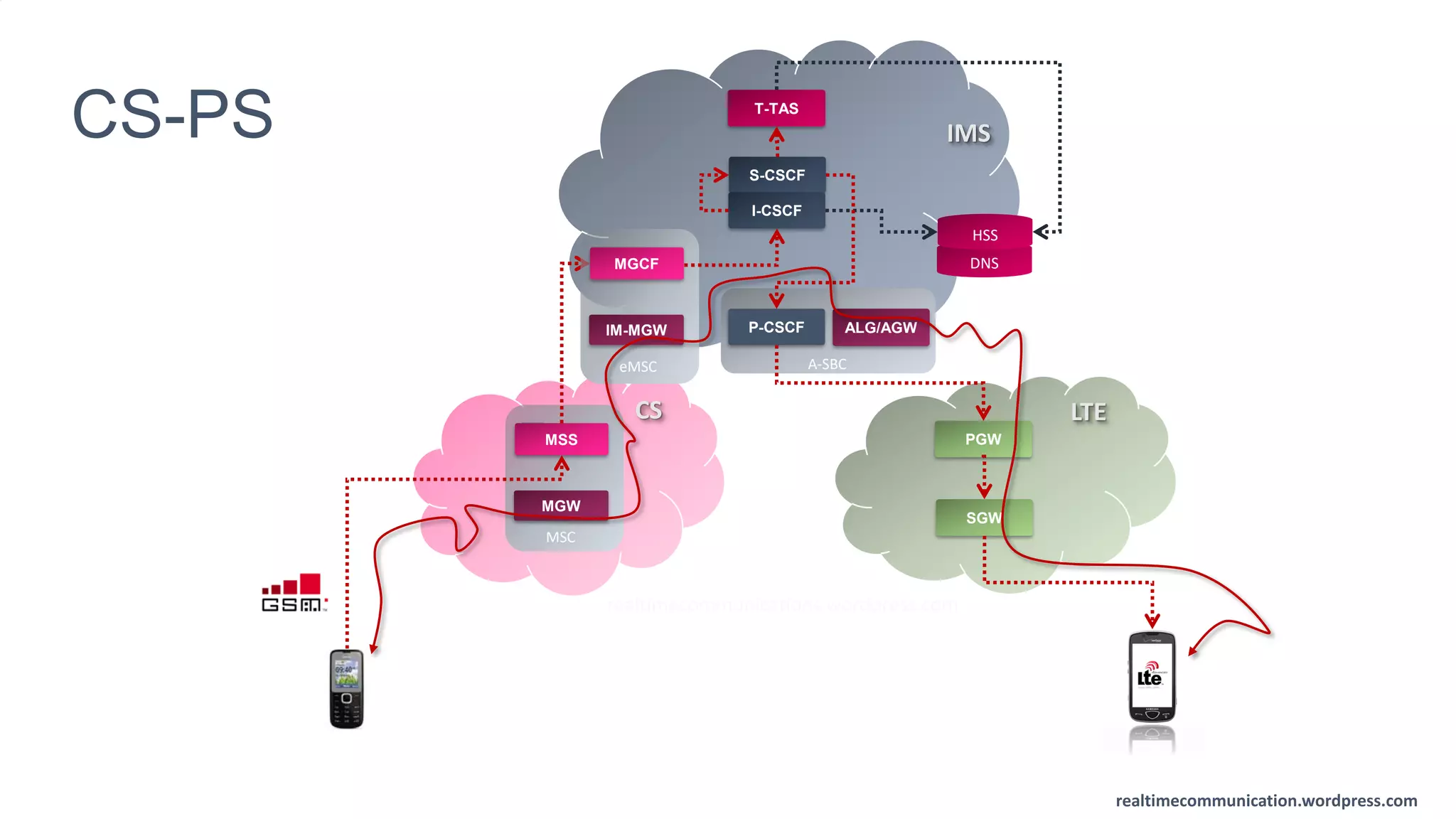
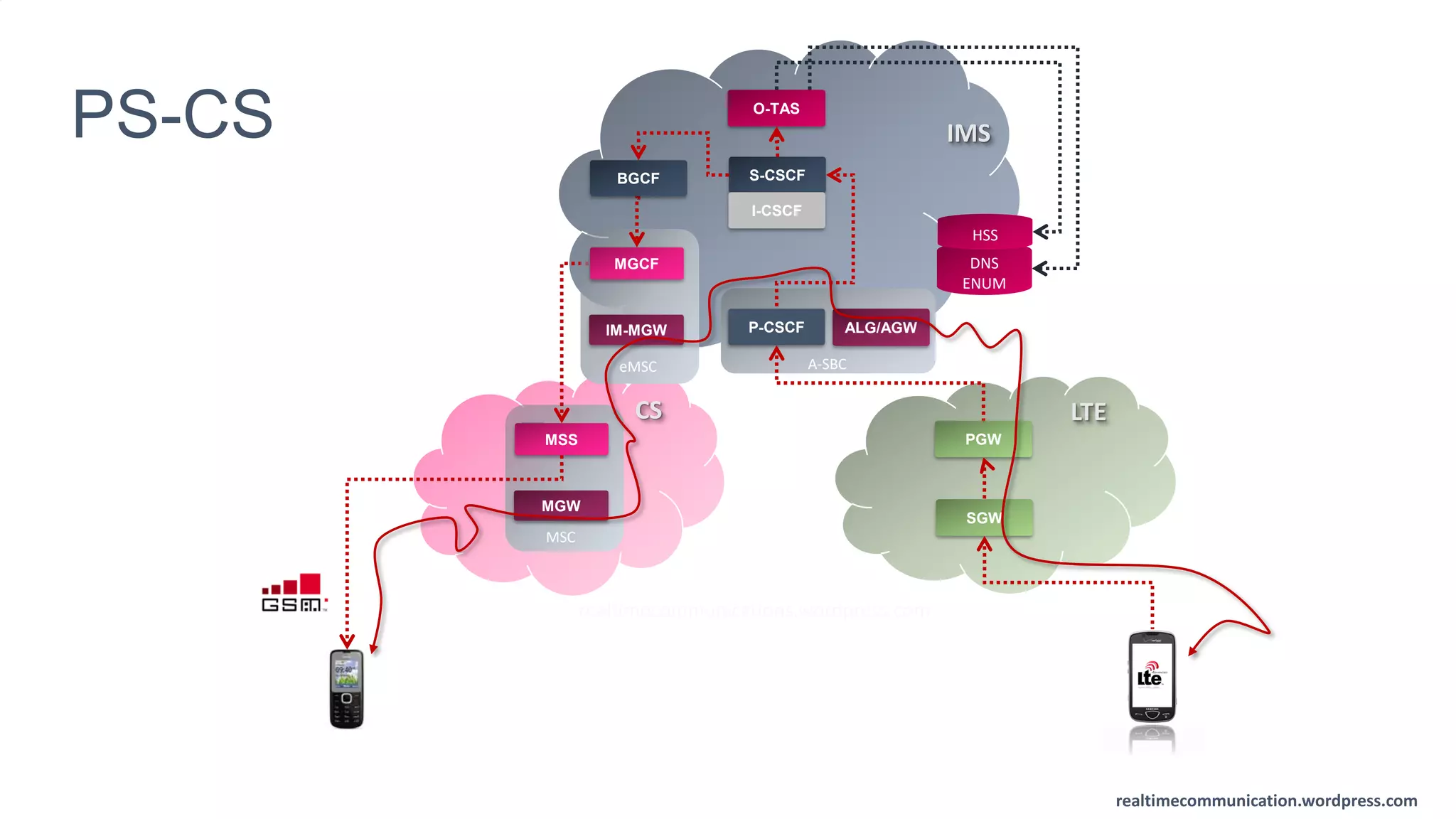
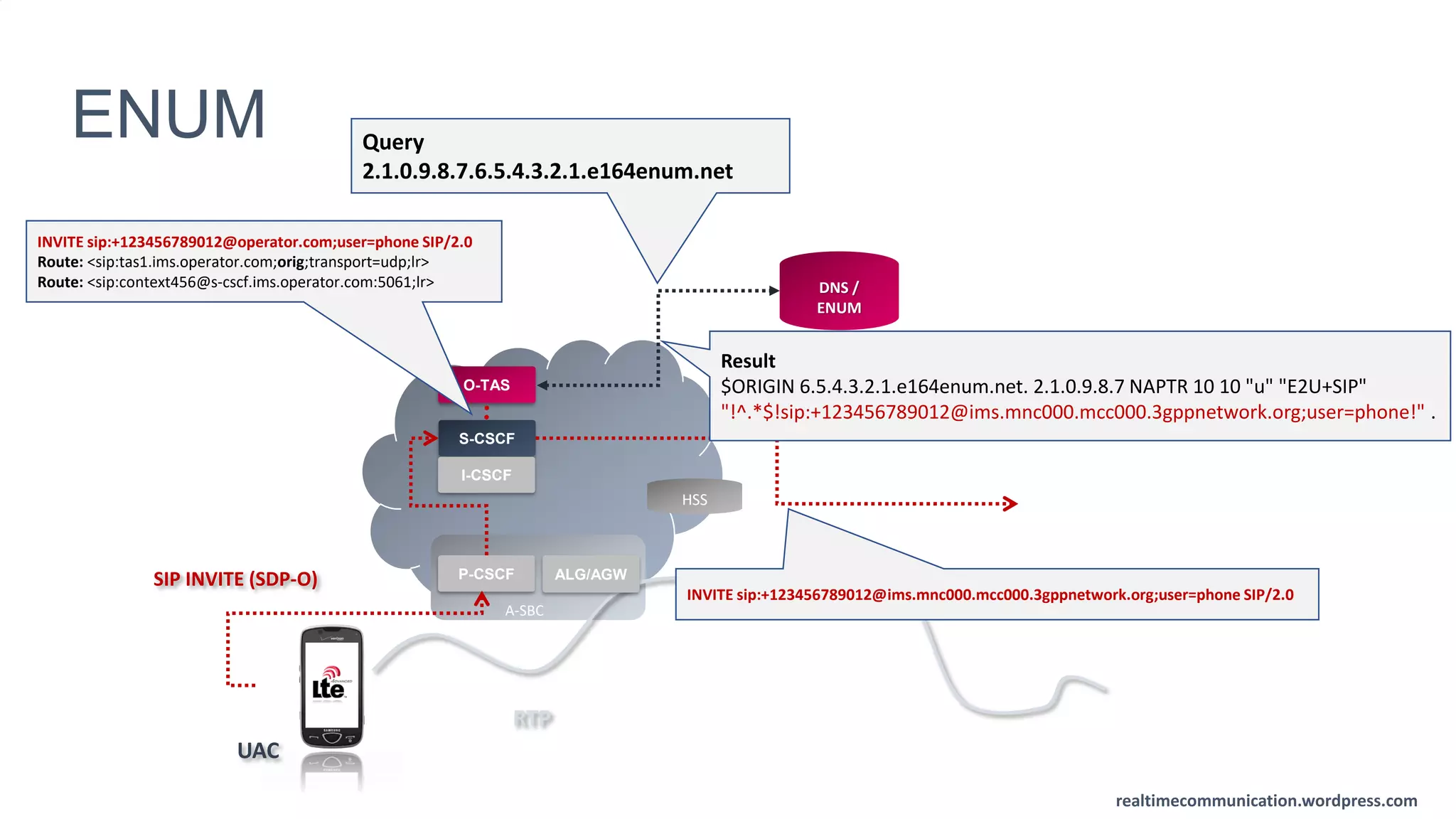
