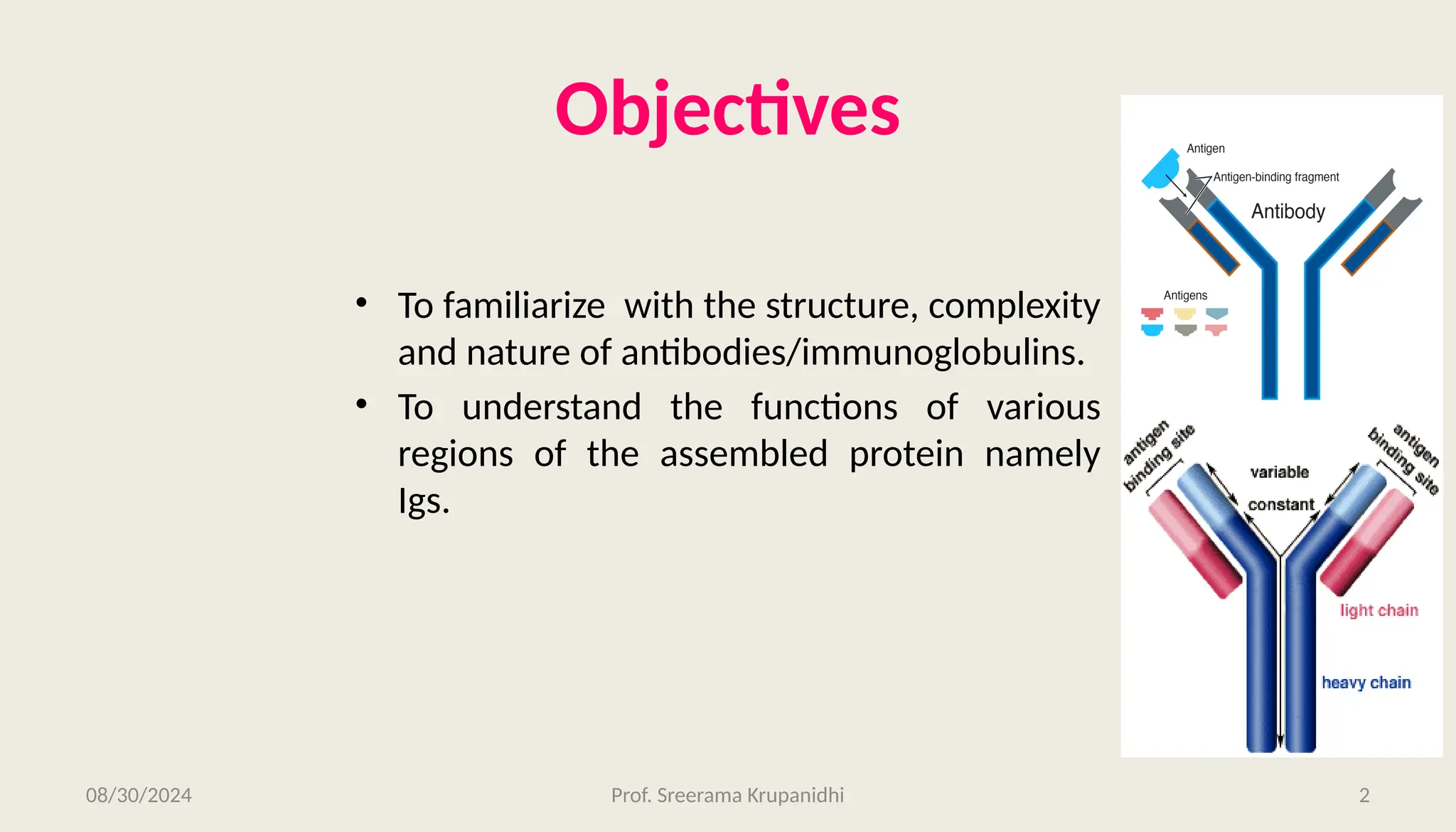
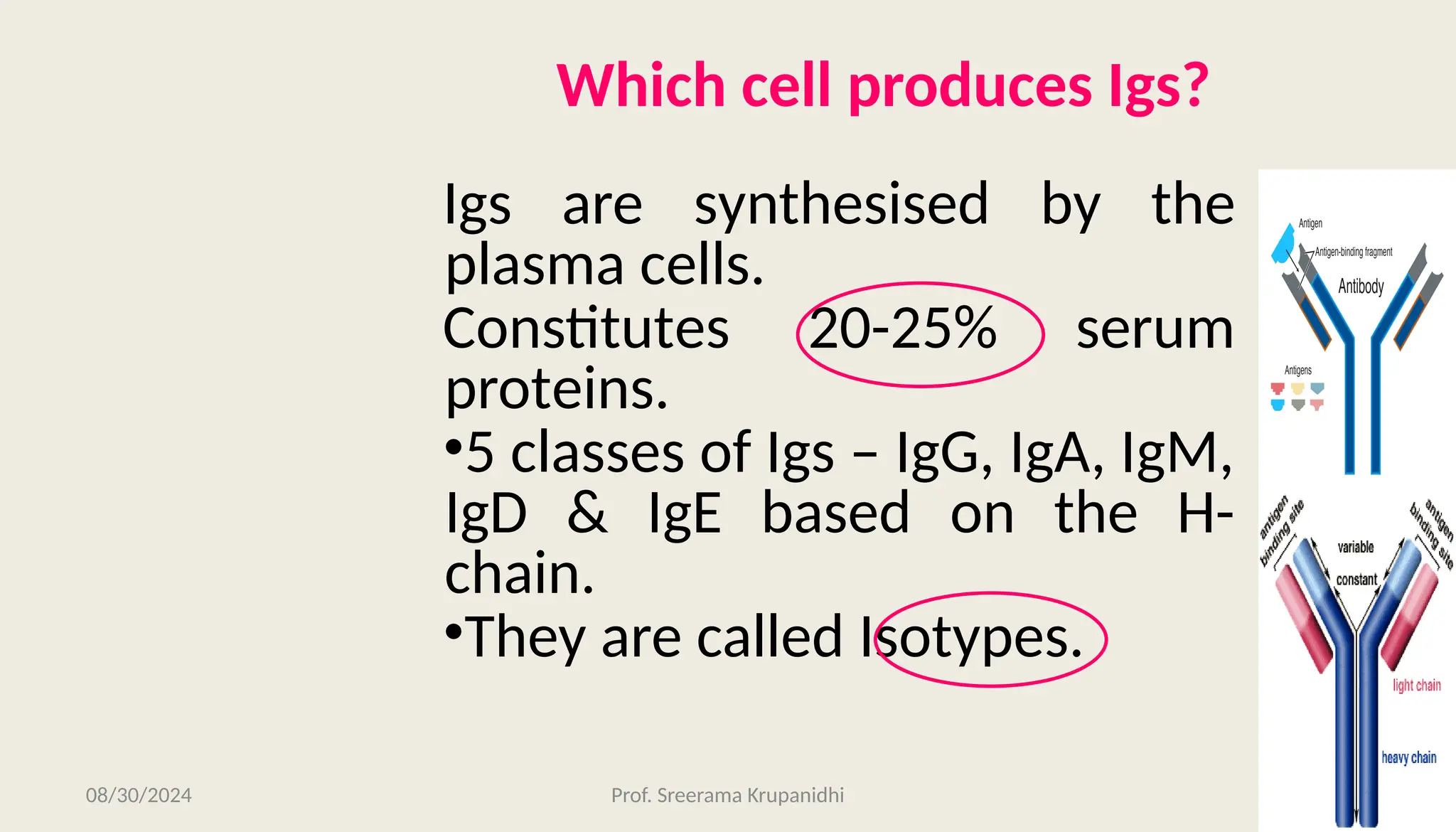
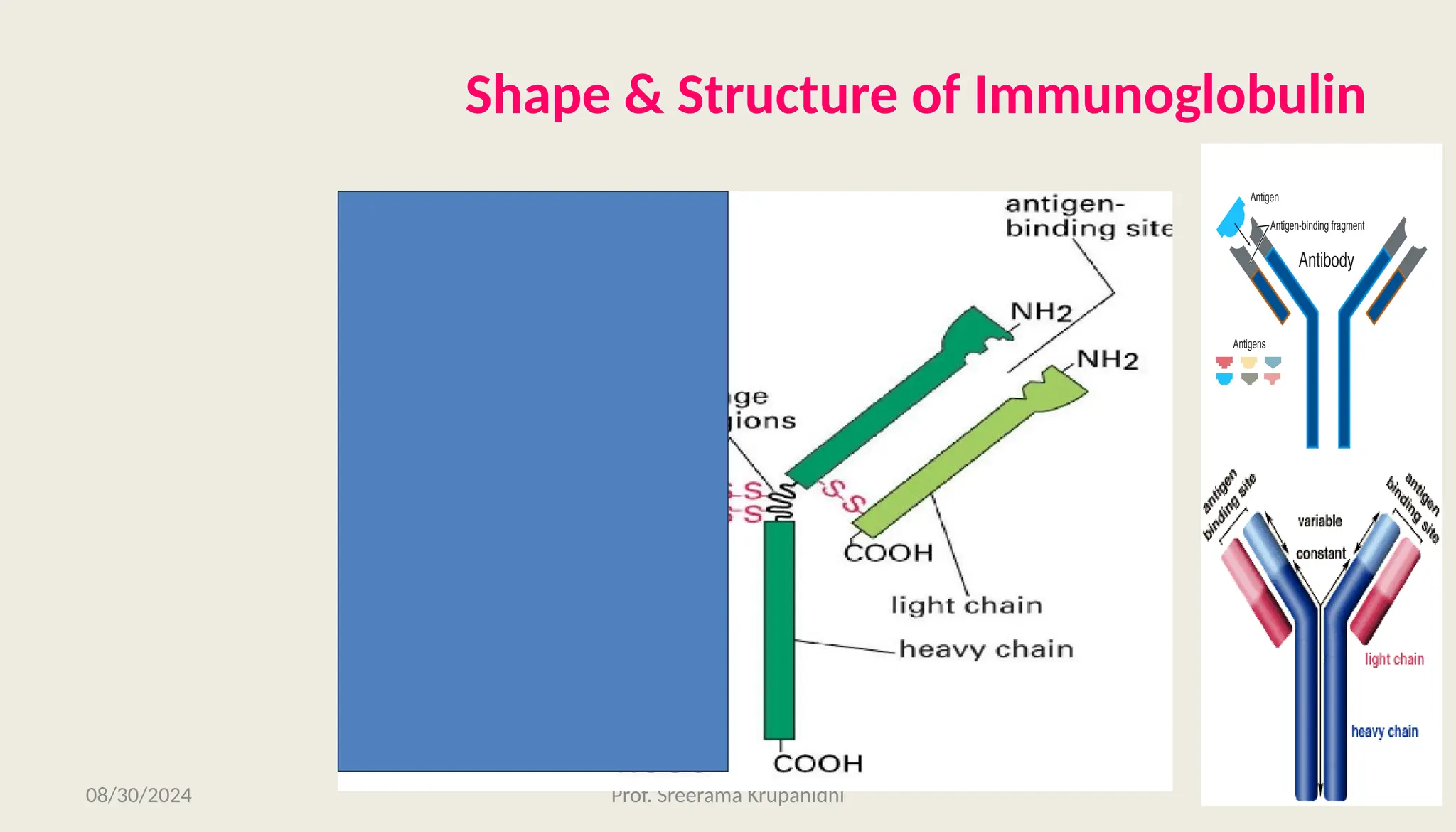
