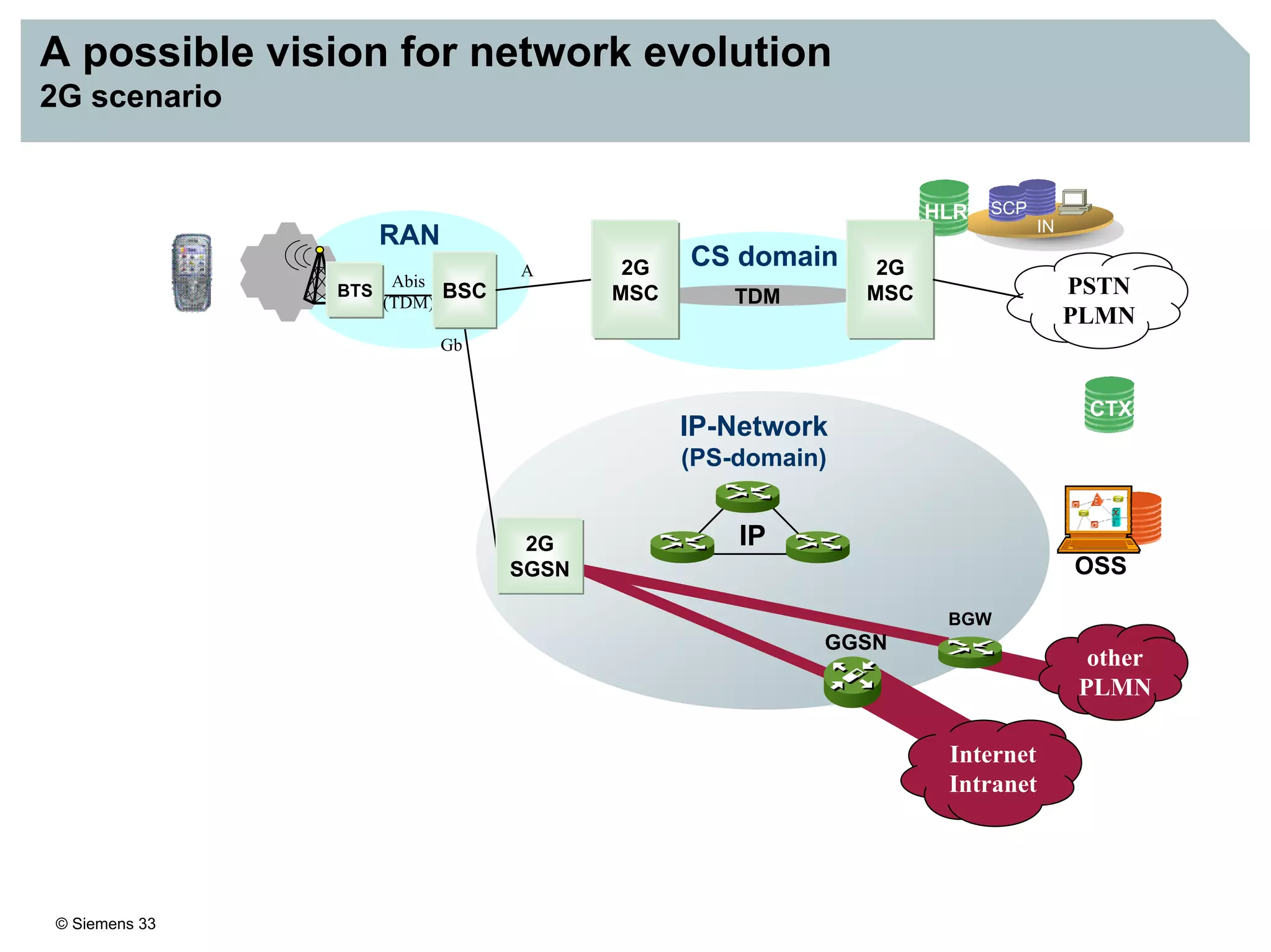
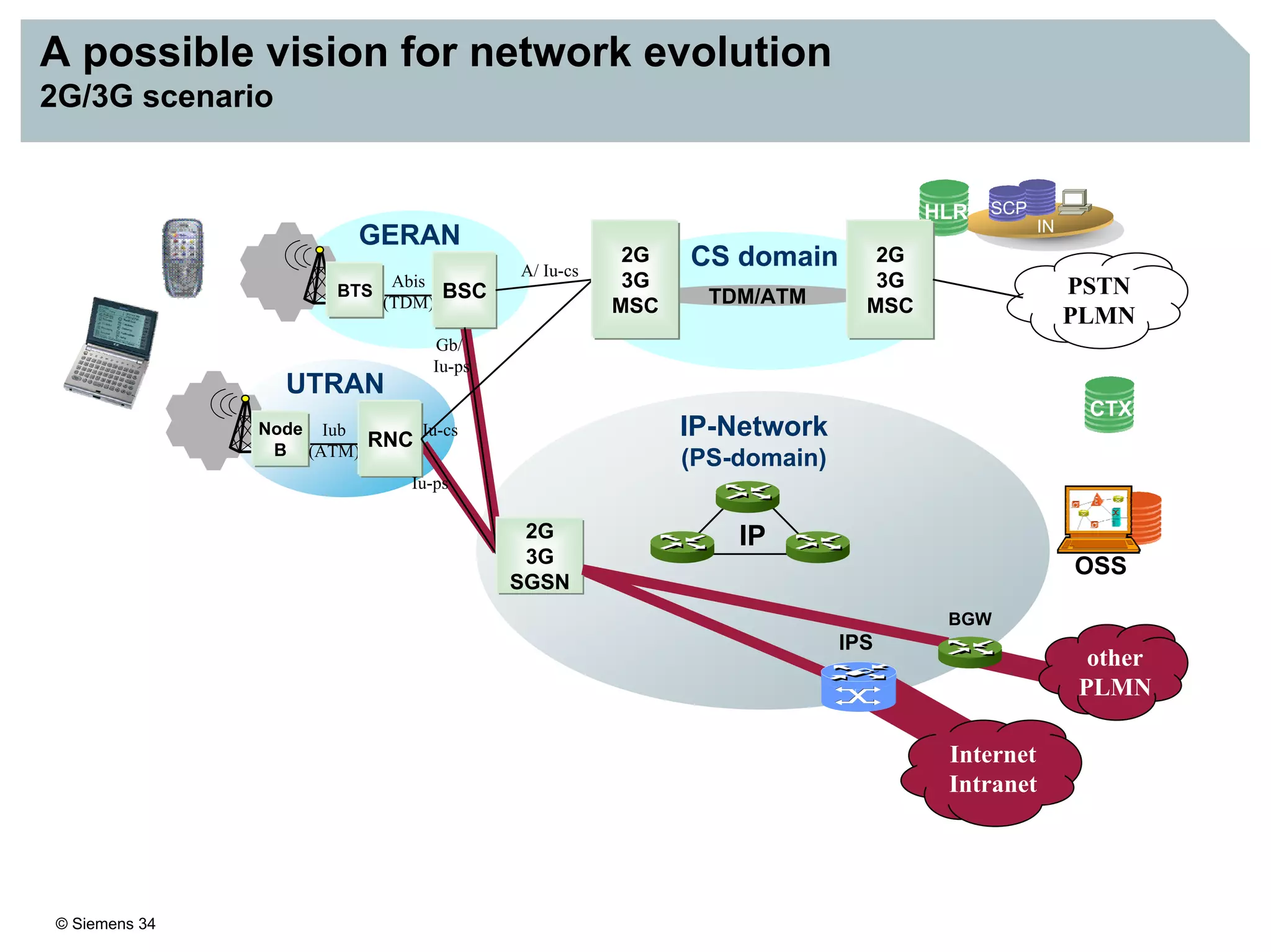
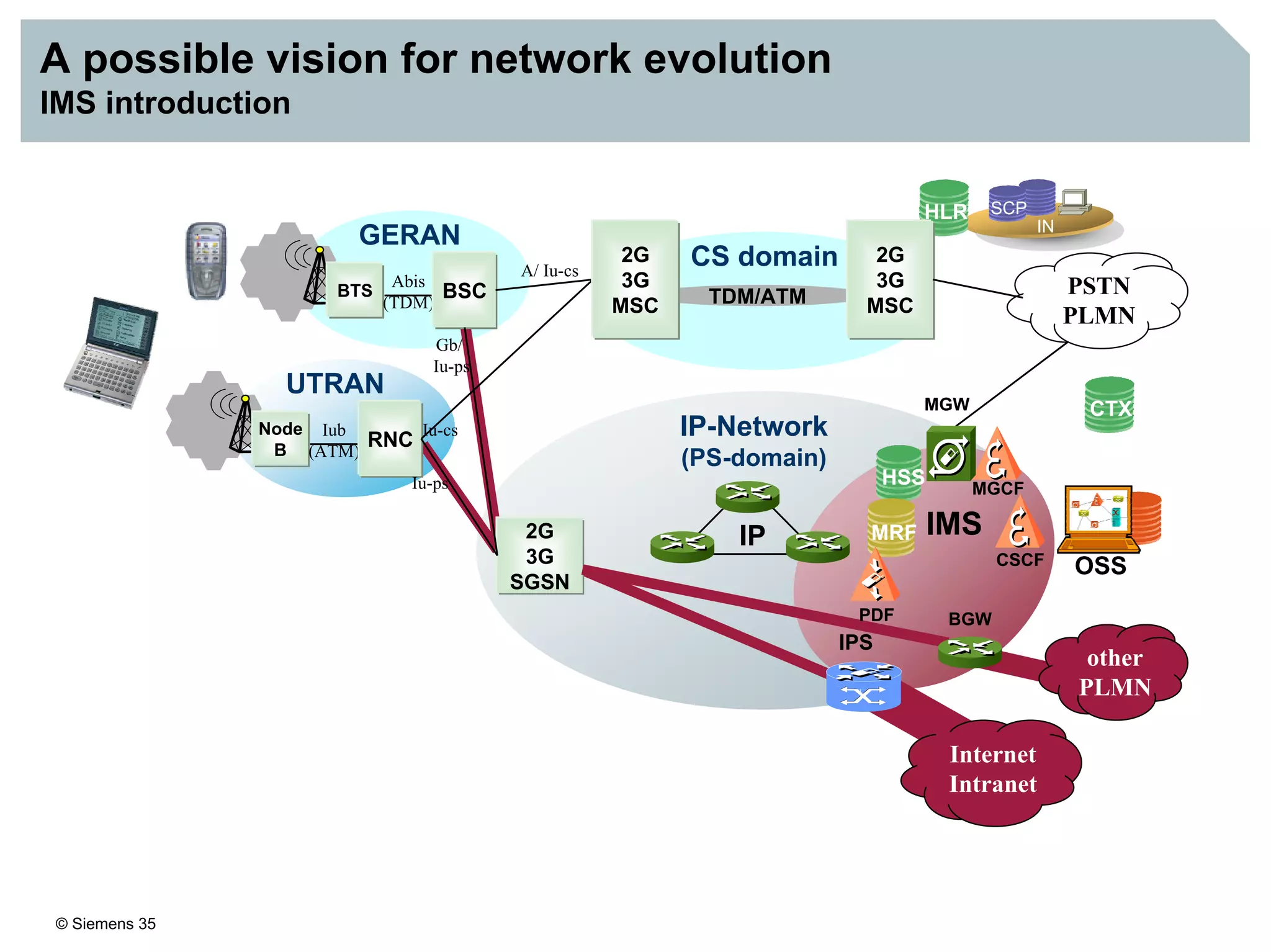
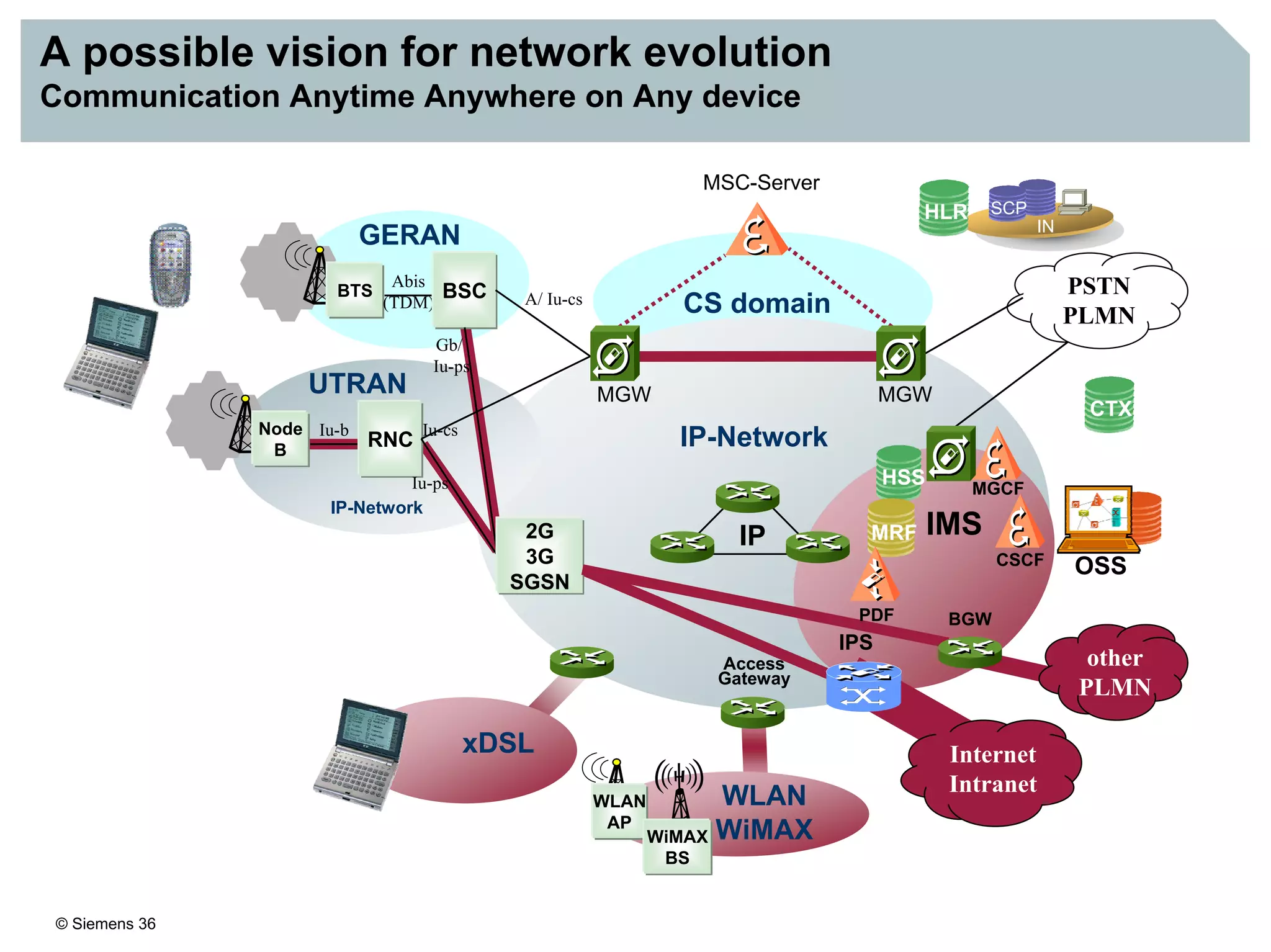
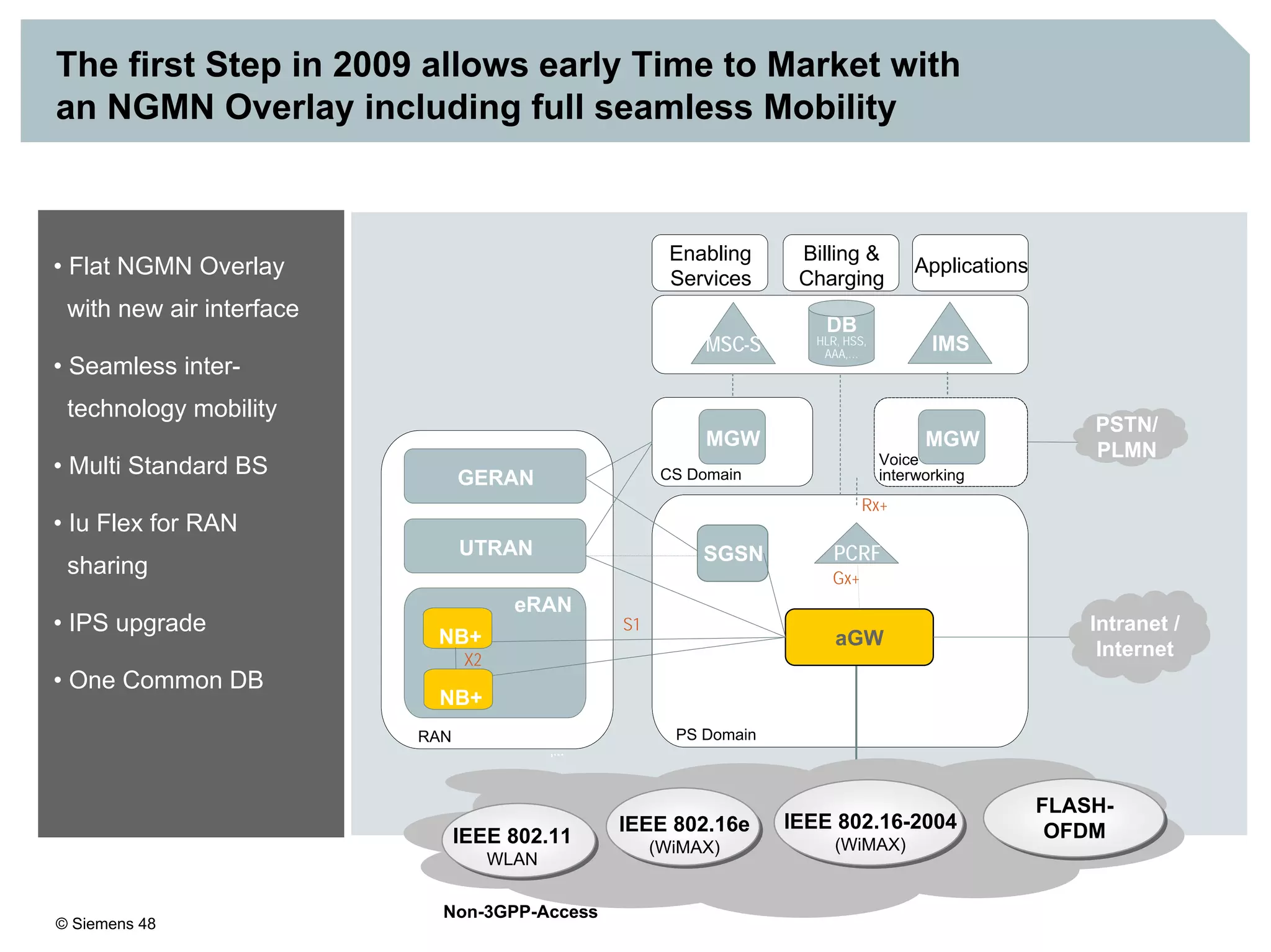
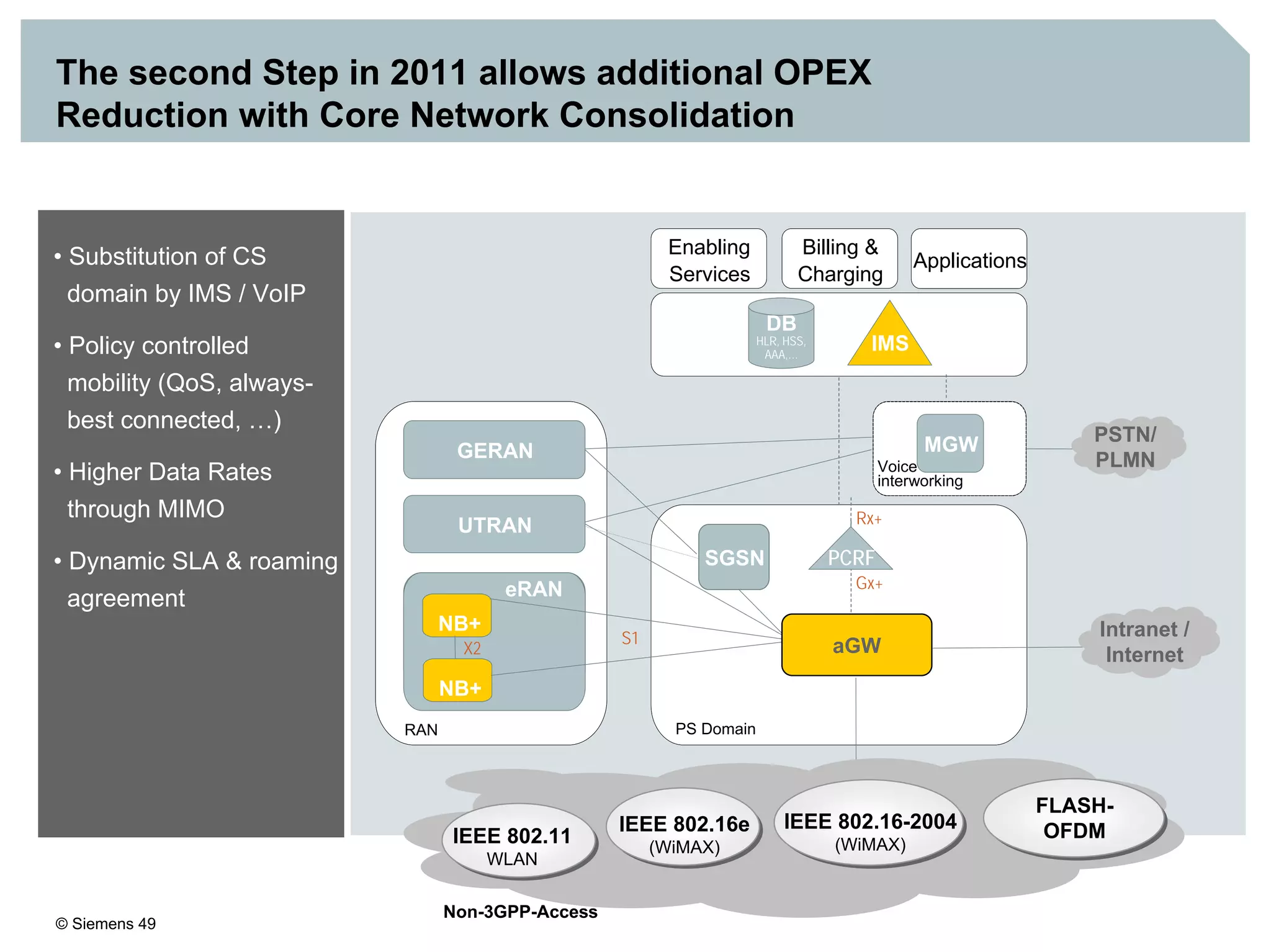
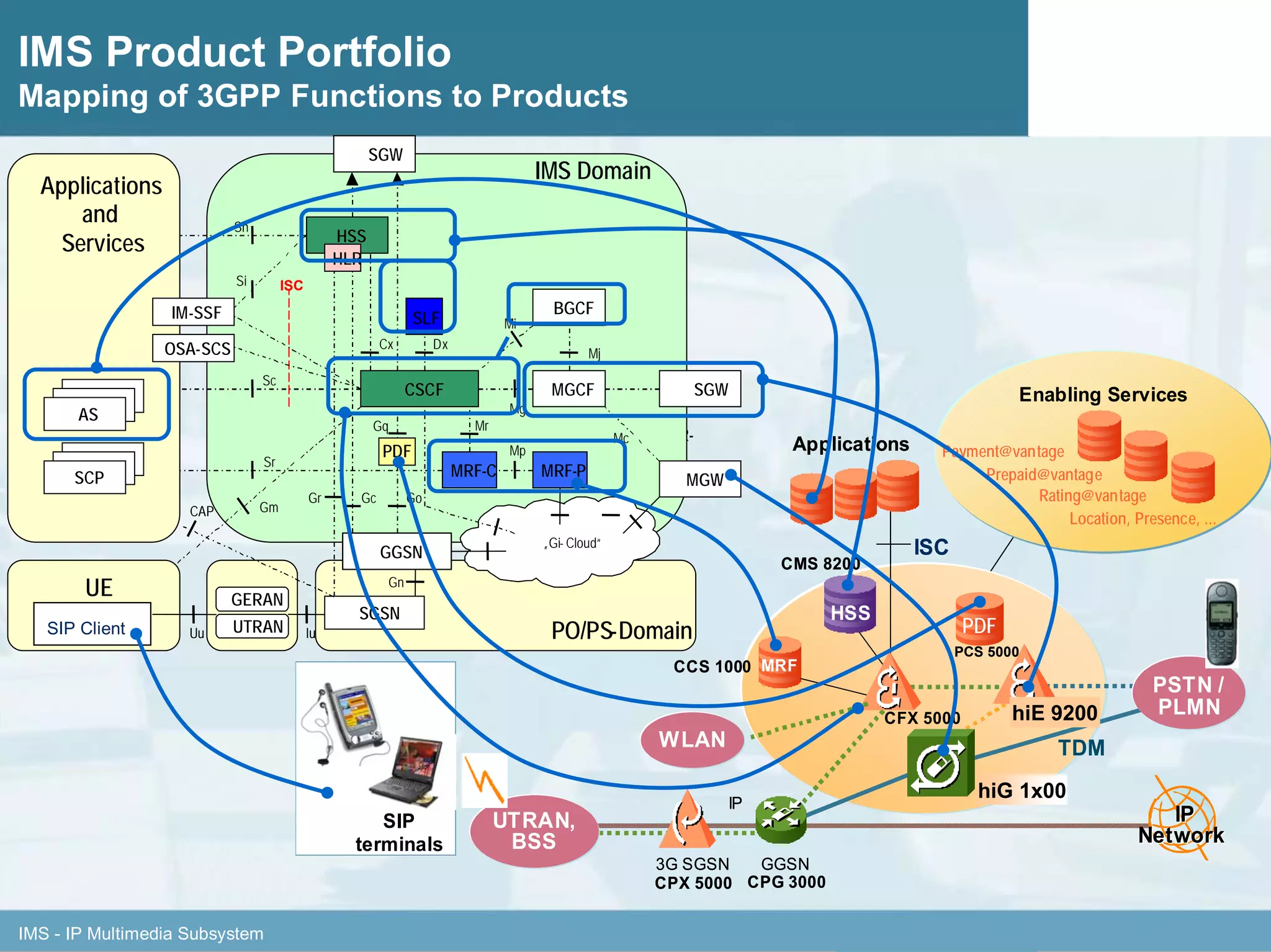
