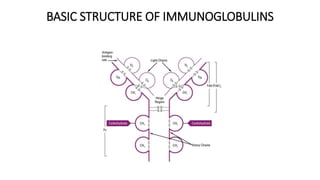
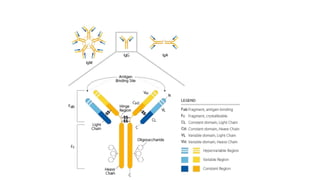
This document summarizes the structure, types, properties, and functions of immunoglobulins (antibodies). It describes the basic four-chain structure of antibodies, consisting of two heavy chains and two light chains, held together by disulfide bonds. The chains contain variable and constant regions. There are five classes of antibodies (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE) which differ in their heavy chain structure and properties like complement activation, placental transfer, and roles in allergic reactions or parasitic infections. Antibodies have antigen-binding fragments (Fab) and crystallizable fragments (Fc) that mediate different functions.