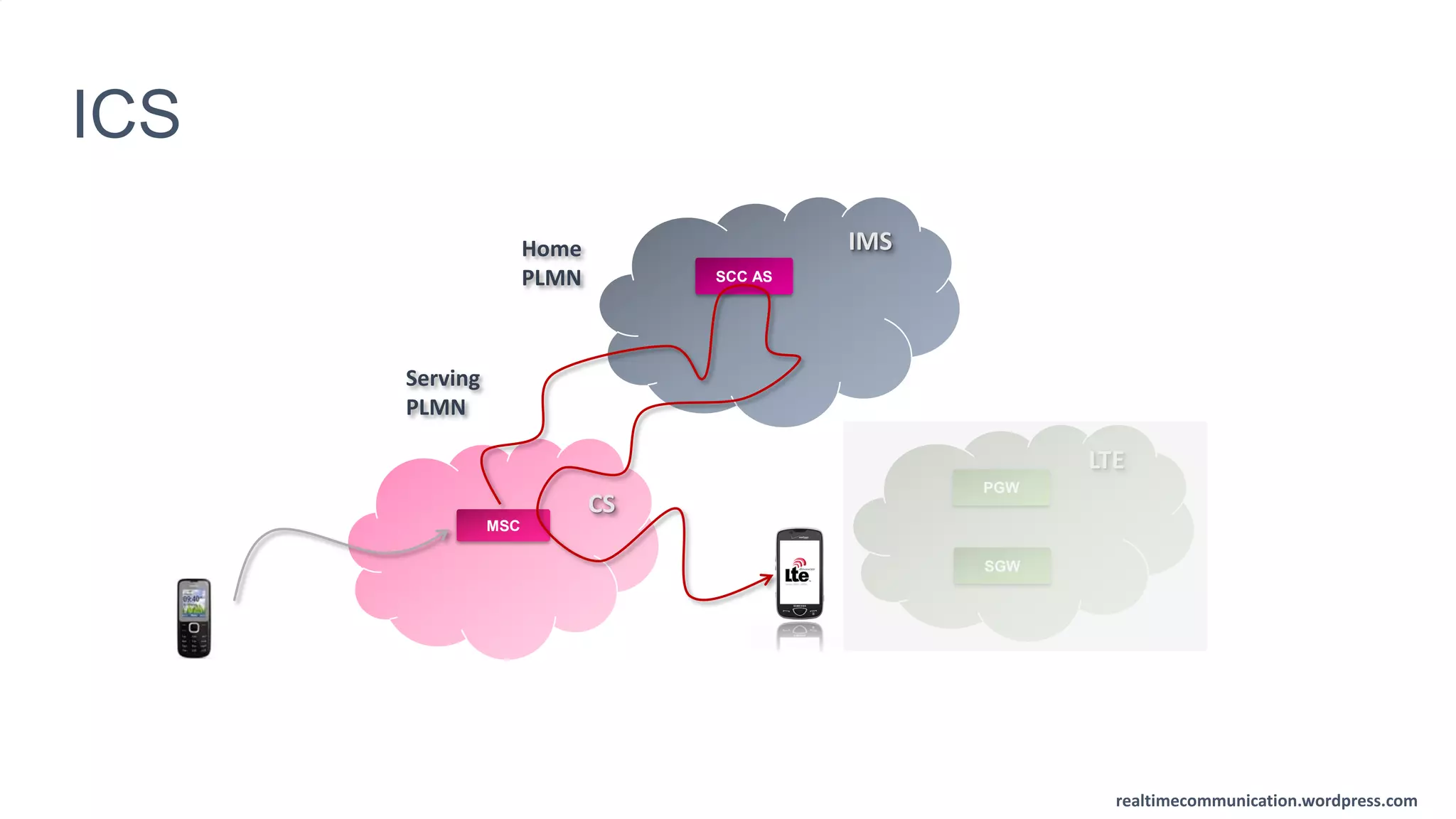
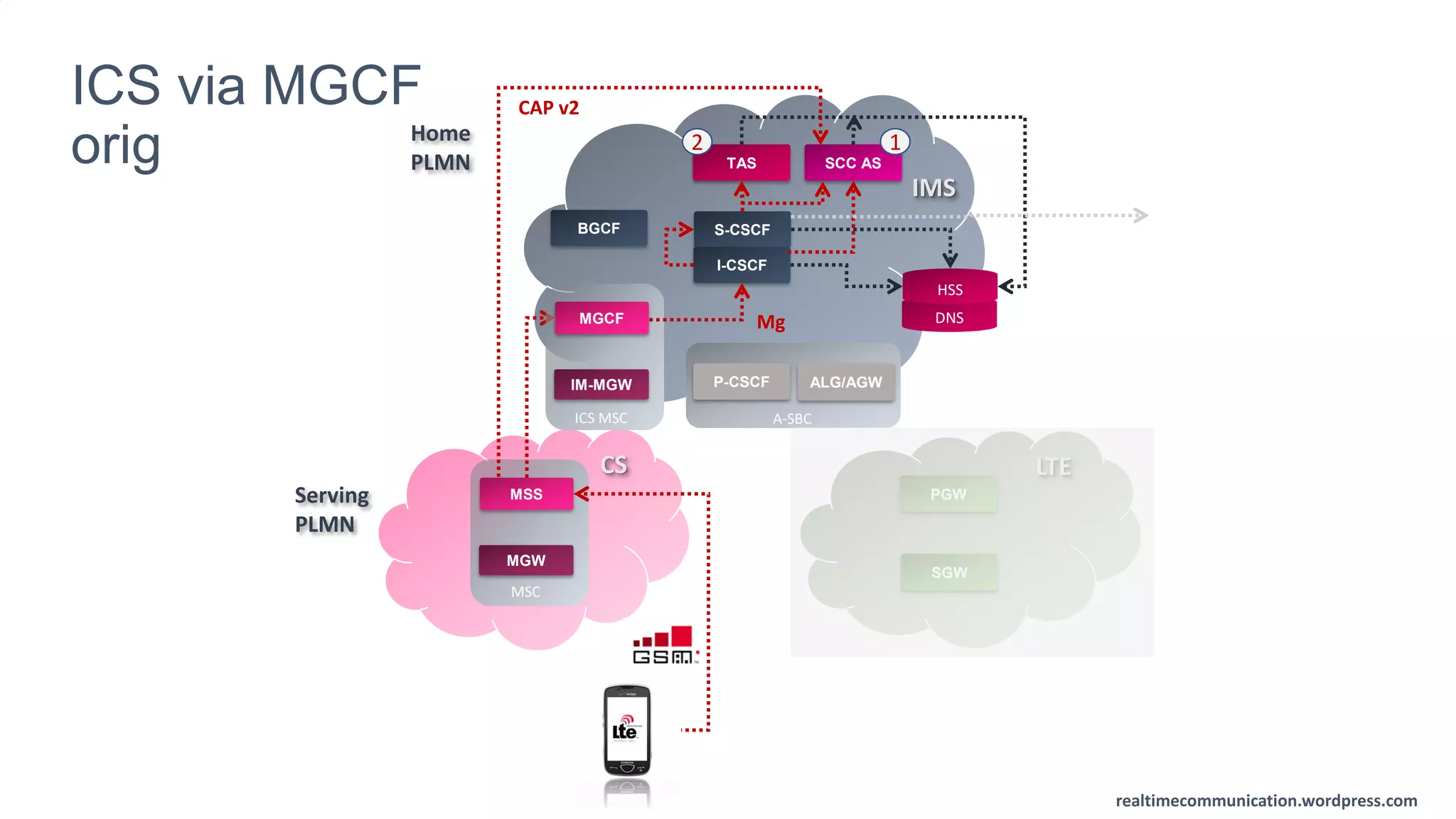
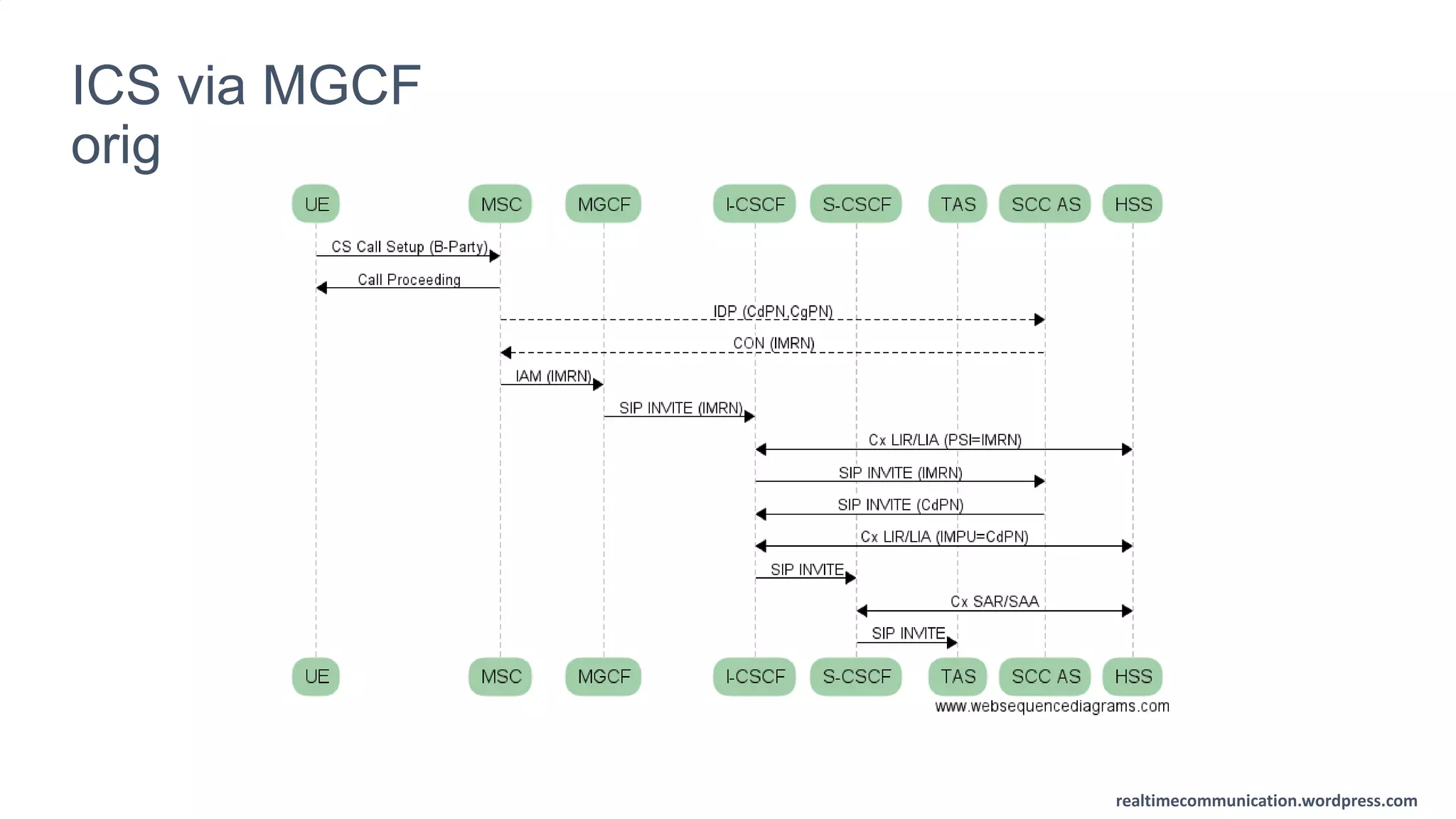
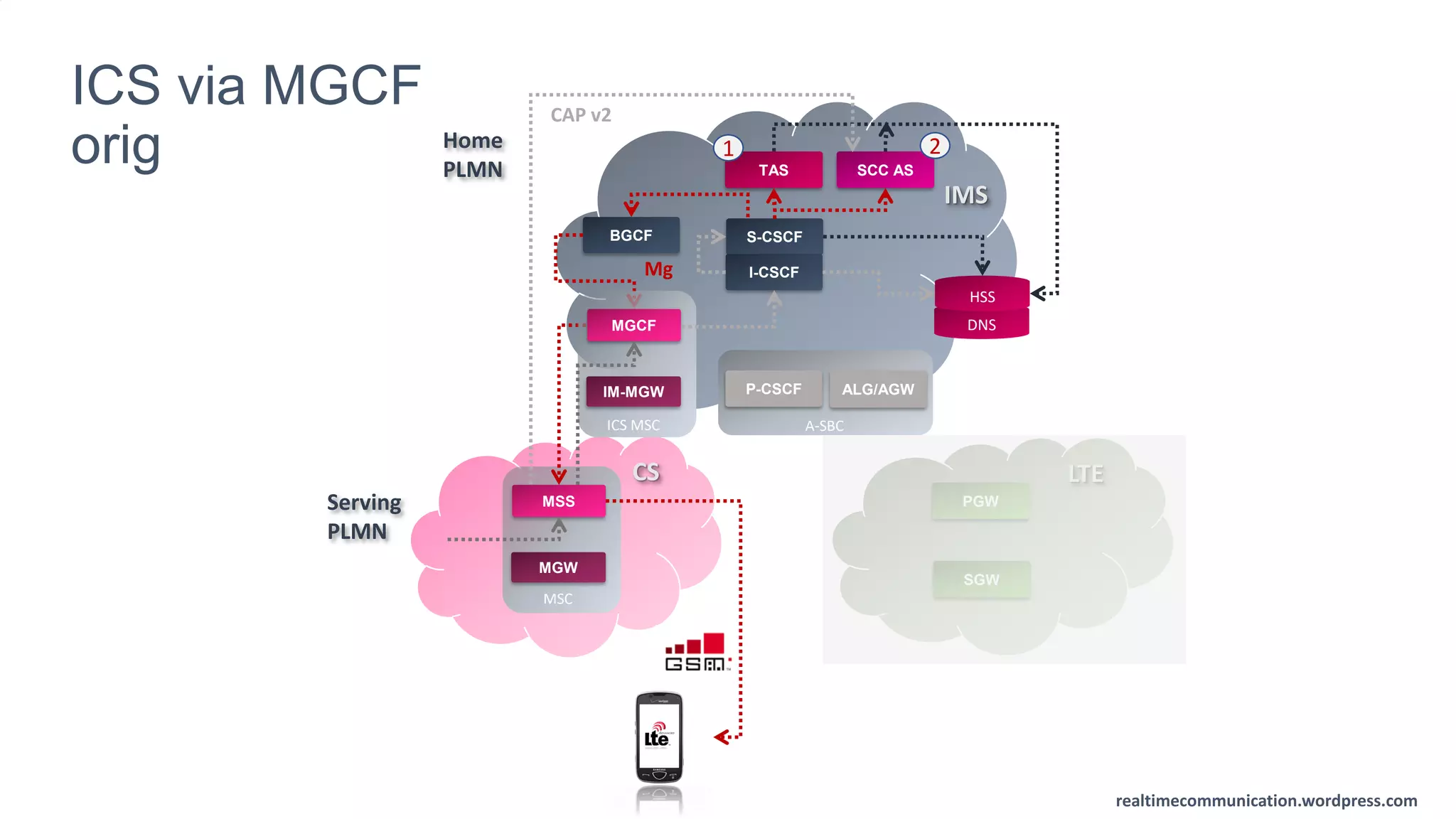