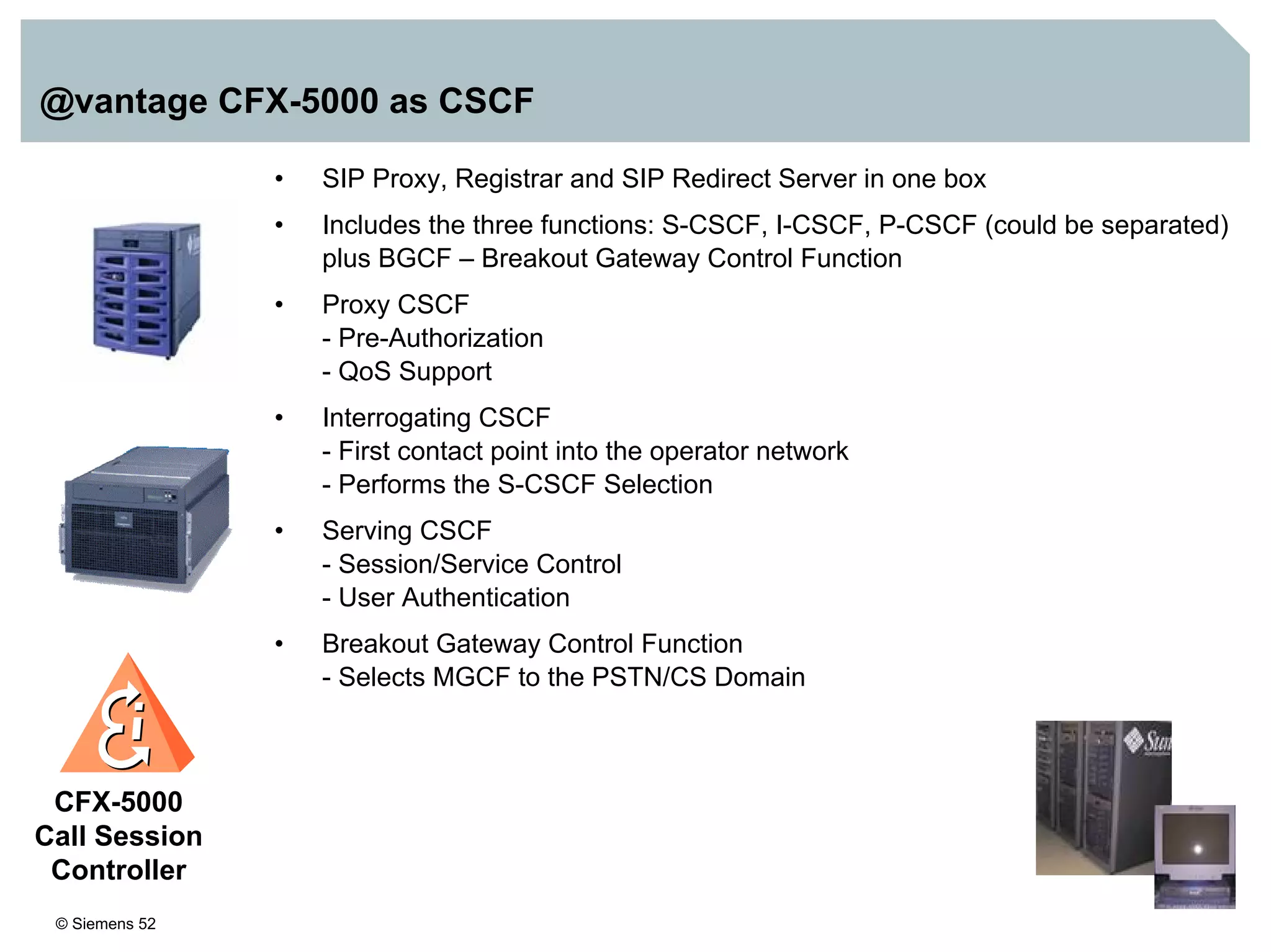
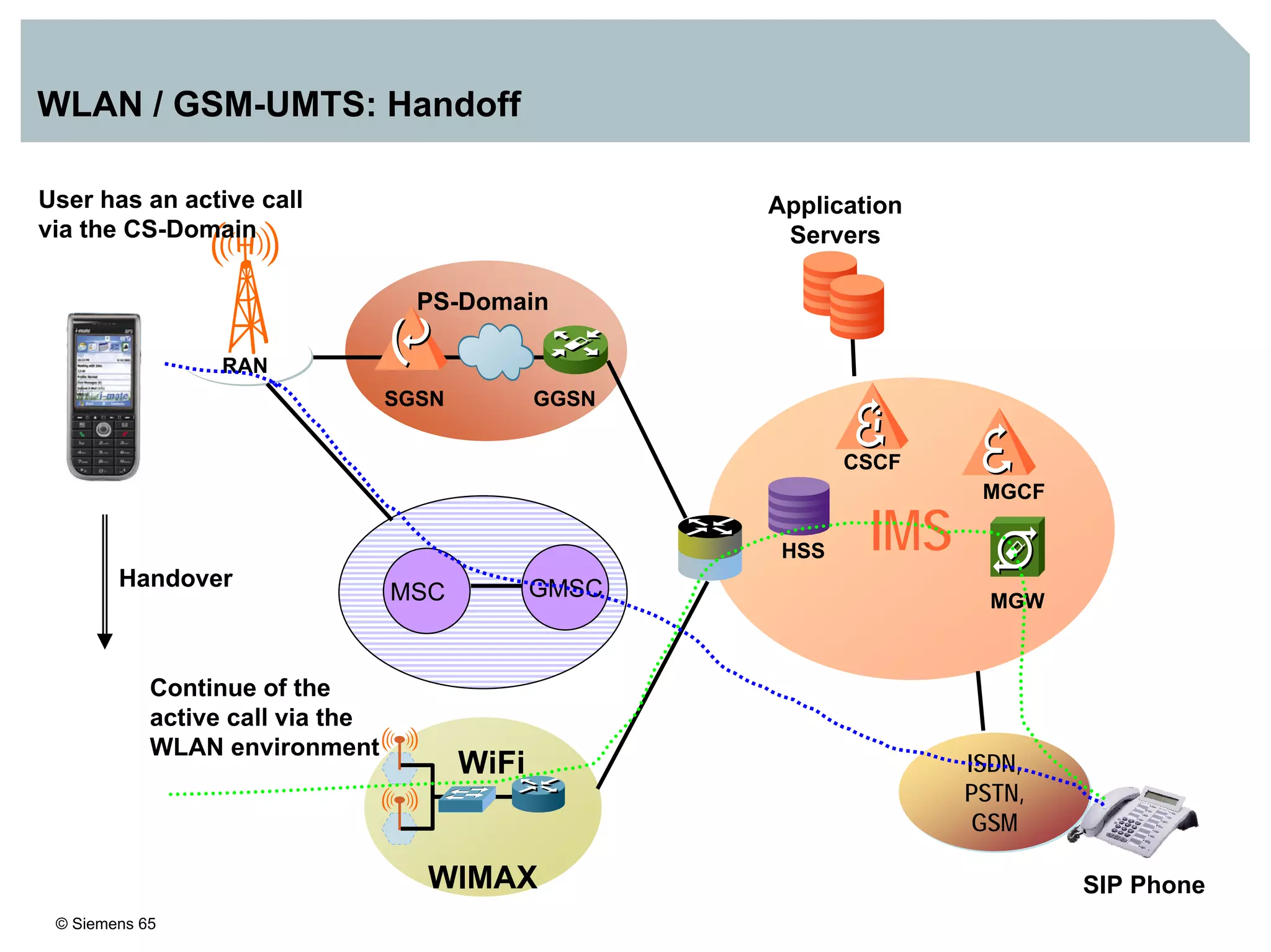
This document discusses IMS architecture and future developments:
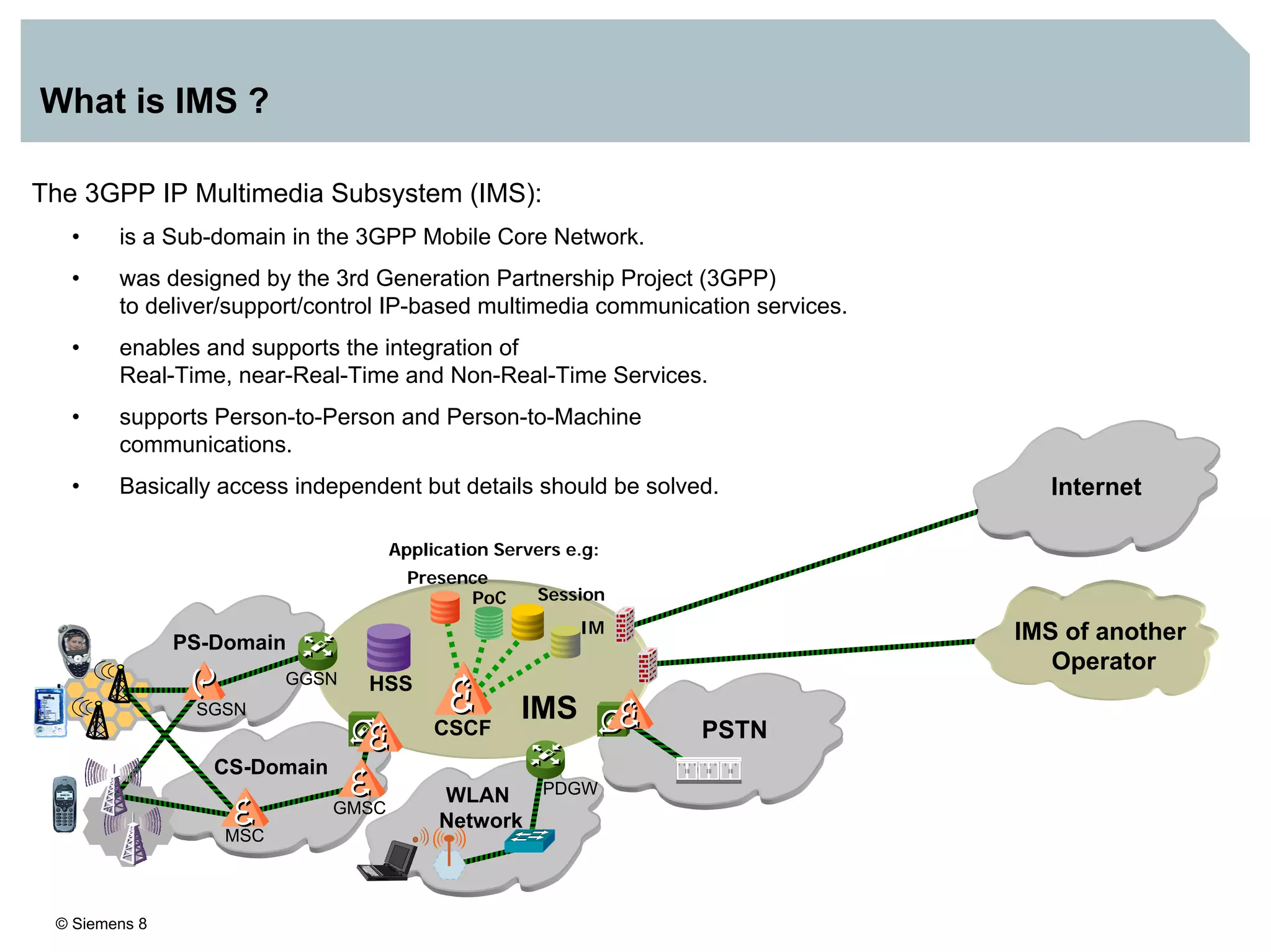
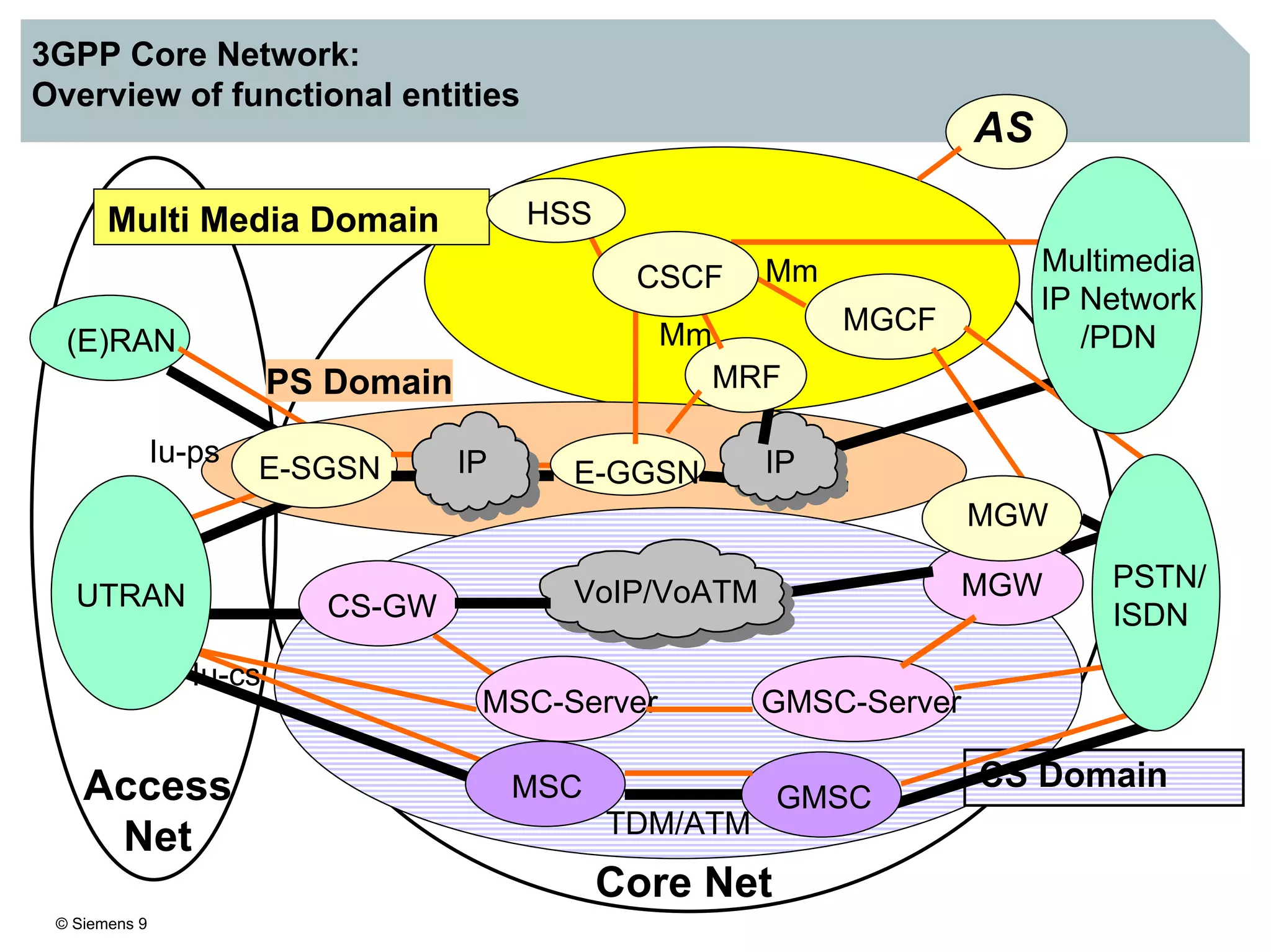
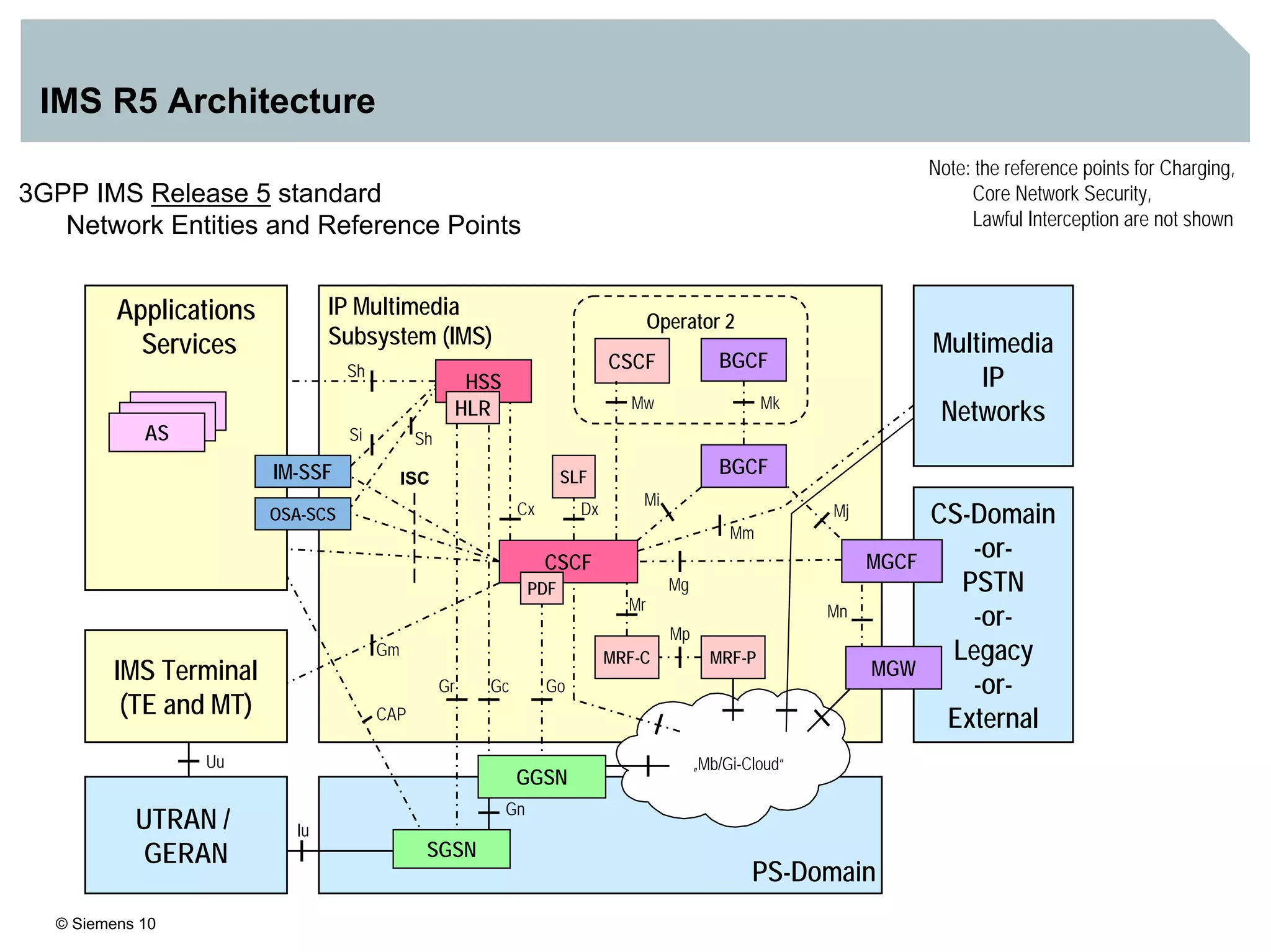
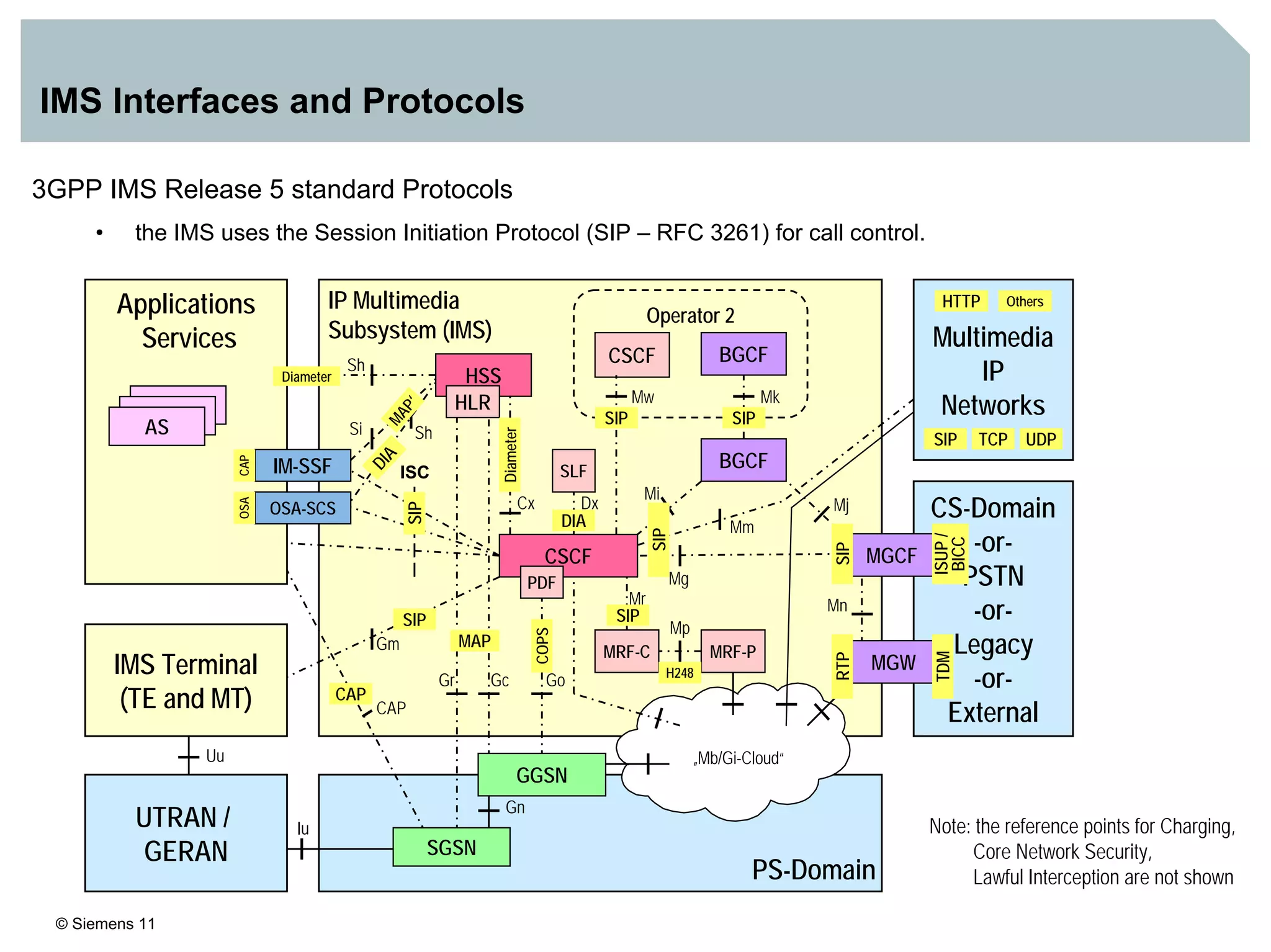