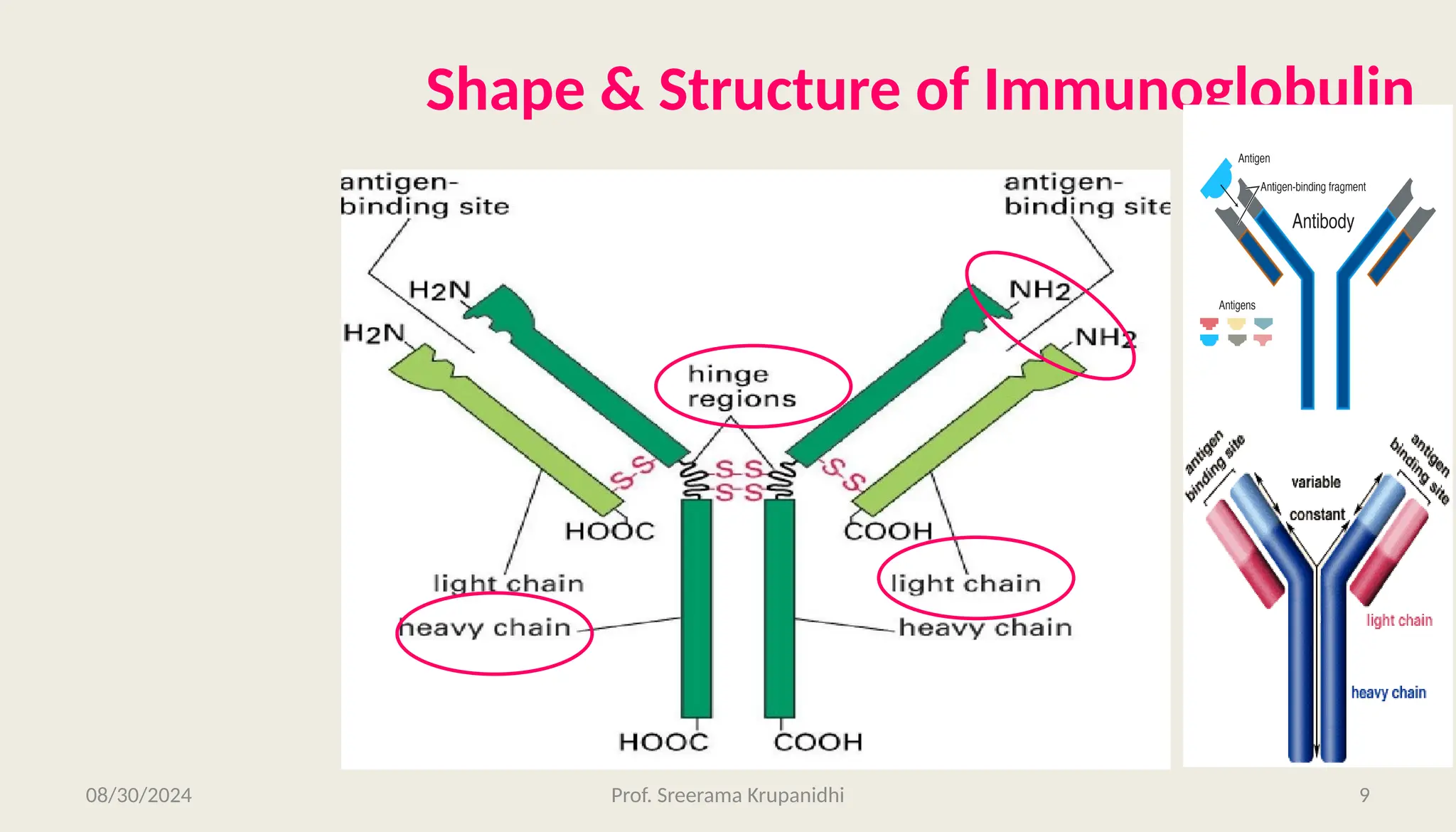
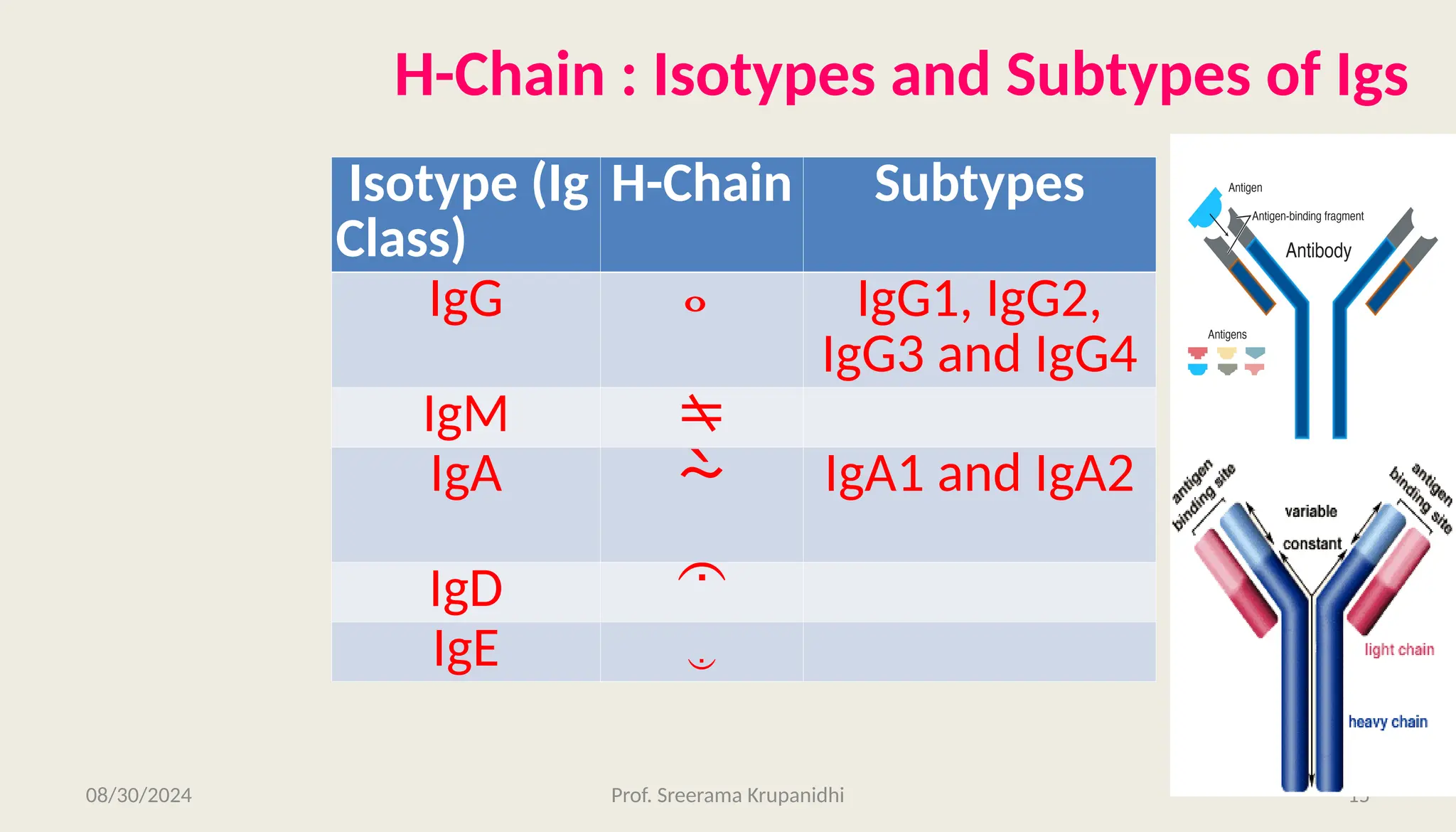
