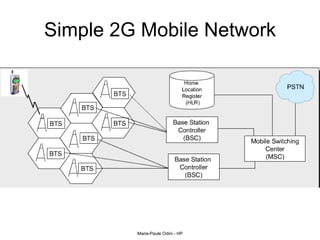
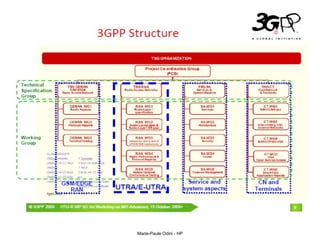
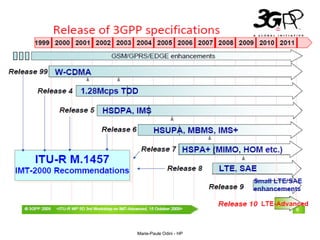
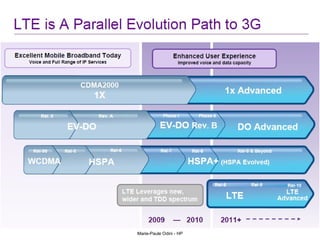
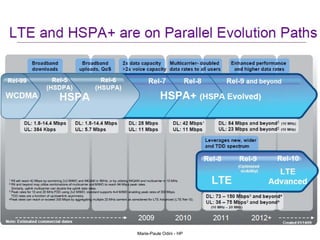
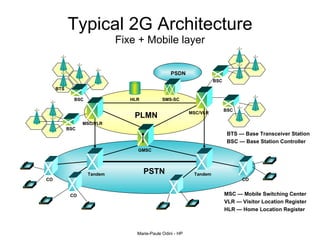
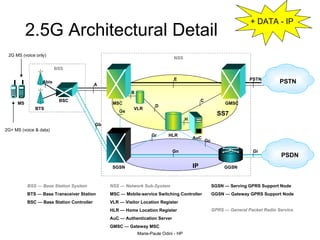
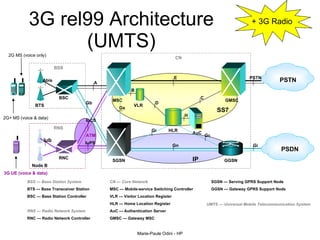
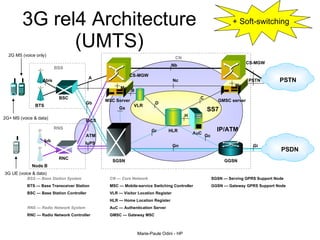
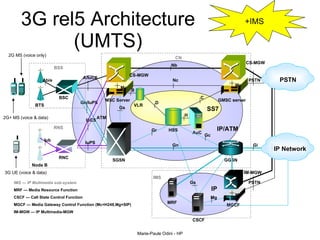
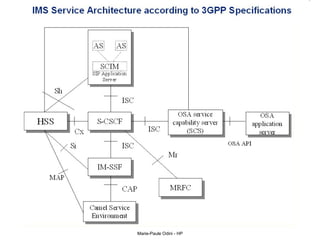
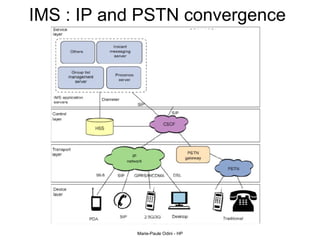
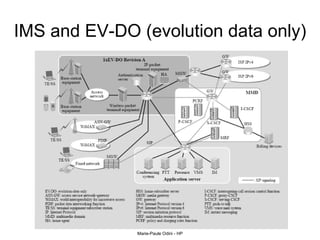
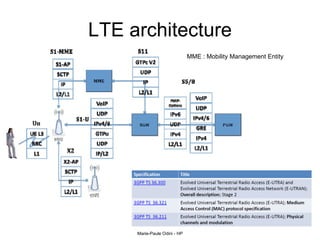
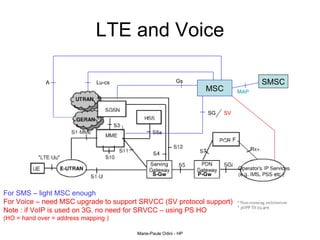
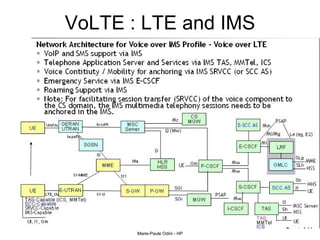
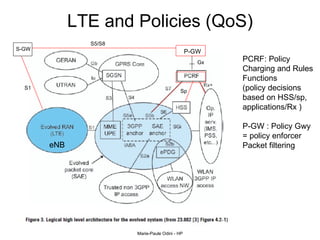
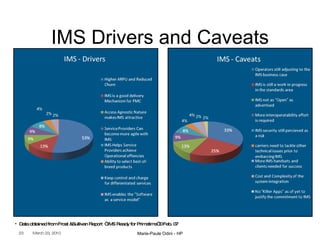
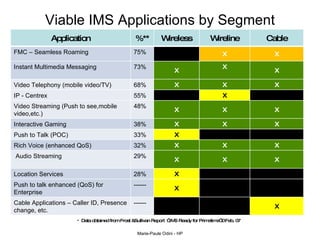
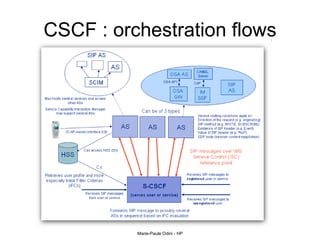
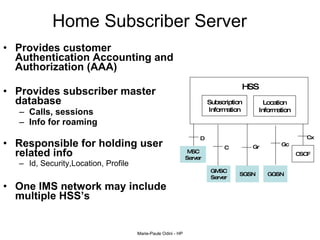
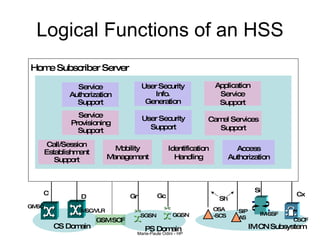