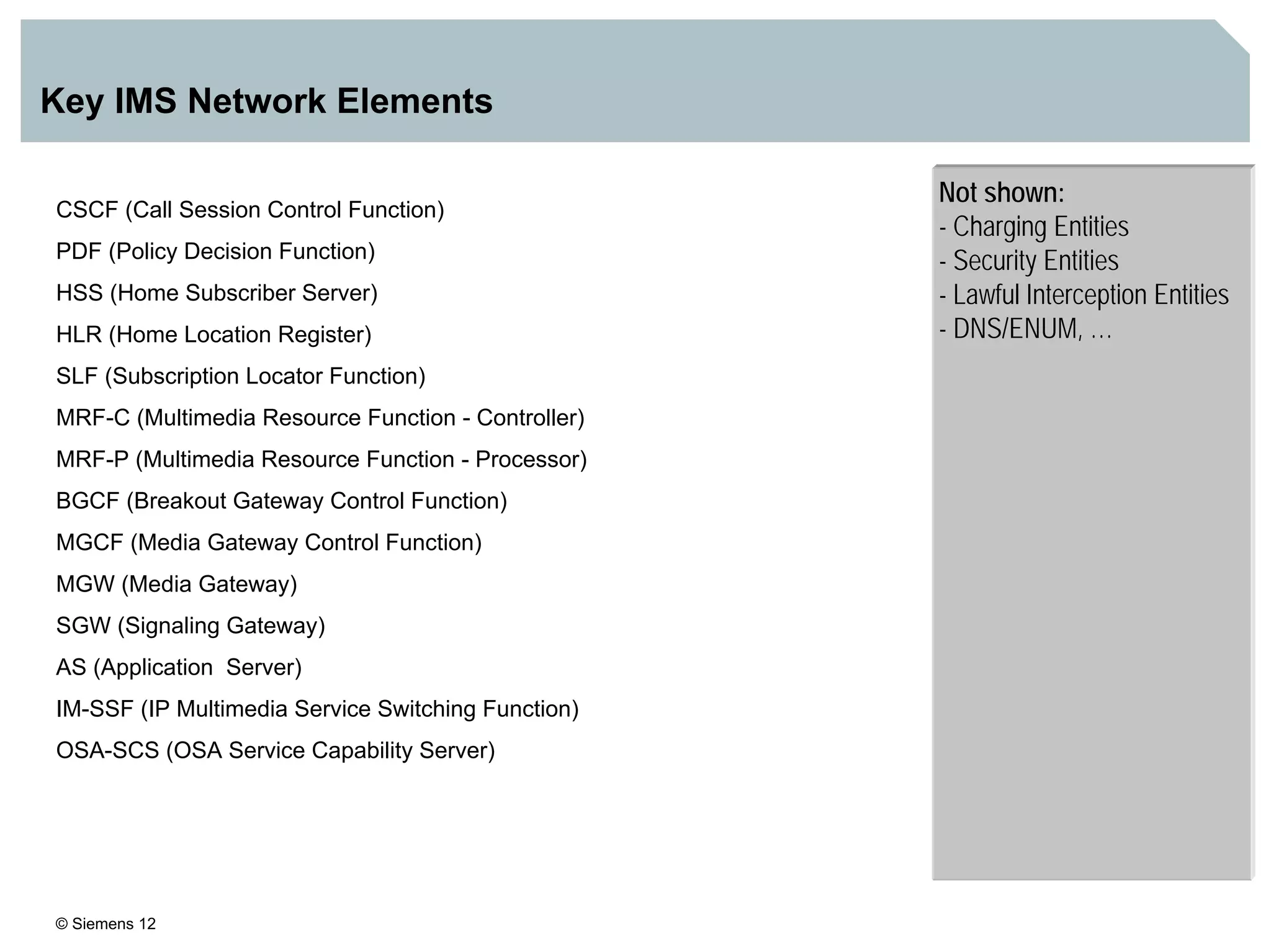
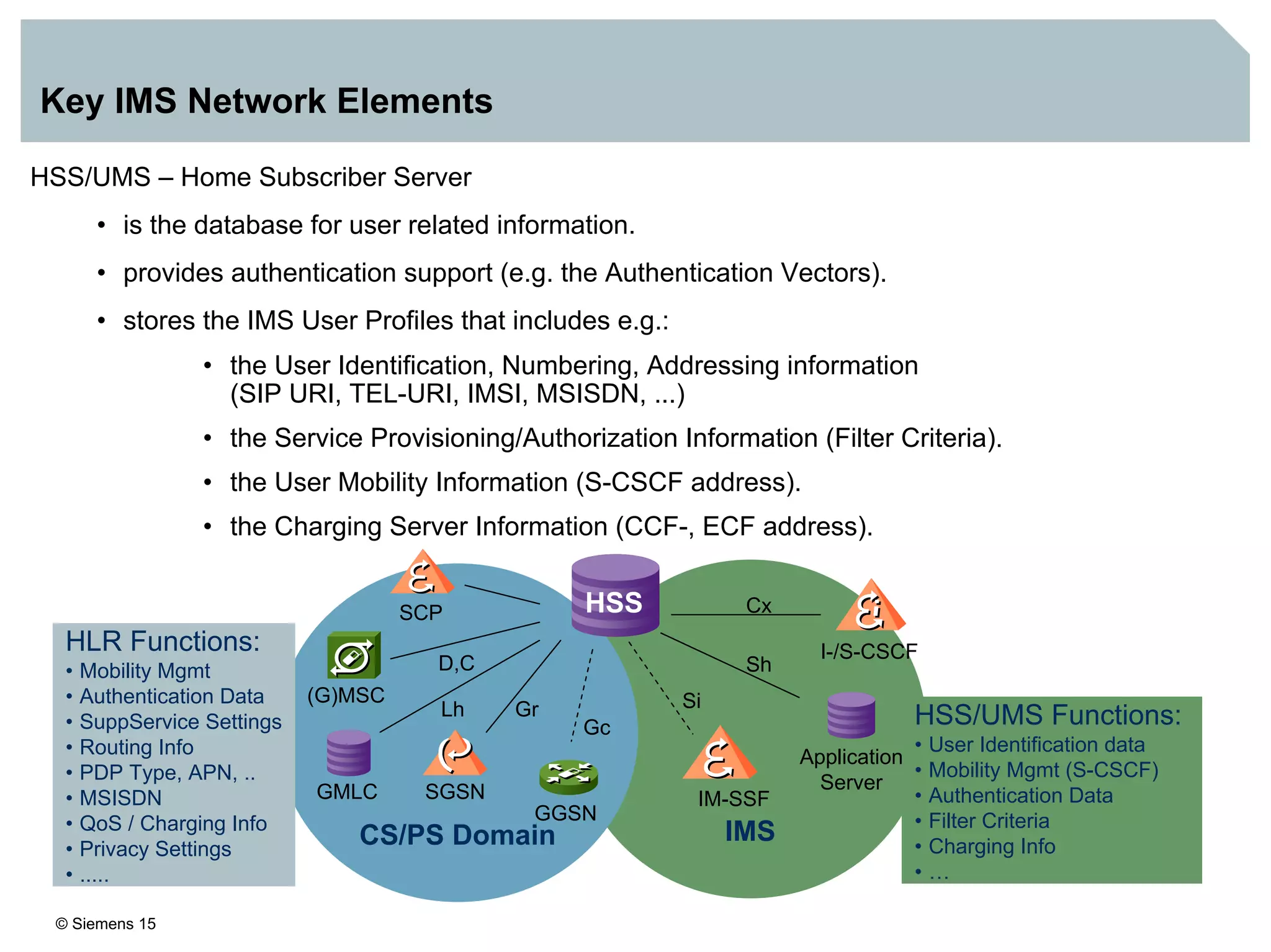
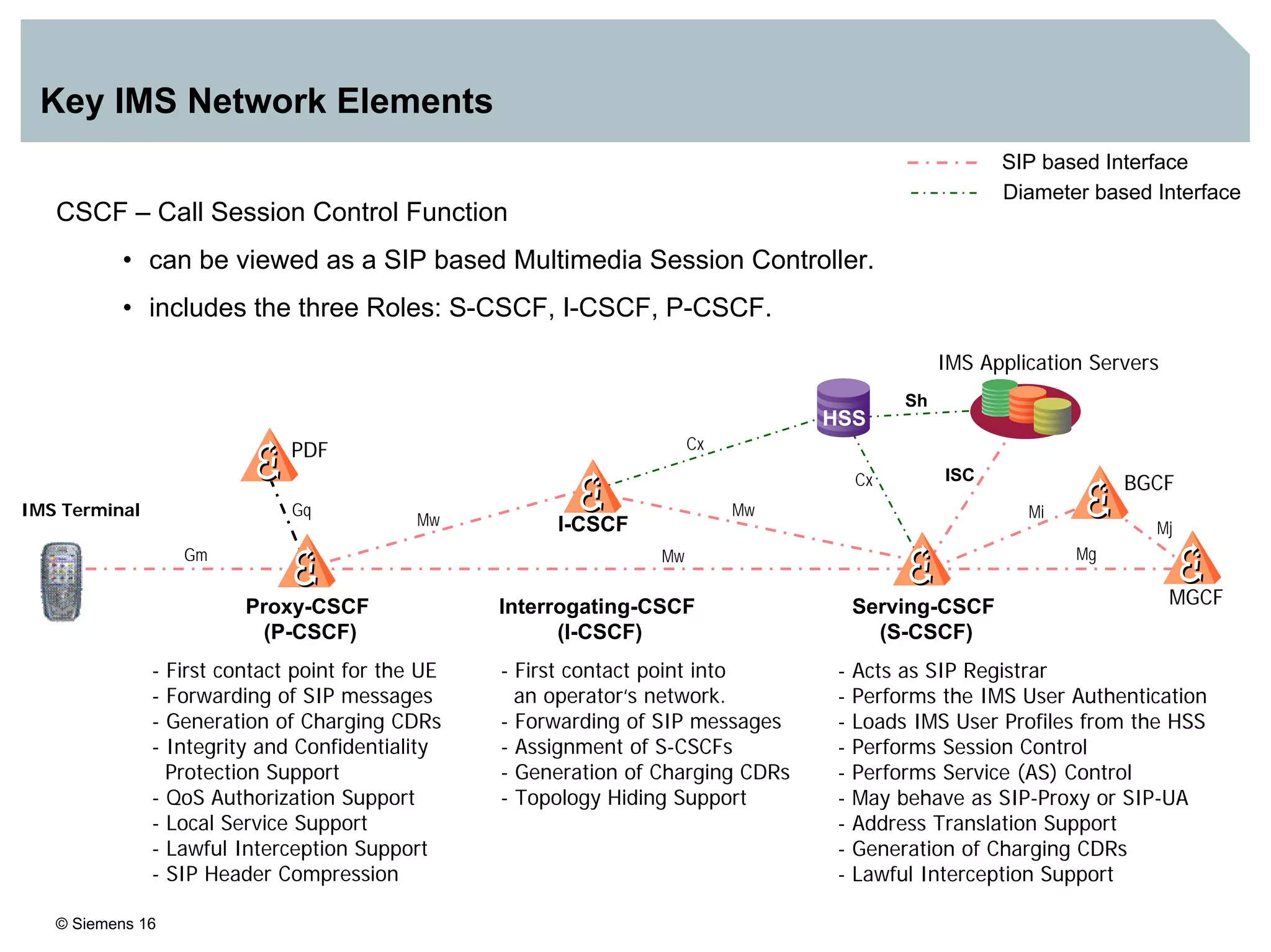
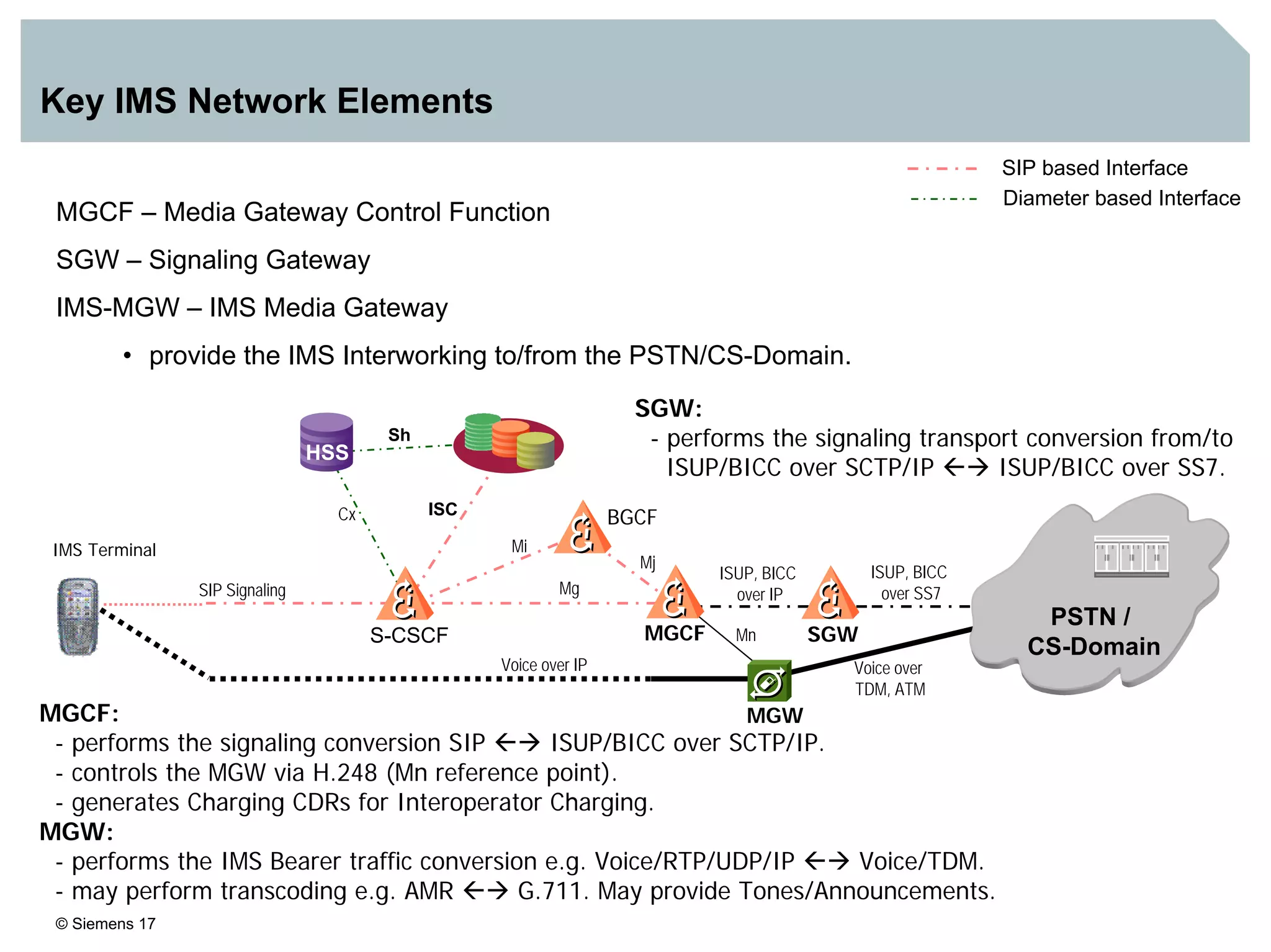
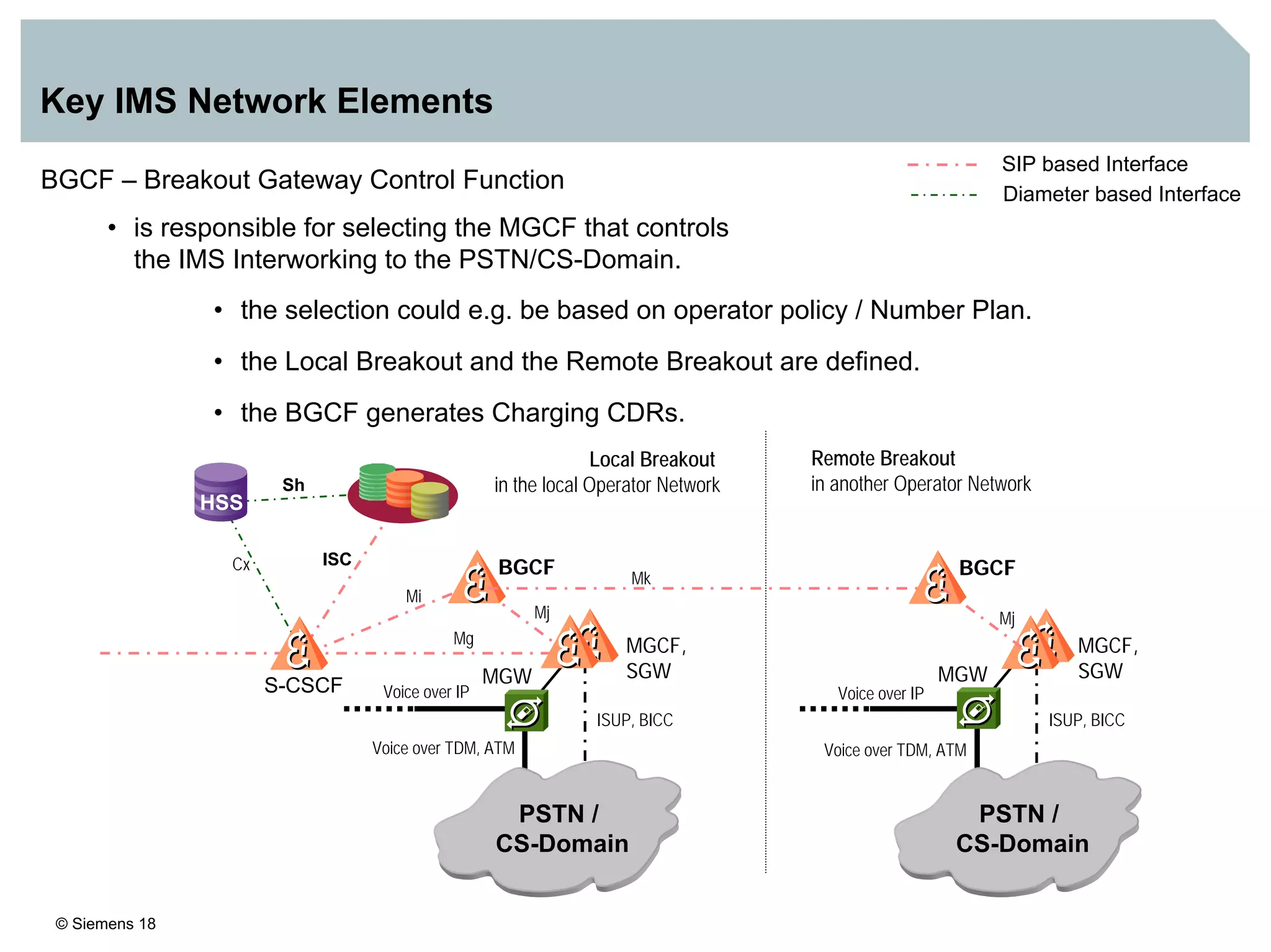
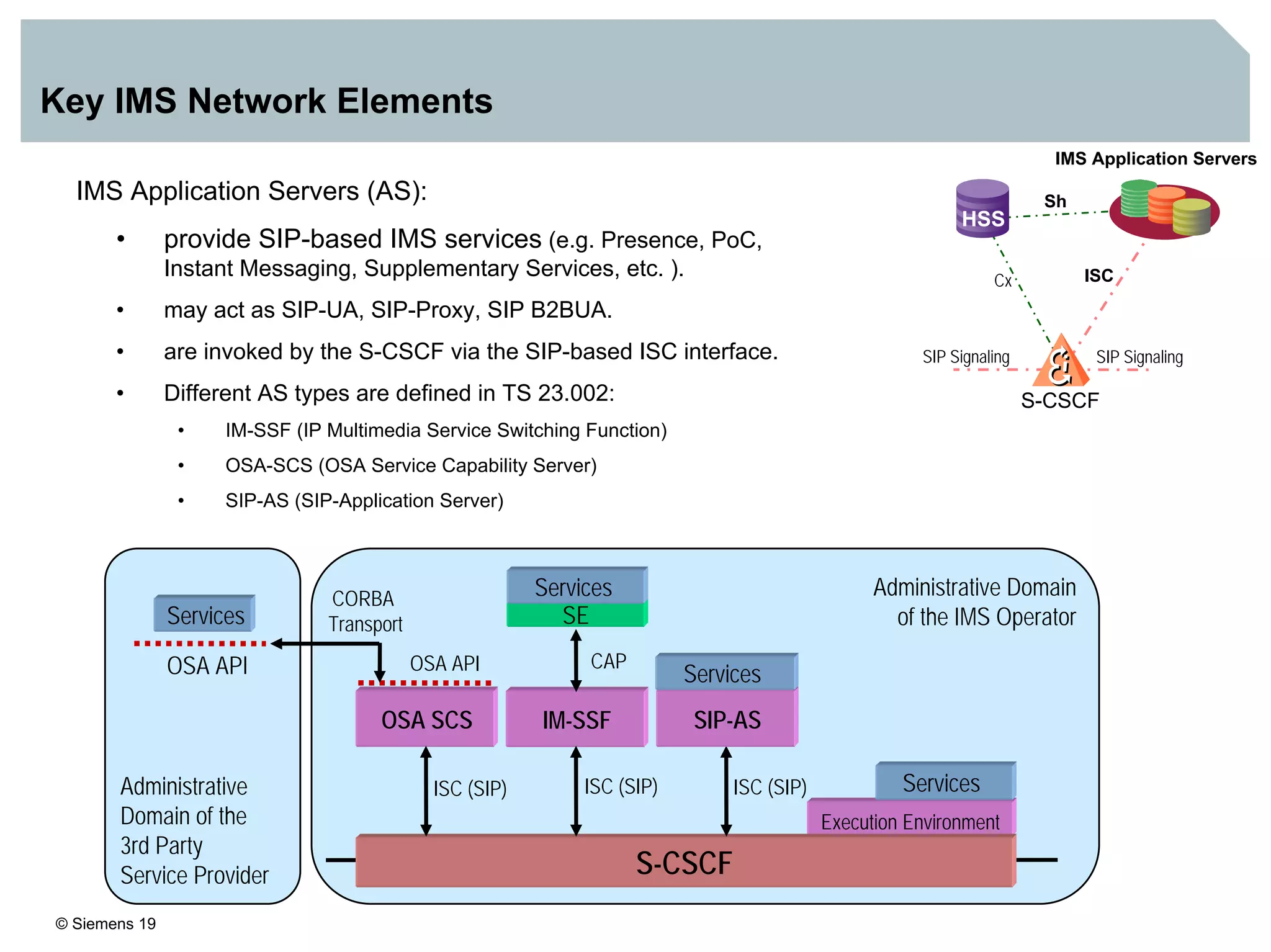
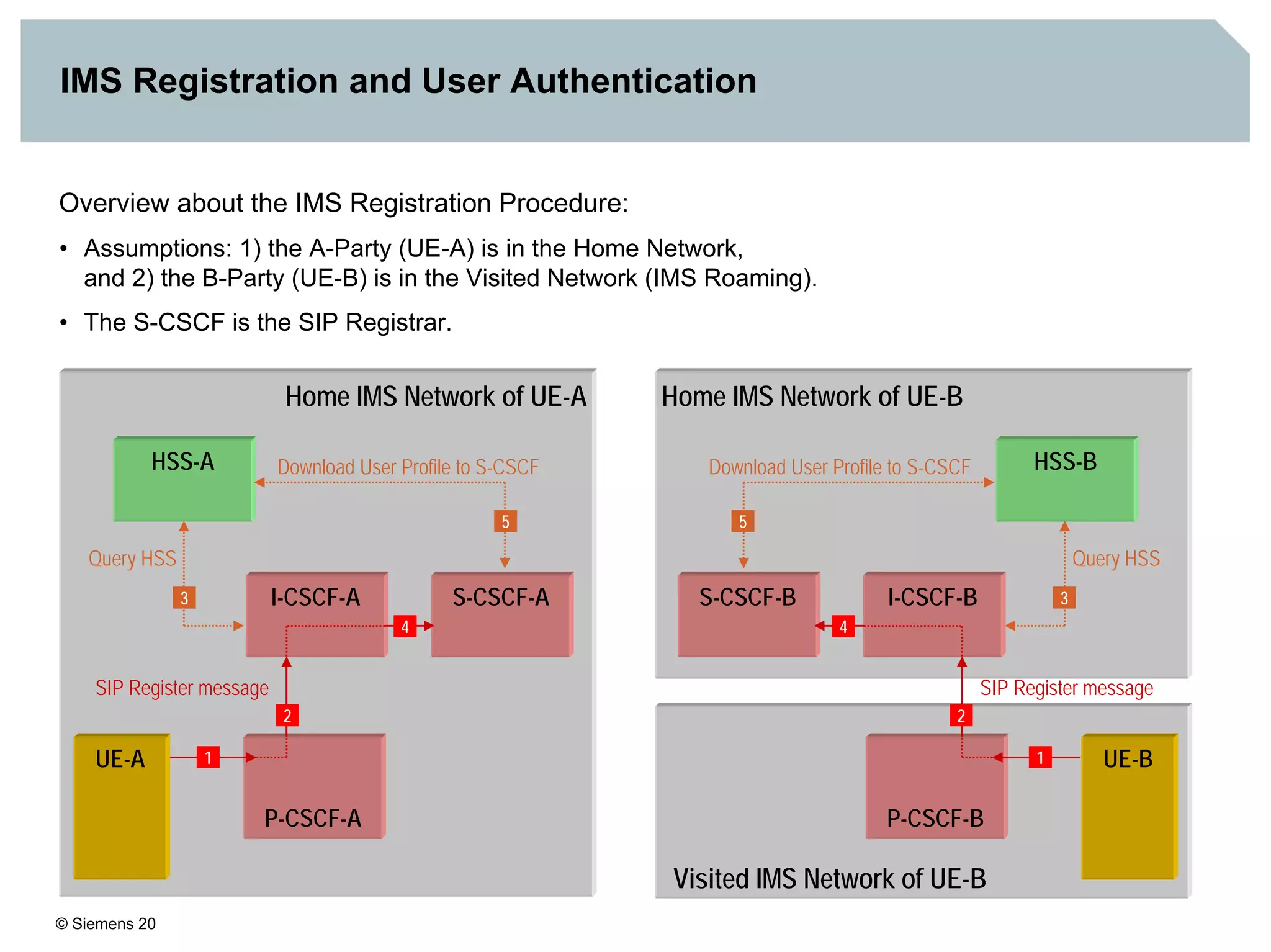
