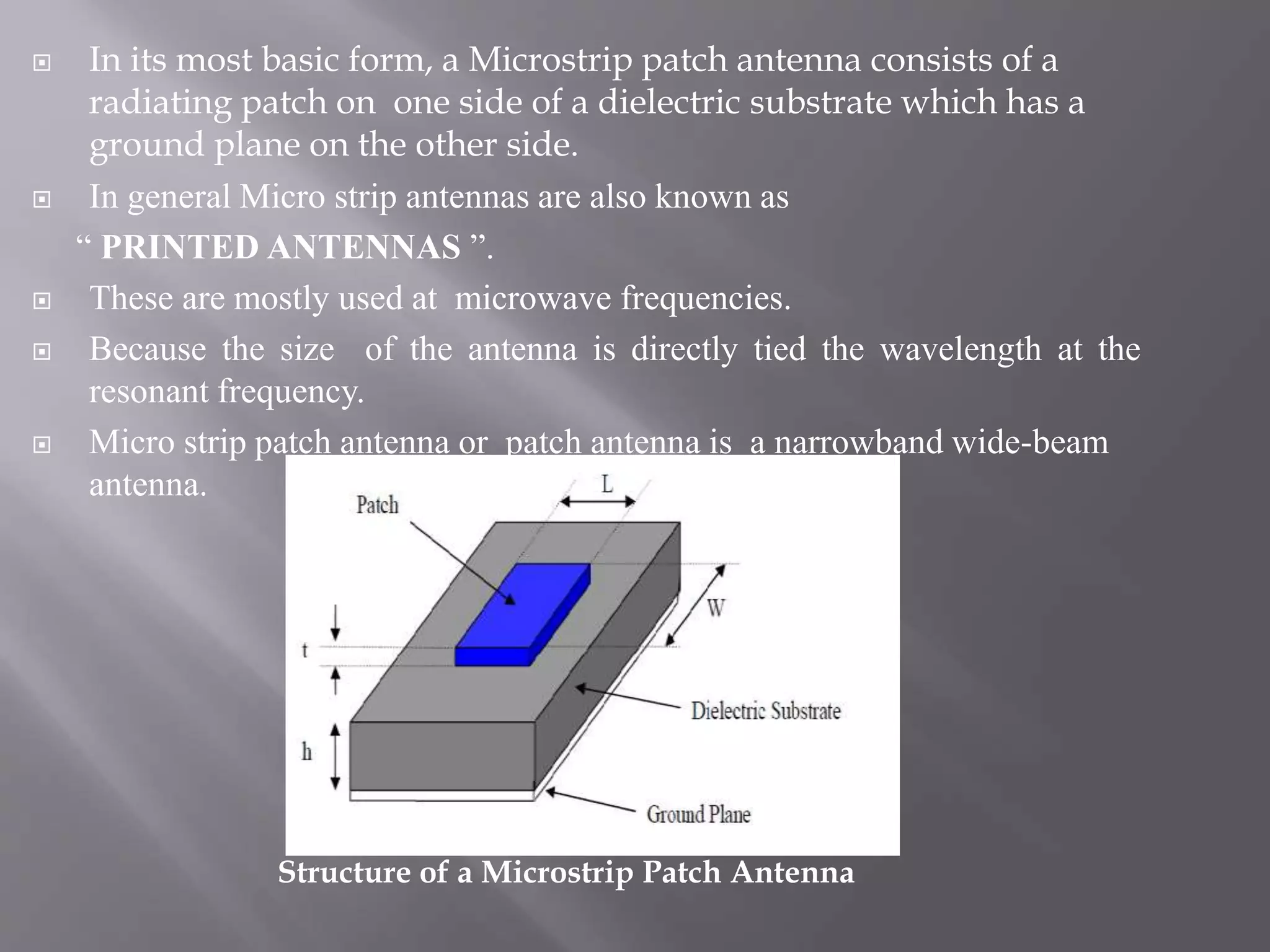
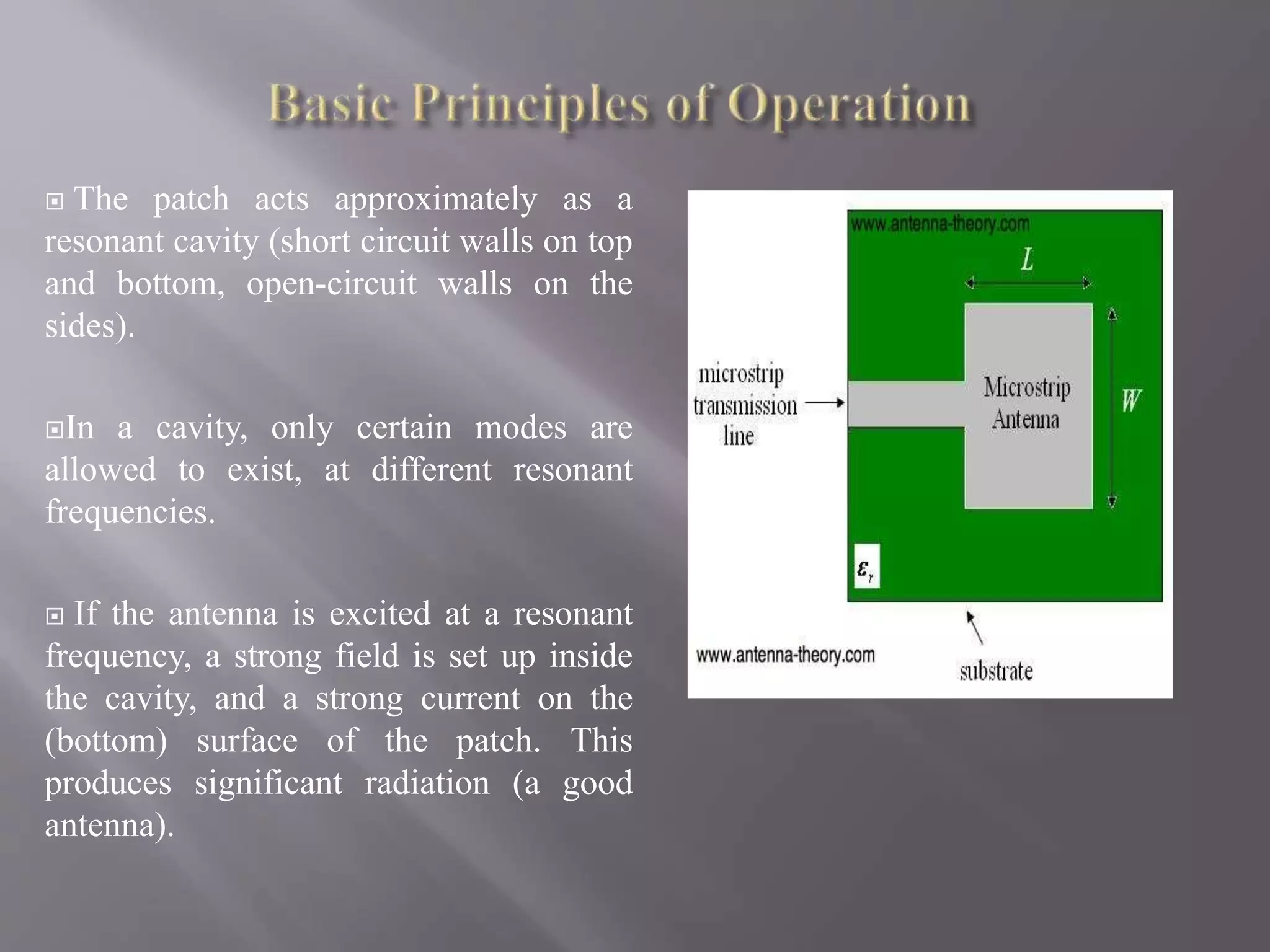
This document discusses microstrip patch antennas. It begins by explaining that microstrip antennas, also known as printed antennas, consist of a radiating metallic patch on a dielectric substrate with a ground plane on the other side. Microstrip antennas are widely used in mobile devices due to their conformal nature which allows them to be integrated into printed circuit boards. Their small size also helps minimize the overall size of mobile devices. The document then describes the basic structure and operating principles of microstrip patch antennas, noting that they function as resonant cavities and radiate strongly at resonant frequencies. It concludes by explaining that the bandwidth and size of microstrip antennas can be improved by defecting the ground plane and properly positioning the patch.