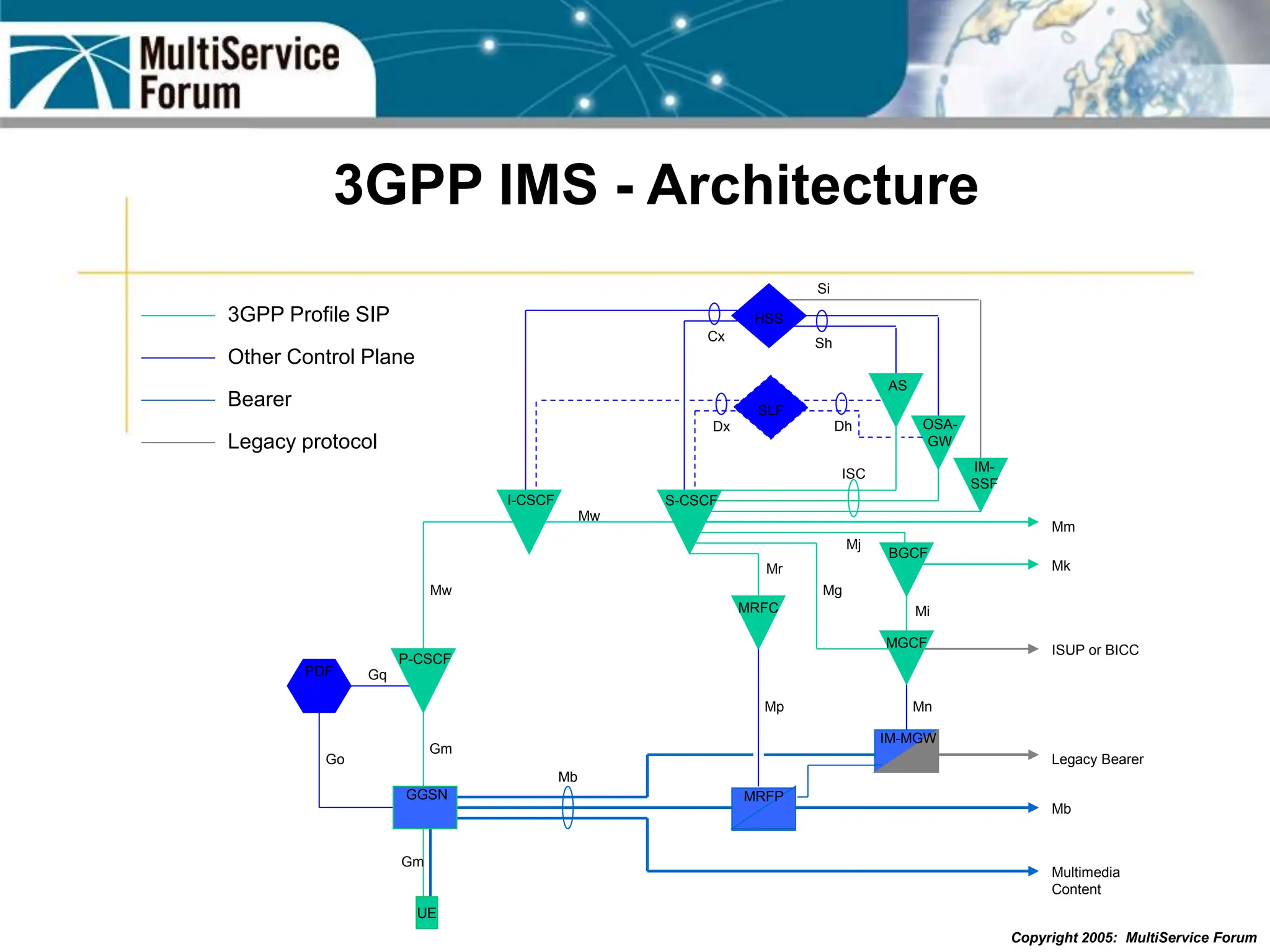
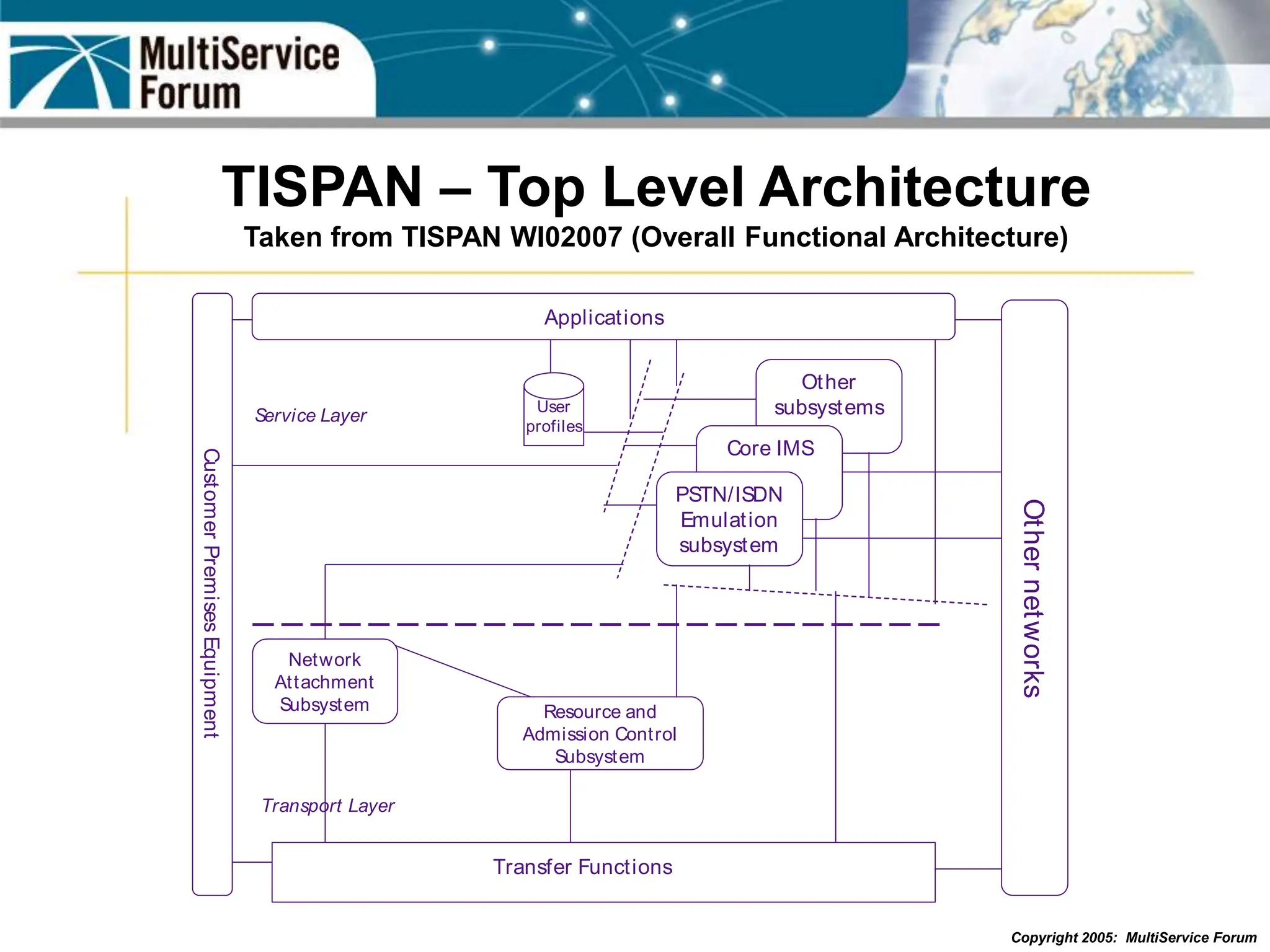
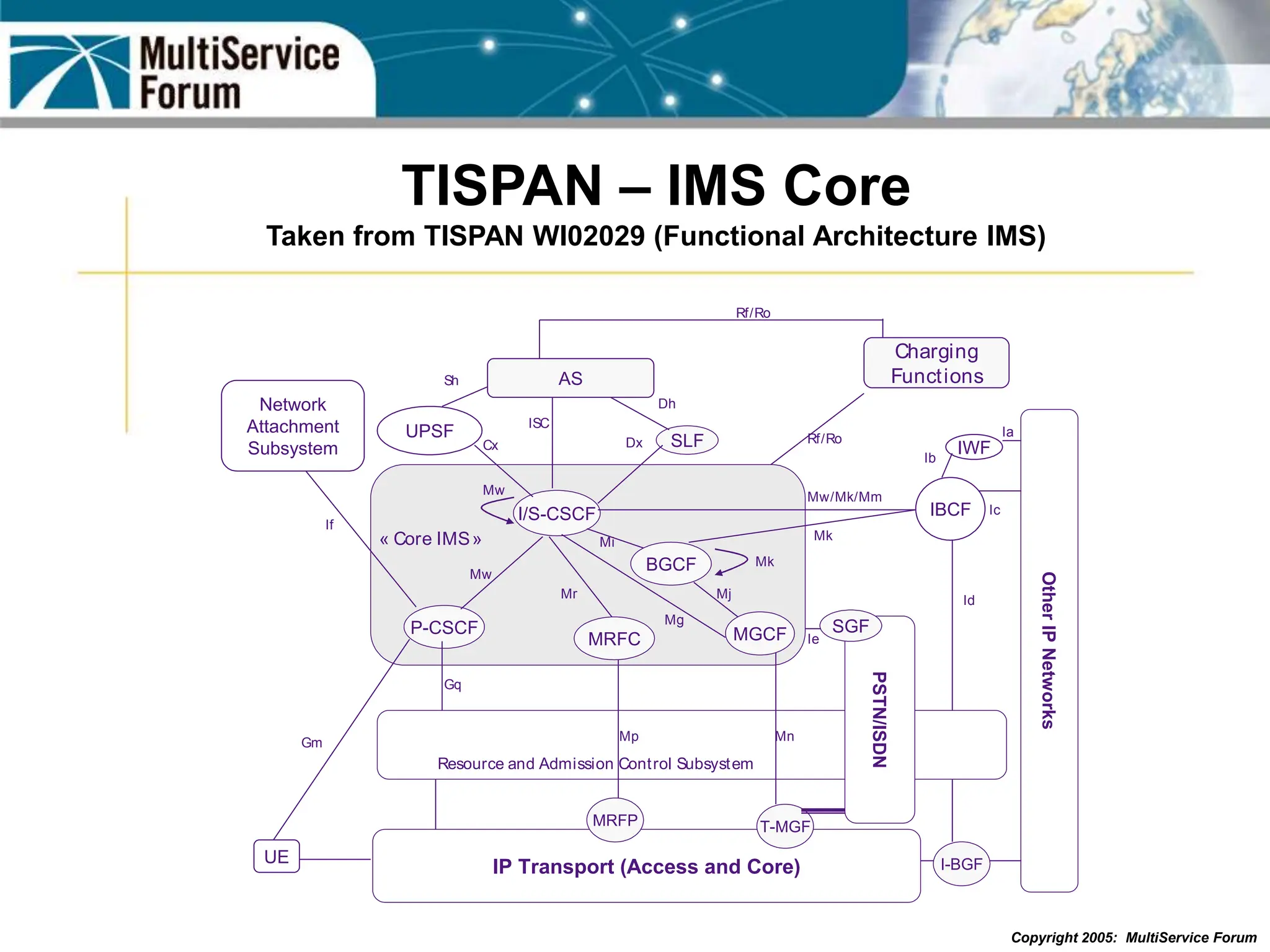
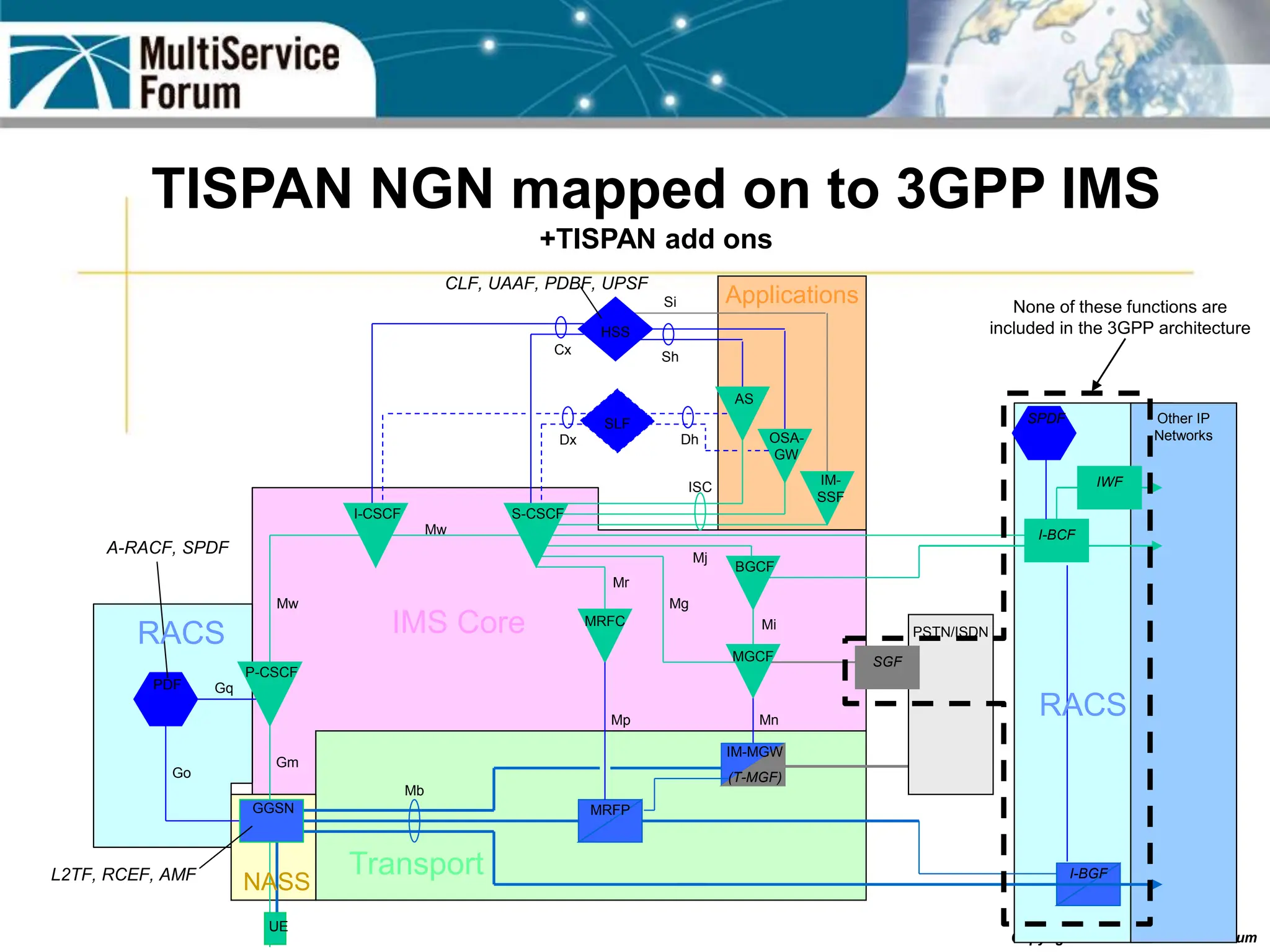