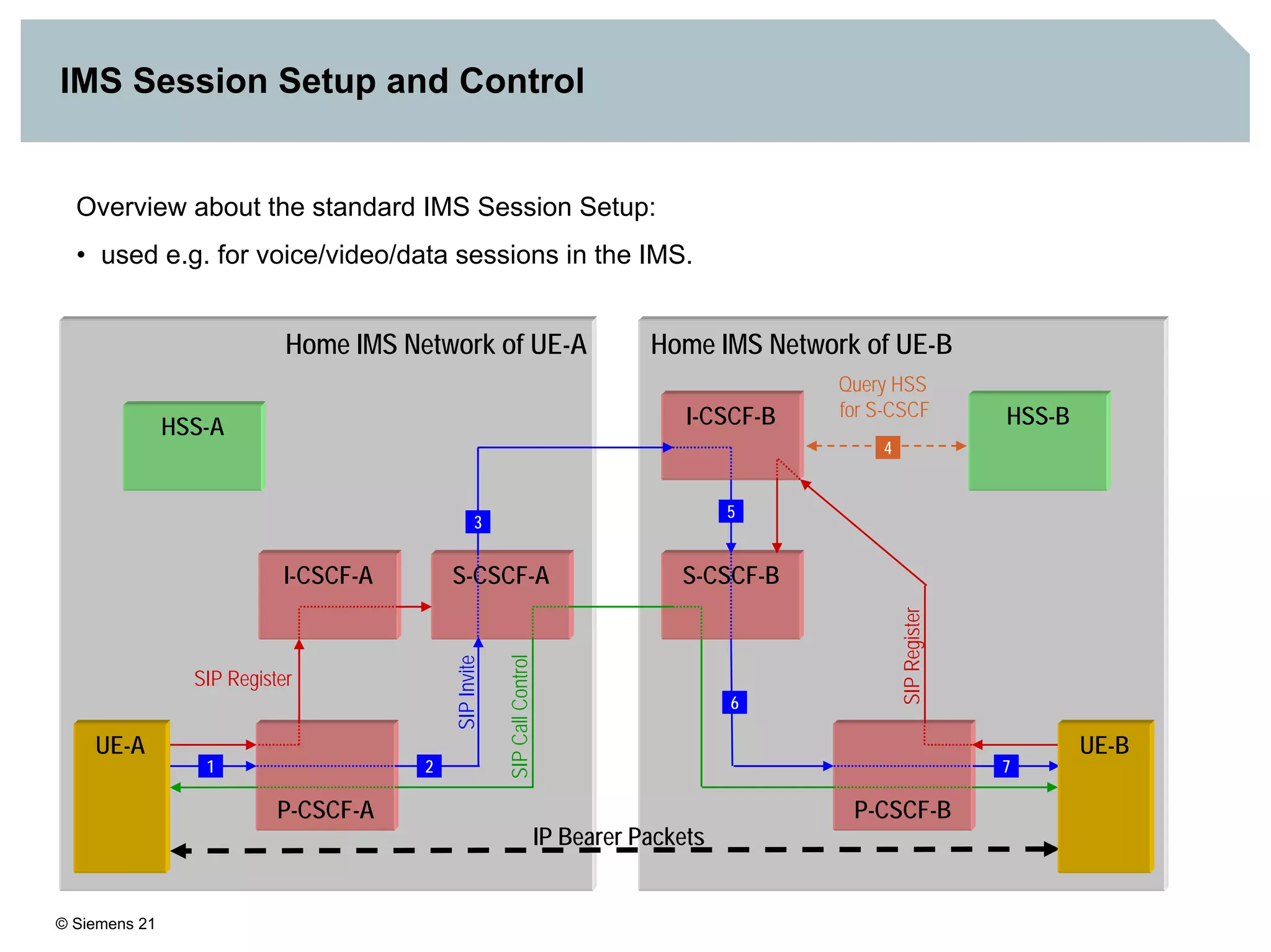
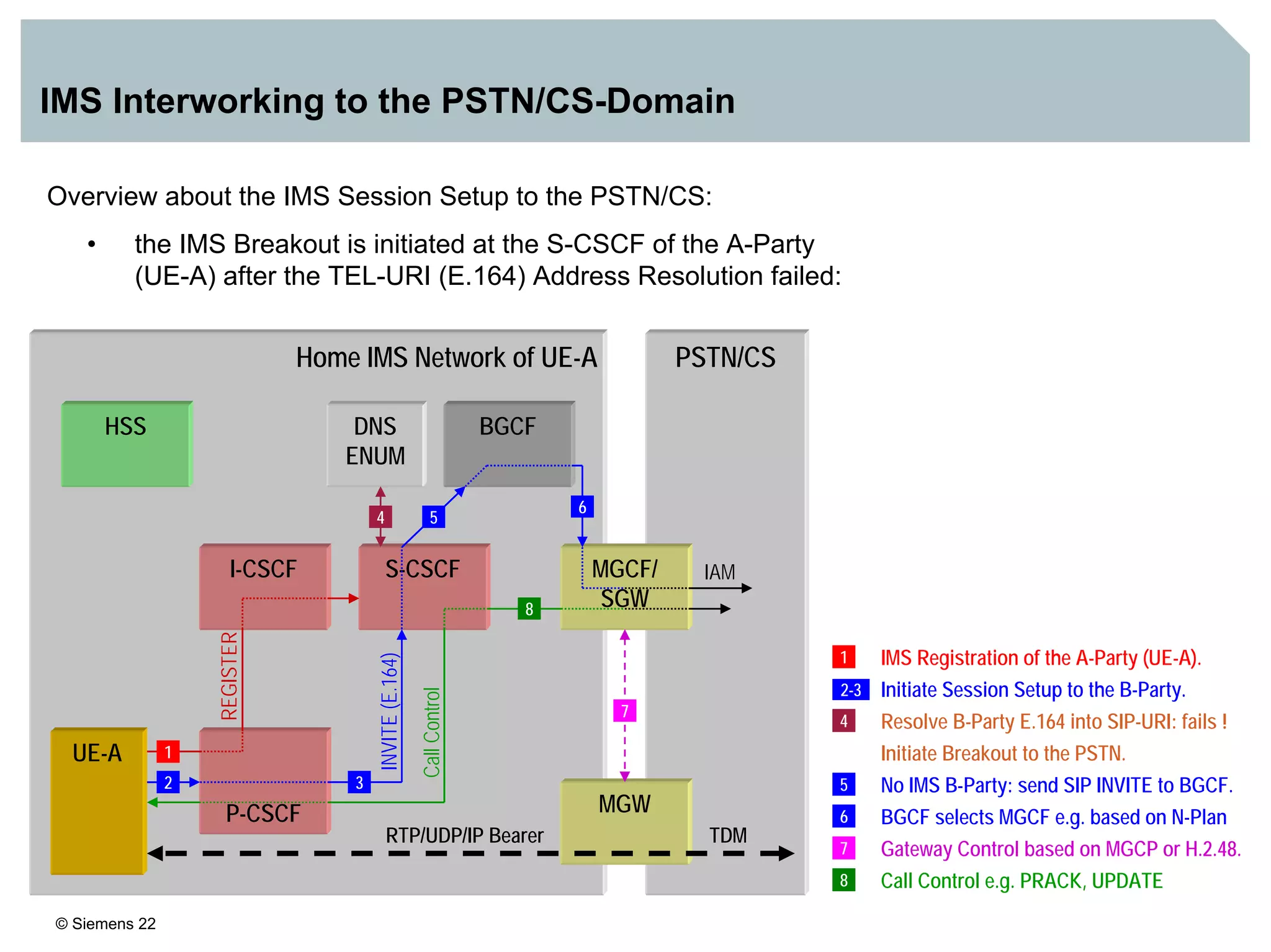
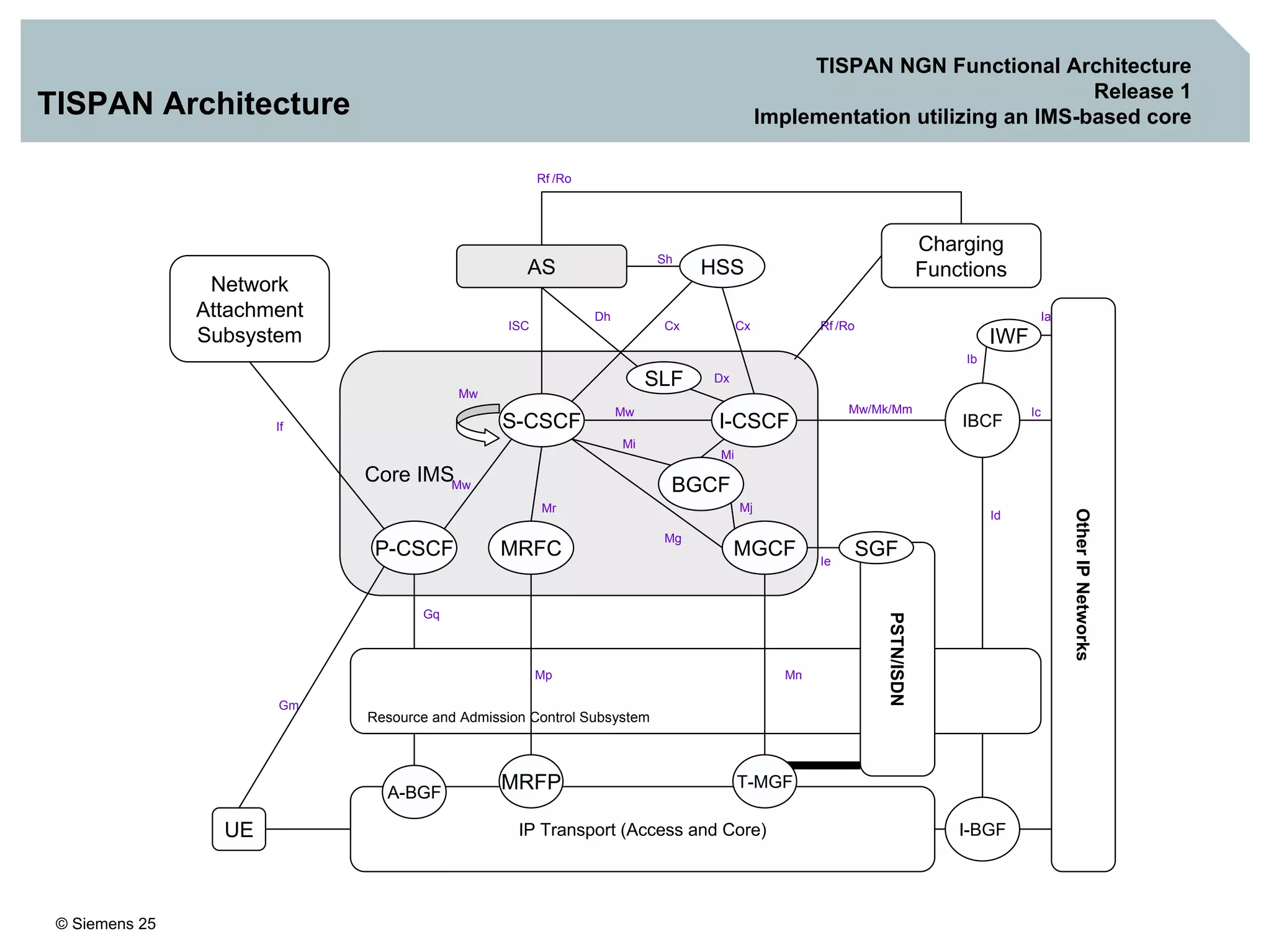
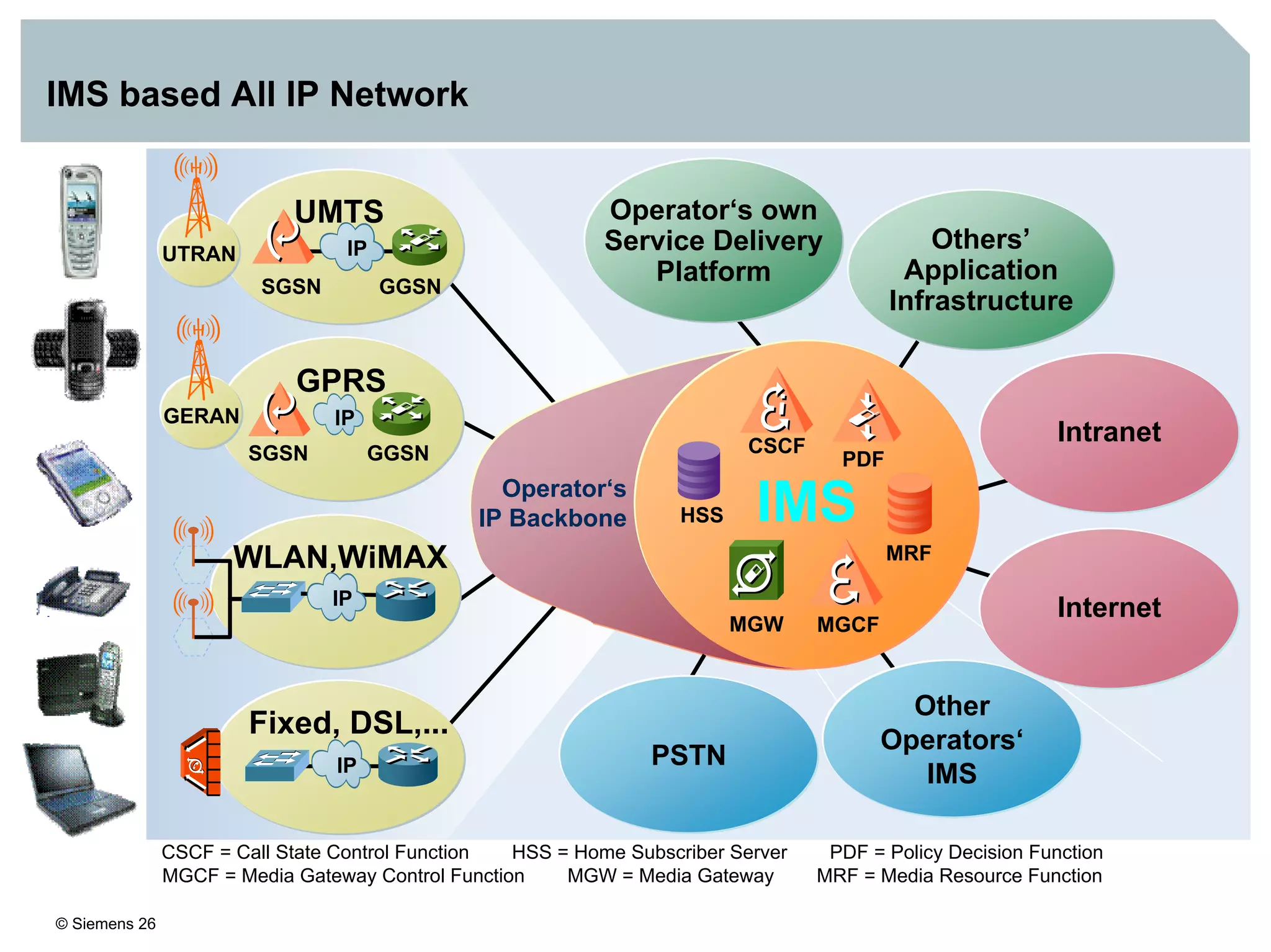
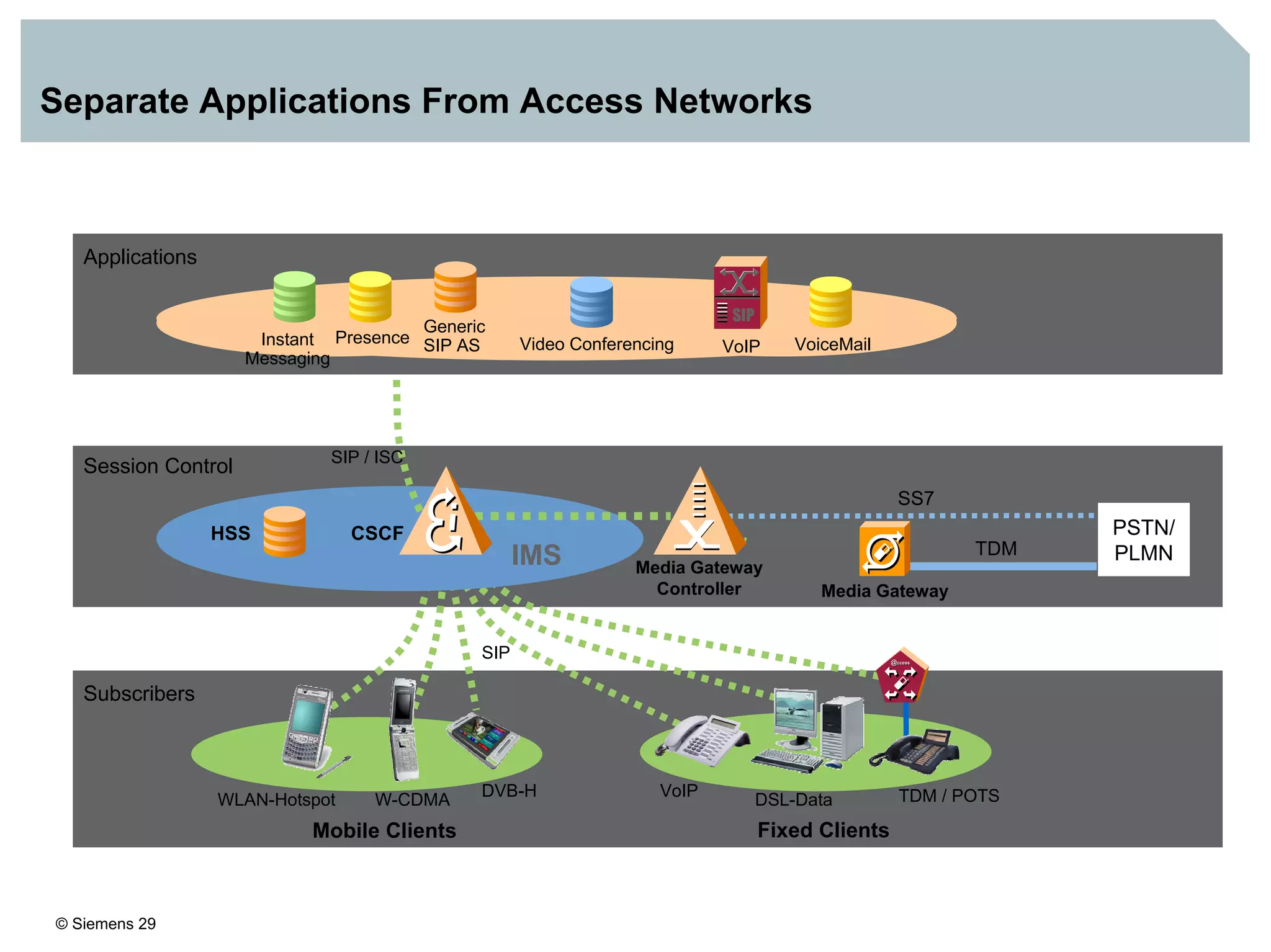
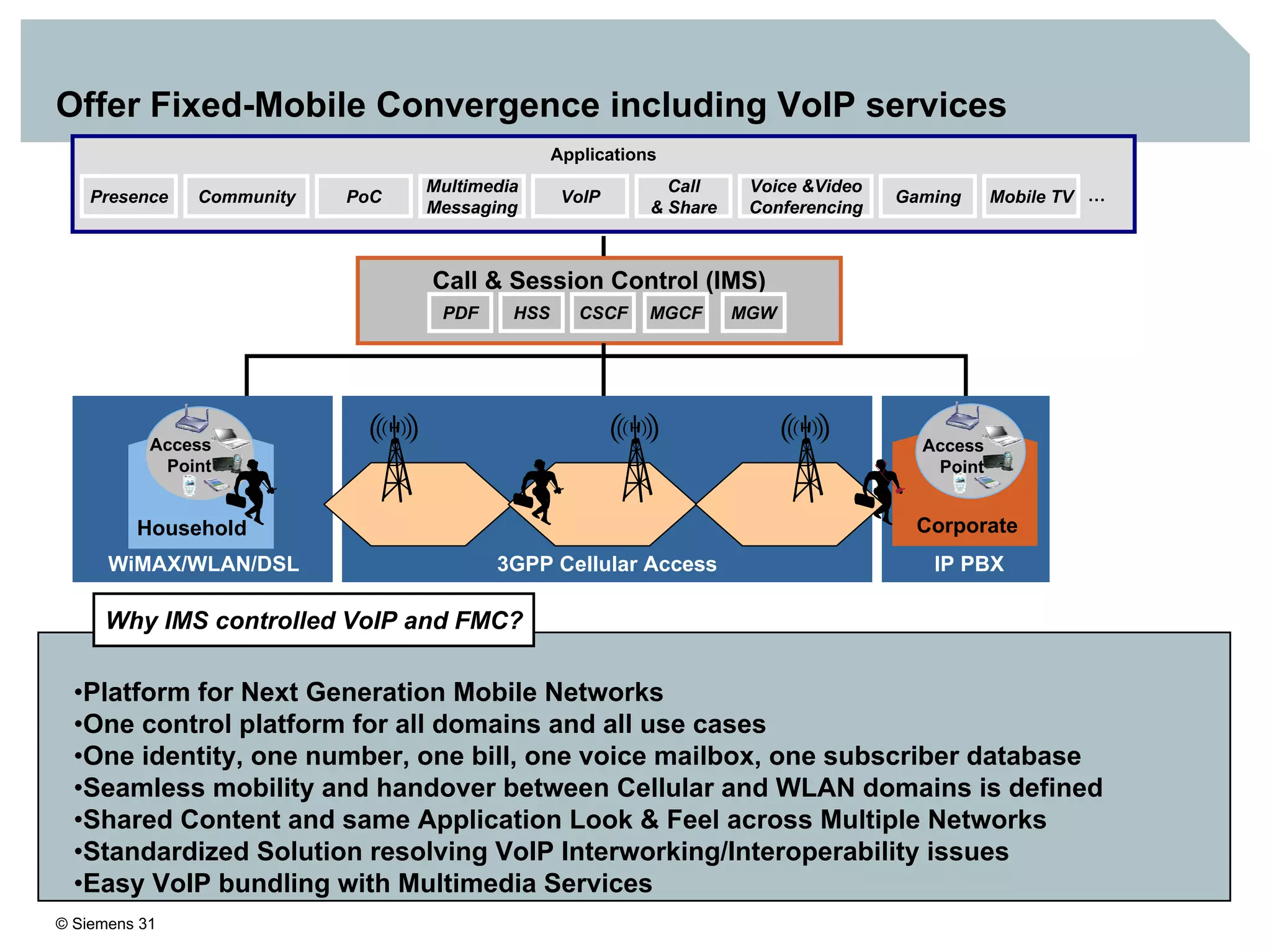
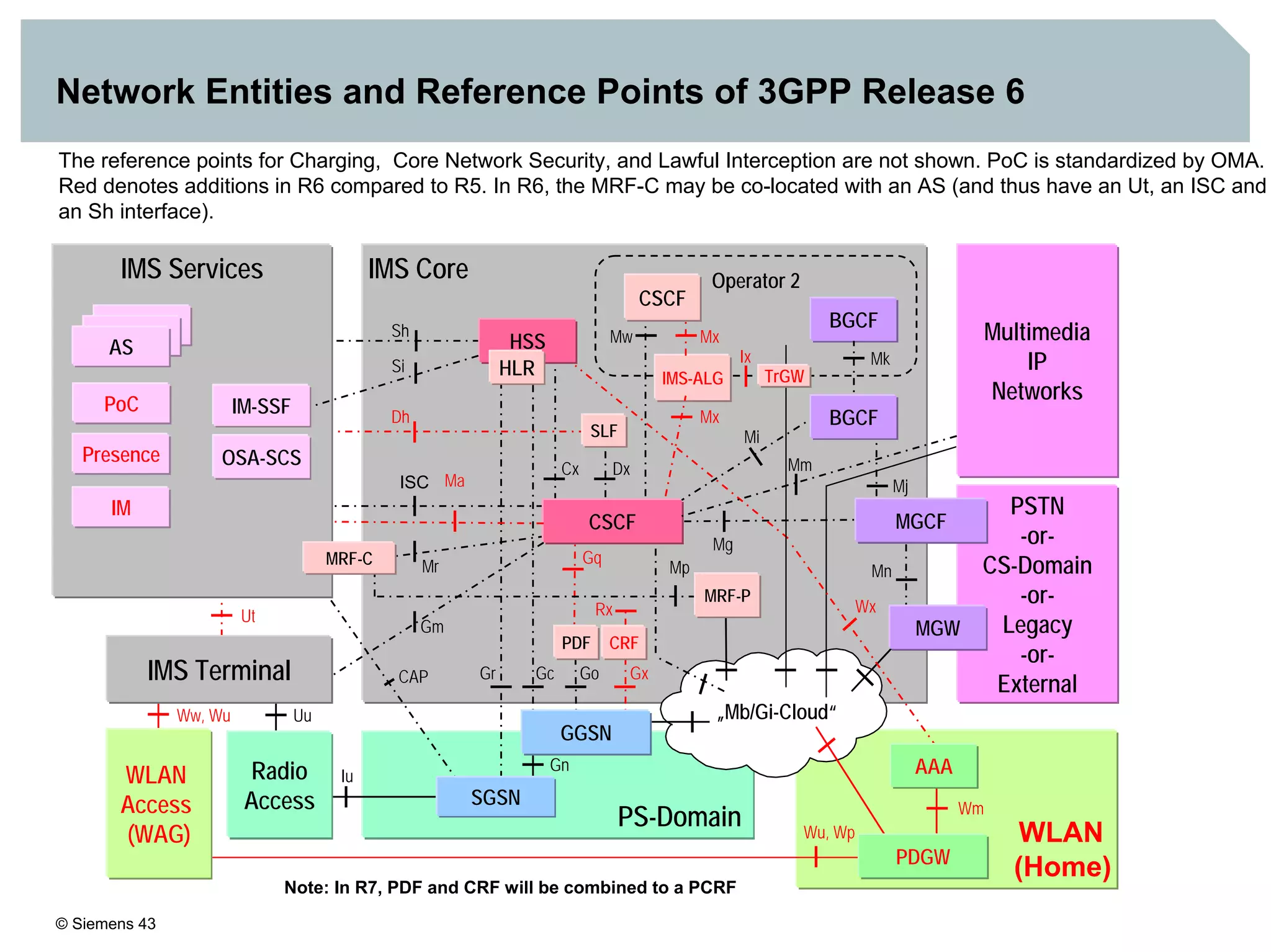
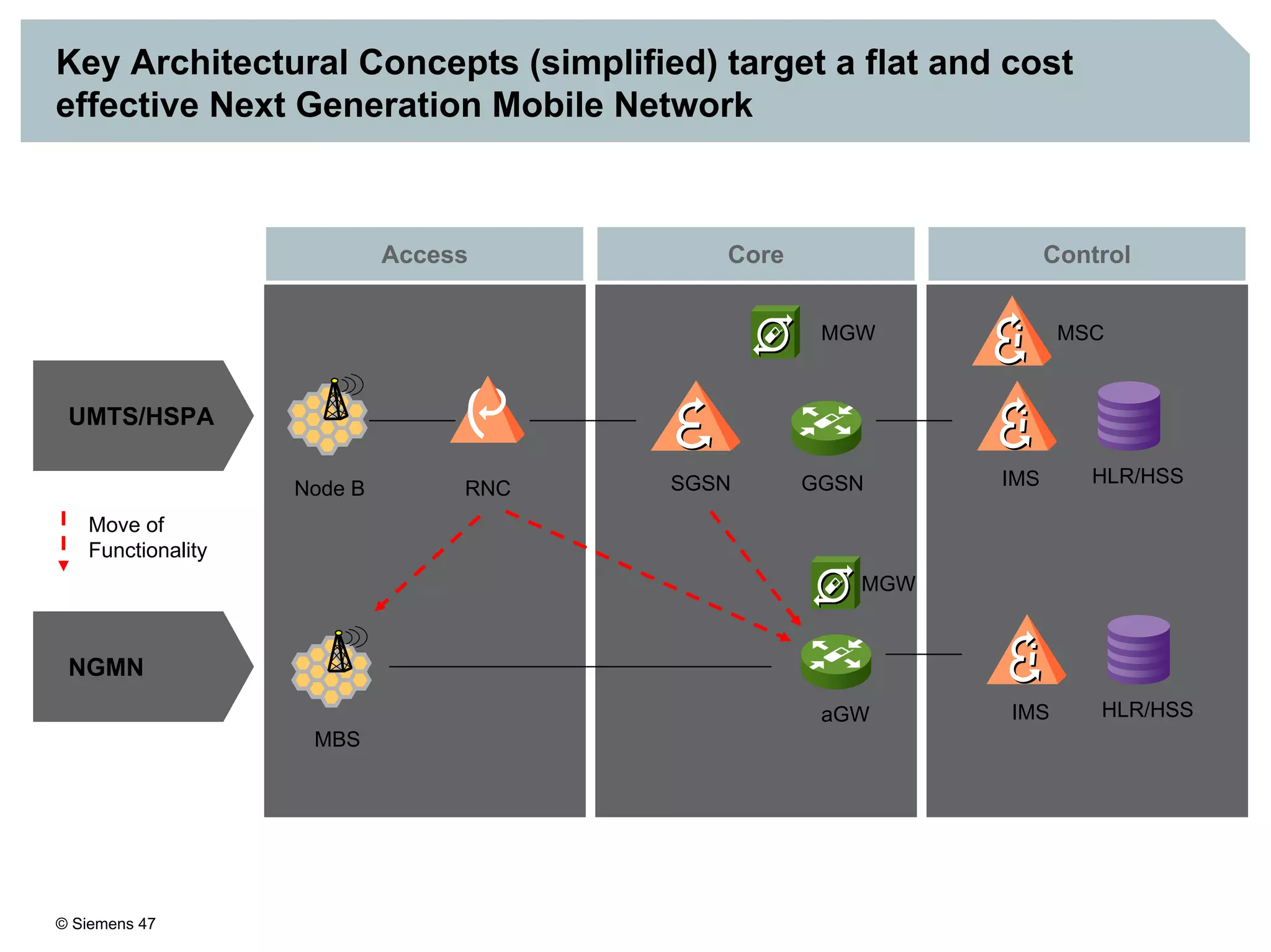
