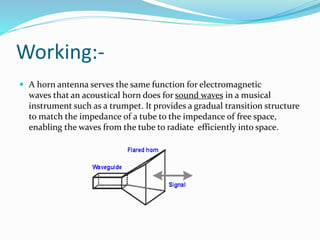
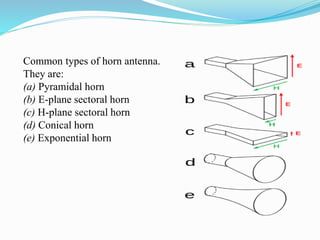
A horn antenna is a flaring metal waveguide that directs radio waves in a beam, commonly used in UHF and microwave frequencies. Various types include pyramidal, sectoral, conical, and exponential horns, each with unique structures and applications. They offer advantages such as wide bandwidth, moderate directivity, and simple construction, making them suitable for uses like radar, calibration, and electromagnetic interference measurements.