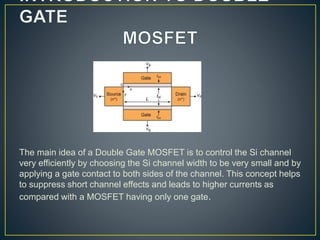
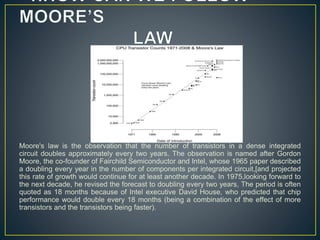
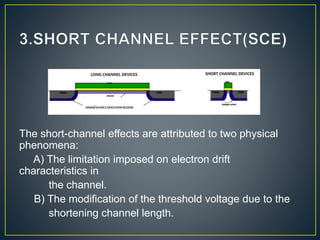
The document discusses the advantages of double gate MOSFETs (DG-MOSFETs) over single gate MOSFETs, emphasizing their improved control of short channel effects, leading to enhanced performance at nanoscale levels. It outlines the significance of following Moore's law to achieve effective scaling, along with a literature survey of comparative studies between single and double gate technologies. Key benefits of DG-MOSFETs include reduced capacitance, higher current drive, and better scalability, particularly in low-dimensional devices.