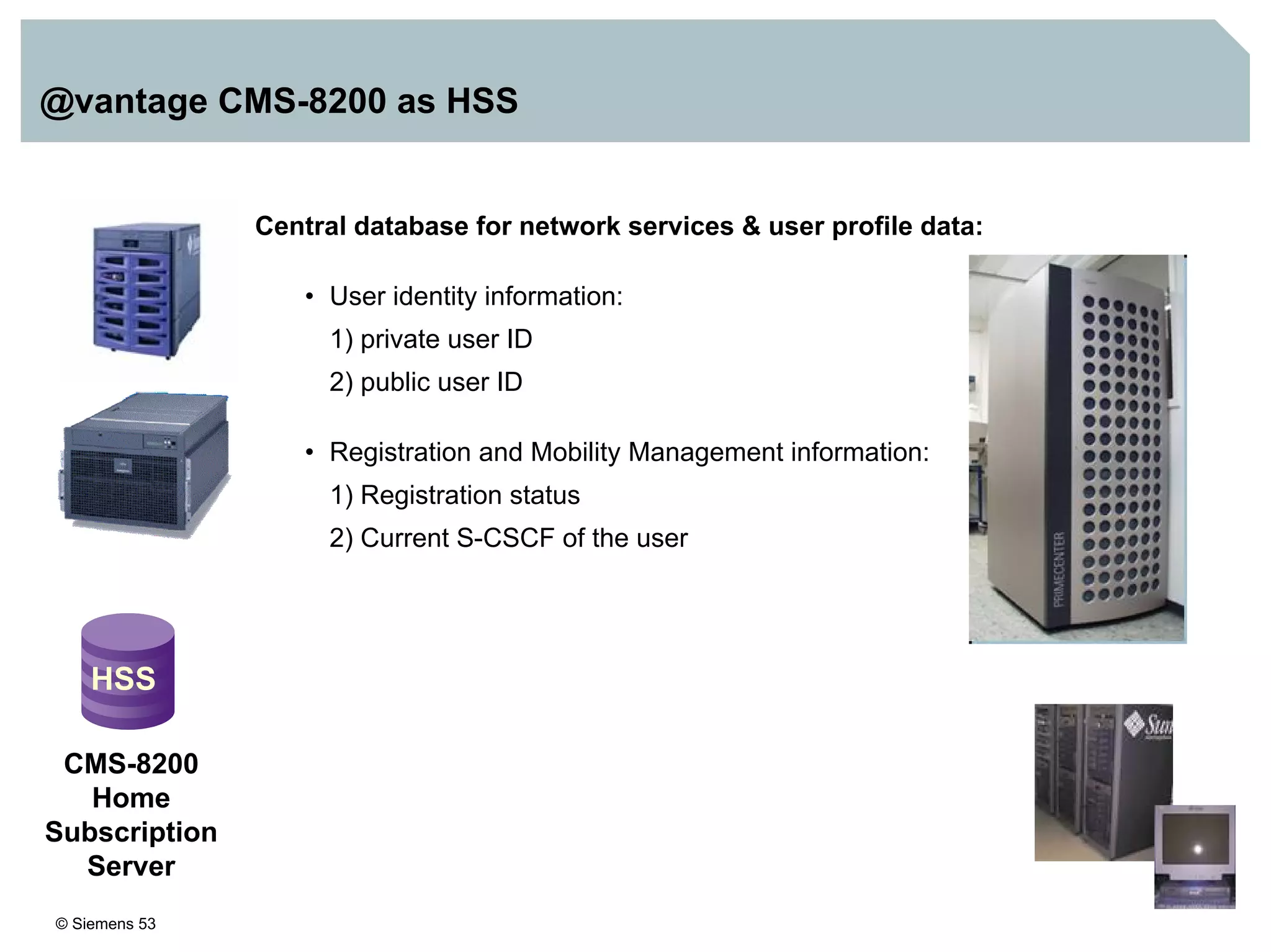
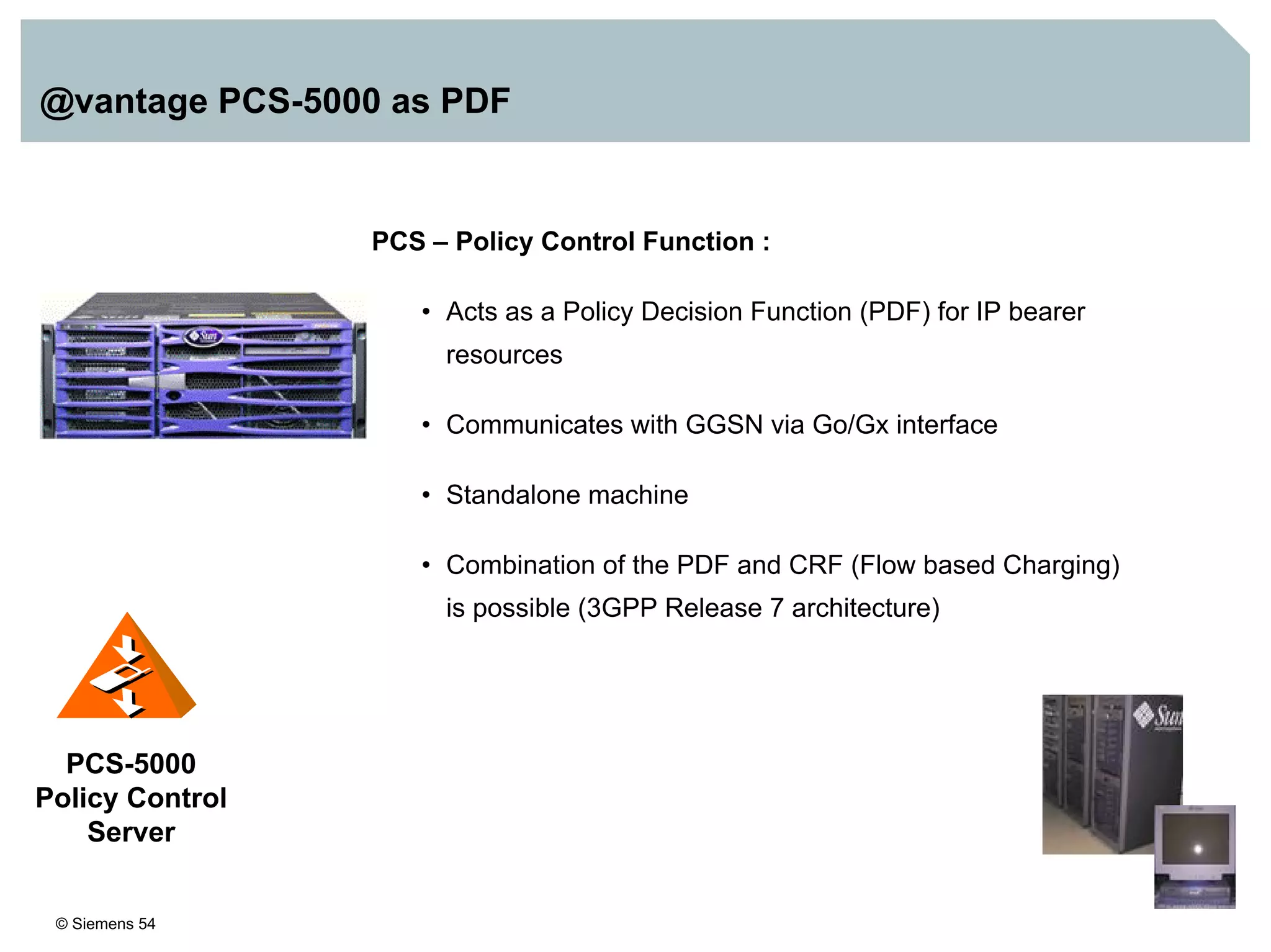
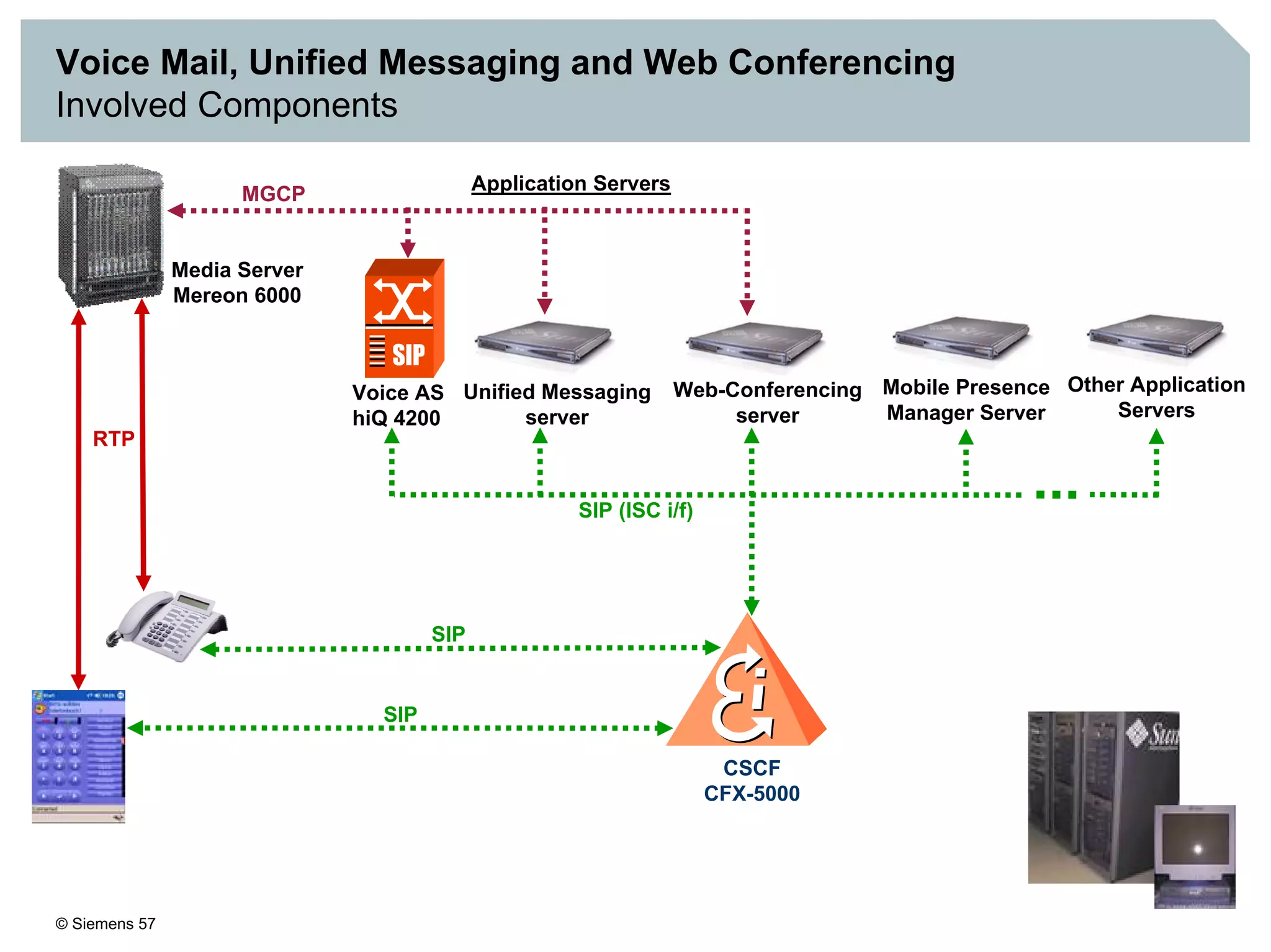
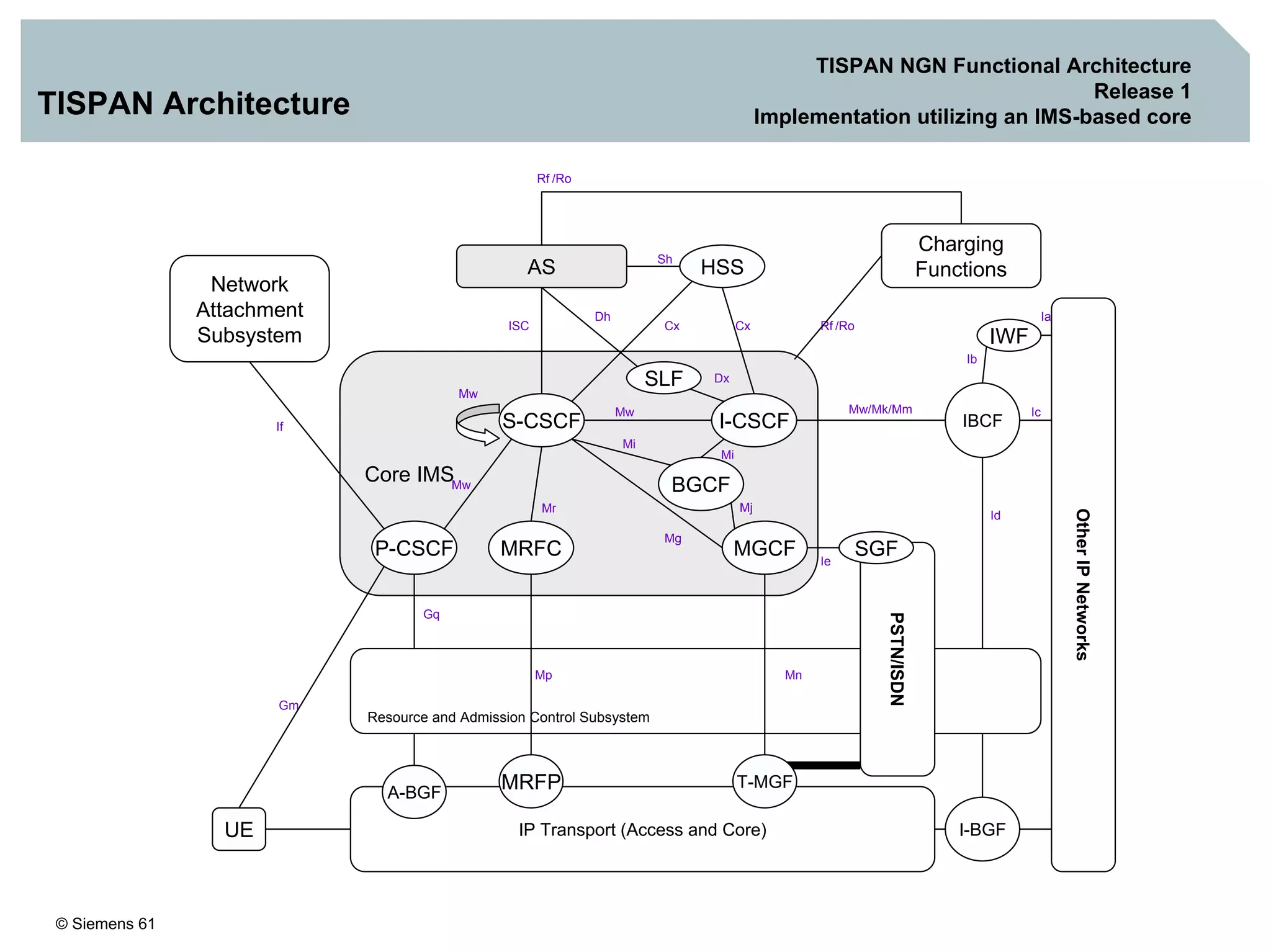
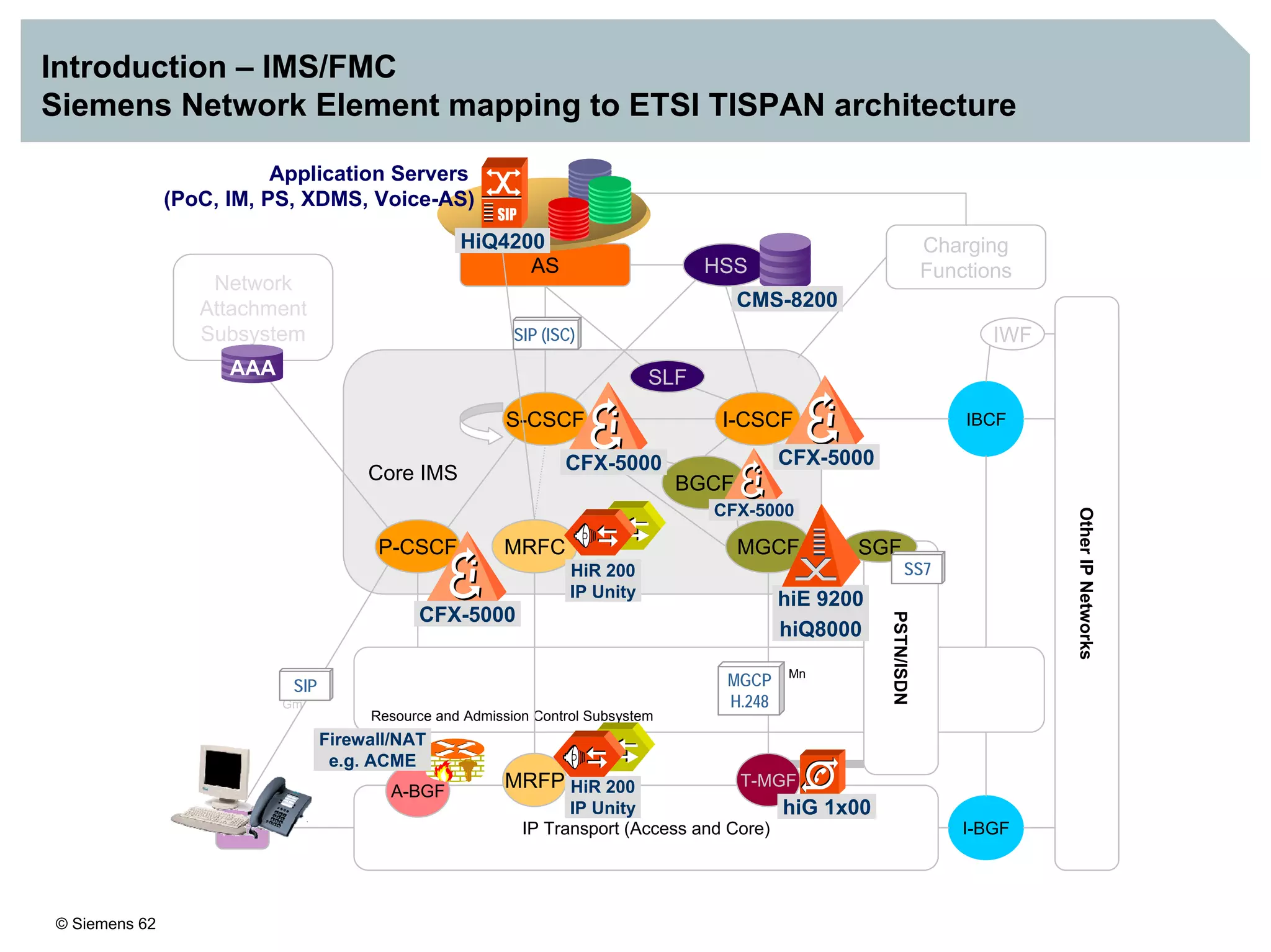
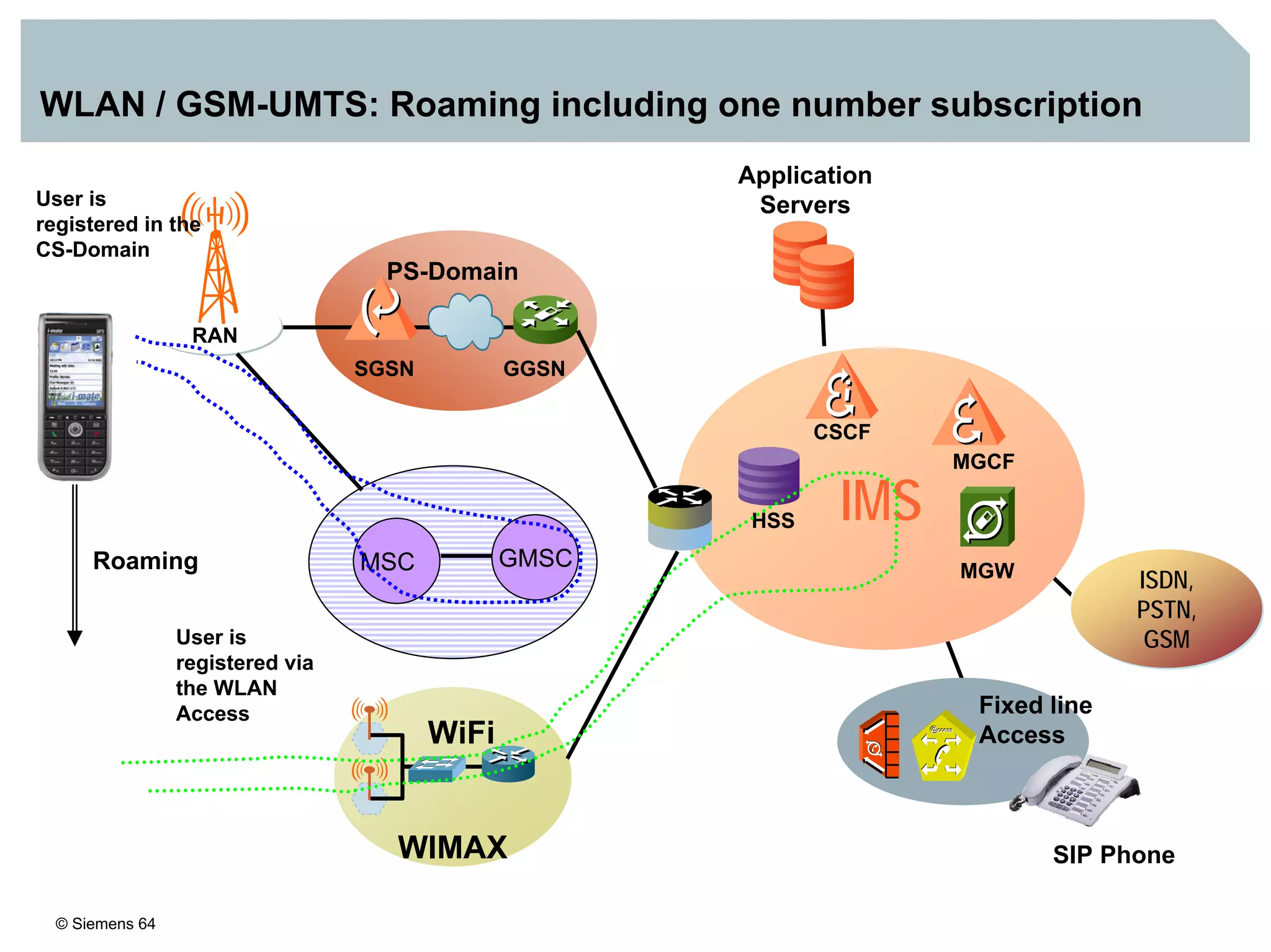