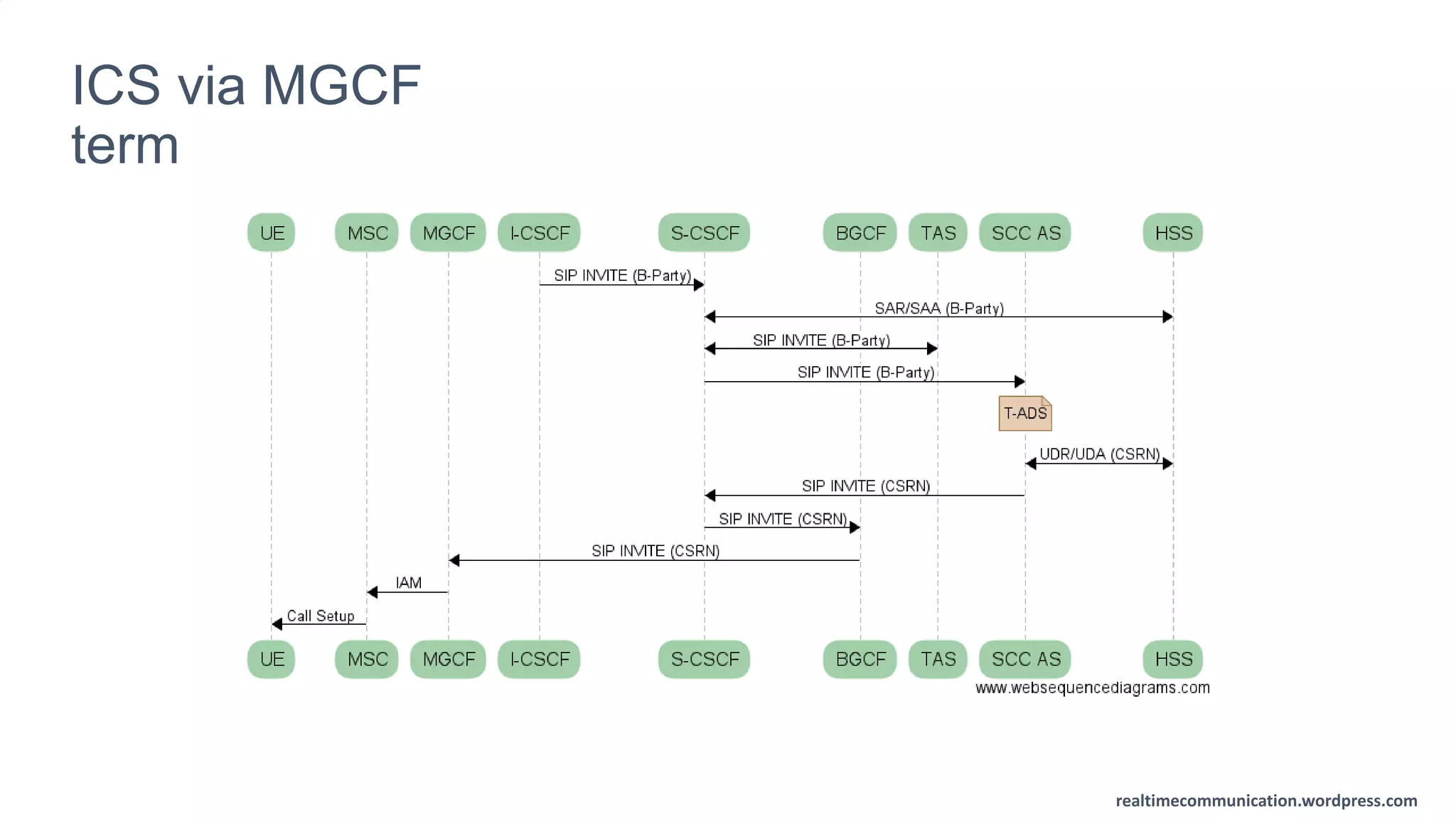
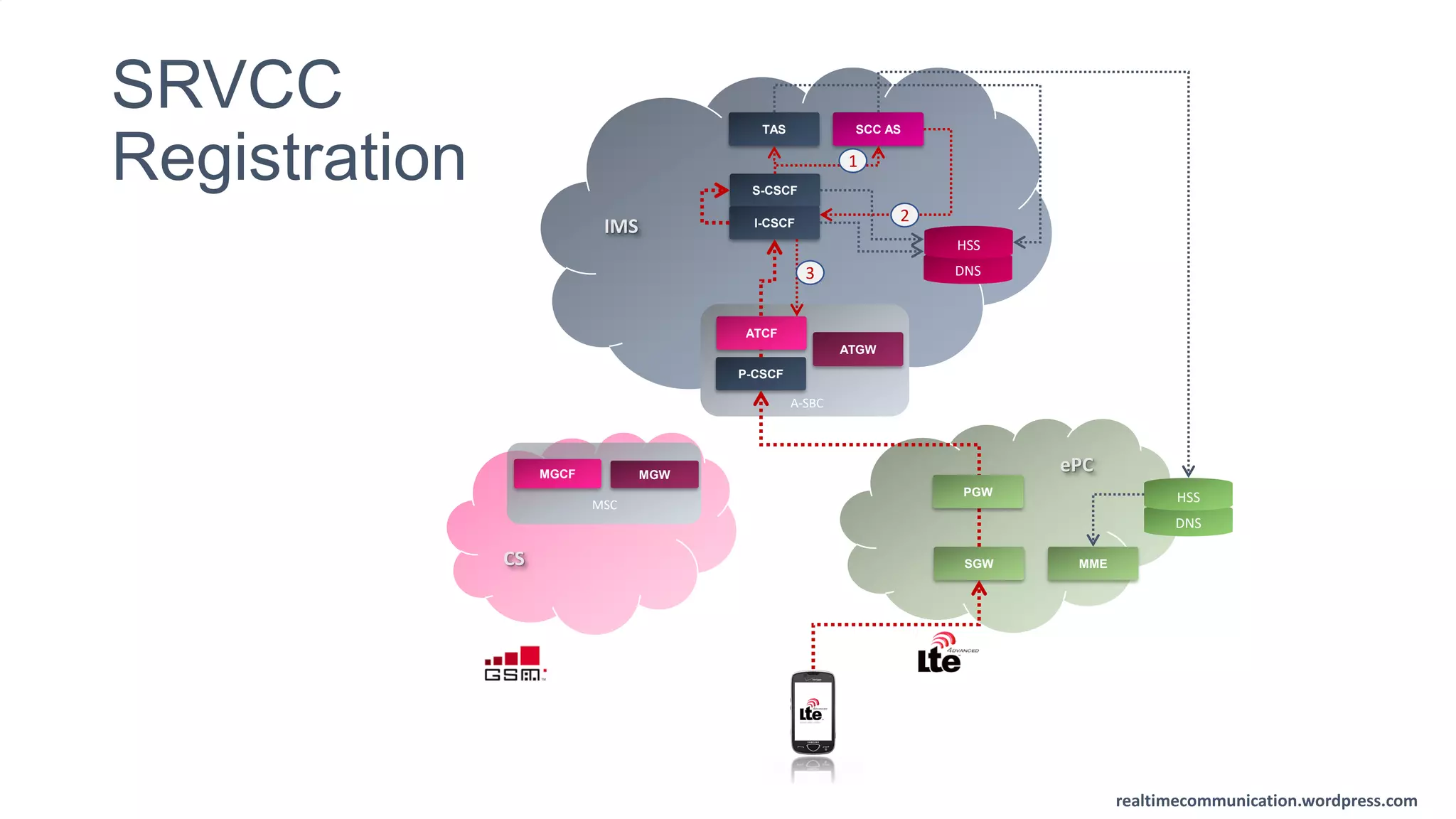
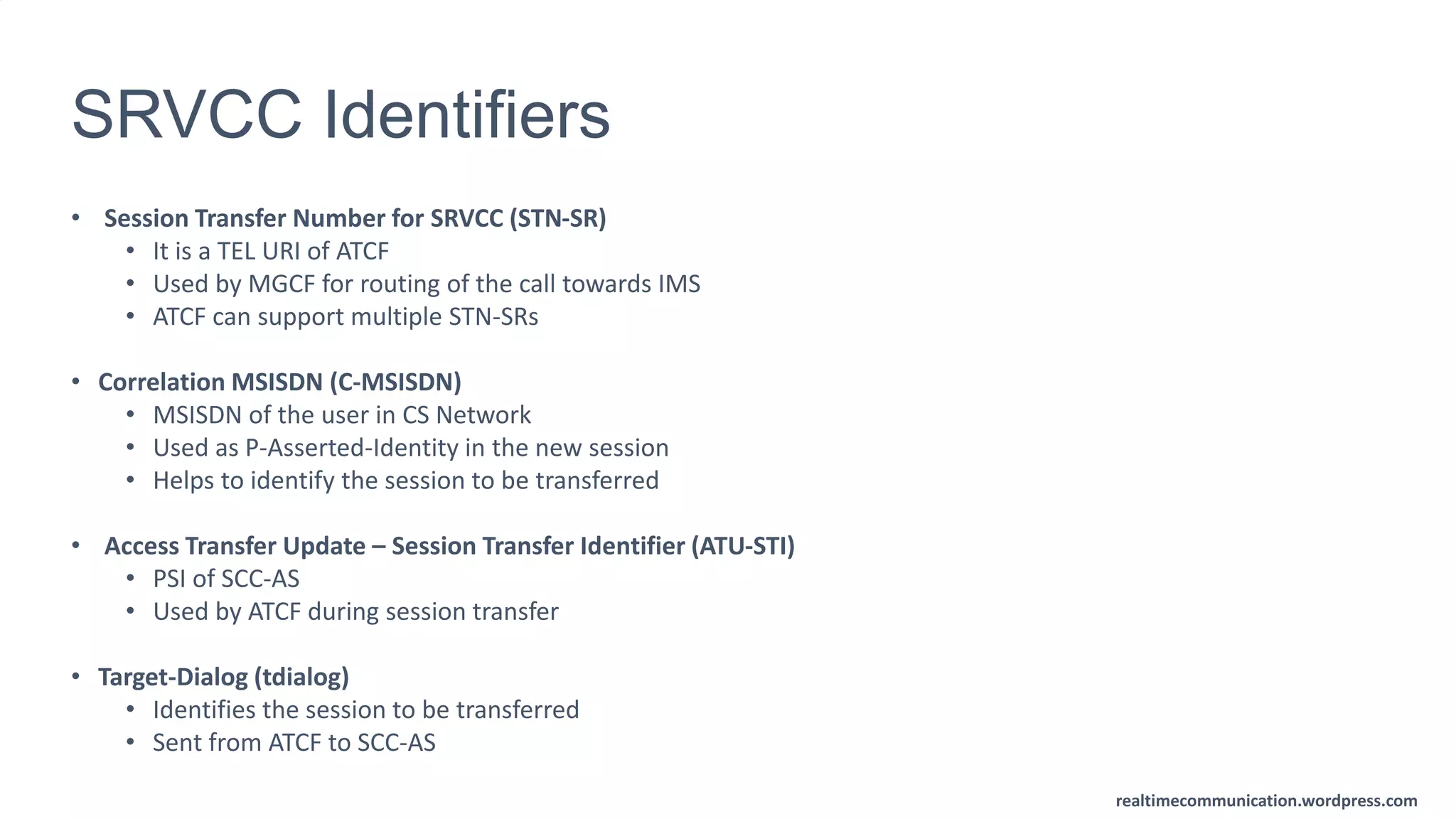
