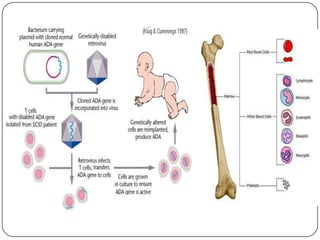
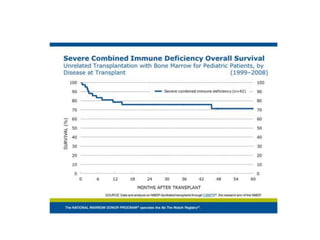
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also known as bubble boy disease, is a genetic disorder where both the B cell and T cell arms of the immune system are impaired. There are several types of SCID resulting from defects in different genes. Symptoms include life-threatening infections from an early age. Treatment involves preventing infections, enzyme therapy, gene therapy, or bone marrow transplant from a matched or half-matched donor to rebuild the immune system. Transplants have been successful but carry risks, as seen in the original "bubble boy" who died from a virus in his transplanted marrow.