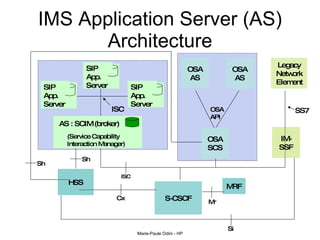
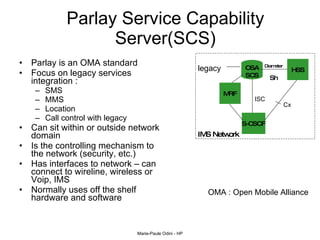
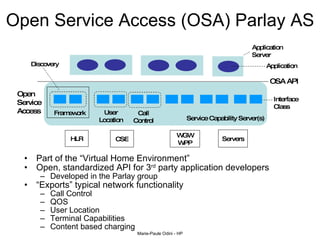
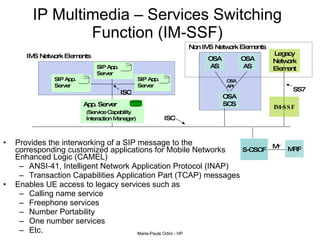
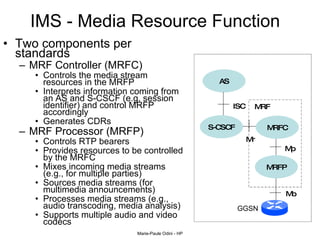
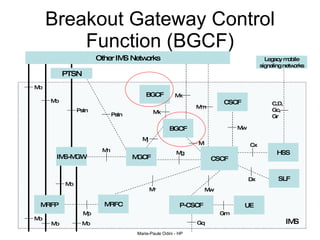
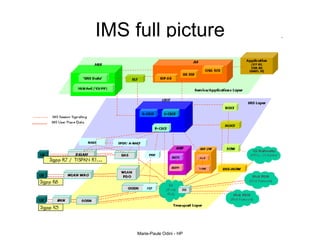
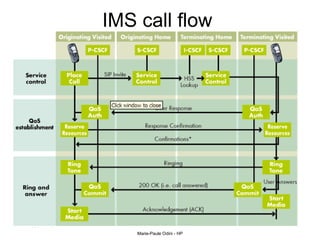
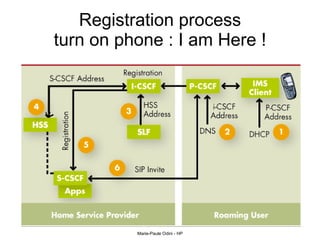
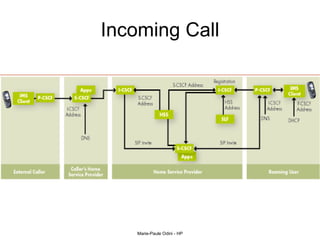
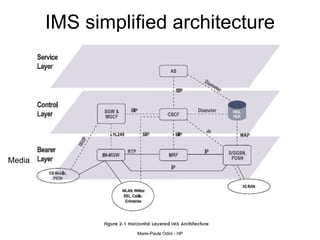
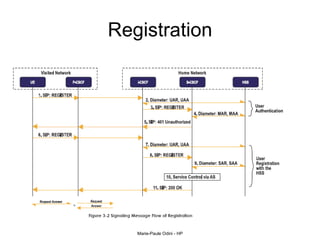
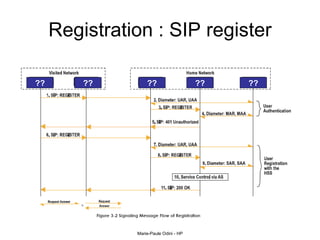
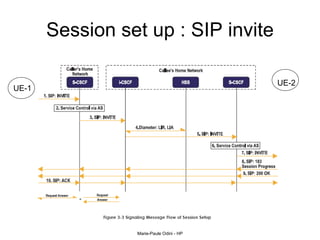
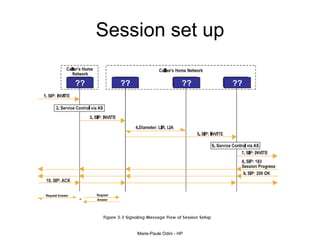
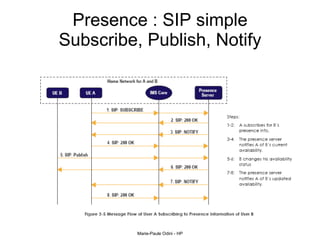
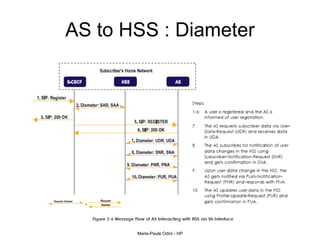
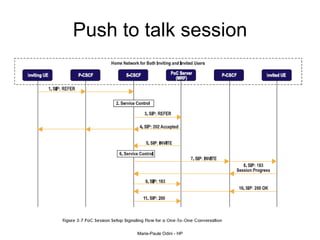
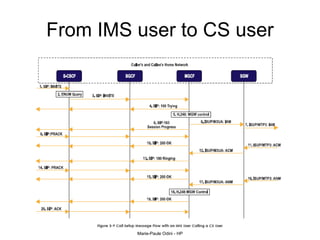
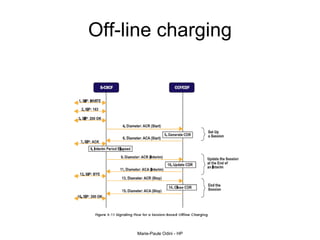
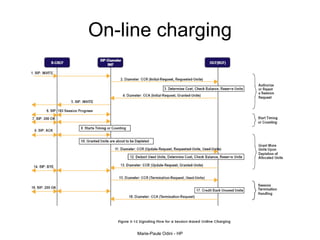
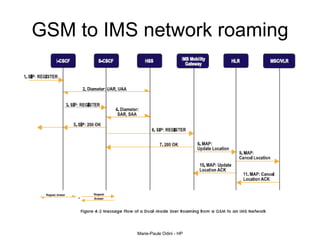
