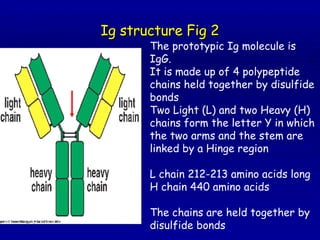
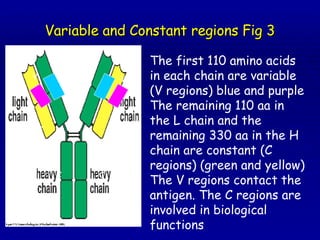
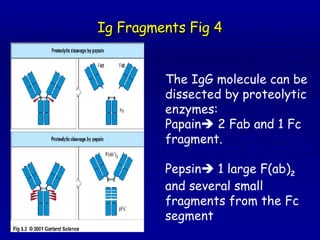
Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are Y-shaped glycoproteins produced by B cells that function to recognize and bind to foreign objects like antigens or pathogens. There are five classes of immunoglobulins - IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE - which differ in size, sugar content, and biological function. Each immunoglobulin molecule contains two light chains and two heavy chains that form variable and constant regions. The variable regions are responsible for binding to antigens while the constant regions mediate different immune functions.