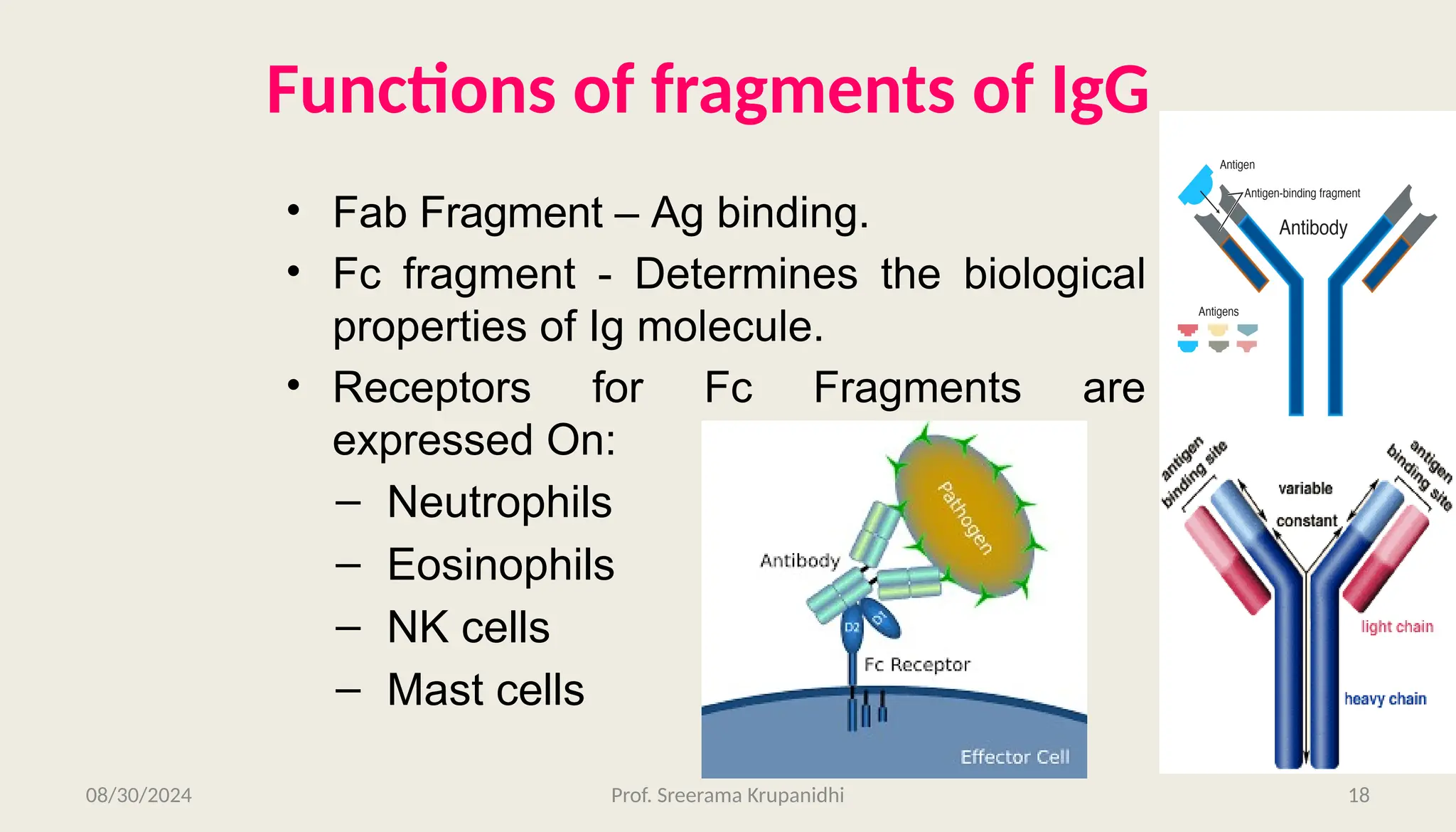
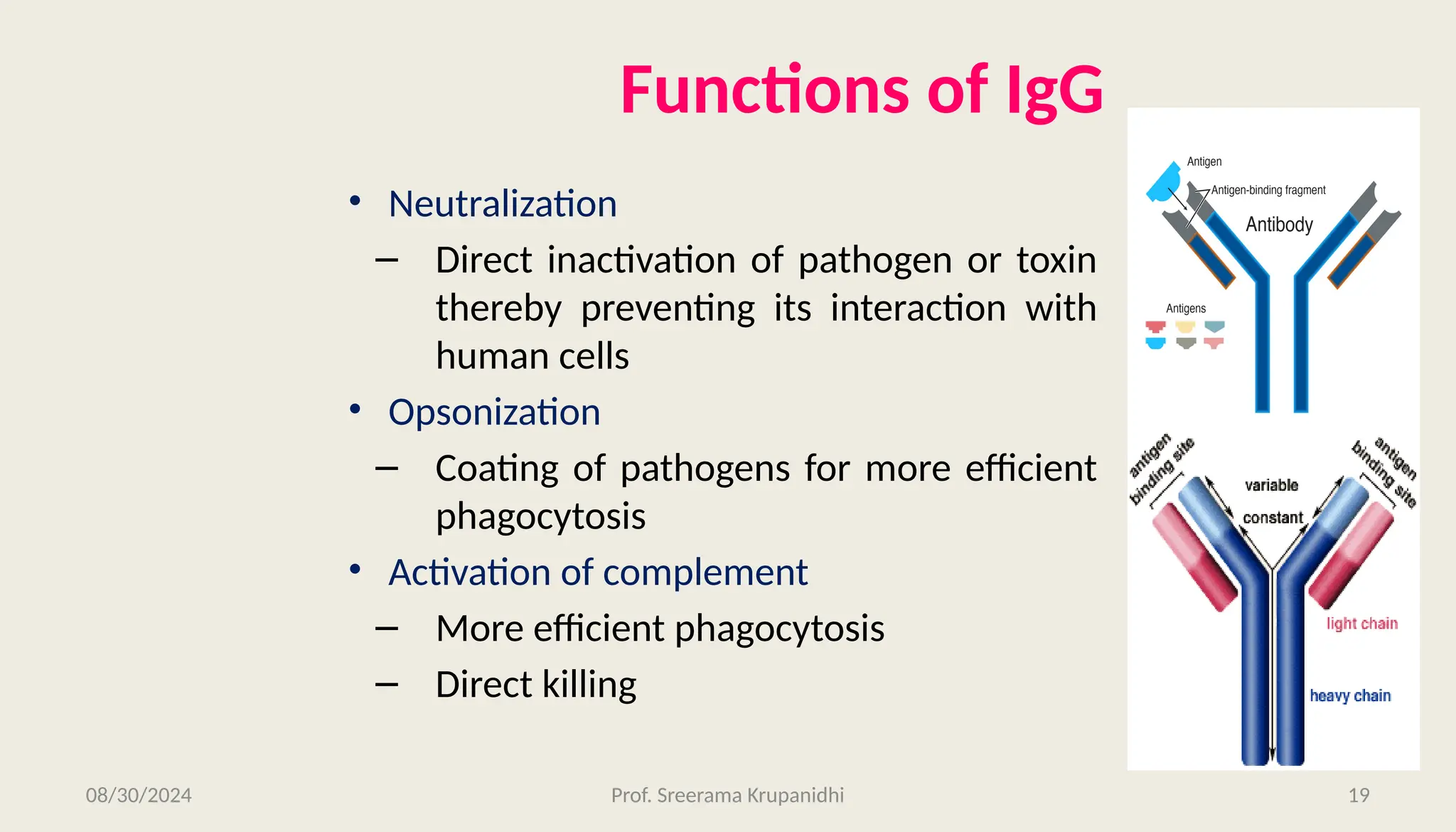
The document discusses the structure, complexity, and function of immunoglobulins (antibodies), explaining their composition as Y-shaped globular proteins produced by plasma cells. It details the types of immunoglobulins, including their heavy and light chains, and introduces hypervariable regions critical for antigen binding. Additionally, the document outlines the various roles of immunoglobulins in immune response, such as neutralization, opsonization, and complement activation.