1. It provides an overview of the IMS architecture, including network elements like CSCF, HSS, and application servers.
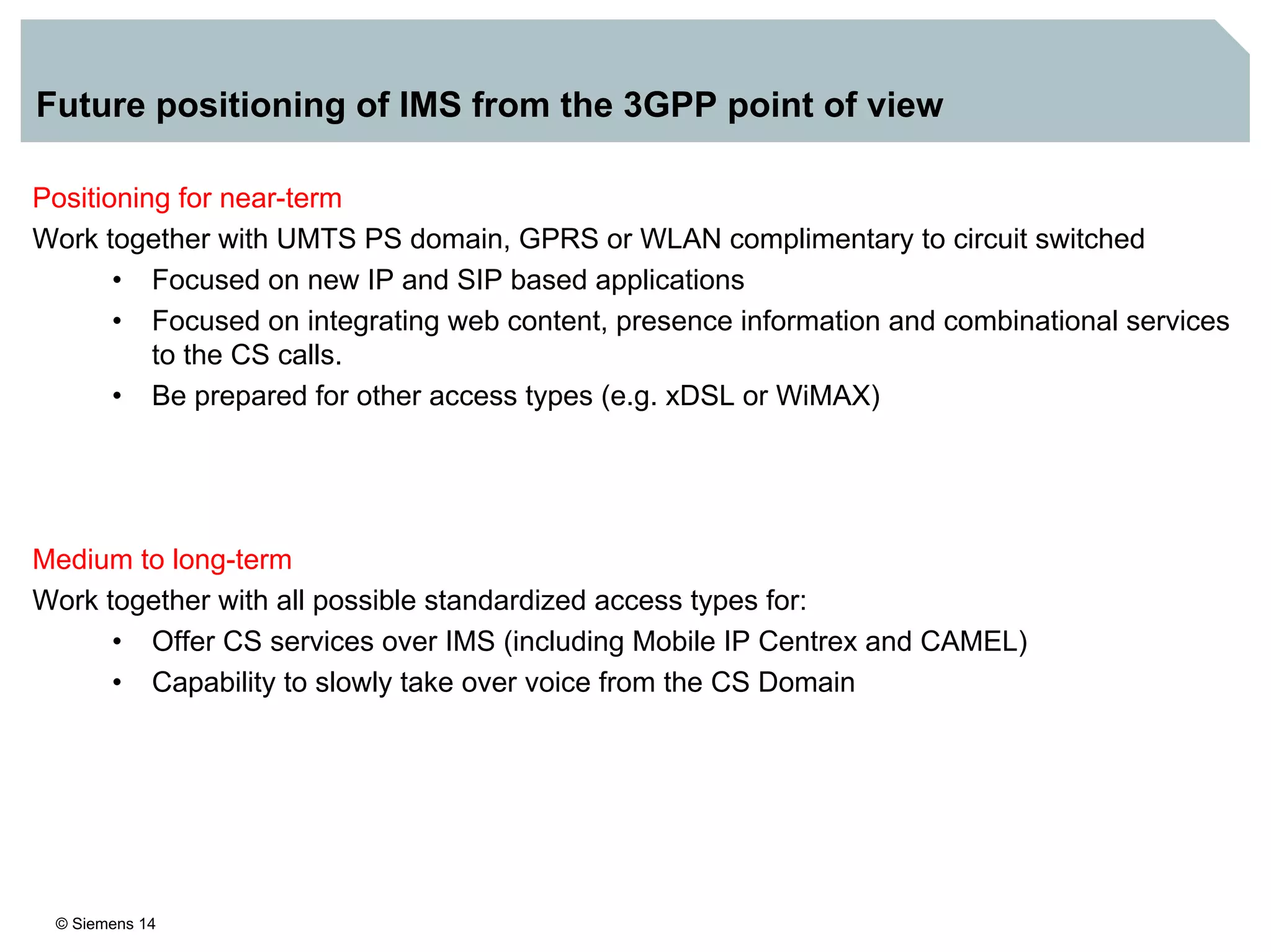
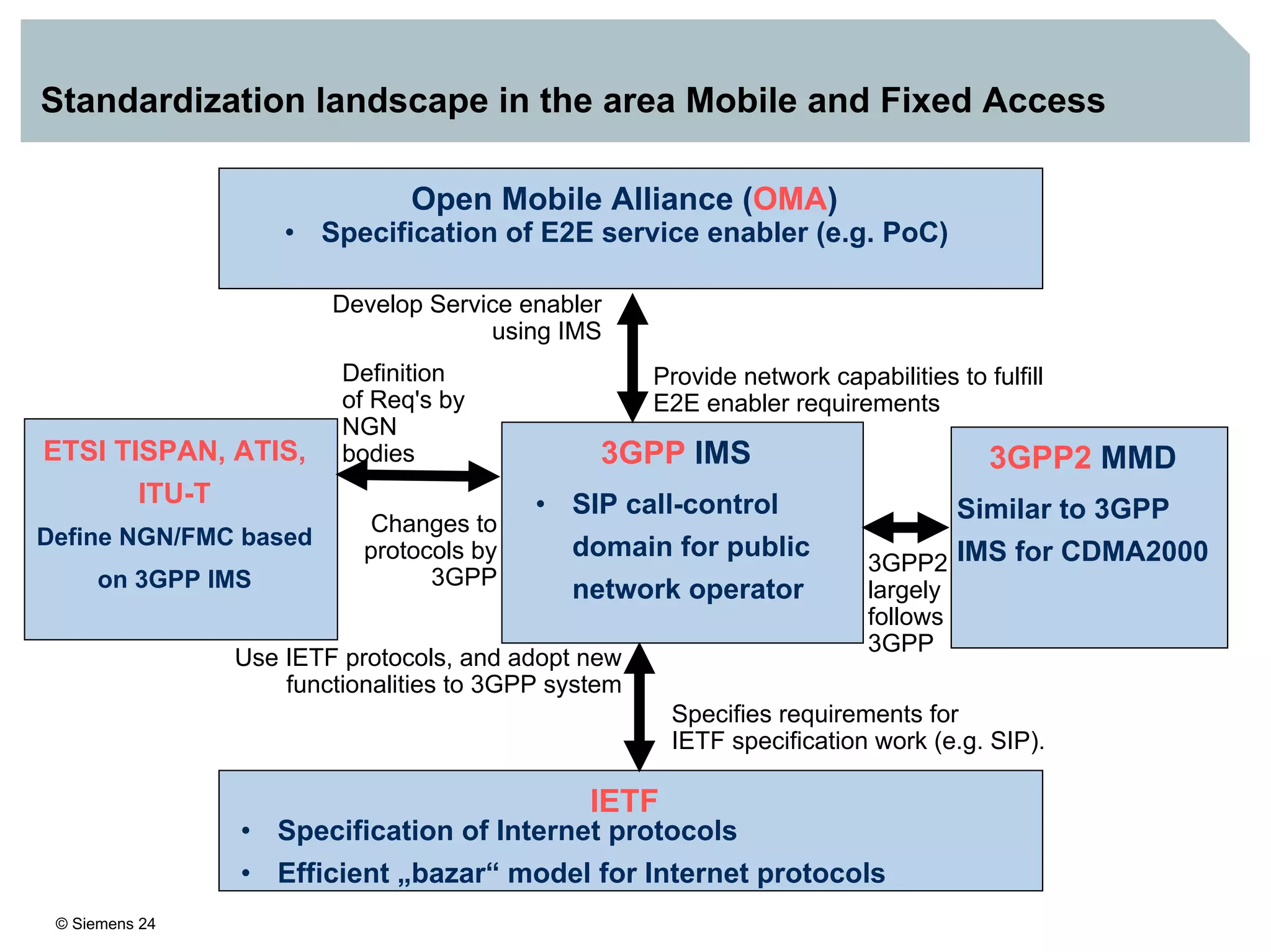
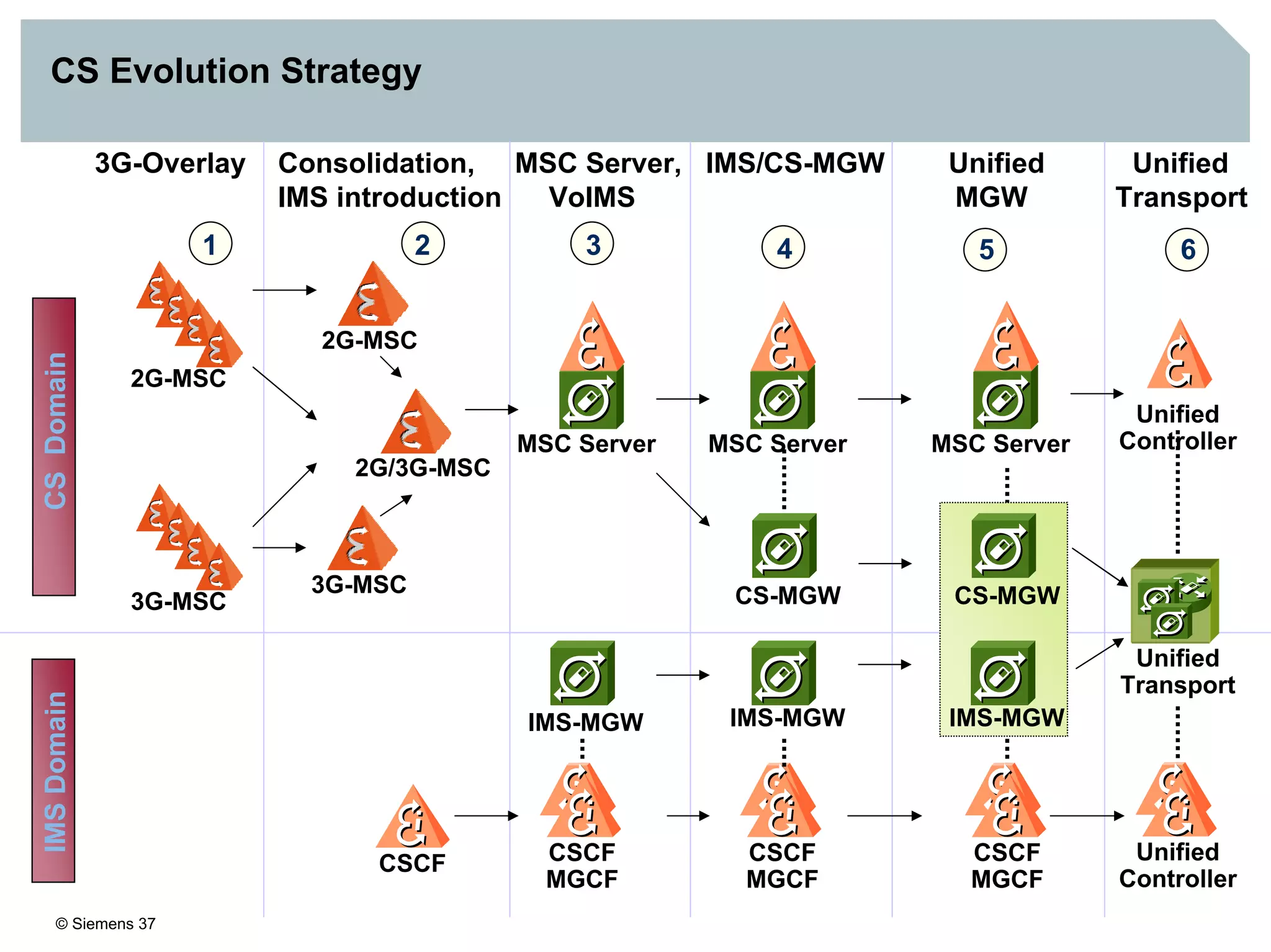
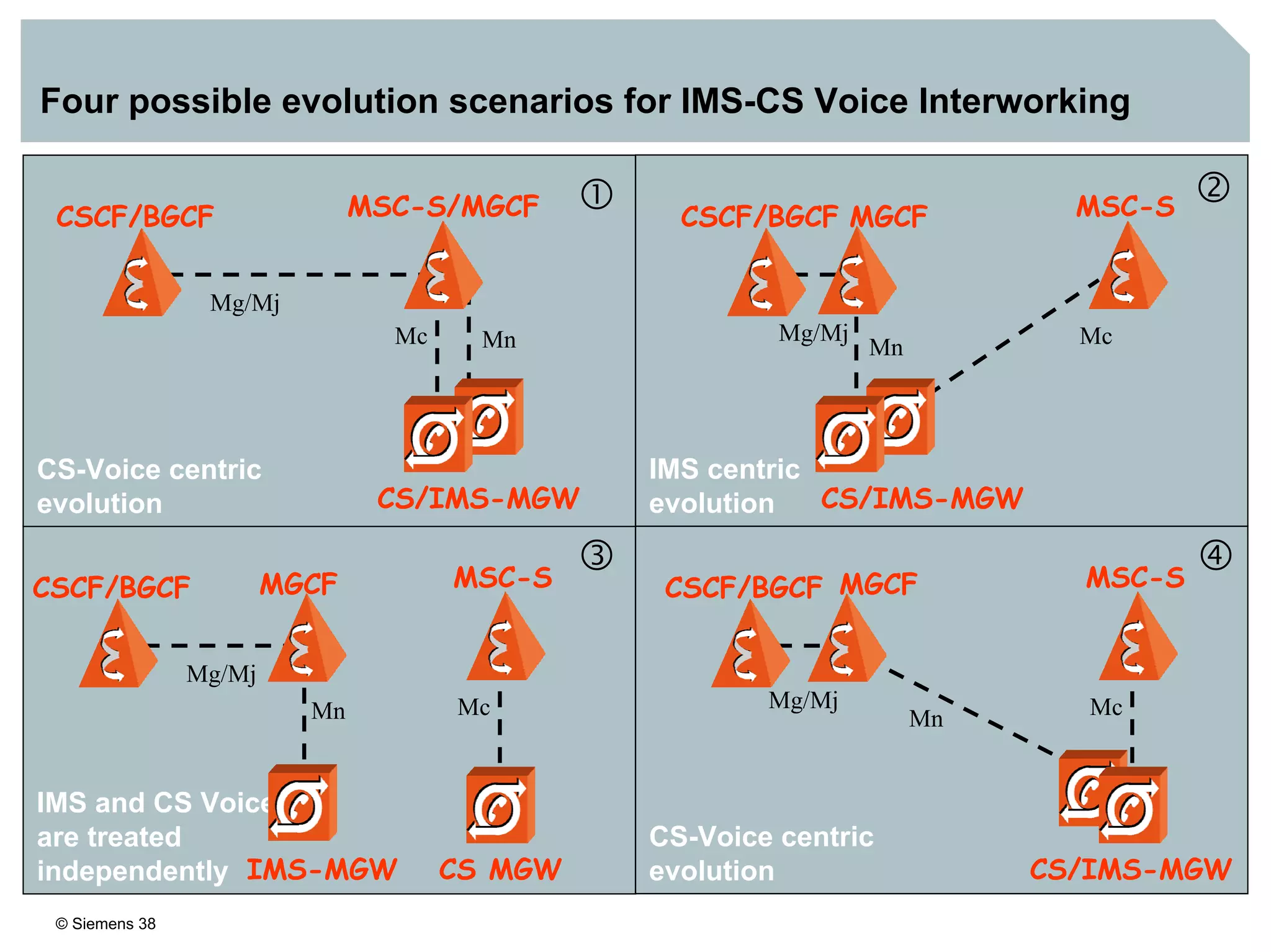
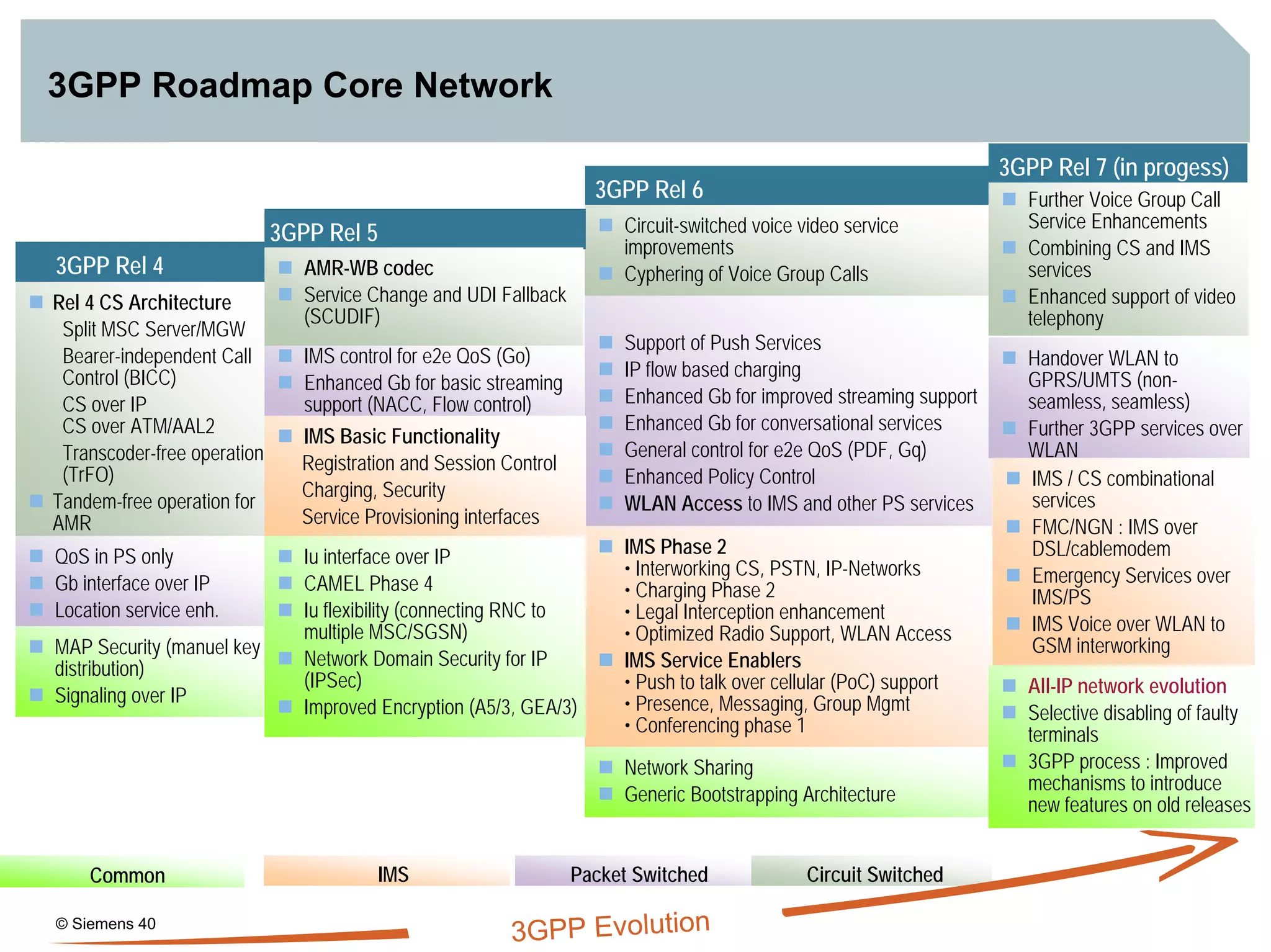