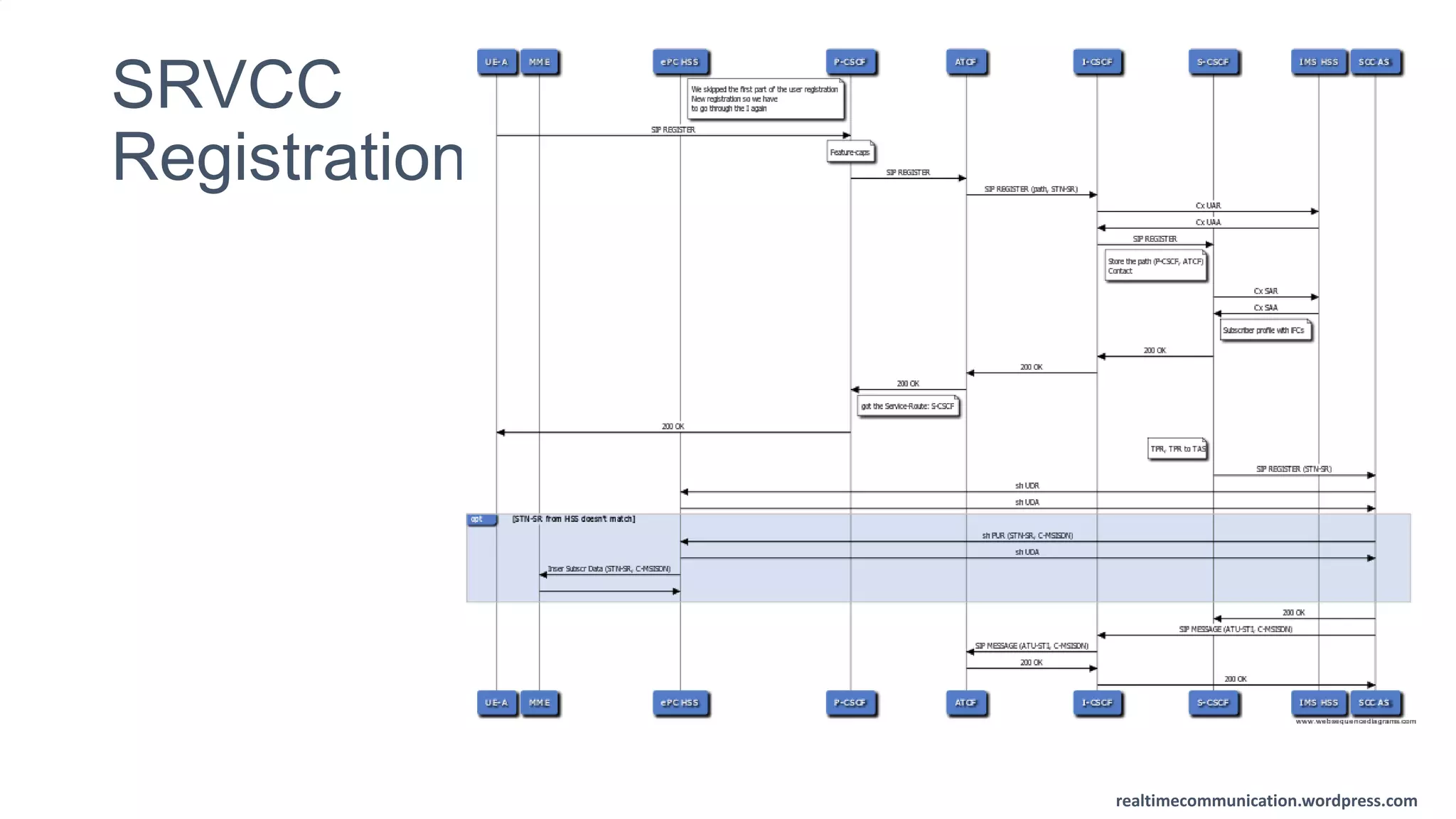
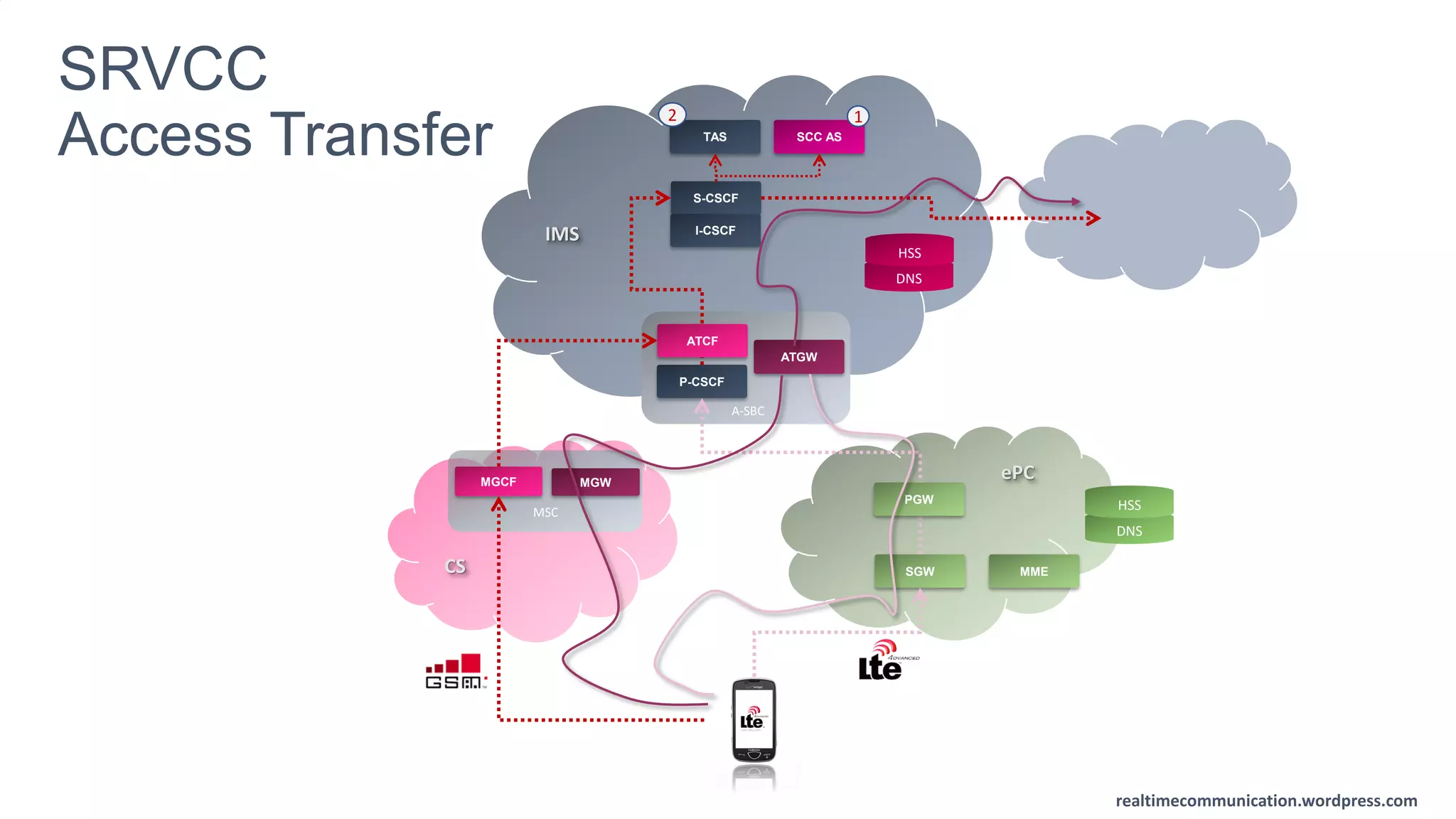
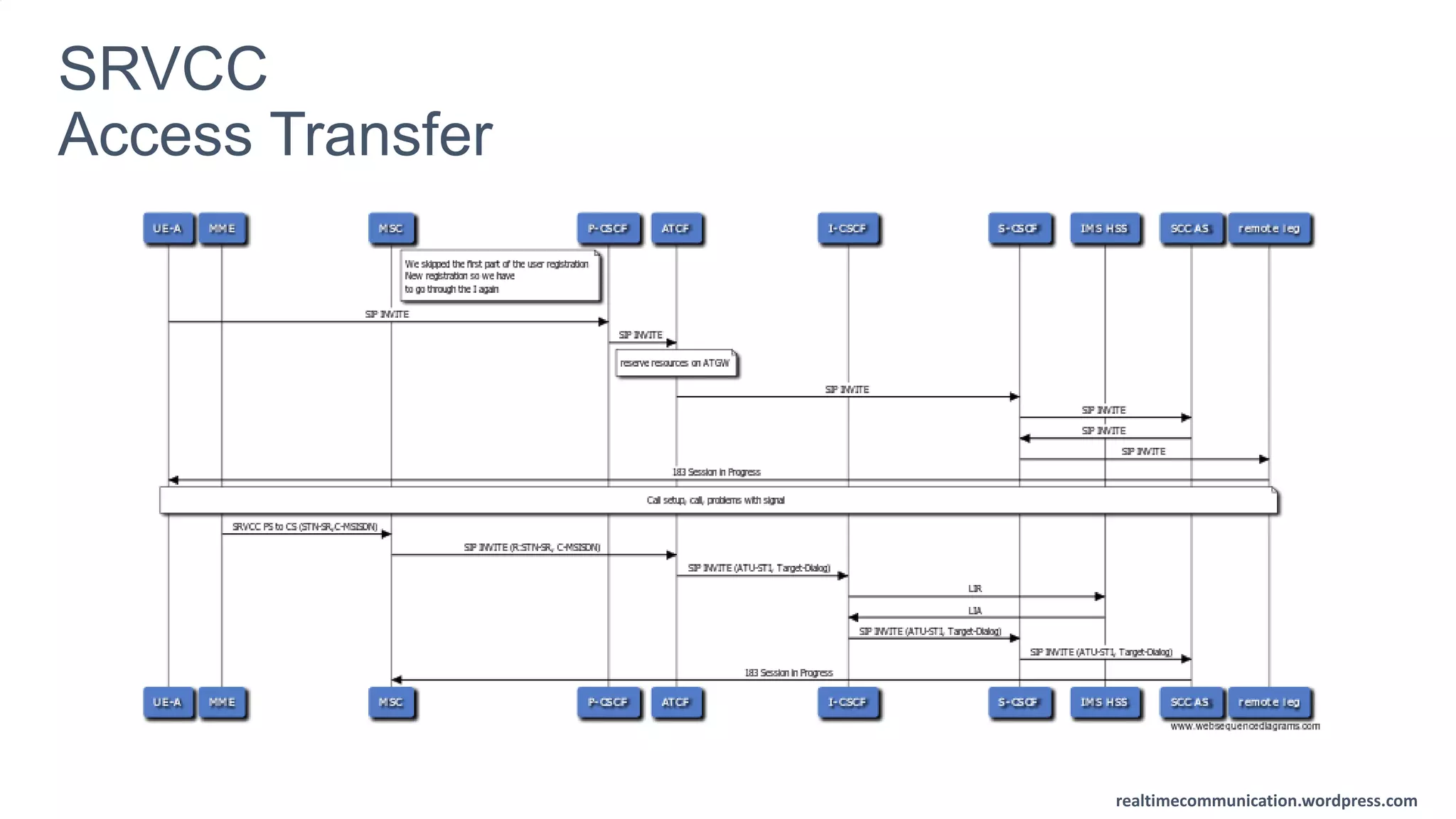
The document outlines the standards and frameworks for Voice over LTE (VoLTE) as defined by GSMA, detailing IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) features for high-quality telephony and SMS services over LTE networks. It discusses call flows, interworking between circuit-switched and IMS, and the role of various IMS components such as the BGCF, MGCF, and SCC AS in managing service continuity and session setup. Key takeaways include the importance of ENUM for routing and the push towards centralizing services within IMS for better integration across networks.