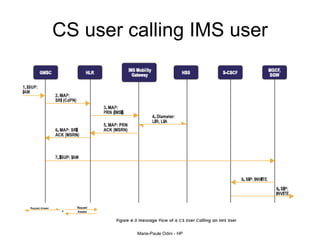
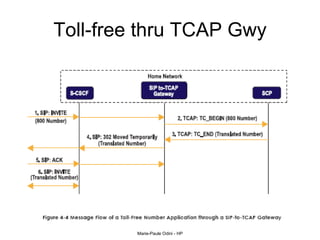
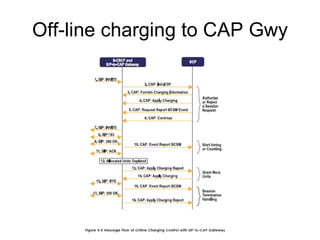
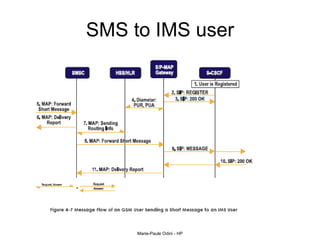
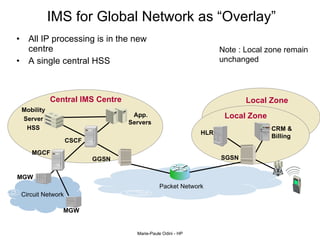
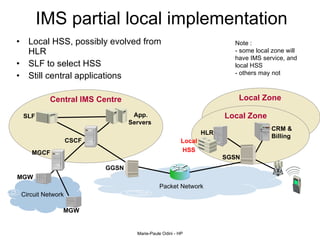
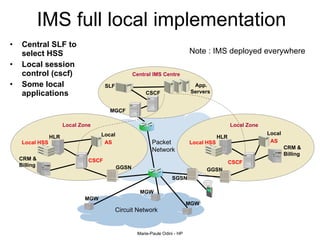
This document provides an overview of the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) standards and architecture. It discusses the evolution from 2G to 3G/4G mobile networks and the integration of IMS. The key components of IMS are described including the Call Session Control Function (CSCF), Home Subscriber Server (HSS), Application Servers (AS), Media Resource Functions (MRF), and Breakout Gateway Control Function (BGCF). Registration and call flow examples are provided to illustrate IMS signaling. Approaches to migrating existing networks to IMS are also summarized.