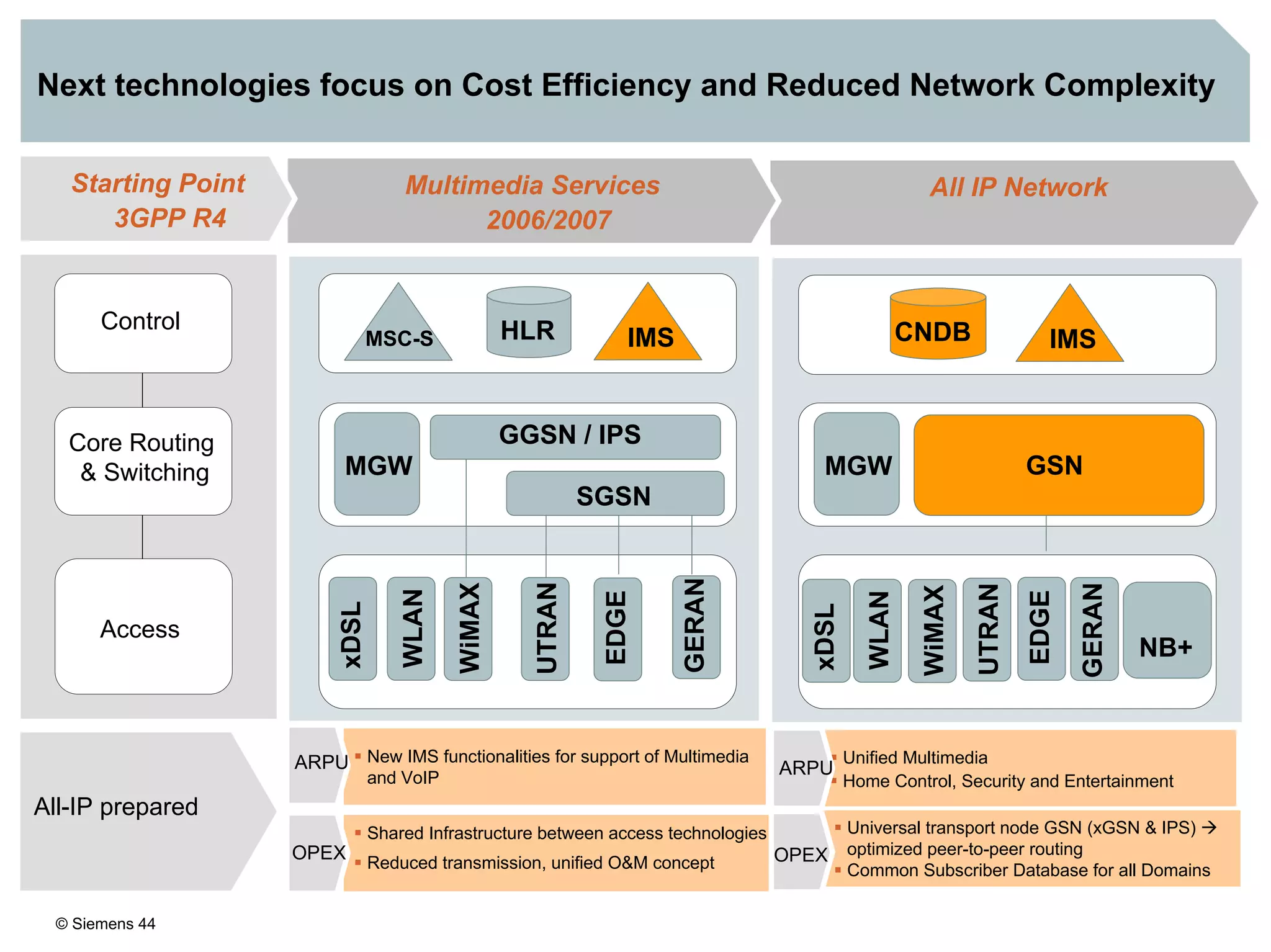
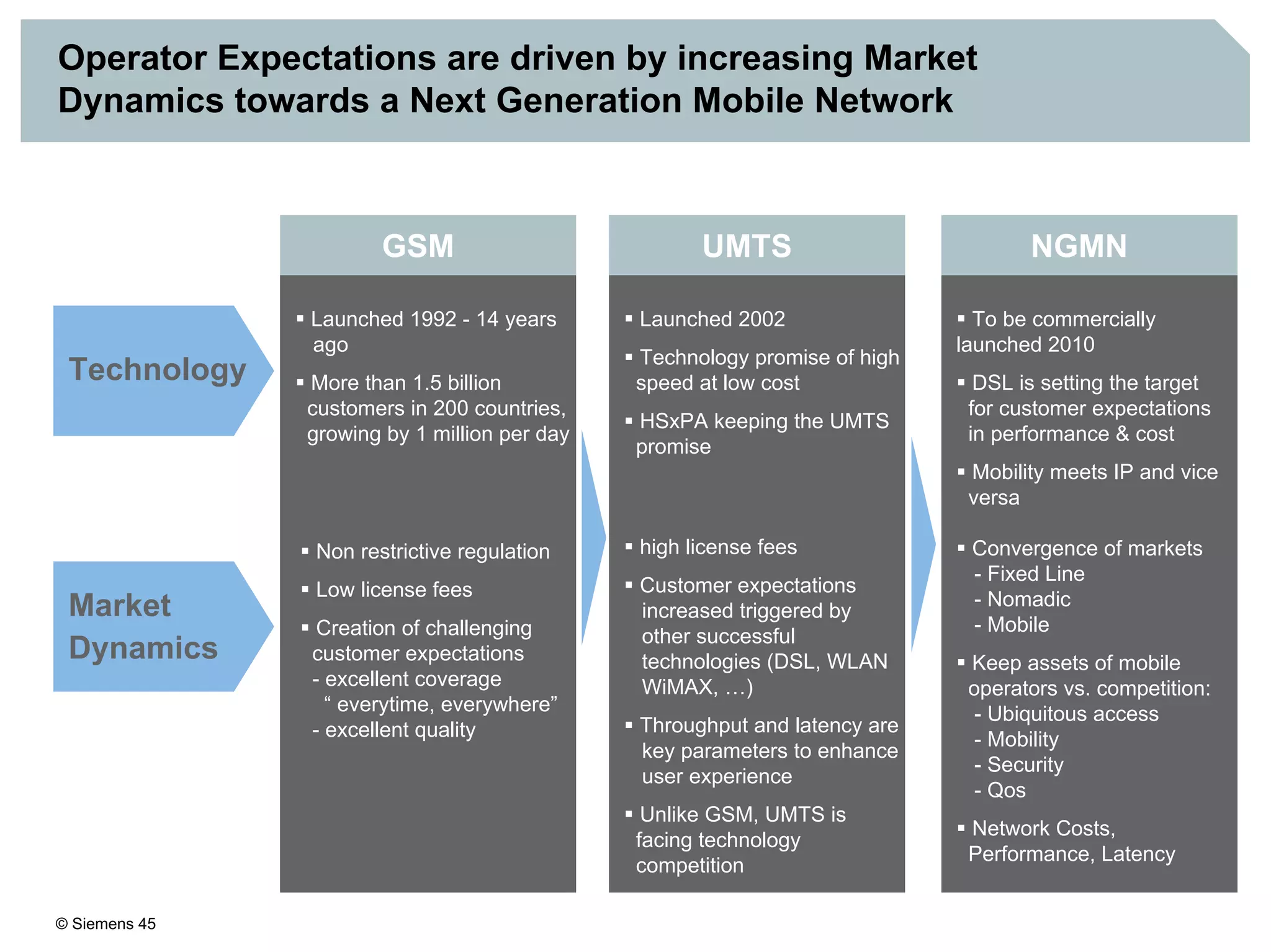
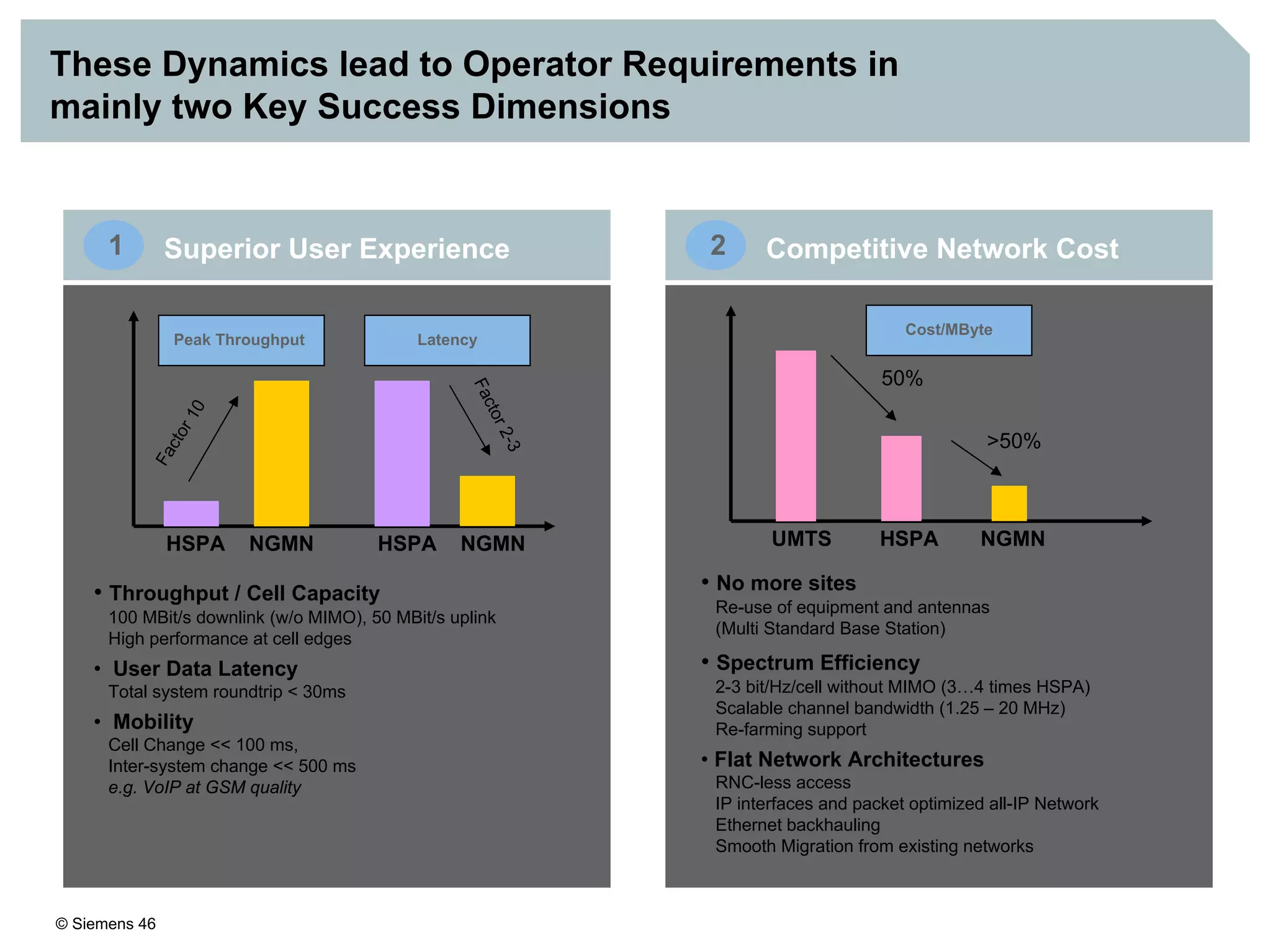
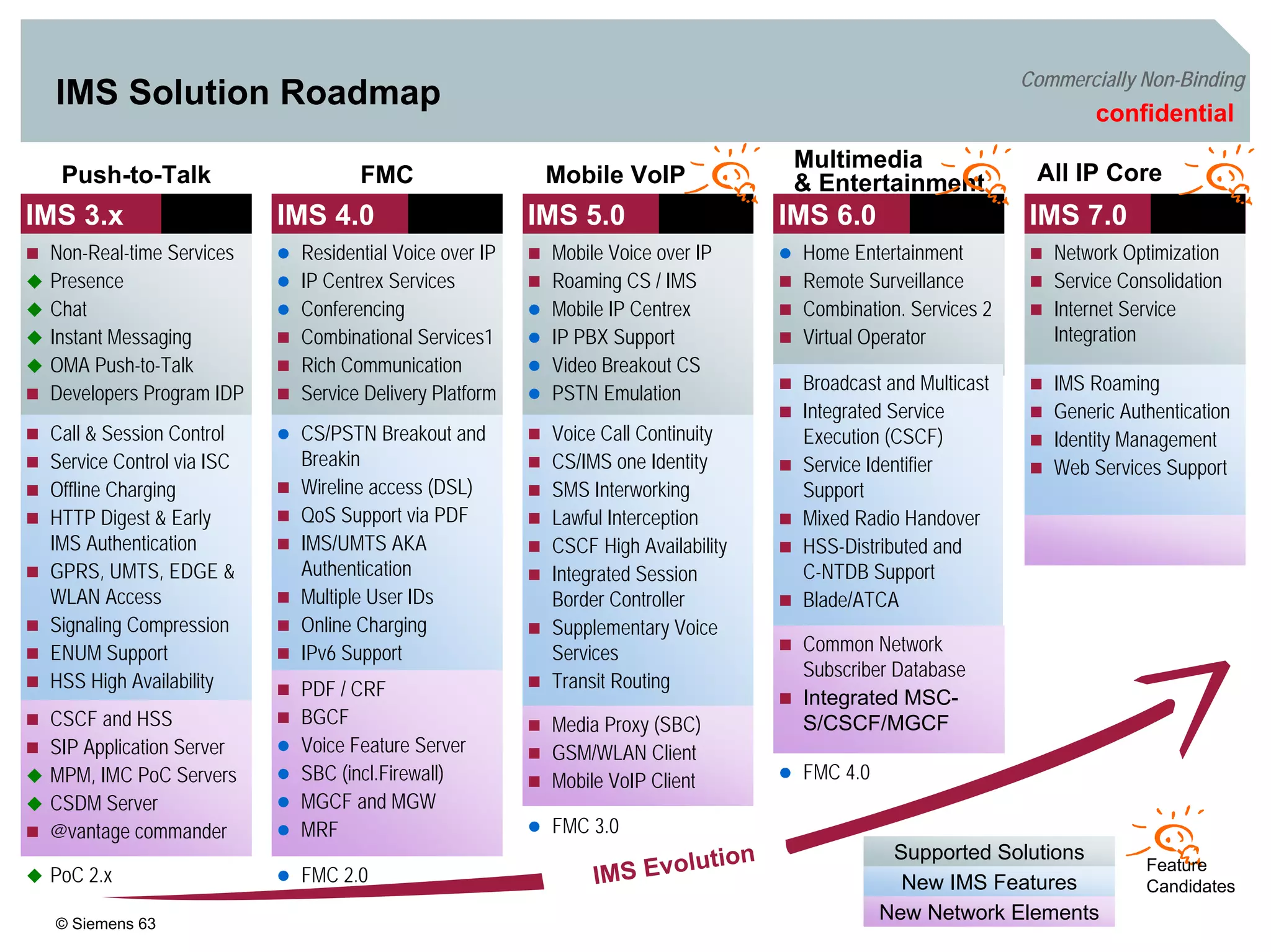
2. It discusses IMS standards and the migration path from Release 4 to Release 5. Future releases will enhance interworking, services, and access types.
