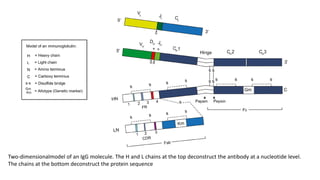
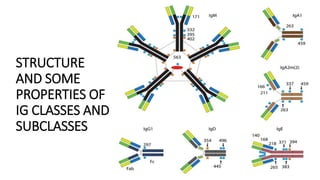
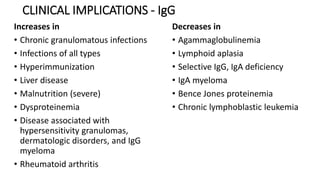
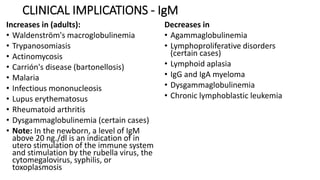
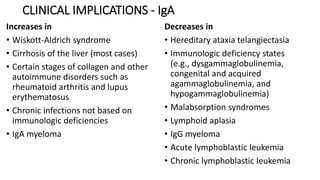
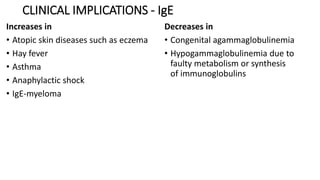
Immunoglobulins are glycoprotein antibodies produced by plasma cells that bind to specific antigens and perform various effector functions. They have a basic structure consisting of heavy and light chains, with variable and constant regions for antigen binding and effector roles. There are five classes of immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE), each differing in structure and function, and they play crucial roles in the immune response.