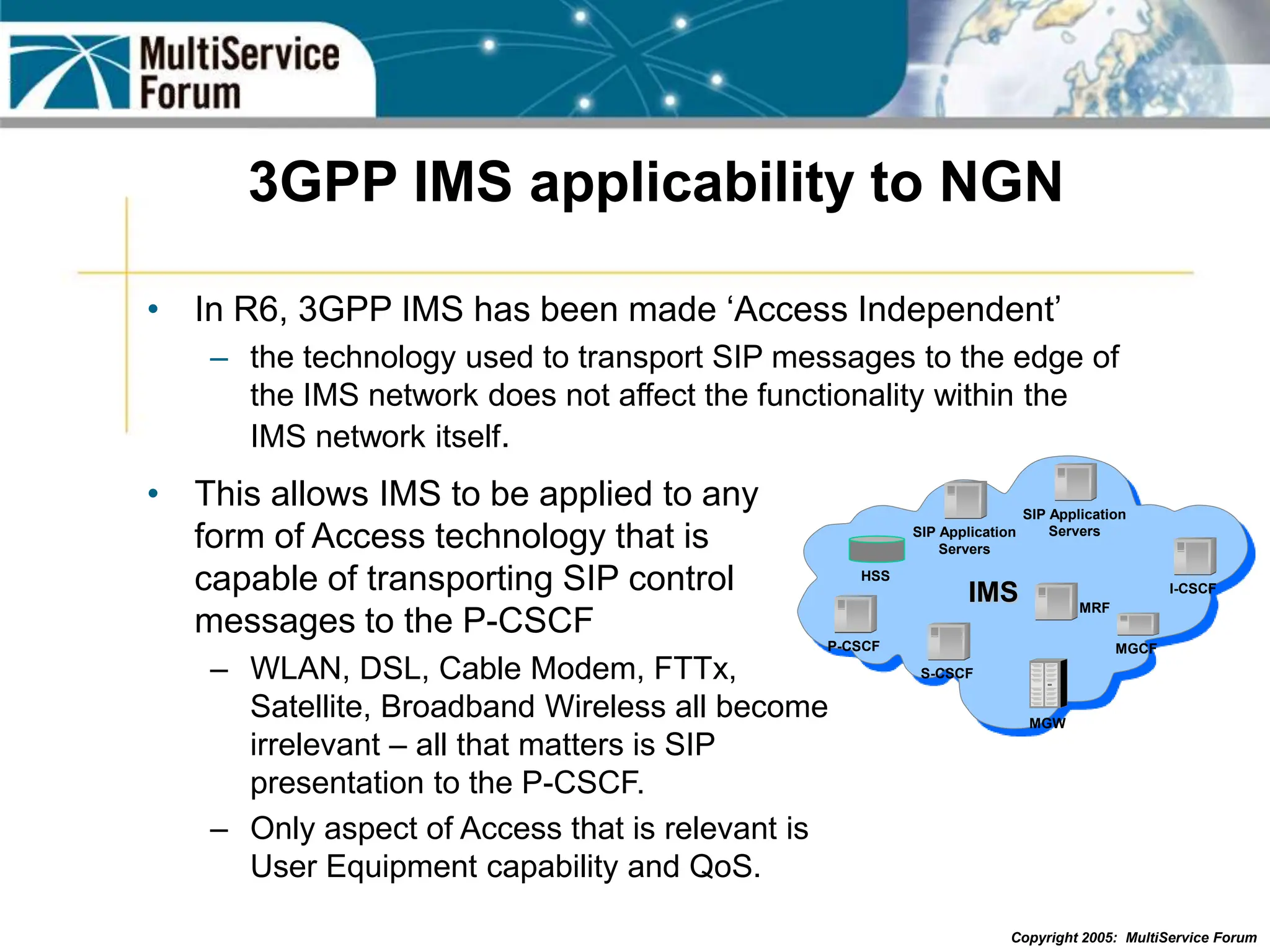
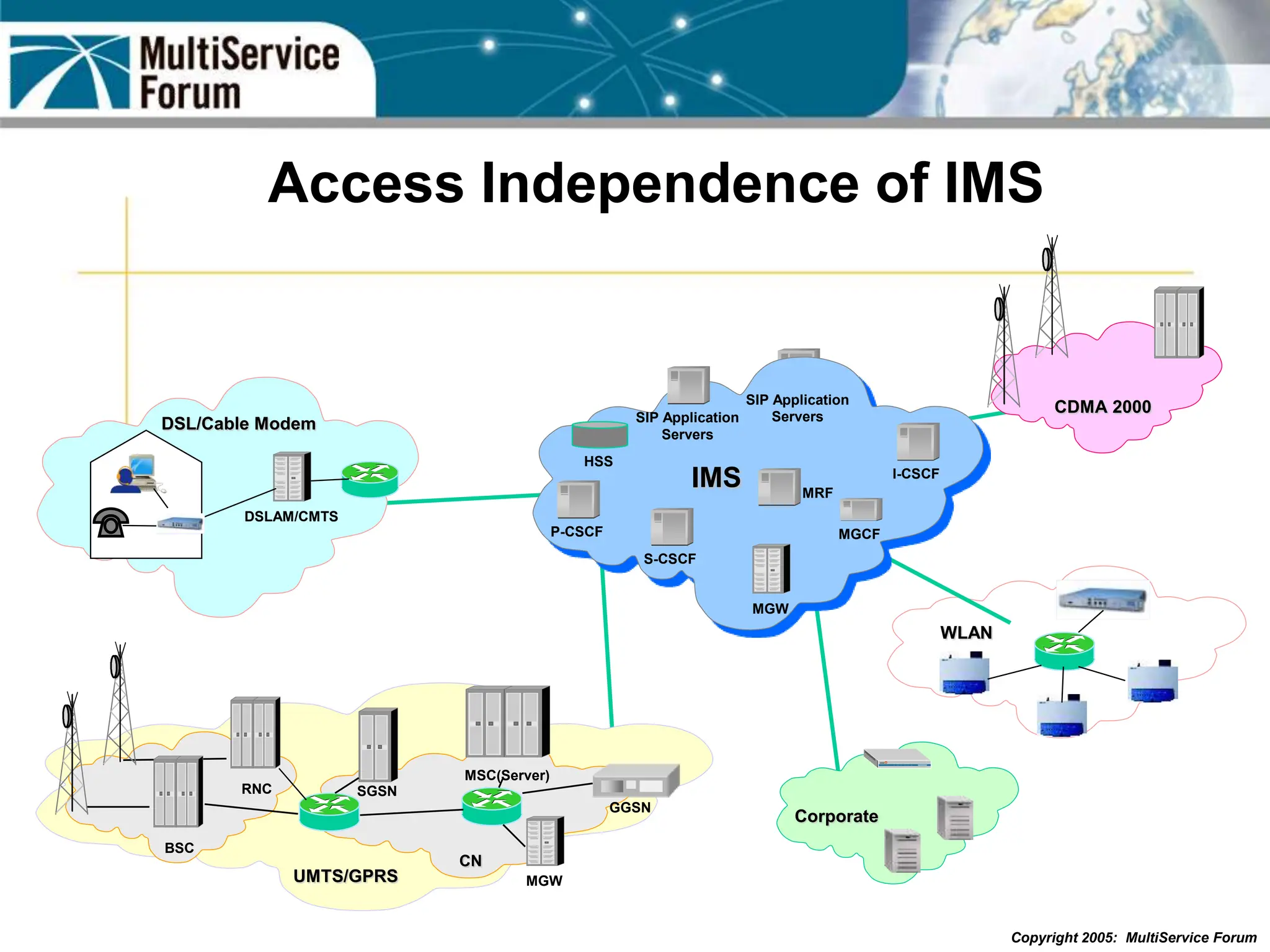
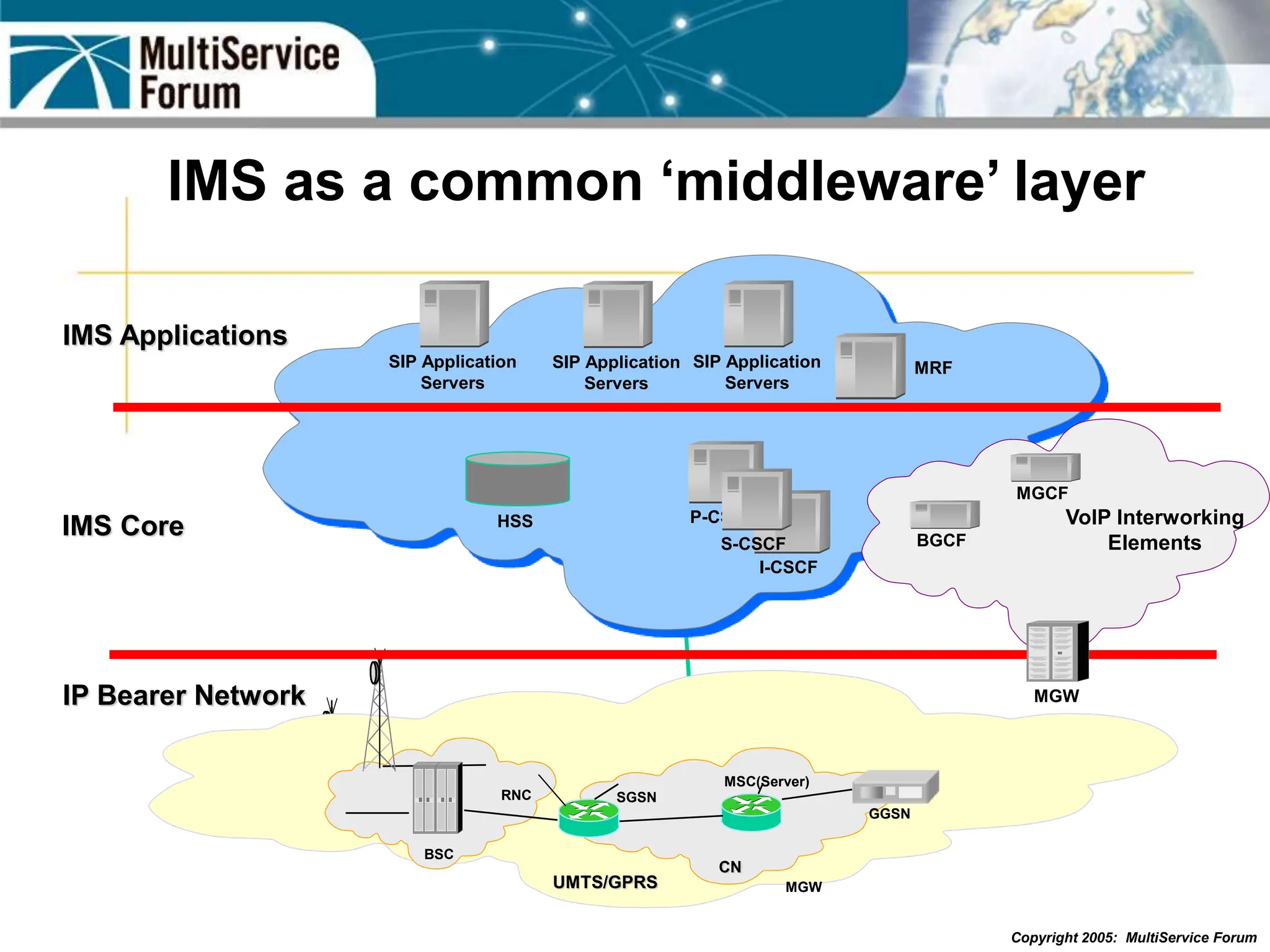
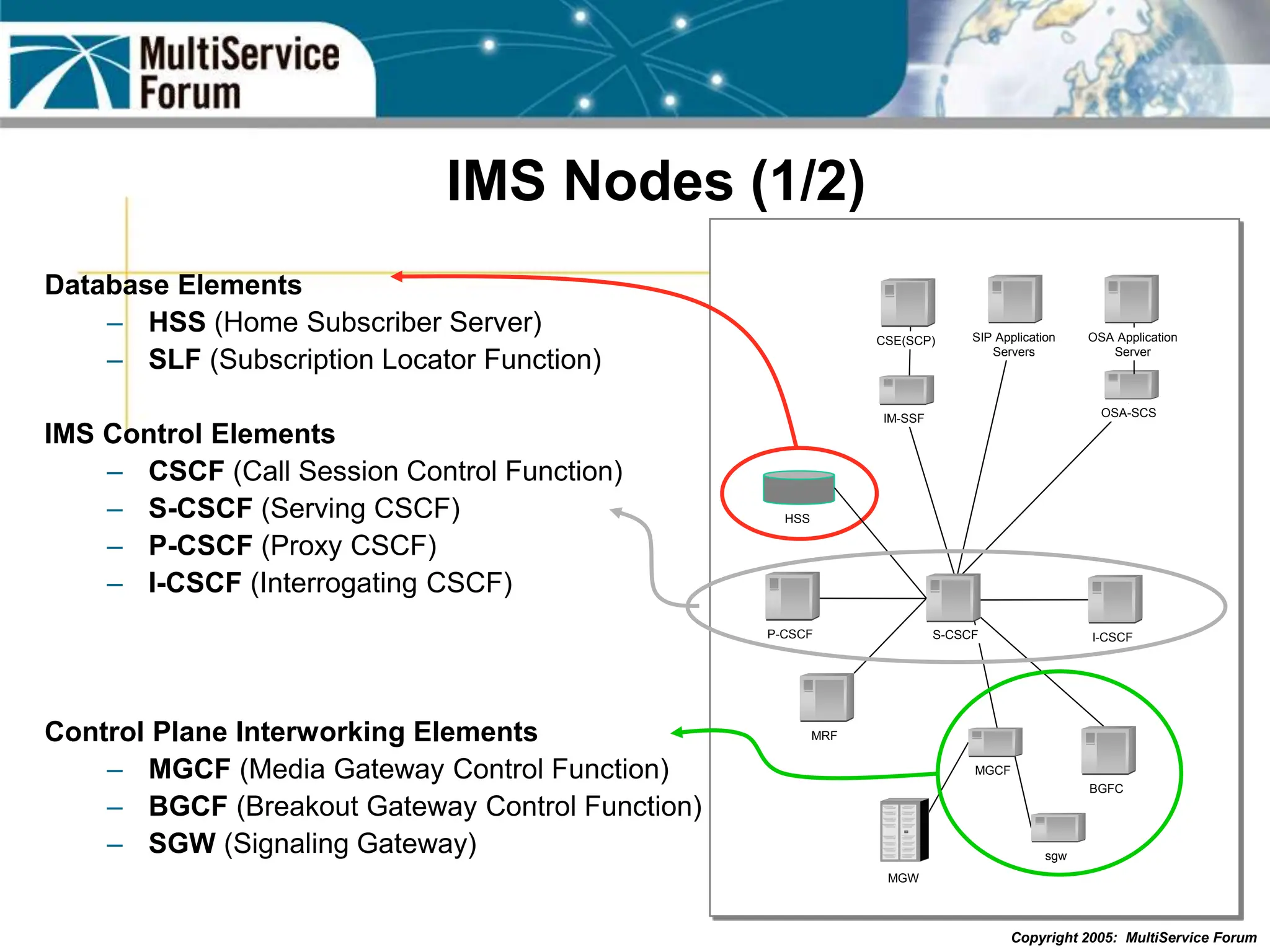
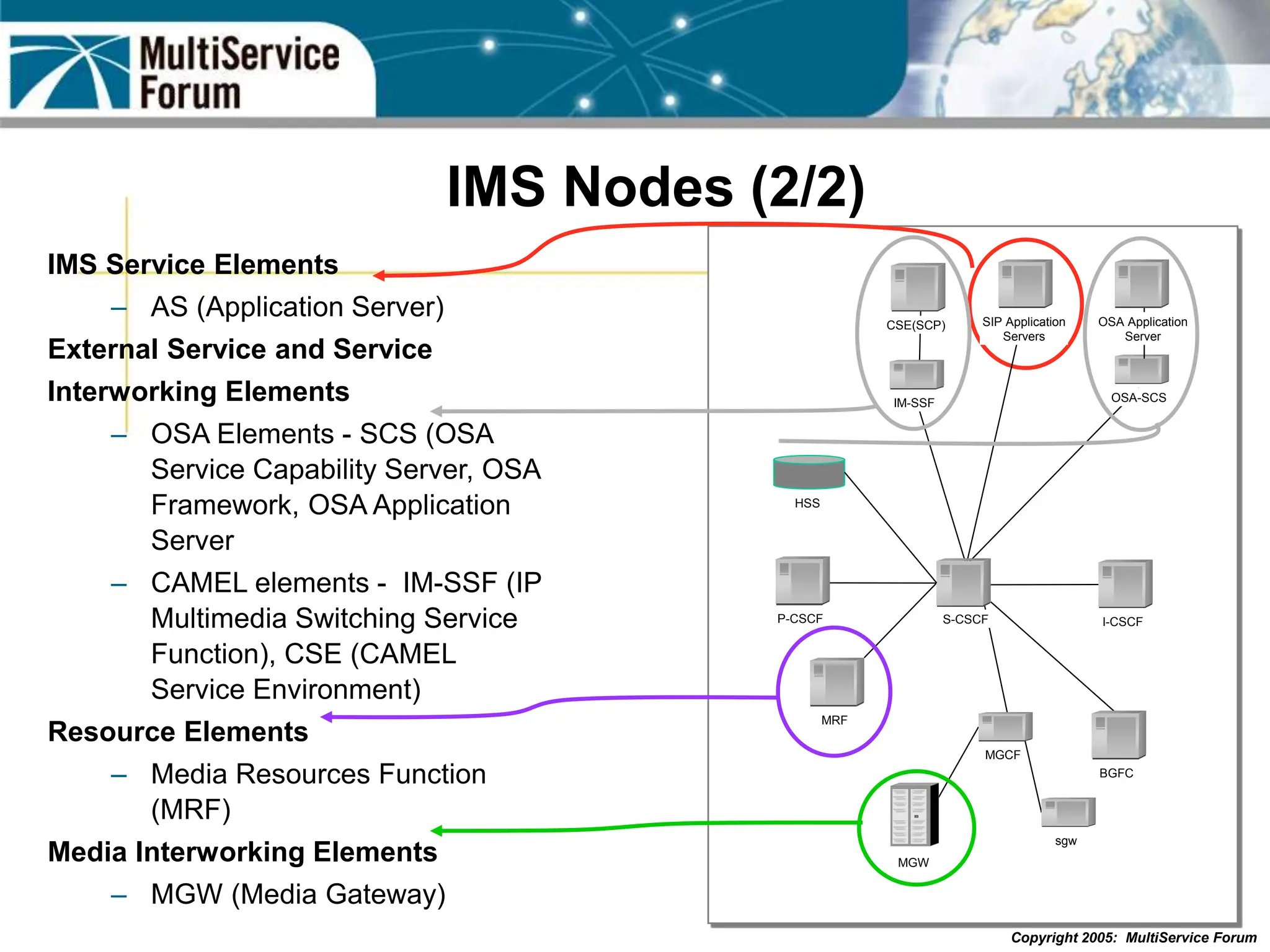