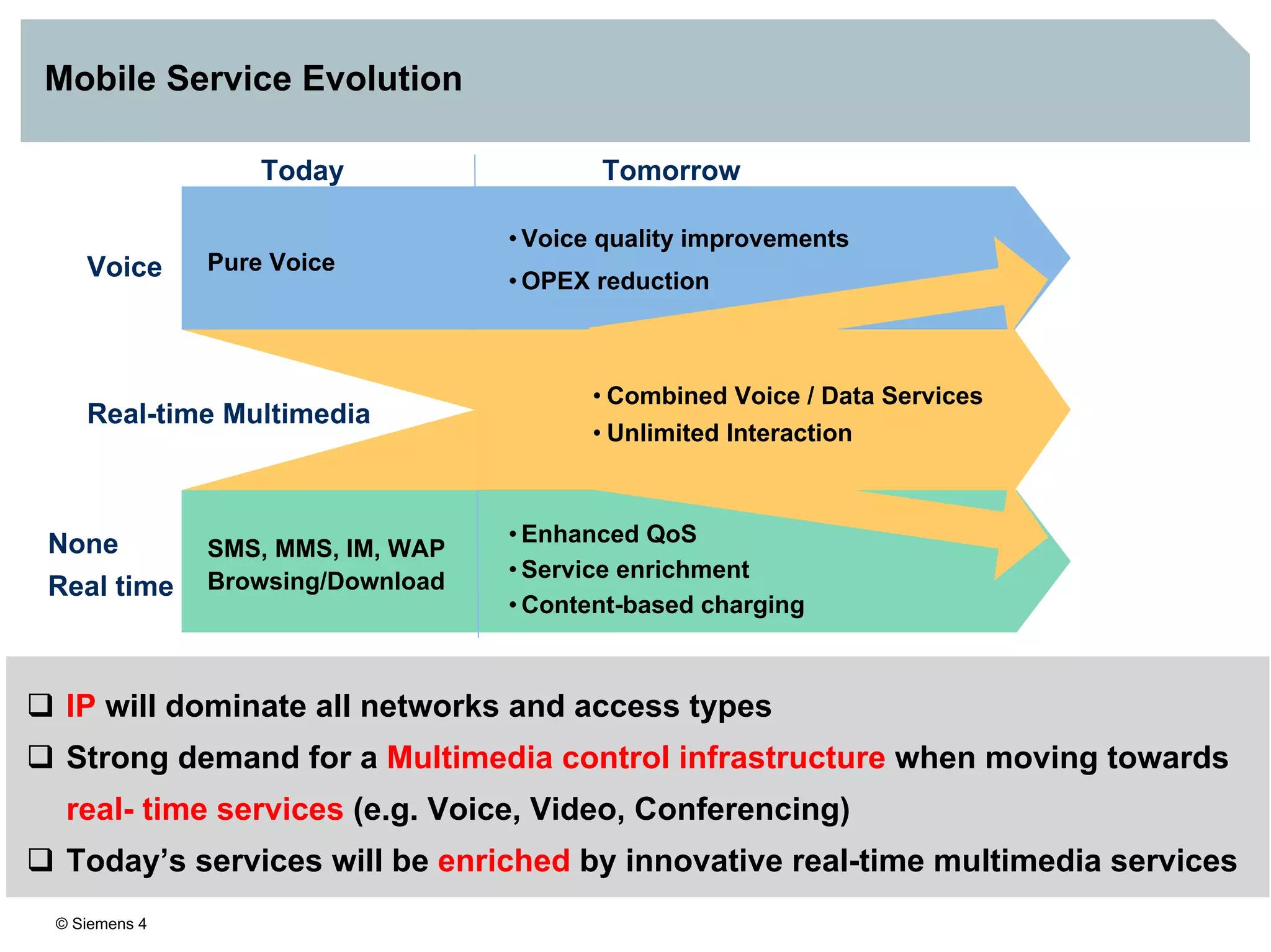
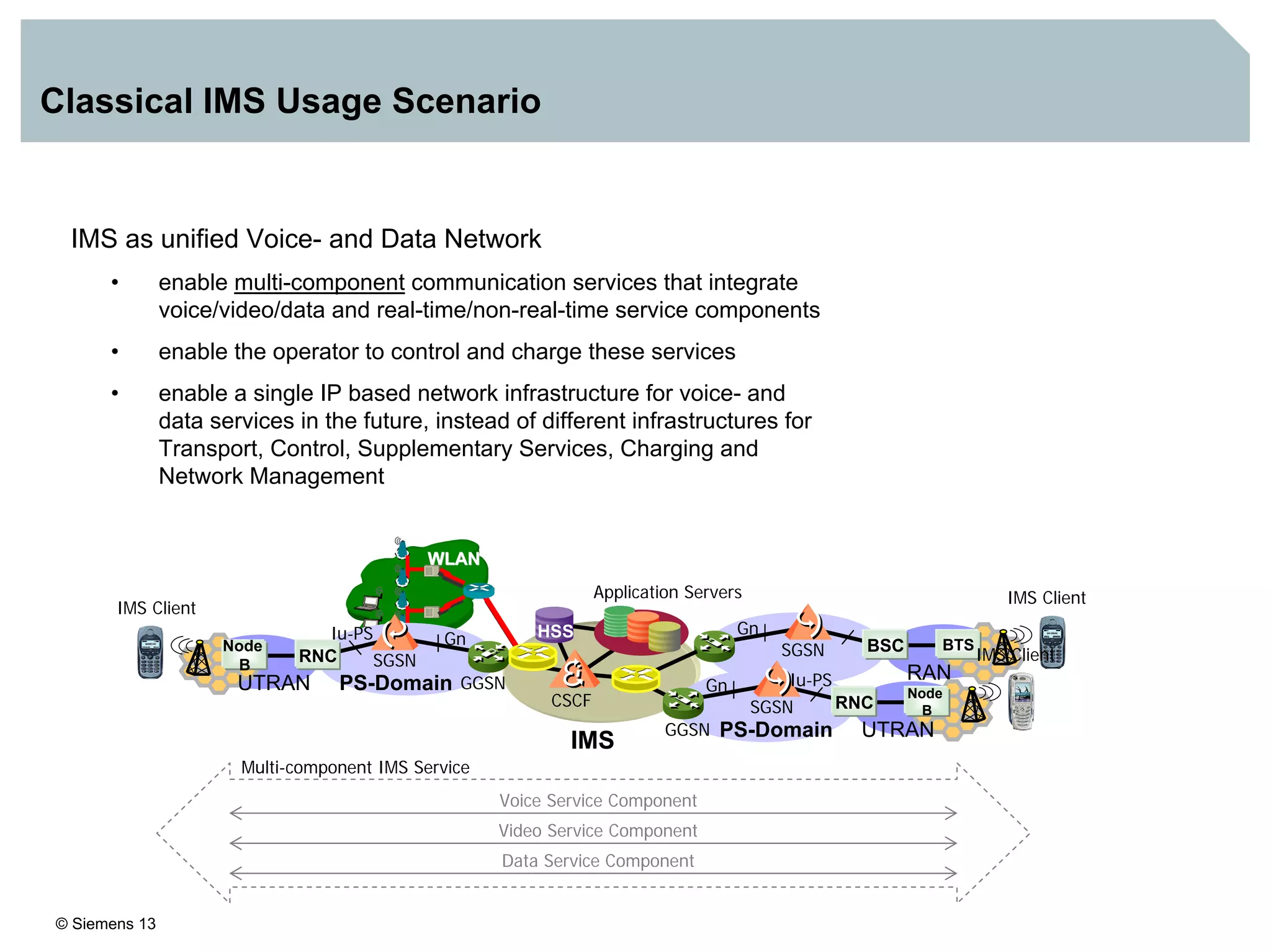
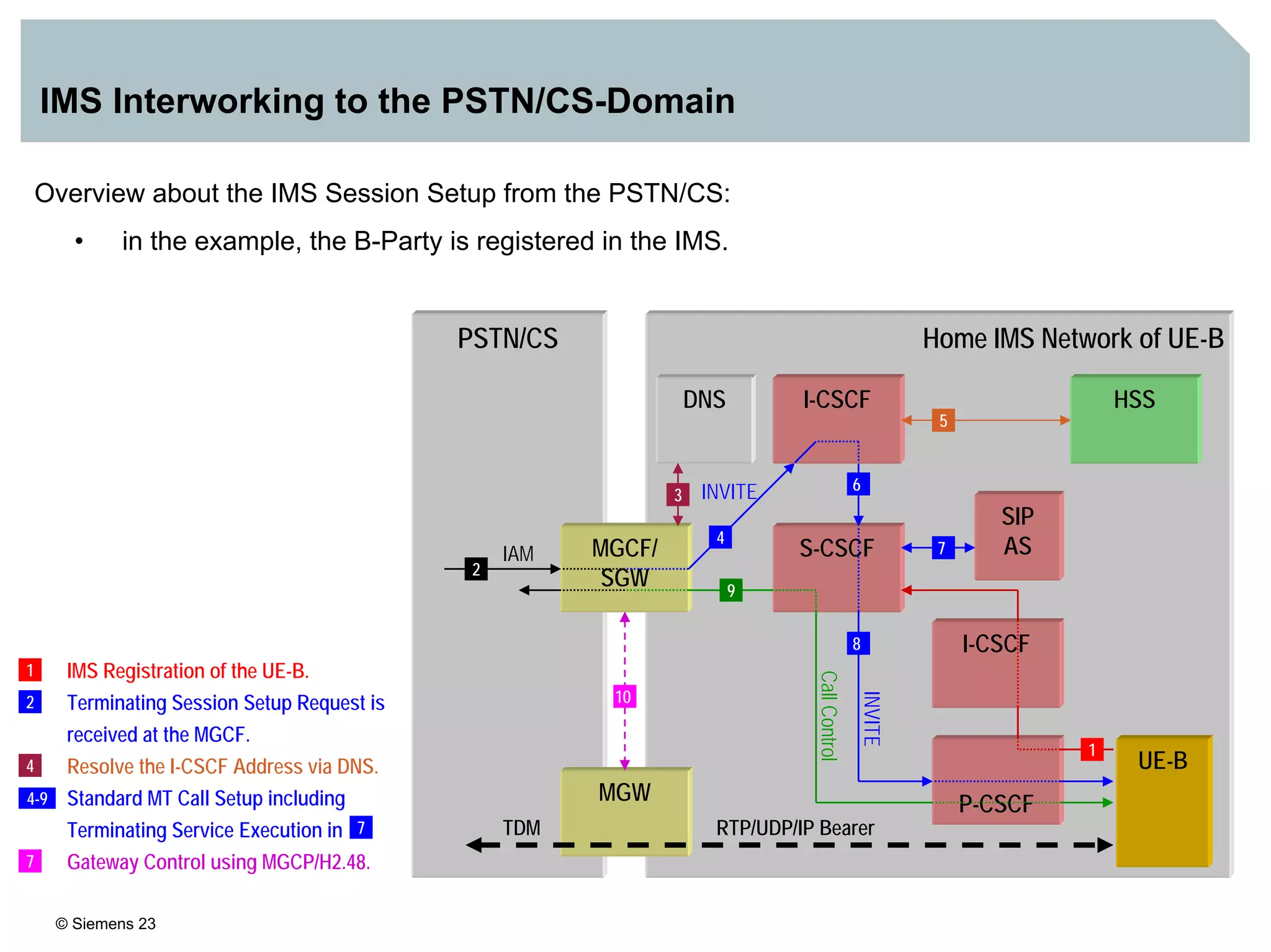
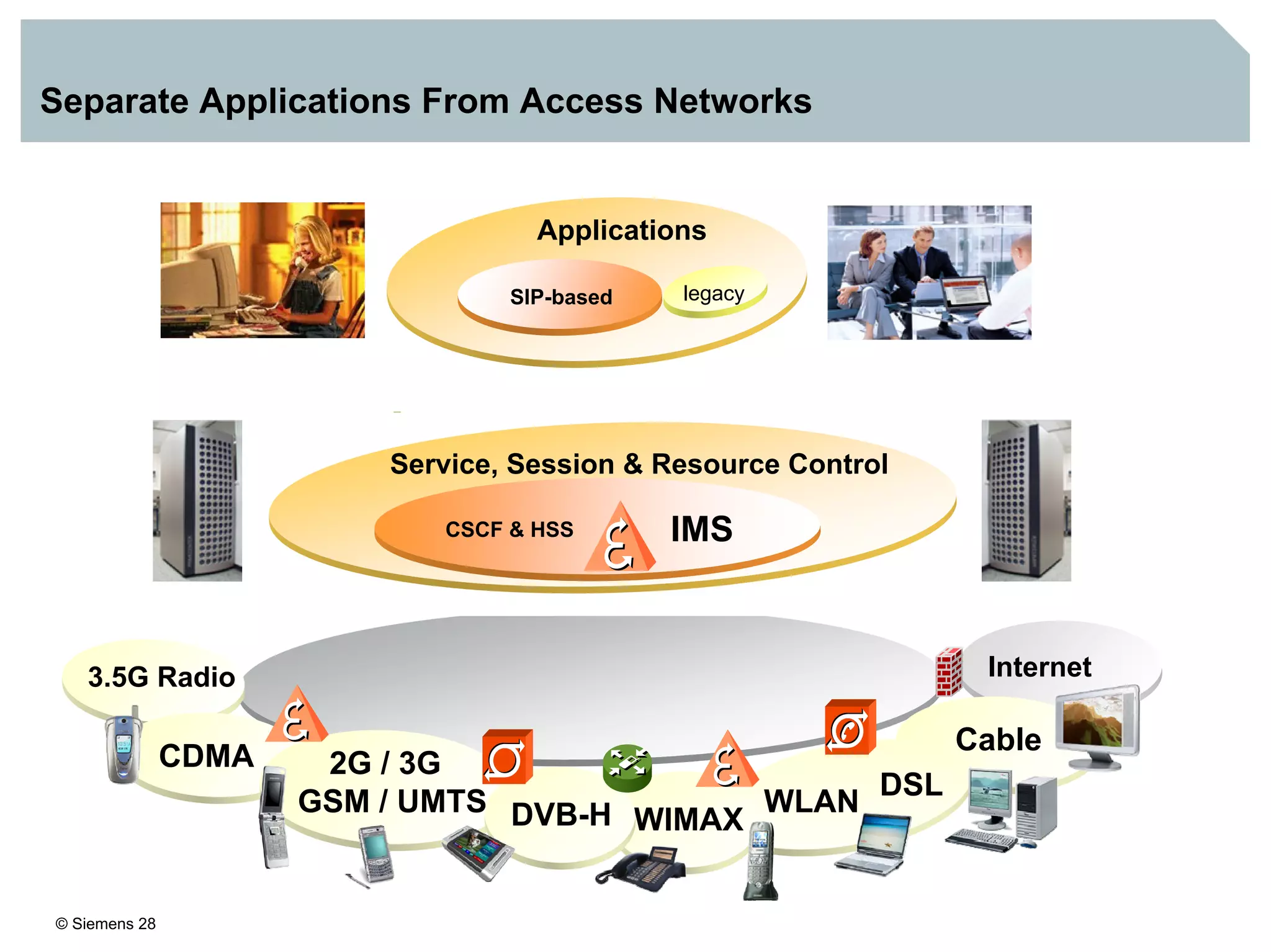
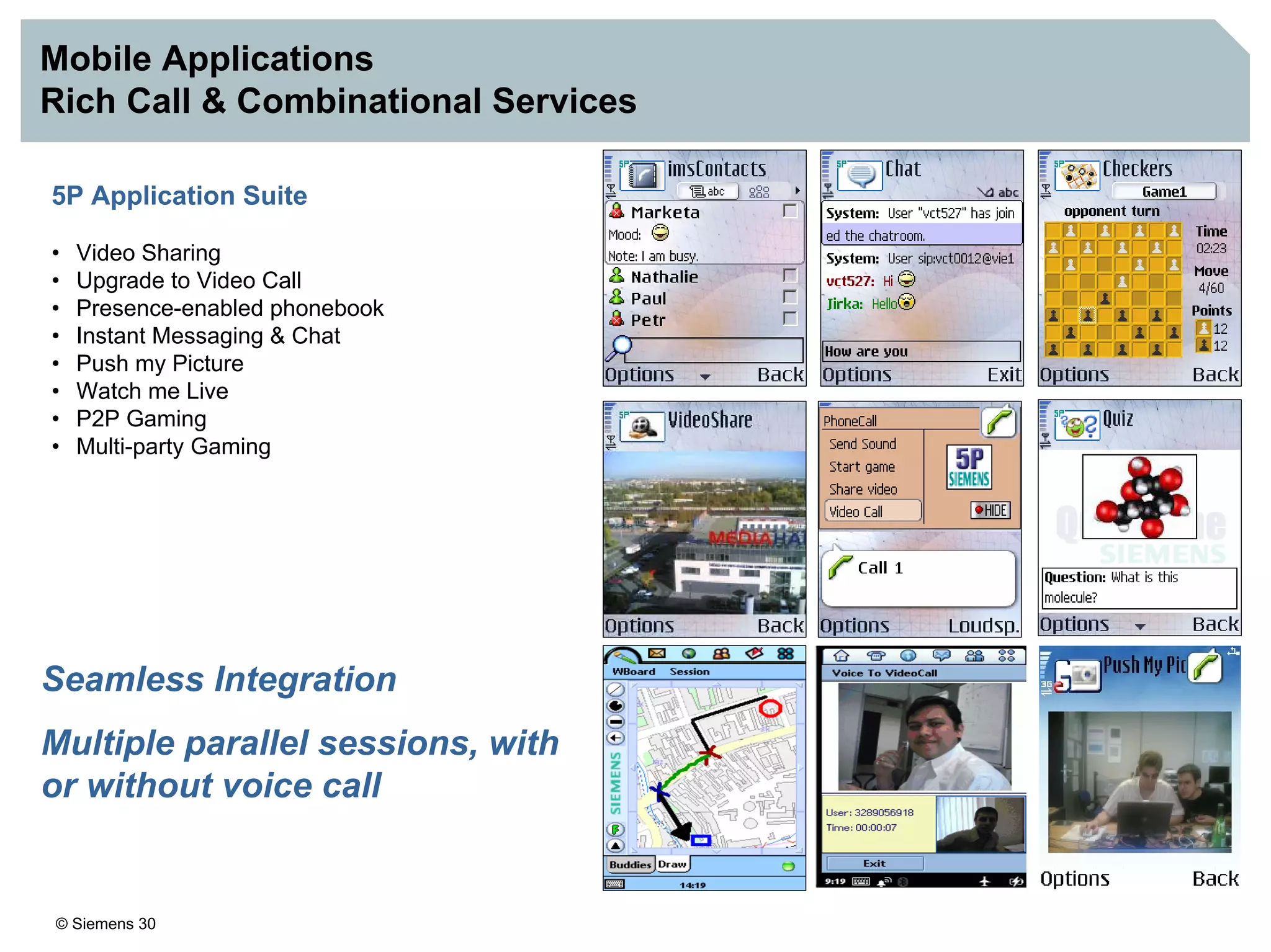
3. IMS provides an IP-based control infrastructure for combining voice, video, and real-time multimedia services on a single network.