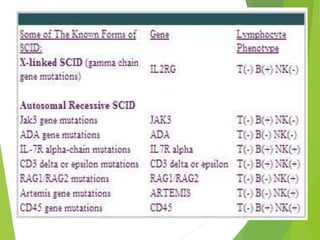
Combined immunodeficiencies are disorders affecting multiple components of the immune system, leading to severe immune deficiencies. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is characterized by mutations that impede the functionality of T and B lymphocytes, resulting in increased vulnerability to infections, particularly in infants. Various types of SCID exist, including X-linked and autosomal recessive forms, and while genetic factors play a significant role in inheritance, treatments such as bone marrow transplants and gene therapy are under investigation.