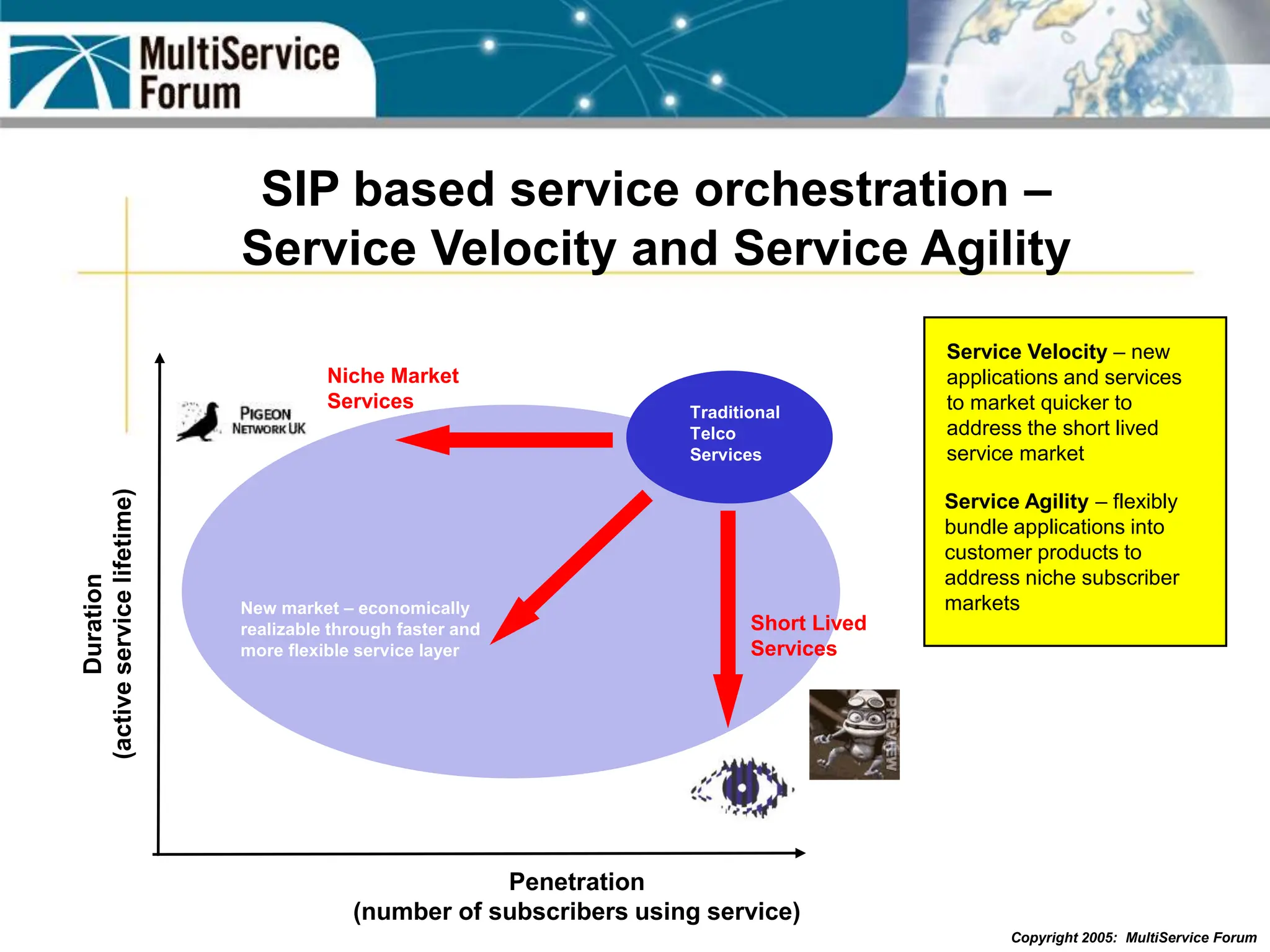
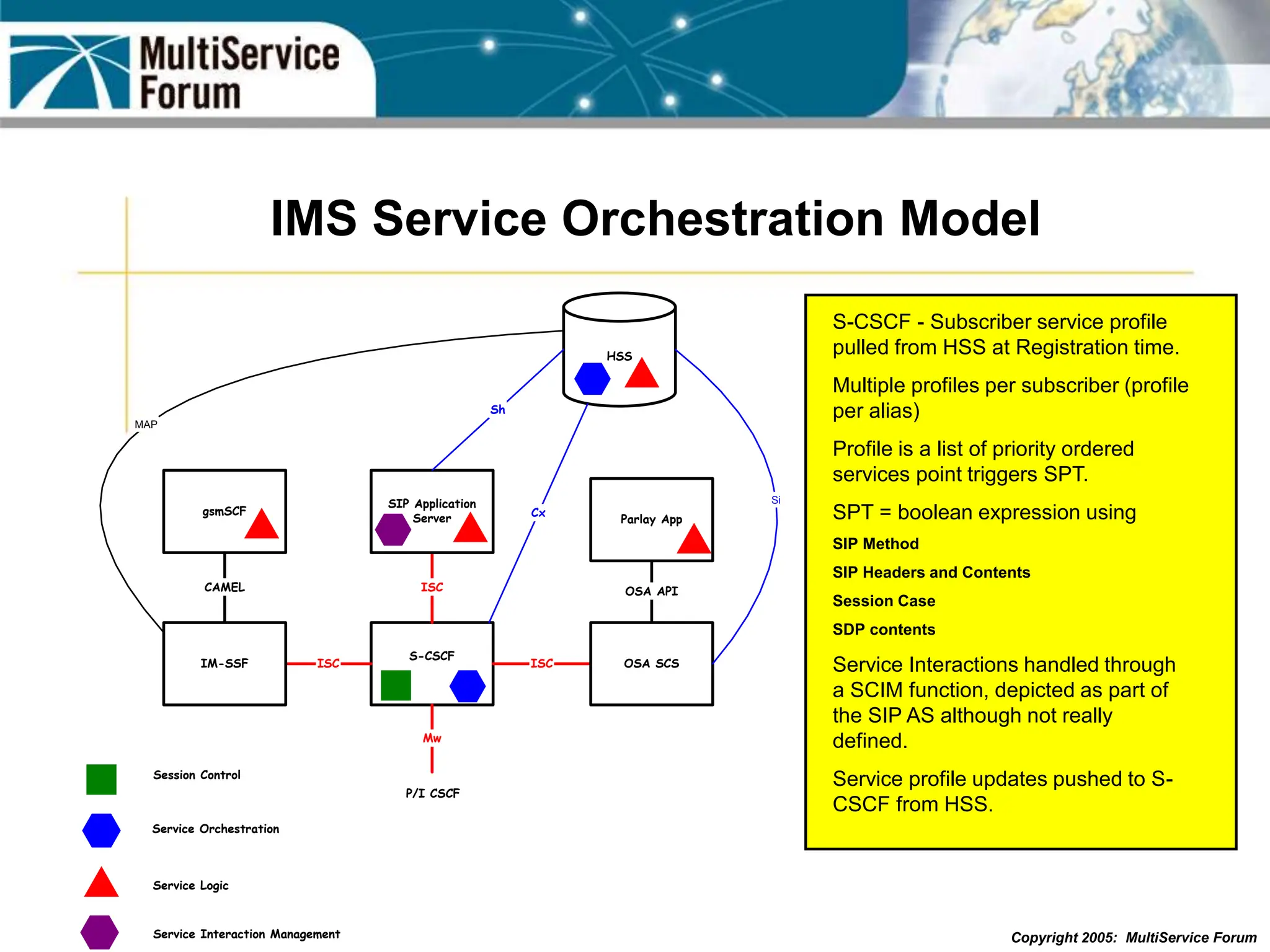
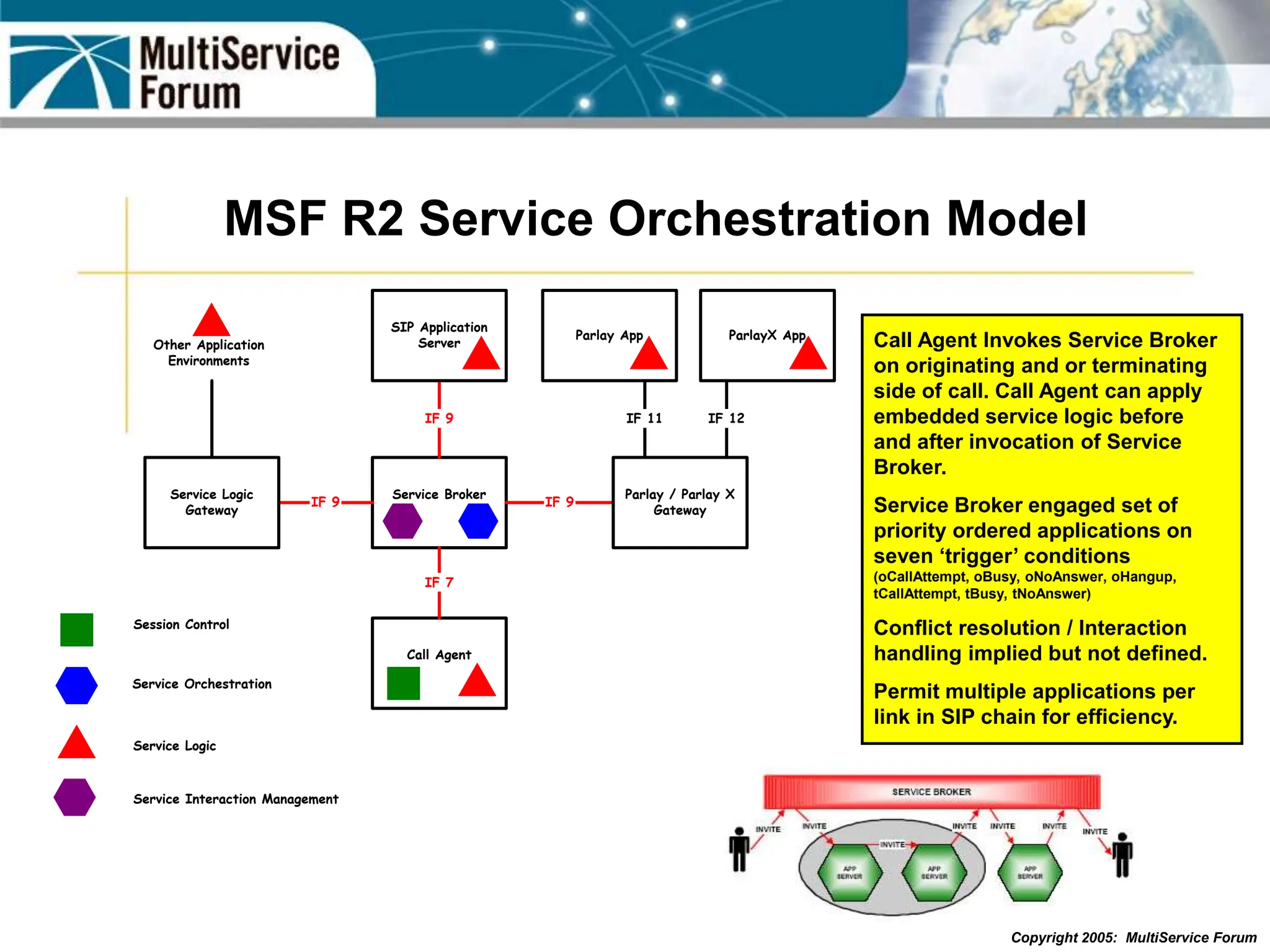
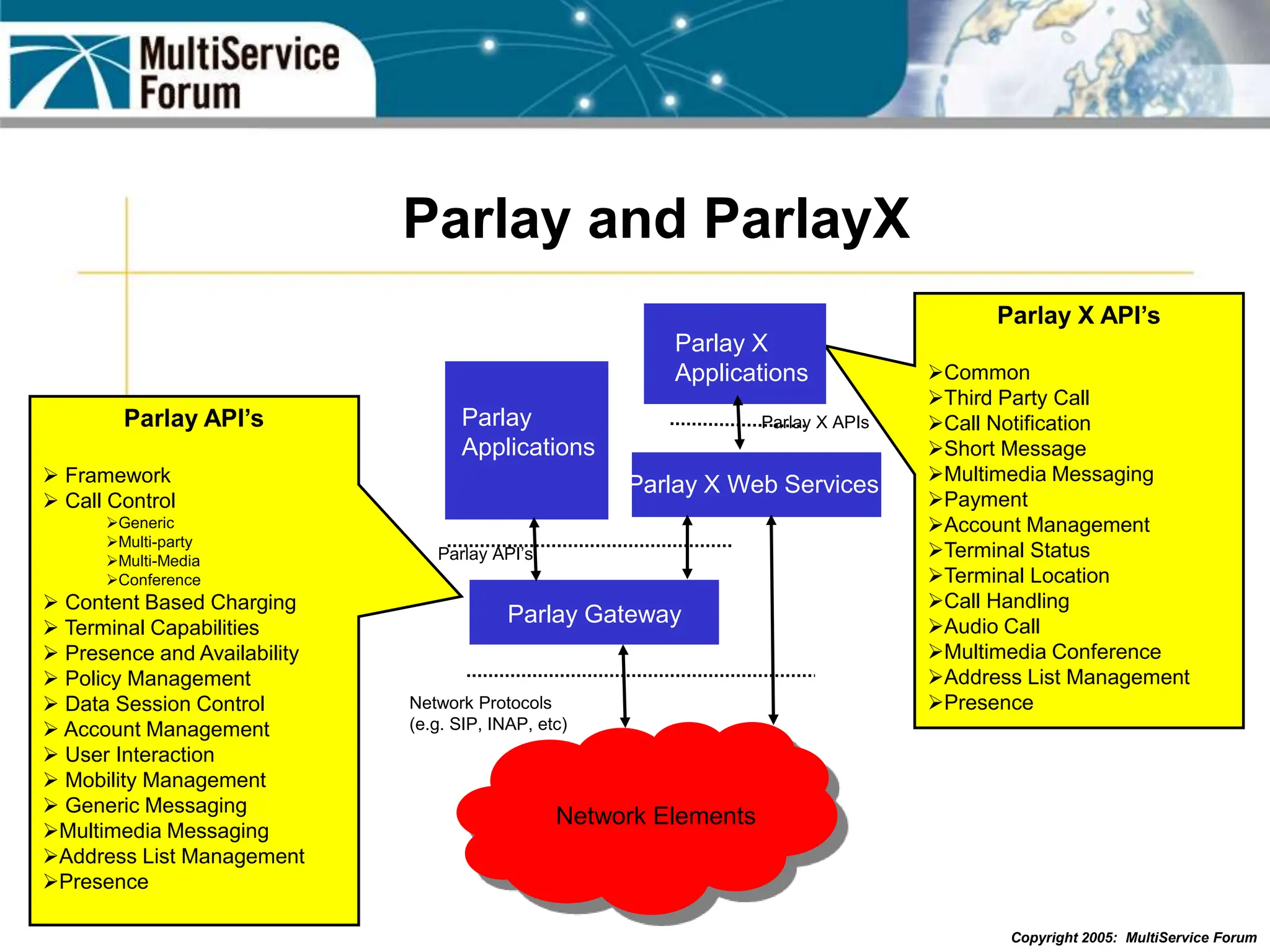
