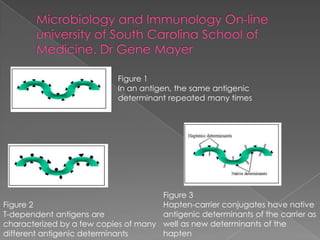
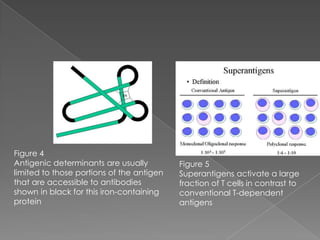
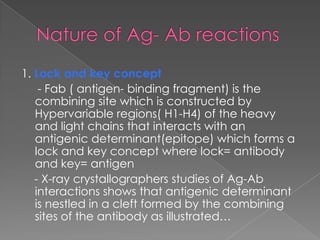
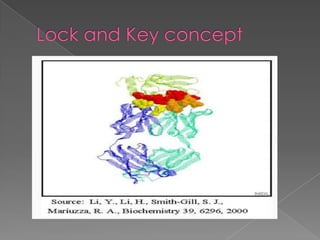
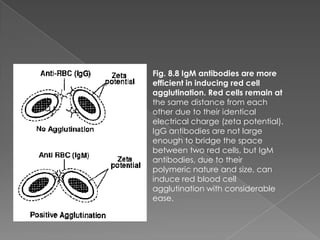
1. Antigen-antibody reactions occur when antigens and antibodies come into contact, such as when foreign substances enter the body.
2. These reactions are characterized by non-covalent bonds between the antigen and antibody, including hydrogen bonds, electrostatic bonds, hydrophobic bonds, and Van der Waals forces.
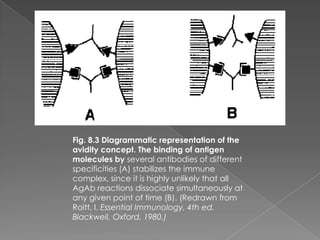
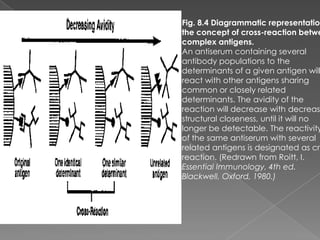
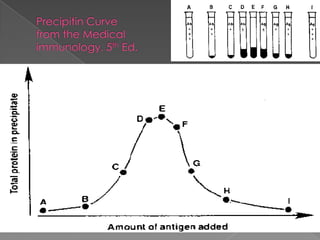
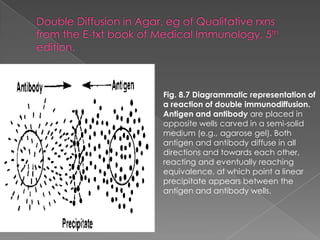
3. Consequences of antigen-antibody reactions include opsonization, activation of immune cells through Fc receptors, complement activation, and neutralization of pathogens or toxins.





















![CAI, Color Atlas of Immunology[PDF]. Burmester G,
Pezzutto A[MD]. Thieme Stuttgart, New York;2003
Google Browser[ database on the Internet]. Mayer. G
[MD]: Southern Carolina University School of Medicine
(US); 2010. Available from:
http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/mayer/ab-agrx.html
Hildamann W.H. Essentials of Immunology. New York,
Elsevier Science Publishers; 1984
MI, Medical Immunology[PDF]. Virella G, ed. 5th Ed.
New York, Marcel Dekker, Inc. 2001](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immunoglobulins-130205171901-phpapp02/85/Immunoglobulins-31-320.jpg)