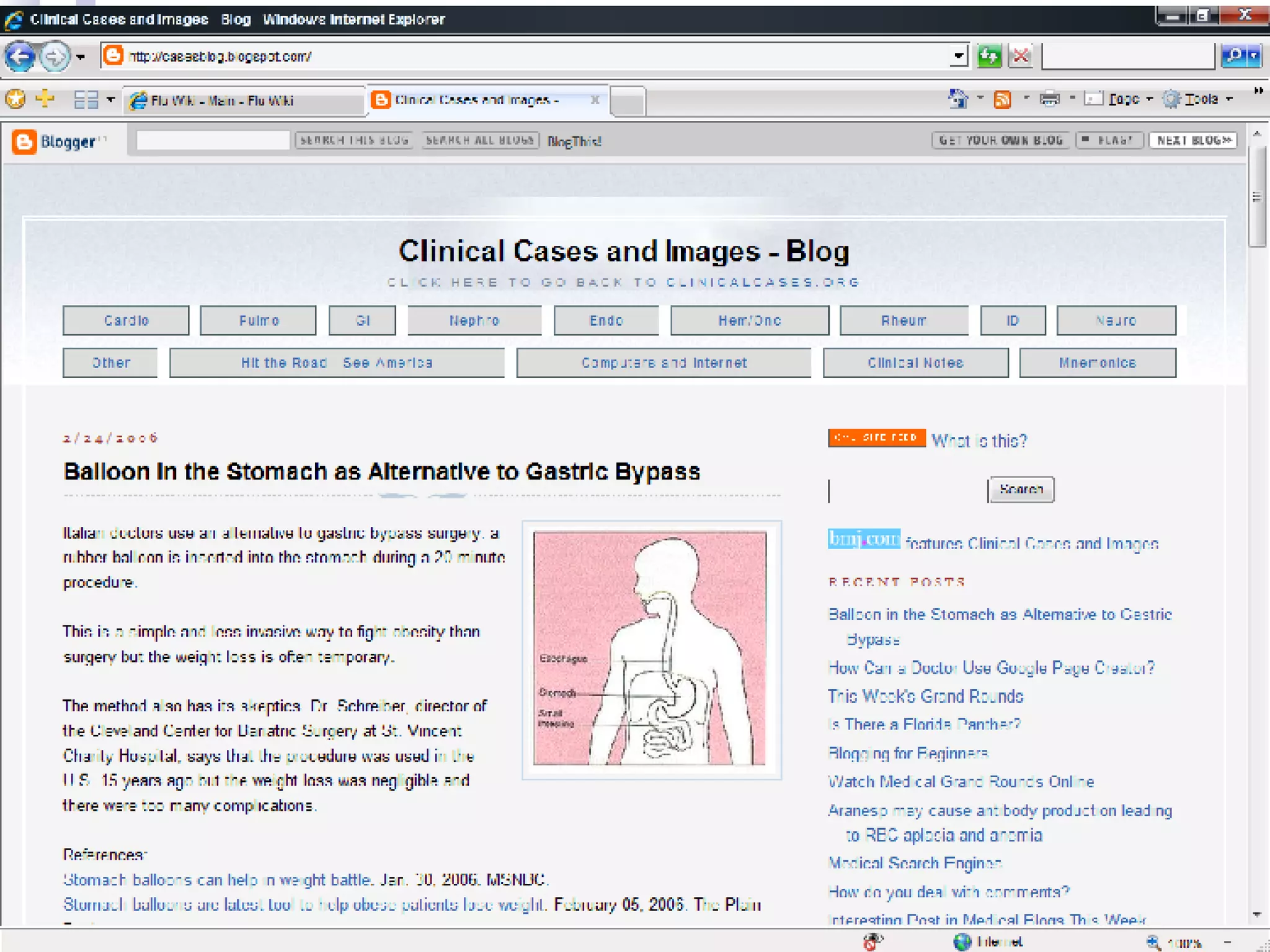
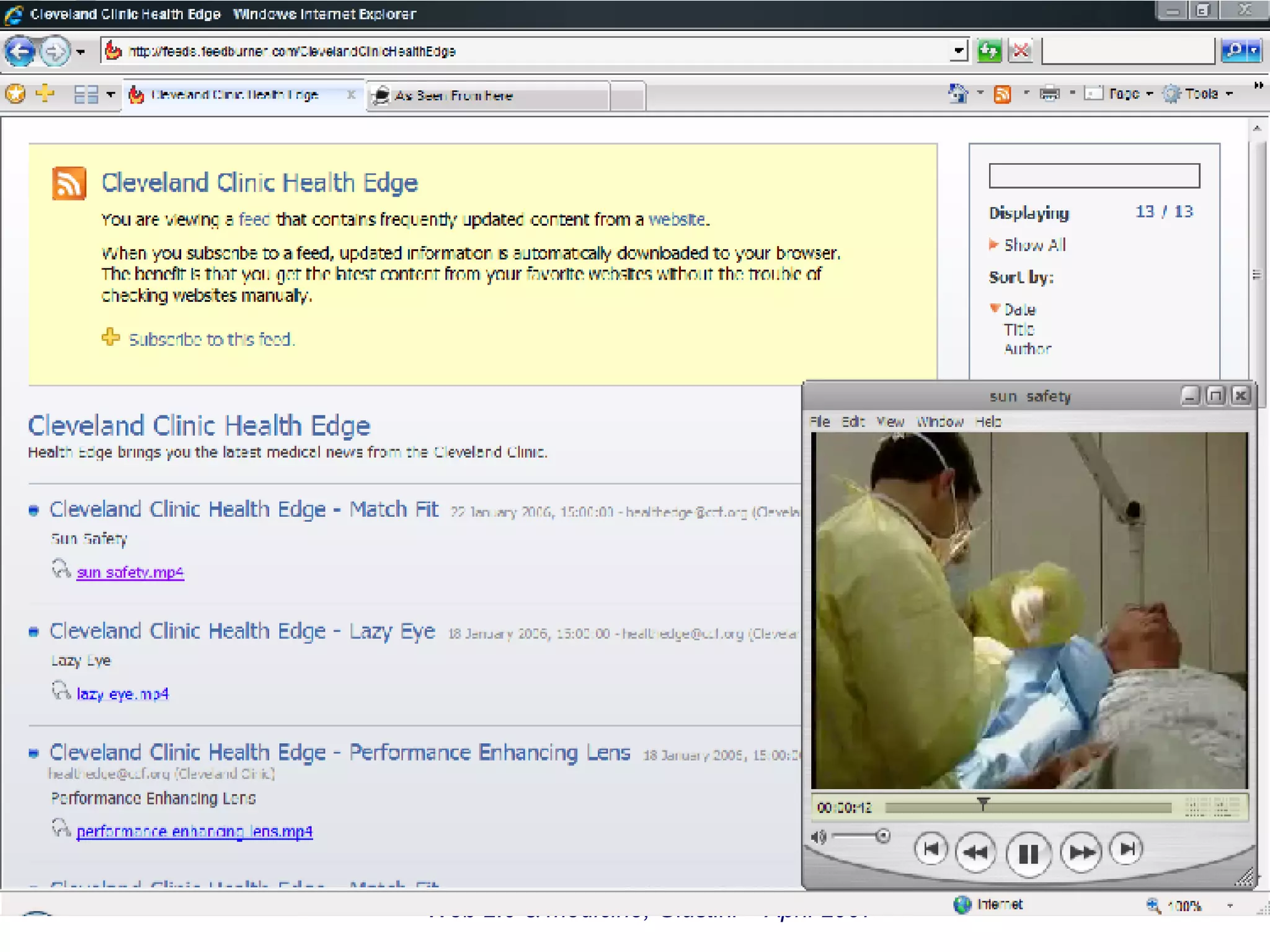
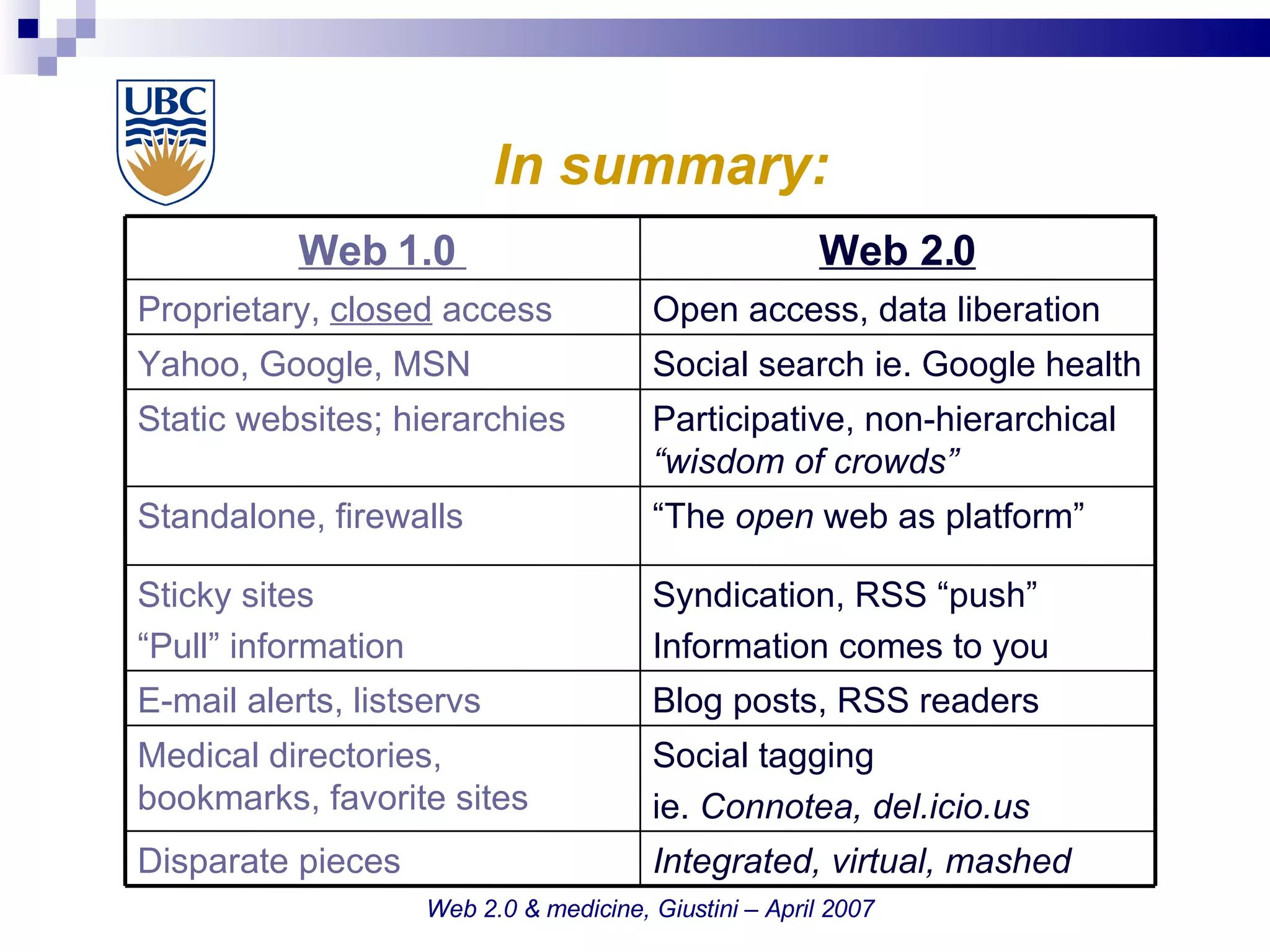
The document discusses the impact of Web 2.0 technologies on the field of medicine, highlighting how social software facilitates communication among doctors and enhances knowledge sharing through blogs, wikis, and podcasts. It emphasizes the shift towards open access medical publishing and patient-physician interactions as a result of these advancements. The conclusion suggests that Web 2.0 is fundamentally transforming medical practice and the collaborative environment for physicians.