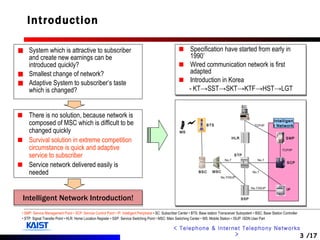
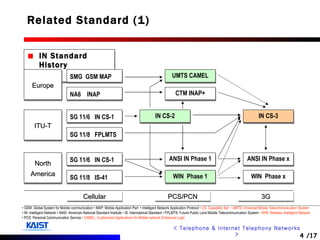
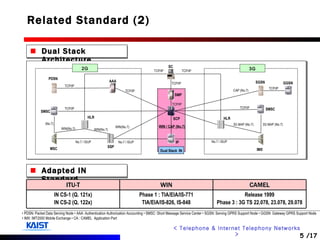
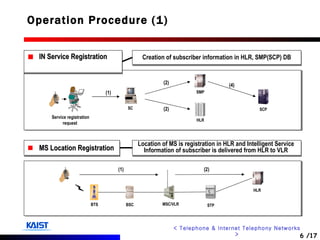
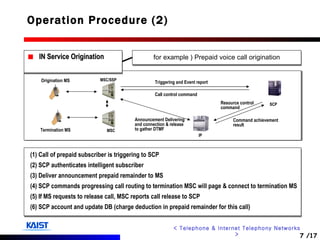
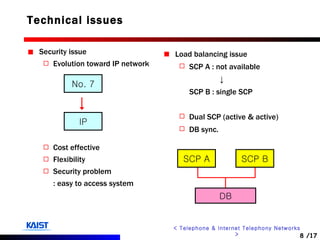
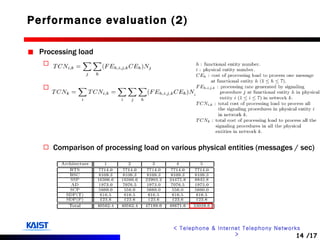
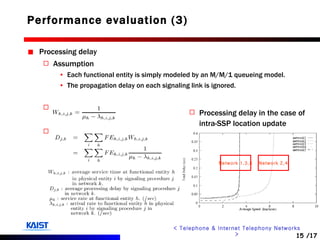
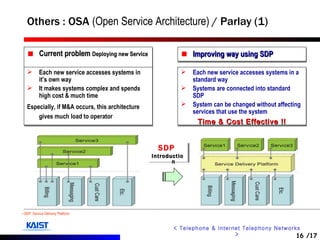
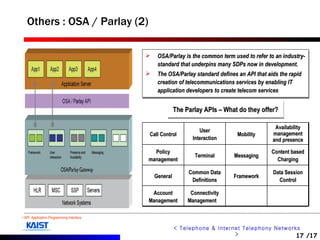
The document discusses intelligent networks and their operation. It introduces intelligent network components like the service control point (SCP) and service switching point (SSP). It describes how intelligent network services are registered and originated, going through authentication, announcement, and call routing procedures. It also addresses related standards, performance evaluation methods, and technical issues regarding security, evolution to IP networks, and cost effectiveness.