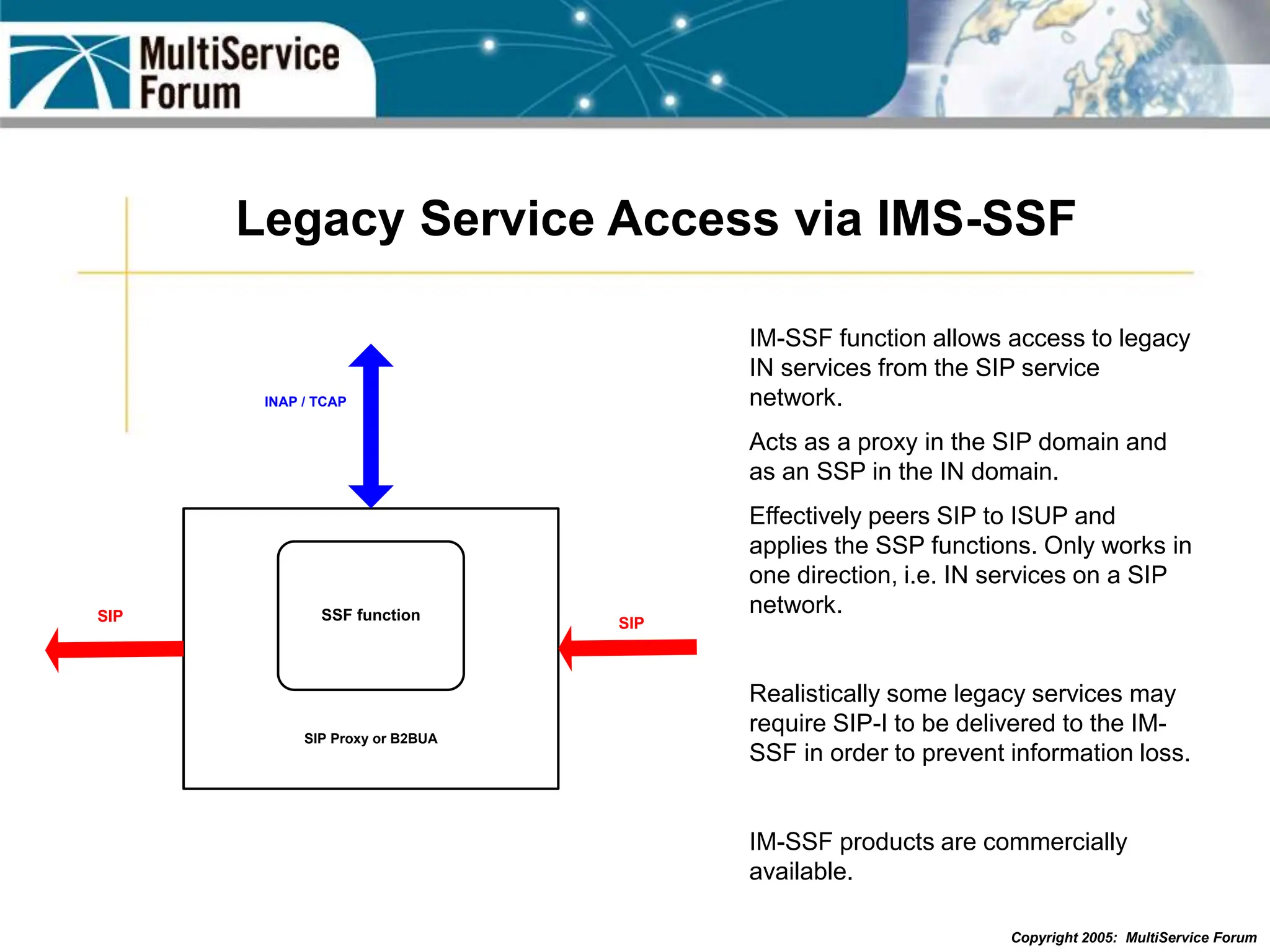
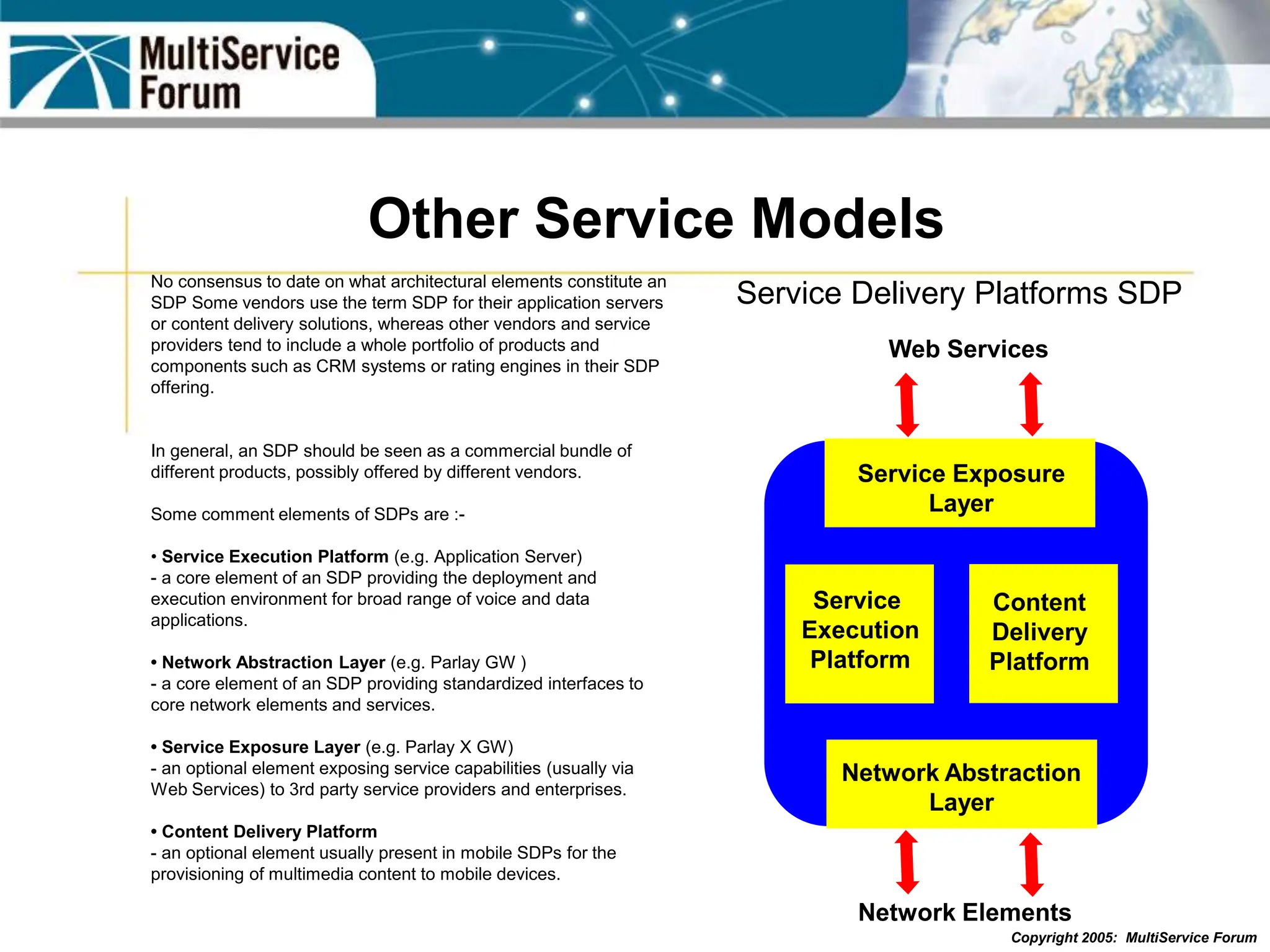
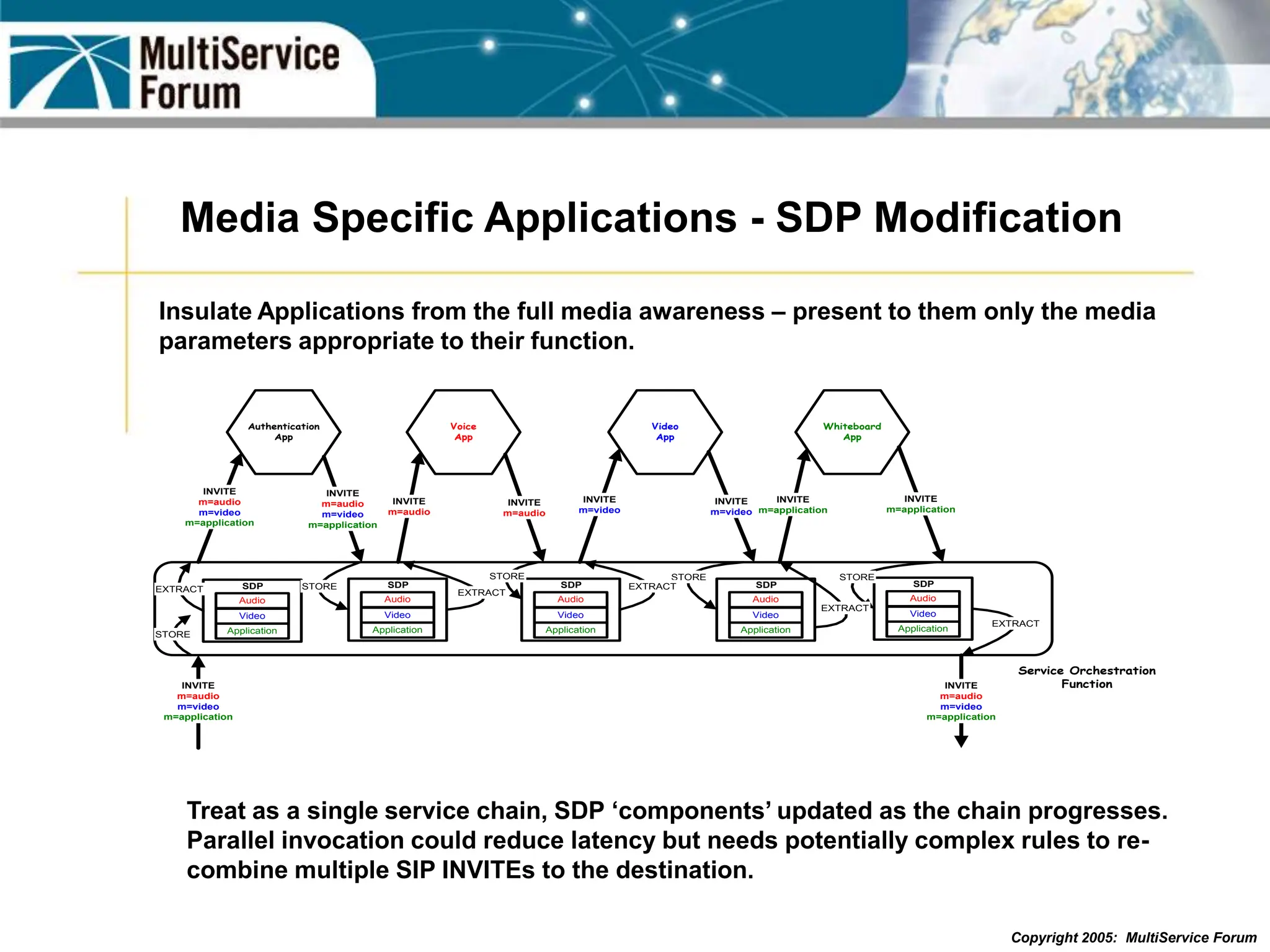
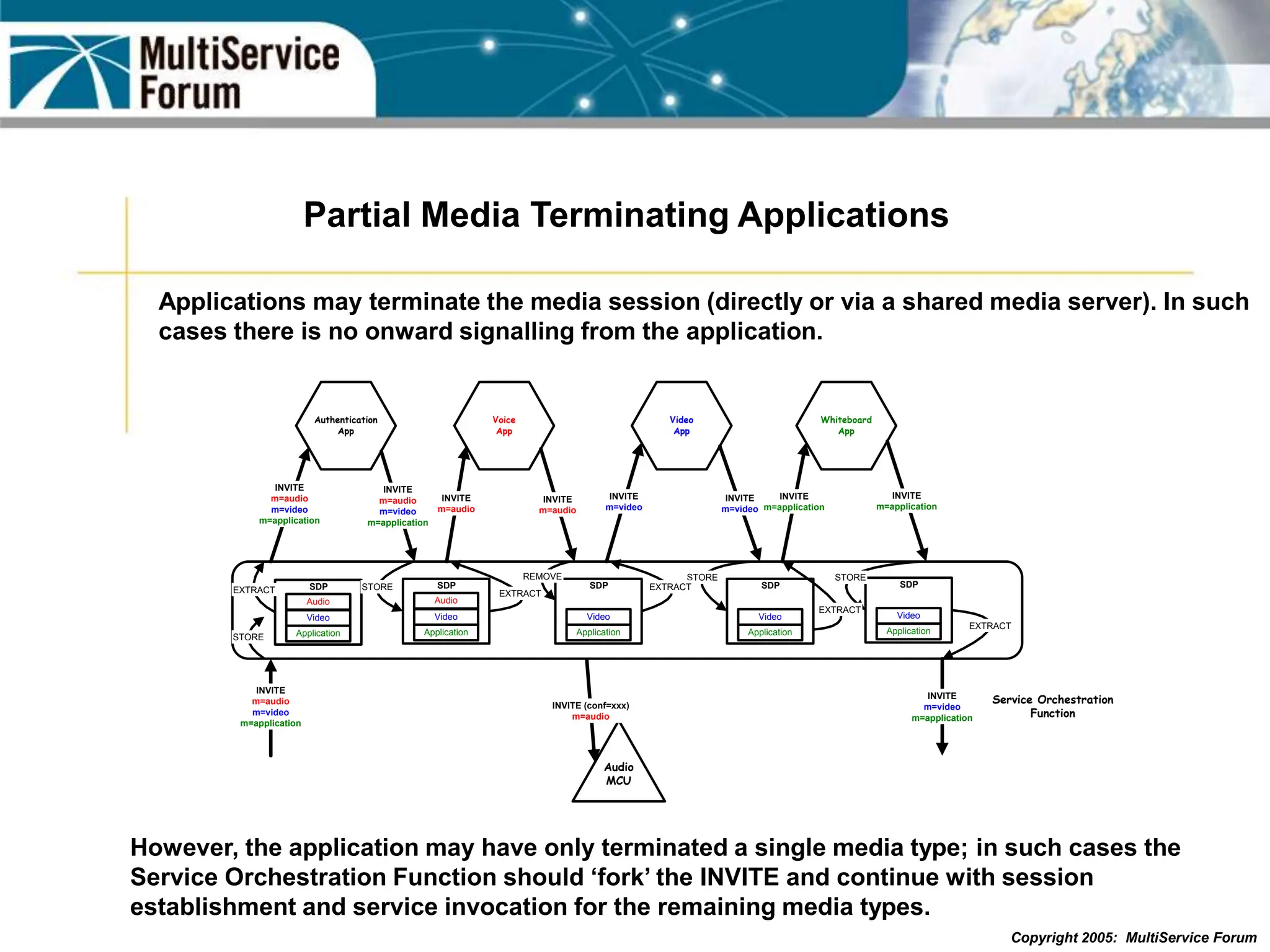
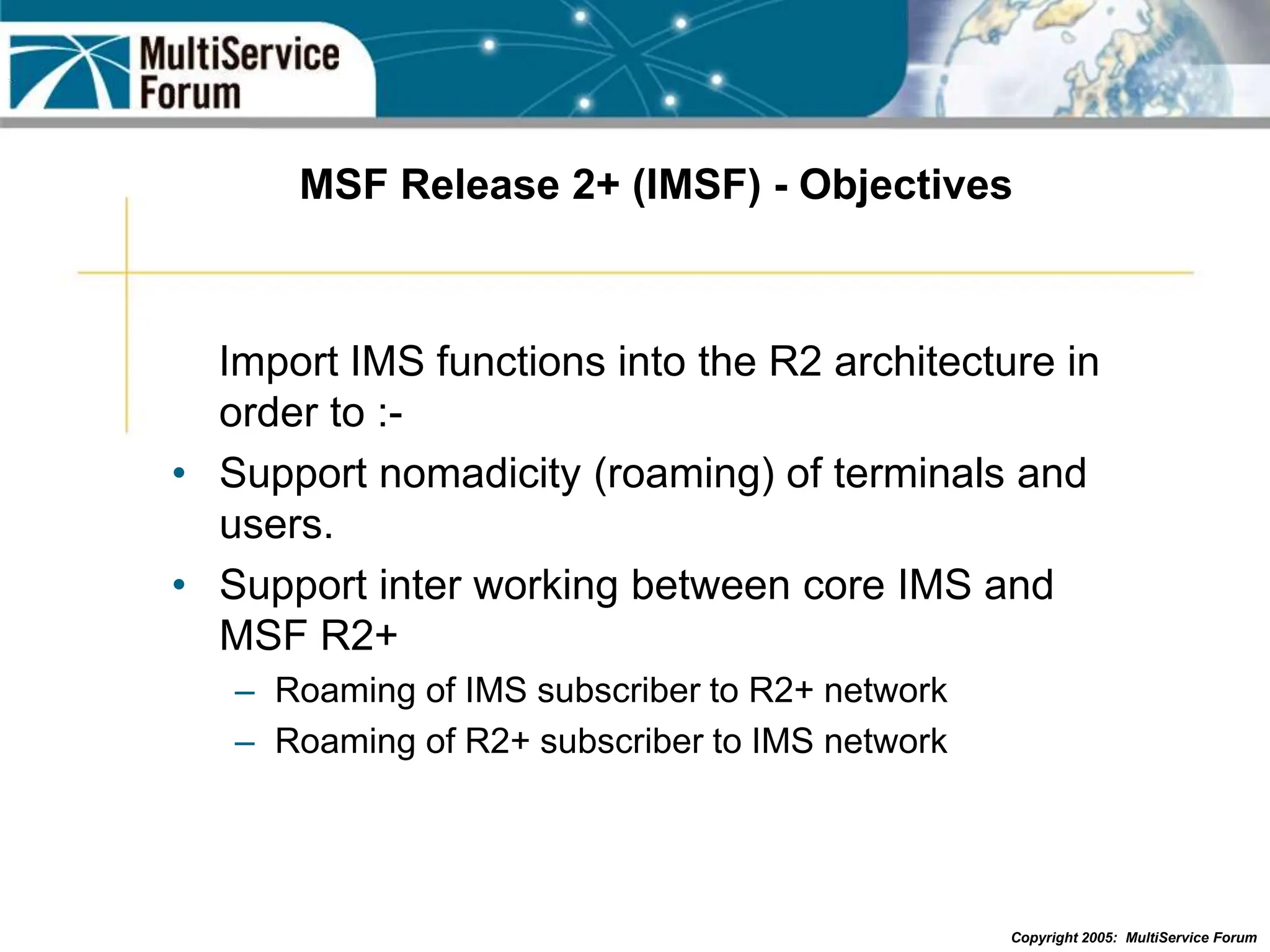
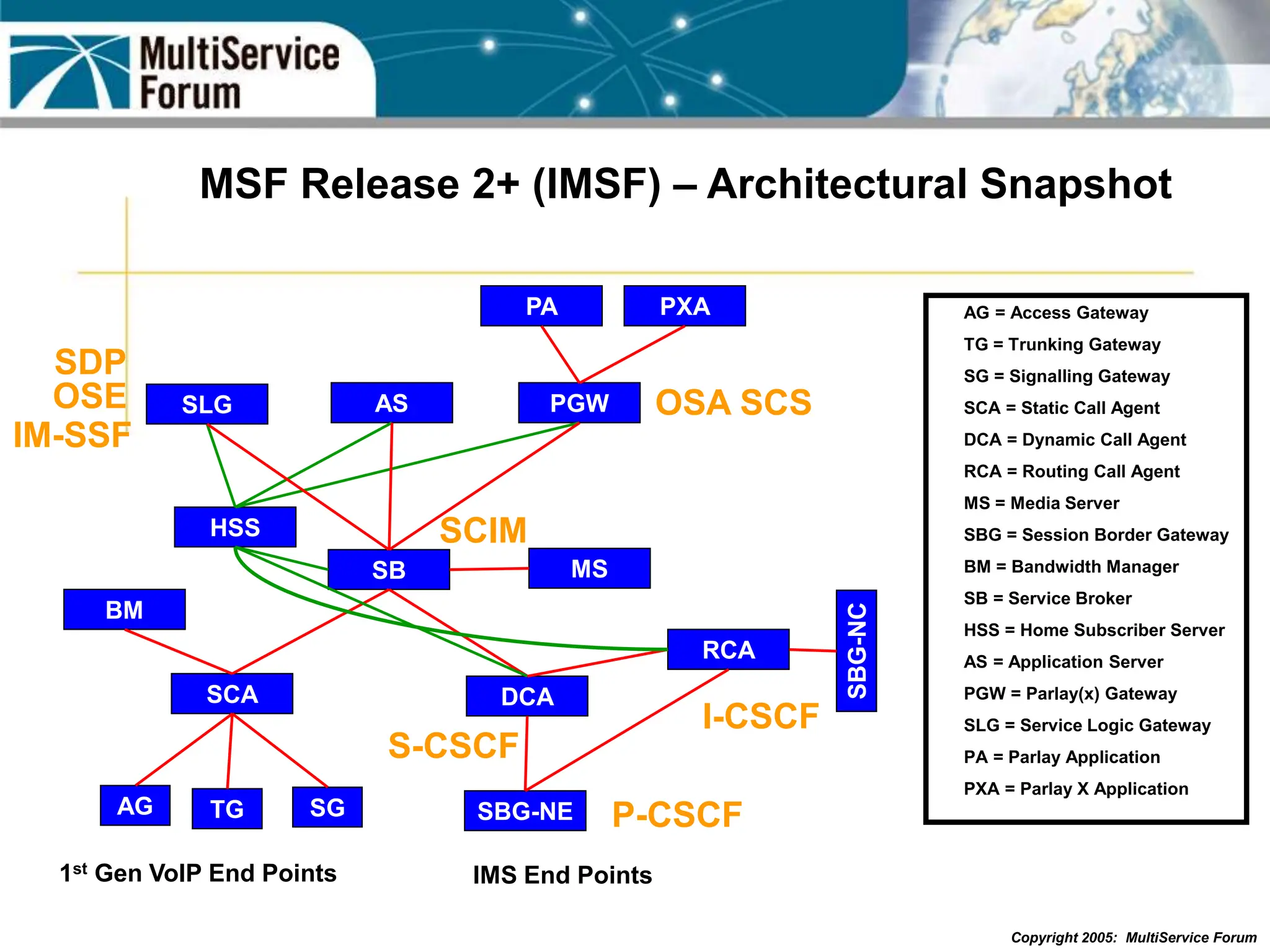
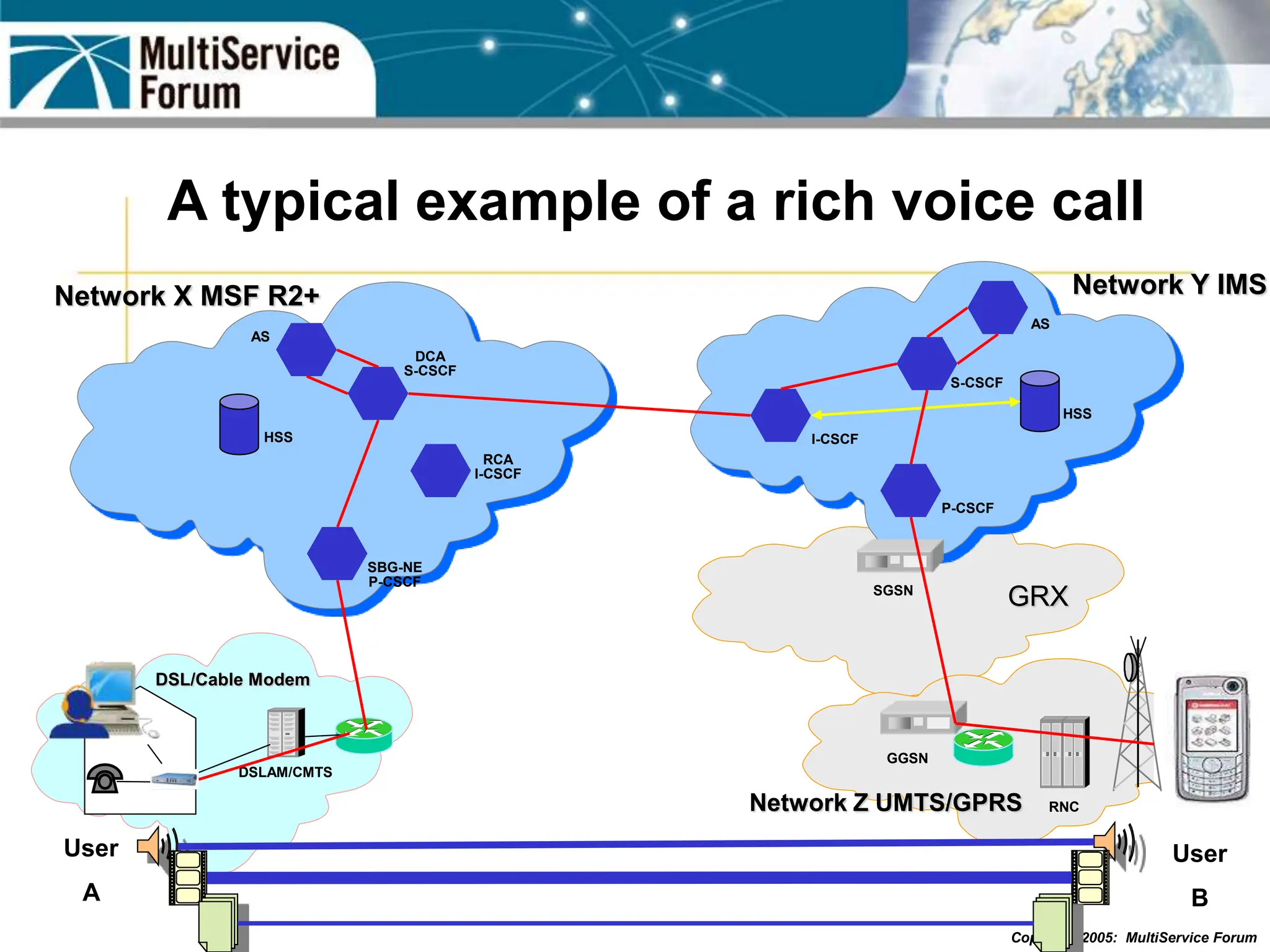
The document discusses the evolution and architecture of IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) in the context of fixed-mobile convergence, highlighting its role in enabling cost efficiencies and richer service offerings. It outlines the benefits to various stakeholders, including manufacturers, operators, and end users, emphasizing the need for a common service framework across different access technologies. Key features of IMS, such as service orchestration and SIP signaling, are also explained as crucial components for delivering next-generation services.